Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Genetic Mutations 2013 Poster
Uploaded by
nailibeth sotilloCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Genetic Mutations 2013 Poster
Uploaded by
nailibeth sotilloCopyright:
Available Formats
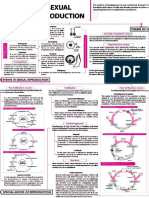
Genetic Mutations and Disease
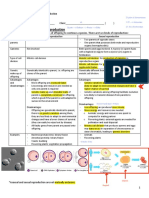
Cell Division
Early in development, cells have the potential to become any type of
cell. As development progresses, cells are more limited in the types
Overview Gamete
Somatic cells
of cells they can become.
Genetic mutations are changes in a DNA sequence that can occur
at any time in an individual’s life and in many different cell types.
Once a mutation occurs in a cell, its daughter cells will carry that
same mutation. A mutation that occurs early in development is
Fertilization
more likely to affect a greater portion of the body than a mutation
Parents occurring later in life. Only some mutations cause disease
depending on where in the genome they occur.
Adult
Somatic cells
Sperm & Development Zygote
In development, one fertilized cell
Egg becomes many different types of
cells through repeated cycles of
cell division and differentiation.
The Germline
The germline (yellow) is the lineage of cells that starts with
the zygote and ultimately gives rise to eggs and sperm (the
Zygote Embryo
Gametes
gametes). Mutations occurring in any cells of the germline
will be present in some or all of the gametes and can be
passed on to the next generation.
Somatic Cells
All the cells in the body that are not part of the germline are called somatic cells (purple). Mutations
that occur in a somatic cell will be passed on to the daughter cells when it divides. However, these
Blastocyst mutations are not inherited by the individual’s offspring since they do not occur in the germline.
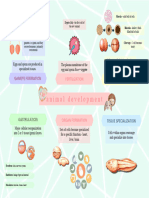
When and Where Mutations Occur Matters Cells and tissues with disease-associated
mutations are highlighted in red
When a mutation is inherited from parent to offspring, all the cells of the If a disease mutation occurs late in the germline lineage, during gamete Hemimegalencephaly is a genetic disorder in which part of the brain grows Cancer results primarily from somatic mutations. While cancer is not
offspring will carry the mutation including the germline. Therefore, the production, offspring may inherit the mutation from the unaffected larger than normal. It is caused by a mutation that arises in a somatic cell inherited, mutations associated with higher risk of cancer can be. For
mutation can be inherited by subsequent generations. Cystic fibrosis individual. This is an example of a new (de novo) mutation. Some cases of early in brain development. The mutation can typically only be detected in example, people who inherit certain mutations in the BRCA1 gene are
(recessive) and Huntington disease (dominant) are well-studied examples. autism have been shown to involve de novo mutations. the affected parts of the brain and nowhere else. more likely to develop breast and ovarian cancer.
© 2013 Howard Hughes Medical Institute. This poster is provided free of charge by HHMI for educational purposes; the poster may not be sold or resold. All other rights reserved.
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Genetics From Genes To Genomes 7th Edition Michael Goldberg Janice Fischer Leroy Hood Leland Hartwell DownloadDocument13 pagesSolution Manual For Genetics From Genes To Genomes 7th Edition Michael Goldberg Janice Fischer Leroy Hood Leland Hartwell DownloadTannerBensonkepaq100% (37)
- Spgbio 2 ReviewerDocument37 pagesSpgbio 2 ReviewerKaycee HeokkaidoNo ratings yet
- 1.6 Cell division-STUDENTDocument60 pages1.6 Cell division-STUDENTmeher singhNo ratings yet
- Meiosis GIZMODocument9 pagesMeiosis GIZMOYeet ThisbichemptyNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Somatic Cells and Gametes: March 2017Document11 pagesDifference Between Somatic Cells and Gametes: March 2017Naveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Genetika Perkembangan: Dewi Imelda Roesma MansyurdinDocument28 pagesGenetika Perkembangan: Dewi Imelda Roesma MansyurdinSisy YuliantyNo ratings yet
- Animation: Mitosis and CytokinesisDocument10 pagesAnimation: Mitosis and CytokinesisTheophilus BaidooNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Genetics 2nd Edition Brooker Solutions ManualDocument15 pagesConcepts of Genetics 2nd Edition Brooker Solutions Manualhuntertaylorpoinrgkfwe100% (14)
- Embryology INTRODocument5 pagesEmbryology INTROdanielle.macariolaNo ratings yet
- Final Cell Proliferation Differentiation inDocument43 pagesFinal Cell Proliferation Differentiation inFady FadyNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis Compared: GametesDocument5 pagesMitosis and Meiosis Compared: GametesLeela SNo ratings yet
- Biology Questions and Answers: GametogenesisDocument25 pagesBiology Questions and Answers: GametogenesisMaria Elena Mora MejiaNo ratings yet
- Gamatogenesis ProccesDocument15 pagesGamatogenesis ProccesvimamufliantiNo ratings yet
- Nayre - Activity 3.2 - Cell TypesDocument1 pageNayre - Activity 3.2 - Cell TypeskiesheenynaderaNo ratings yet
- Group 5 Gametes and FertilizationDocument74 pagesGroup 5 Gametes and FertilizationLira PagaraNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Genetics 2nd Edition Brooker Solutions ManualDocument10 pagesConcepts of Genetics 2nd Edition Brooker Solutions Manualcariboumycology.d37qfo100% (20)
- Somatic Cell and Gamete CellsDocument4 pagesSomatic Cell and Gamete Cellsj_ngetich_k7375No ratings yet
- Full Download Concepts of Genetics 2nd Edition Brooker Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Concepts of Genetics 2nd Edition Brooker Solutions Manual PDF Full Chapterrawhide.forwrap1q9z100% (13)
- Concepts of Genetics 2nd Edition Brooker Solutions ManualDocument14 pagesConcepts of Genetics 2nd Edition Brooker Solutions ManualgeoffreyjimenezxtyfnzwrkcNo ratings yet
- CYTOGEN: Chapter 3 Meiosis, Development, and AgingDocument6 pagesCYTOGEN: Chapter 3 Meiosis, Development, and AgingpangetkoNo ratings yet
- Adult Stem Cells Show Anti-Aging PotentialDocument6 pagesAdult Stem Cells Show Anti-Aging PotentialJose RuizNo ratings yet
- Activity 3Document6 pagesActivity 3Kalea Kassandra MatthewsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Cell Division: Chapt 5:1/5Document5 pagesChapter 5 Cell Division: Chapt 5:1/5ctazimaNo ratings yet
- Chap 5 Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesChap 5 Cell DivisionMy fluffy MochiNo ratings yet
- 2 Process Involved in Morphogenesis Lecture 2Document24 pages2 Process Involved in Morphogenesis Lecture 2Alec LiuNo ratings yet
- How Organisn ReproduceDocument1 pageHow Organisn ReproduceSanket VermaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 04 Aug 2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 04 Aug 2023J Nathiya ShreeNo ratings yet
- Concept Map Sexual ReproductionDocument1 pageConcept Map Sexual ReproductionSalil ShauNo ratings yet
- B2.3 Biology NotesDocument2 pagesB2.3 Biology Noteskounis2011No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument10 pagesCell DivisionMEDRANO, Hana Jhiemyka O.No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Heredity and Variation: 1. Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesChapter 3 Heredity and Variation: 1. Cell DivisionnamikNo ratings yet
- BIO 105 Lab 9 Mitosis and Meiosis ONL Version-1Document9 pagesBIO 105 Lab 9 Mitosis and Meiosis ONL Version-1Bruce QuitoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell DivisionDocument120 pagesChapter 3 Cell DivisionChe NorasiykinNo ratings yet
- Biology Marathon A4 DocumentDocument12 pagesBiology Marathon A4 DocumentSamiksha ChettriNo ratings yet
- Output GenBio Week1B EsperidaDocument3 pagesOutput GenBio Week1B EsperidaBanana QNo ratings yet
- Germ CellDocument2 pagesGerm CellCyrene John CruzNo ratings yet
- IncompletoDocument3 pagesIncompletospeedwagonNo ratings yet
- GametogenesisDocument4 pagesGametogenesiskirsten evidenteNo ratings yet
- Meiosis Phases (2021 - 12 - 19 23 - 29 - 01 UTC)Document14 pagesMeiosis Phases (2021 - 12 - 19 23 - 29 - 01 UTC)Selenia BonoNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Vs Meiosis: FunctionDocument2 pagesMitosis Vs Meiosis: FunctionHari NirmalNo ratings yet
- Gametogenesis: Cell Division Gametes Biological Life Cycle Organism Meiotic Gametocytes Mitotic PlantsDocument8 pagesGametogenesis: Cell Division Gametes Biological Life Cycle Organism Meiotic Gametocytes Mitotic PlantsHerne BalberdeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy 1Document48 pagesAnatomy 1aryan.ragupathyNo ratings yet
- Vasquez, Angelica, Bio30lL, Activity 4 - 2021Document5 pagesVasquez, Angelica, Bio30lL, Activity 4 - 2021Angelica VasquezNo ratings yet
- Control of Growth and DevelopmentDocument24 pagesControl of Growth and DevelopmentKriss Arthur Huiza AriNo ratings yet
- Biology Unit 2 Notes VCEDocument8 pagesBiology Unit 2 Notes VCEMy Name is JeffNo ratings yet
- Lesson 17: Reproduction & DevelopmentDocument20 pagesLesson 17: Reproduction & DevelopmentRichy BritchNo ratings yet
- S T e MC e L L S: Clinical ApplicationsDocument79 pagesS T e MC e L L S: Clinical ApplicationsAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Mitotic Cell Cycle 2022Document26 pagesMitotic Cell Cycle 2022Riza FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- 15 Development of The Nervous SystemDocument47 pages15 Development of The Nervous SystemAleynaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis: Emmel, Keisya, Florencia, Joci, Joseph 9BDocument23 pagesMitosis and Meiosis: Emmel, Keisya, Florencia, Joci, Joseph 9BJoshlyn AnnabelleNo ratings yet
- Form 4 - 2 - ch16 - Notes - 2122Document20 pagesForm 4 - 2 - ch16 - Notes - 2122Jeremy HsuNo ratings yet
- Plant Embryogenesis (Zygotic and Somatic) : Introductory ArticleDocument10 pagesPlant Embryogenesis (Zygotic and Somatic) : Introductory ArticleJessica Asitimbay ZuritaNo ratings yet
- Animals Development Concept MapDocument1 pageAnimals Development Concept MapkpenalesNo ratings yet
- The Genetic Basis of Development: Powerpoint Lectures ForDocument61 pagesThe Genetic Basis of Development: Powerpoint Lectures Forxo_simpledreamNo ratings yet
- GIZMO - MeiosisDocument8 pagesGIZMO - MeiosisTide PodsNo ratings yet
- Anaphy and Phisiology Midterm NotesDocument19 pagesAnaphy and Phisiology Midterm NotesLucy AlmonteNo ratings yet
- 15.1 - Totipotency and Cell SpecialisationDocument24 pages15.1 - Totipotency and Cell Specialisationsohailnoreen5062No ratings yet
- Embryology ReviewerDocument6 pagesEmbryology ReviewerJoanna Michelle AlmedaNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle ReviewerDocument2 pagesThe Cell Cycle ReviewerNcle NaborNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesCell Divisionzade zadeNo ratings yet
- BCBT-52822 - Lecture - Dulith AbeykoonDocument84 pagesBCBT-52822 - Lecture - Dulith Abeykoonkaneeshka namasivayamNo ratings yet
- Mechanisms of EvolutionDocument23 pagesMechanisms of EvolutionVeancy WangNo ratings yet
- Lesson-3 Protein-Synthesis WorksheetDocument10 pagesLesson-3 Protein-Synthesis WorksheetEnriquez, Hannah Roniella R.No ratings yet
- Science 10 Lesson PlanDocument7 pagesScience 10 Lesson PlanThesairah Taule100% (1)
- AMP CancerDocument20 pagesAMP Cancerprateek bhatiaNo ratings yet
- Biotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 6 Mutation - FinalDocument13 pagesBiotech STE 8 Q2 Lesson 6 Mutation - FinalAileen Ocampo100% (1)
- (H2) CI2.4 - Gene MutationDocument17 pages(H2) CI2.4 - Gene MutationTimothy HandokoNo ratings yet
- Widespread Somatic L1 Retrotransposition in Normal Colorectal EpitheliumDocument27 pagesWidespread Somatic L1 Retrotransposition in Normal Colorectal Epithelium6ypywxdqmkNo ratings yet
- Etiologi Ca Alexandrov2018Document12 pagesEtiologi Ca Alexandrov2018Mastifa HanasitaNo ratings yet
- Eva 412Document6 pagesEva 412Khairul hakimiNo ratings yet
- Evo101 - 03 - Mechanisms - The Process of Evolution - UEDocument34 pagesEvo101 - 03 - Mechanisms - The Process of Evolution - UEJanice LerioratoNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 5 Effect of Mutation On ProteinDocument20 pagesScience: Quarter 3 - Module 5 Effect of Mutation On ProteinBxcon BloxNo ratings yet
- Mutation: Prof. Harshraj. S. Shinde K. K. Wagh College of Agril. Biotech, Nashik. IndiaDocument24 pagesMutation: Prof. Harshraj. S. Shinde K. K. Wagh College of Agril. Biotech, Nashik. IndiaMonika shankarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Mutation 23-11Document22 pagesLecture 6 Mutation 23-11Saif MohamedNo ratings yet
- D1.3 Mutations and Gene EditingDocument17 pagesD1.3 Mutations and Gene Editingatasay2024No ratings yet
- Principles of Life 2Nd Edition Hillis Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument55 pagesPrinciples of Life 2Nd Edition Hillis Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmarthalouisaq6x100% (8)
- Mutations FinalDocument13 pagesMutations FinalMuhammad Tazeem MunawarNo ratings yet
- MutationDocument24 pagesMutationVivion JacobNo ratings yet
- Post-Harvest Physiology and Crop PreservationDocument574 pagesPost-Harvest Physiology and Crop PreservationRendy PramudyaNo ratings yet
- Best Practices For Variant Calling in Clinical Sequencing: Review Open AccessDocument13 pagesBest Practices For Variant Calling in Clinical Sequencing: Review Open AccessAhmad SolihinNo ratings yet