Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Reviewer in English 9
Reviewer in English 9
Uploaded by
Kathleen Clarrise S. Gonzales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesIf-clauses introduce conditional sentences and state a condition, while the main clause states the result. There are three types of conditional sentences: real, unreal, and mixed. Real conditionals express factual situations, unreal conditionals convey hypothetical situations, and mixed conditionals combine real and unreal elements. There are also different forms of conditional sentences that denote the time frame of the condition. Additionally, speech styles range from frozen to intimate depending on the level of formality and direction of communication.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIf-clauses introduce conditional sentences and state a condition, while the main clause states the result. There are three types of conditional sentences: real, unreal, and mixed. Real conditionals express factual situations, unreal conditionals convey hypothetical situations, and mixed conditionals combine real and unreal elements. There are also different forms of conditional sentences that denote the time frame of the condition. Additionally, speech styles range from frozen to intimate depending on the level of formality and direction of communication.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesReviewer in English 9
Reviewer in English 9
Uploaded by
Kathleen Clarrise S. GonzalesIf-clauses introduce conditional sentences and state a condition, while the main clause states the result. There are three types of conditional sentences: real, unreal, and mixed. Real conditionals express factual situations, unreal conditionals convey hypothetical situations, and mixed conditionals combine real and unreal elements. There are also different forms of conditional sentences that denote the time frame of the condition. Additionally, speech styles range from frozen to intimate depending on the level of formality and direction of communication.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
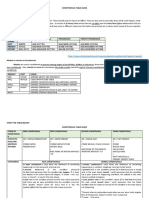
Reviewer in English 9 Conditionals or conditional sentences express a
real or an unreal condition. A conditional sentence
1st Periodical Exam
consists of two parts: an if-clause and a main clause.
Modals – a type of verb that contextually indicates
If-clause it introduces a condition.
a modality such as likelihood, ability, permission,
request, capacity, suggestion, order, obligation, or Main clause is the result of a condition.
advice.
Real conditionals express true situations that are
Modals expressing Permission factual and very likely to happen.
Can Unreal conditionals convey untrue situations,
May hypothetical conditions, or imaginary present, past
or future, and they have no probability to happen.
Modals denoting Ability
Zero Conditionals is used when the results are
Can always true, like a scientific facts and general
Could truths.
Modals for Possibility Follows the form [If + present tense of a
Might verb,] + [present tense of a verb].
Will First Conditionals is used to talk about conditions
Modals for Obligation that might happen in the future.
Must Follows the form [If + present tense of a
verb,] + [will + base form of a verb]
Have to
Ought to Second Conditionals is used to: (1) talk about
Should conditions in the future that are probably not going
to happen; and (2) talk about something in the
Modals for Prohibition present, which is impossible and imaginary.
Must not It follows the form [If + simple past tense
Can not of a verb,] + [would + base form of a
Should not verb]
Permission – the act of allowing someone to do Third Conditionals is often used when we regret
something. something or imagine a past unreal situation; a past
condition that did not happen
Prohibition – the act of forbidding something.
It follows the form [If + past perfect tense
Obligation – a duty or commitment. of a verb,] + [would + have + past
participle form of a verb]
Paragraph – a group of sentences that tells about
one subject or area. Communication the act of giving, sharing and
getting information.
Parts of a Paragraph
A speech style is a form of language that the
Title
speaker employs according to the level of formality
Topic sentence (Martin Joos 1967).
Supporting sentence
Conclusion
Frozen is the highest form of communication,
identified as fixed speech. It is specific in form as it
uses complex grammatical sentence structure and
vocabulary known by experts in a particular field.
Formal is used normally in writing rather than in
speaking, thus, eliciting a more formal kind of
speech. Use of ellipsis, contractions, and qualifying
adverbials is eliminated. Typically, it is
unidirectional and informative, but just pure
information can sometimes be dull, therefore it’s
occasionally persuasive, too.
Consultative is also called unplanned speech
because it allows the speaker to use the participation
and feedback of the listener. It is bidirectional or
sometimes multi-directional in nature wherein the
speaker supplies the necessary information and the
listener participates continuously.
Casual employs a free and easy participation of
both the speaker and listener. It is also called
informal style since it is common among peers and
friends. It is multi-directional and typically spoken
in nature by people who belong in the same group
or team, but it can also be used in writing, text
messaging, emails, or online chats.
Intimate style is private and practiced in dialogs
between very close individuals leading to a high
chance of nonverbal communication. Bidirectional
and typically spoken in nature, it can also be used in
writing, text messaging, emails, or online chats with
close family members and close friends. Similar to
casual style, it also employs free and easy
participation of both the speaker and the listener.
You might also like
- EDGE Placement Teacher MannualDocument16 pagesEDGE Placement Teacher Mannualmammad200050% (2)
- Sum Up Unit 5 Cause and EffectDocument1 pageSum Up Unit 5 Cause and EffectDhamar GLNo ratings yet
- English 1 4qDocument6 pagesEnglish 1 4qmayinthemay12No ratings yet
- Reviewer in EnglishDocument3 pagesReviewer in EnglishOliver ElicoNo ratings yet
- English 9 Quarter 1 ReviewerDocument4 pagesEnglish 9 Quarter 1 ReviewerEugenio Muella100% (1)
- English For Computer Use: Web PageDocument10 pagesEnglish For Computer Use: Web PageSally LuNo ratings yet
- English - Quarter 1Document3 pagesEnglish - Quarter 186x2yr8ng4No ratings yet
- 7 - M17 - S3, Grammar3, The Remaining Lectures, Weeks 7+8+9+10, Pr. ElmouhtarimDocument18 pages7 - M17 - S3, Grammar3, The Remaining Lectures, Weeks 7+8+9+10, Pr. ElmouhtarimSimo SimoNo ratings yet
- Topics of ClassDocument1 pageTopics of ClassFanny SFNo ratings yet
- LanguageDocument15 pagesLanguageAgustina RealNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument21 pagesConditionalsmd yasin hasanNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument1 pageConditionalsDaniel Ovalle 10No ratings yet
- Module 1 2 English 9Document6 pagesModule 1 2 English 9Sharlyn GalonoNo ratings yet
- English 9: Grade 9 Milflores Teacher: Ms. Celeste A. de Vera, LPTDocument15 pagesEnglish 9: Grade 9 Milflores Teacher: Ms. Celeste A. de Vera, LPTCeleste De VeraNo ratings yet
- Conditional ClausesDocument4 pagesConditional ClausesPetra BajacNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggri 1Document15 pagesBahasa Inggri 1masayususanti62No ratings yet
- Conditional Sentence Dan BargainingDocument14 pagesConditional Sentence Dan BargainingDiwa TamaNo ratings yet
- Progcheck Pre-InterDocument6 pagesProgcheck Pre-Intermls2795No ratings yet
- Review of The TopicsDocument8 pagesReview of The TopicsHumberto Gomez MuñozNo ratings yet
- English: If + Conditional, Will + ConsequenceDocument2 pagesEnglish: If + Conditional, Will + ConsequenceHeart GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Eng9 Essay 1-3Document3 pagesEng9 Essay 1-3Clarissa godenezNo ratings yet
- Simplified Learning and Assessment Sheet (Slash) : Most Essential Learning Competency: Presentation of LessonDocument9 pagesSimplified Learning and Assessment Sheet (Slash) : Most Essential Learning Competency: Presentation of LessonUltra PassNo ratings yet
- Cowan ResumenDocument18 pagesCowan ResumenvictoriaNo ratings yet
- CONDITIONALSDocument5 pagesCONDITIONALSANGELO SHIBUNo ratings yet
- Basic Communication SkillsDocument19 pagesBasic Communication SkillsChristian GallardoNo ratings yet
- Adverbial Clause - Wikipedia PDFDocument13 pagesAdverbial Clause - Wikipedia PDFDhiraj ChandraNo ratings yet
- Grammar Space 1 SB (Letter)Document100 pagesGrammar Space 1 SB (Letter)C.K. LeeNo ratings yet
- Week 009-Module Correct UsageDocument16 pagesWeek 009-Module Correct UsageKenberly DingleNo ratings yet
- ConditionalsDocument23 pagesConditionalsFatïma ZohraNo ratings yet
- Catatan Kelompok 4 GrammarDocument6 pagesCatatan Kelompok 4 GrammarIkhlas PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Eng Lec 5BDocument13 pagesEng Lec 5BAhmad Usman JavedNo ratings yet
- Class 8: Present Simple Using A Modal Verb Lesson SummaryDocument4 pagesClass 8: Present Simple Using A Modal Verb Lesson SummaryEnmanuel Neri Uscuvilca LoayzaNo ratings yet
- Grammar - Conditional and SubjunctiveDocument3 pagesGrammar - Conditional and SubjunctiveCherrie Mae NietesNo ratings yet
- Modality: Sri Shophiatur Rahayu (2c)Document15 pagesModality: Sri Shophiatur Rahayu (2c)Ayu NuraeniNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument17 pagesConditional SentencesQyuBeeNo ratings yet
- Engl111 Week 4Document19 pagesEngl111 Week 4Beverly A PanganibanNo ratings yet
- EnglishDocument8 pagesEnglishHannas PrettyNo ratings yet
- English Reviewer q4Document4 pagesEnglish Reviewer q4zarahobinaNo ratings yet
- 【英语】一张图看懂高考核心语法知识点Document16 pages【英语】一张图看懂高考核心语法知识点enyaerNo ratings yet
- Tugas Makalah Bahasa InggrisDocument15 pagesTugas Makalah Bahasa InggrisMysteri OusNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Conditionals I Wish 1Document4 pagesUnit 2 Conditionals I Wish 1Jagor1240 OfficialNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 Ideational MetaphorDocument93 pagesLecture 8 Ideational Metaphorfadhlan ramadhanNo ratings yet
- Conjunction and Conditional SentencesDocument11 pagesConjunction and Conditional SentencesRahmatia Candra DewiNo ratings yet
- Pre-Intermediate English Level: Natalia CifuentesDocument10 pagesPre-Intermediate English Level: Natalia CifuentesLUIS GERMAN GUARNIZO MEDINANo ratings yet
- Moods in The SentencesDocument4 pagesMoods in The SentencesNabin NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Adverbial ClauseDocument5 pagesAdverbial ClauseYuna ZhangNo ratings yet
- Colombian V.S. American IdiomsDocument20 pagesColombian V.S. American IdiomsmnocuaNo ratings yet
- Conditional TranslationDocument7 pagesConditional TranslationAnto Roldan OliveraNo ratings yet
- The Syntax of The Complex SentenceDocument31 pagesThe Syntax of The Complex SentenceNerv RulzNo ratings yet
- Conditional SentencesDocument5 pagesConditional SentencesCampbell MariaNo ratings yet
- English 8 Quarter 1 Concept Notes 1Document18 pagesEnglish 8 Quarter 1 Concept Notes 1Villegas Kate Andrea BNo ratings yet
- Grammar - QuantifiersDocument3 pagesGrammar - QuantifiersCherrie Mae NietesNo ratings yet
- Module 2 ConditionalsDocument6 pagesModule 2 ConditionalsIva CameroNo ratings yet
- q1 - Conditionals Table GuideDocument4 pagesq1 - Conditionals Table GuideNoralyn AgbayNo ratings yet
- GRAMMAR Preparation For Assignment 2Document4 pagesGRAMMAR Preparation For Assignment 2Ian KopelowitzNo ratings yet
- TensesDocument7 pagesTensesredchillipaperNo ratings yet
- CH 2Document12 pagesCH 2YuliaNo ratings yet
- GR9 Unit 2 EnglishDocument25 pagesGR9 Unit 2 EnglishTipa JacoNo ratings yet
- Sintaksa Eng, III Kol, TeorijaDocument2 pagesSintaksa Eng, III Kol, TeorijaMatea CrljenićNo ratings yet
- MODALSDocument4 pagesMODALSMarnel DincolNo ratings yet
- 2-Active Learning SpacesDocument14 pages2-Active Learning SpacesSamuel OkohNo ratings yet
- Welcome To A Career That Will Help Shape Your CareerDocument6 pagesWelcome To A Career That Will Help Shape Your Careerrohan_sohanNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For Conducting Service Quality Research PDFDocument12 pagesGuidelines For Conducting Service Quality Research PDFgaluhvitaNo ratings yet
- Graduate School: Premise: The Educators Are of Course An Integral Element of The Earning EcosystemDocument2 pagesGraduate School: Premise: The Educators Are of Course An Integral Element of The Earning EcosystemJomajFalcatanDelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Course DesignDocument16 pagesCourse DesignSelvin CayNo ratings yet
- Minor Requirements: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Subject NCM 119Document6 pagesMinor Requirements: in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements For The Subject NCM 119ingridNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Activity Sheets Practical Research 2-Quarter 1, Week 5 Writing A Research TitleDocument4 pagesWeekly Learning Activity Sheets Practical Research 2-Quarter 1, Week 5 Writing A Research TitleShekaina Faith Cuizon Lozada100% (1)
- فرهنگ ترکیبی فلسفهDocument582 pagesفرهنگ ترکیبی فلسفهmrafzaliNo ratings yet
- Leadership DevelopmentDocument14 pagesLeadership DevelopmentNashwa SaadNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Quarter 1 Activity SheetsDocument8 pagesPractical Research 2 Quarter 1 Activity SheetsJonnis Estillore100% (1)
- Bsed2b Educ20 Simon, Charlene Joy-MidtermDocument19 pagesBsed2b Educ20 Simon, Charlene Joy-MidtermCharlene Joy SimonNo ratings yet
- K-Bridge Ecdis and K-Nav Ecdis Familiarisation Course (E-Learning)Document1 pageK-Bridge Ecdis and K-Nav Ecdis Familiarisation Course (E-Learning)Wasim AliNo ratings yet
- n362 Professional Development 1Document2 pagesn362 Professional Development 1api-302574067100% (1)
- Seven Transformations of LeadershipDocument17 pagesSeven Transformations of Leadershippraval1908100% (1)
- Writingpracticetest1 v9 1500002Document4 pagesWritingpracticetest1 v9 1500002Crystal taehyungNo ratings yet
- Breaking FreeDocument2 pagesBreaking FreeBenjo HodzicNo ratings yet
- Unit V, Chapter 2Document8 pagesUnit V, Chapter 2ashivaramakrishnaNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Friends Global 10 - Unit 6 ListeningDocument5 pagesLESSON PLAN Friends Global 10 - Unit 6 ListeningLinh PhạmNo ratings yet
- The Project in The Organizational StructureDocument40 pagesThe Project in The Organizational StructureMohola Tebello GriffithNo ratings yet
- 2020 School Improvement Plan WebsiteDocument8 pages2020 School Improvement Plan WebsiteAiza BananNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: INTRODUCTION Background of The StudyDocument3 pagesChapter 1: INTRODUCTION Background of The StudyJhelo CruzNo ratings yet
- English 6-PT-Q2Document1 pageEnglish 6-PT-Q2Mhadz Reyes100% (1)
- Parent Handbook: For Special EducationDocument56 pagesParent Handbook: For Special EducationRhea De Matta BilbesNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional PurposesDocument2 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional PurposesCarmela HernandezNo ratings yet
- Thesis Evaluation Report TW - 2Document3 pagesThesis Evaluation Report TW - 2Yonael Mezmure100% (2)
- Cambridge IGCSE™: Chinese As A Second Language 0523/01 May/June 2021Document9 pagesCambridge IGCSE™: Chinese As A Second Language 0523/01 May/June 2021For GamingNo ratings yet
- Vision Transformers: Revolutionizing Computer VisionDocument14 pagesVision Transformers: Revolutionizing Computer VisionPremanand SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Cognitive AnthropologyDocument22 pagesCognitive AnthropologyAnirban GoswamiNo ratings yet
- What Are The Reasons For The Existence of Multi-Grade Classes?Document2 pagesWhat Are The Reasons For The Existence of Multi-Grade Classes?jade tagabNo ratings yet