Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Uti
Uploaded by
Jeleya graceOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Uti
Uploaded by
Jeleya graceCopyright:
Available Formats
COLEGIO DE DAGUPAN
SCHOOL OF HEALTH SCIENCES
Arellano St., Dagupan City, Pangasinan
DRUG STUDY
Name: __________________________________________ Date: _________________ Inclusive Dates of Rotation: _____________
Year & Block: ____________ Area/ Shift/Days: ________ Clinical Instructor: ____________________________________________
Patient’s Name (Optional)/ Case Number:
Medical Diagnosis: URINARY TRACT INFECTION
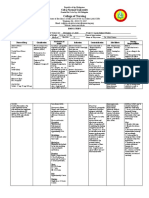
DRUG NAME: CEPHALEXIN
DRUG CLASSIFICATION: First-generation cephalosporins
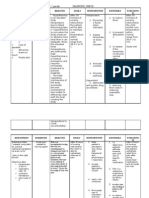
MECHANISM OF INDICATIONS & CONTRAINDICATIONS ADVERSE EFFECTS INTERACTIONS NURSING
ACTION DOSAGES & CAUTIONS IMPLICATIONS WITH
PATIENT TEACHINGS
Inhibits bacterial cell Upper, lower CONTRAINDICATIONS: ADVERSE EFFECTS NTERACTIONS NURSING
wall synthesis, respiratory tract, Hypersensitivity to CNS: Headache, Individual drugs CONSIDERATIONS
rendering cell wall urinary tract, skin, cephalosporins, infants dizziness, weakness, Probenecid: increased Assessment
osmotically unstable, bone infections; ,1 mo paresthesia, fever, chills, toxicity • Assess patient for
leading to cell death by otitis me Precautions: Pregnancy seizures (high doses) Drug classifications previous sensitivity
binding to cell wall B, breastfeeding, GI: Nausea, vomiting, Aminoglycosides, reaction
membrane, lysis mediated Moderate infections hypersensitivity to diarrhea, anorexia, diuretics (loop): increased to penicillins or other
by cell wall autolytic Adult: PO 250-500 mg penicillins, renal disease pain, glossitis, bleeding; toxicity cephalosporins;
enzymes q6hr, max 4 g/day increased AST, ALT, Anticoagulants: increased crosssensitivity between
Child: PO 25-100 bilirubin, LDH, alkaline protime; use cautiously penicillins and
mg/kg/day in 4 equal phosphatase; abdominal Oral contraceptives: cephalosporins is
doses, pain, pseudomembranous decreased effectiveness common
max 4 g/day colitis possible; use another • Assess patient for signs
Moderate skin infections GU: Proteinuria, form of contraception and symptoms of
Adult: PO 500 mg q12hr vaginitis, pruritus, Drug/lab test infection including
Endocarditis prophylaxis candidiasis, increased Increased: AST, ALT, characteristics of wounds,
2 g 1 hr before procedure BUN, nephrotoxicity, alkaline phosphatase, sputum, urine, stool,
Severe infections renal LDH, WBC .10,000/mm3
Adult: PO 500 mg-1 g failure BUN, creatinine, ,
q6hr, max 4 g HEMA: Leukopenia, bilirubin earache, fever; obtain
Child: PO 50-100 thrombocytopenia, False positive: urinary baseline information and
mg/kg/day in 4 equal agranulocytosis, anemia, protein, direct Coombs’ during treatment
doses, neutropenia, test, urine glucose • Obtain C&S before
max 4 g/day lymphocytosis, Interference: cross- beginning product
Renal dose eosinophilia, matching therapy
Adult: PO CCr 10-40 pancytopenia, to identify if correct
ml/min 250-500 mg, then hemolytic anemia treatment has been
250-500 mg q8-12hr; CCr INTEG: Rash, urticaria, initiated
,10 mg/min 250- dermatitis • Assess for anaphylaxis:
500 mg, then 250-500 mg MS: Arthralgia, arthritis rash, urticaria,
q12-24hr RESP: Dyspnea pruritus, chills, fever,
Available forms: Caps SYST: Anaphylaxis, joint pain; angioedema
250, 500 mg; tabs serum sickness, may occur a few days
250, 500 mg, 1 g; oral superinfection, Stevens- after therapy begins;
susp 125, 250 mg/5 ml Johnson syndrome epinephrine and
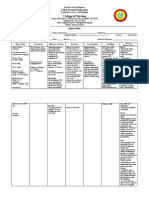
resuscitation equipment
should
be available for
anaphylactic reaction
• Identify urine output; if
decreasing, notify
prescriber (may indicate
nephrotoxicity); also
check for increased BUN,
creatinine
• Monitor blood studies:
AST, ALT, CBC, Hct,
bilirubin, LDH, alkaline
phosphatase, Coombs’
test monthly if patient is
on long-term therapy
• Monitor electrolytes:
potassium, sodium,
chloride monthly if
patient is on long-term
therapy
• Assess bowel pattern
daily; if severe diarrhea
occurs, product should be
discontinued; may
indicate
pseudomembranous
colitis
• Monitor for bleeding:
ecchymosis, bleeding
gums, hematuria, stool
guaiac daily if on
longterm therapy
• Assess for
superinfection: perineal
itching,
fever, malaise, redness,
pain, swelling, drainage,
rash, diarrhea, change in
cough, sputum
Patient/family education •
Teach patient to report sore
throat, bruising, bleeding,
joint pain; may indicate blood
dyscrasias (rare) • Advise
patient to contact prescriber
if vaginal itching, loose foul-
smelling stools, furry tongue
occur; may indicate
superinfection • Instruct
patient to take all medication
prescribed for the length of
time ordered • Advise patient
to notify prescriber of
diarrhea with blood, pus,
mucus, which may indicate
pseudomembranous colitis
______________________________________________ __________________________________________________
Patient/ Significant Other’s Signature Student Nurse’s Signature
You might also like
- Chapter 5 Drug StudyDocument16 pagesChapter 5 Drug StudyRegee Rose LacsonNo ratings yet
- Trachomatis - Adult: PO 500 MG Qid X 7 Days. Syphilis. Adult/adolescent: PO 500 MG Qid XDocument26 pagesTrachomatis - Adult: PO 500 MG Qid X 7 Days. Syphilis. Adult/adolescent: PO 500 MG Qid XlaniNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudySwag MasterNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin DRUGSTUDYDocument3 pagesVancomycin DRUGSTUDYEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GuideDocument5 pagesDrug Study GuidePAOLA LUZ CRUZNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDYDocument8 pagesDRUGSTUDYWinnie Salazar AriolaNo ratings yet
- CaptoprilDocument2 pagesCaptoprilVina Jane P Laurel100% (2)
- Prescribed dosage and administration of Suprax antibioticDocument3 pagesPrescribed dosage and administration of Suprax antibioticHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- LevofloxacinDocument3 pagesLevofloxacinLIEZEL GRACE VELAYO100% (1)
- DrugDocument2 pagesDrugthe_greatpasawayNo ratings yet
- University of Cebu - BaniladDocument6 pagesUniversity of Cebu - BaniladCHINGCHONG SLAYERNo ratings yet
- Material, Vincent M. Drug Study - (Ceftriaxone and Salbutamol)Document6 pagesMaterial, Vincent M. Drug Study - (Ceftriaxone and Salbutamol)vincent materialNo ratings yet
- Pedia Care Study - Appendix B - Drug StudyDocument8 pagesPedia Care Study - Appendix B - Drug Studyryan100% (1)
- Losartan Drug Study for Acute Kidney FailureDocument3 pagesLosartan Drug Study for Acute Kidney FailureLouie Danielle SegarraNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComDocument2 pagesCephalexin Drug Study RNpedia ComTaraKyleUyNo ratings yet
- Drug study nursing considerationsDocument4 pagesDrug study nursing considerationsMilky Lescano LargozaNo ratings yet
- Zinacef: Brand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationDocument2 pagesZinacef: Brand Name: Generic Name: Drug ClassificationChristine Pialan SalimbagatNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin PDFDocument3 pagesAmpicillin PDFandriNo ratings yet
- Name: Ma Rupina B. Ponce Course: Bachelor of Science Major in Nursing Section: C Cholera DefinitionDocument17 pagesName: Ma Rupina B. Ponce Course: Bachelor of Science Major in Nursing Section: C Cholera DefinitionMaria Pina Barbado PonceNo ratings yet
- Go Piperacillin-TazobactamDocument4 pagesGo Piperacillin-TazobactamSAMANTHA T. MODESTONo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY-FORMAT - CopyDocument8 pagesDRUG-STUDY-FORMAT - CopyShyne HazyNo ratings yet
- Drug CiproDocument1 pageDrug CiproSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Cephalexin dosage, mechanism of action, adverse effectsDocument1 pageCephalexin dosage, mechanism of action, adverse effectsJoover AquinoNo ratings yet
- Questions:: Clinical Case Analysis Name of Patient Age: 52 Gender: M Address Date Admitted: Diagnosis Nursing HistoryDocument12 pagesQuestions:: Clinical Case Analysis Name of Patient Age: 52 Gender: M Address Date Admitted: Diagnosis Nursing Historyaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDrug Study - CefuroximeErika Jane EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDY AmpicillinsodiumDocument3 pagesDRUGSTUDY AmpicillinsodiumMicaela Andrea CieloNo ratings yet
- Generic Name: Brand Name: Pharmacologic Class: Action: CNS: DizzinessDocument8 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name: Pharmacologic Class: Action: CNS: DizzinessMaricon BautistaNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument4 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingDocument3 pagesDrugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingHazel Palomares100% (1)
- FaciitisDocument17 pagesFaciitisdalaginding clophNo ratings yet
- أروى حكميDocument16 pagesأروى حكميArwa HakamiNo ratings yet
- Drugs PediaDocument3 pagesDrugs PediaMark Ianne AngNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin Drug Study: Bactericidal Antibiotic with Ototoxic and Nephrotoxic RisksDocument1 pageVancomycin Drug Study: Bactericidal Antibiotic with Ototoxic and Nephrotoxic RisksJUSTINE ALLYSA MAY CASTILLONo ratings yet
- Dolan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDolan Drug StudyLian Robbie BautistaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Contradiction Nursing ConsiderationDocument16 pagesDrug Name Mechanism of Action Indication Side Effects/ Adverse Reaction Contradiction Nursing ConsiderationLouwella RamosNo ratings yet
- CaspofunginDocument2 pagesCaspofunginSapna thakurNo ratings yet
- FluconazoleDocument3 pagesFluconazoleMary Kate ClarosNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Actions: Indications: Side Effects: Nursing ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesTherapeutic Actions: Indications: Side Effects: Nursing Considerationsmilette-mendoza-3355No ratings yet
- Therapeutic Actions: Indications: Side Effects: Nursing ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesTherapeutic Actions: Indications: Side Effects: Nursing Considerationsmilette-mendoza-3355No ratings yet
- PiperacillinDocument3 pagesPiperacillinNicholas TagleNo ratings yet
- Covid19-Drug StudyDocument7 pagesCovid19-Drug StudynicoleNo ratings yet
- Drug Study AngelaDocument8 pagesDrug Study AngelaIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Axetil (Oral)Document2 pagesCefuroxime Axetil (Oral)STORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- MARCOS, ARIAN MAY S. DRUG STUDY BSN 2faDocument10 pagesMARCOS, ARIAN MAY S. DRUG STUDY BSN 2faArian May MarcosNo ratings yet
- DS - Format - MedDocument3 pagesDS - Format - MedChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDYxNCP - WEEK2 - ST - VICTORIADocument8 pagesDRUG STUDYxNCP - WEEK2 - ST - VICTORIAKent Martin AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Piperacillin / TazobactamDocument3 pagesDrug Study: Piperacillin / Tazobactammyer pasandalanNo ratings yet
- Oxacillin antibiotic for bacterial infectionsDocument3 pagesOxacillin antibiotic for bacterial infectionsPrince Mark BadilloNo ratings yet
- 13 Med MNGTDocument19 pages13 Med MNGTKate ChavezNo ratings yet
- Medications and Treatments for Fever, Pain, and InfectionsDocument15 pagesMedications and Treatments for Fever, Pain, and Infectionsghian carloNo ratings yet
- CececeDocument57 pagesCececeBSRT1A BERBANO, IAN JEWEL M.No ratings yet
- Cefuroxime 1Document3 pagesCefuroxime 1Gwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- StreptomycinDocument1 pageStreptomycinDemilyn Fat100% (2)
- Antibiotics: Mos.: 25-50 Mg/kg/day in 3 Divided Doses. Children 3 Mos and Younger: 30Document9 pagesAntibiotics: Mos.: 25-50 Mg/kg/day in 3 Divided Doses. Children 3 Mos and Younger: 30Kath TagamolilaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pagesDrug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaRichelle Sandriel C. de CastroNo ratings yet
- Ampicillin DRUG STUDYDocument2 pagesAmpicillin DRUG STUDYJuliana CarpinteroNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime and Ketorolac Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCefuroxime and Ketorolac Drug StudyDeva HiyasNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone DrugStudyDocument8 pagesDexamethasone DrugStudySophia IbuyanNo ratings yet
- HyperbilirubinemiaDocument10 pagesHyperbilirubinemiachiboogs456100% (1)
- Sources and Tests for GlucoseDocument3 pagesSources and Tests for GlucoseJeleya graceNo ratings yet
- Dacdac, Jeleah Grace 11-Bsn-01 (Lab)Document1 pageDacdac, Jeleah Grace 11-Bsn-01 (Lab)Jeleya graceNo ratings yet
- Elephant ToothpasteDocument7 pagesElephant ToothpasteJeleya graceNo ratings yet
- Dacdac, Jeleah Grace - 12-BSN-01 - Health Education LectureDocument9 pagesDacdac, Jeleah Grace - 12-BSN-01 - Health Education LectureJeleya graceNo ratings yet
- Dacdac, Jeleah Grace 11-BSN-01 - Blending With RemotoDocument5 pagesDacdac, Jeleah Grace 11-BSN-01 - Blending With RemotoJeleya graceNo ratings yet
- Dacdac, Jeleah Grace 11-Bsn-01 - Personal EssayDocument2 pagesDacdac, Jeleah Grace 11-Bsn-01 - Personal EssayJeleya graceNo ratings yet
- IruvarDocument5 pagesIruvarKarthikeya KaredlaNo ratings yet
- A Daily Morning PrayerDocument8 pagesA Daily Morning Prayerjhustine05100% (1)
- Conditions For The Emergence of Life On The Early Earth: Summary and ReflectionsDocument15 pagesConditions For The Emergence of Life On The Early Earth: Summary and Reflectionsapi-3713202No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans for ChildrenDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans for ChildrenAlexander Rodriguez OlipasNo ratings yet
- The Greatest Showman PDFDocument22 pagesThe Greatest Showman PDFMJ RecordNo ratings yet
- (Jean Oliver and Alison Middleditch (Auth.) ) Funct (B-Ok - CC)Document332 pages(Jean Oliver and Alison Middleditch (Auth.) ) Funct (B-Ok - CC)Lorena BurdujocNo ratings yet
- I3rc Insights Pvt. Ltd. India - Company Credentials PDFDocument28 pagesI3rc Insights Pvt. Ltd. India - Company Credentials PDFManoj Kumar JhaNo ratings yet
- CNC Instructables PDFDocument13 pagesCNC Instructables PDFNadim AhmedNo ratings yet
- Band Theory and Bloch Theorem in Solid State PhysicsDocument8 pagesBand Theory and Bloch Theorem in Solid State PhysicsVicky VickyNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Permutations and CombinationsDocument14 pages6.4 Permutations and CombinationsAns SembiringNo ratings yet
- Acrogym: by Ahana AnandDocument9 pagesAcrogym: by Ahana AnandAhana AnandNo ratings yet
- Fairfield Institute of Management & Technology E-Commerce: Lab/Practical File Subject Code: 112Document24 pagesFairfield Institute of Management & Technology E-Commerce: Lab/Practical File Subject Code: 112AYUSHNo ratings yet
- Accounting Project Topics and Materials in NigeriaDocument97 pagesAccounting Project Topics and Materials in NigeriaProject Championz100% (2)
- PDI 14 Asthma Admission RateDocument2 pagesPDI 14 Asthma Admission RatejrmyfngNo ratings yet
- Compiler Design and Linux System AdministrationDocument47 pagesCompiler Design and Linux System AdministrationGouri ShankerNo ratings yet
- DownloadDocument2 pagesDownloadAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Mens Care Active Concepts PDFDocument19 pagesMens Care Active Concepts PDFFredy MendocillaNo ratings yet
- ORPHEUS by GRS Mead - Electronic Text EditionDocument199 pagesORPHEUS by GRS Mead - Electronic Text EditionMartin EuserNo ratings yet
- Omega: Mahdi Alinaghian, Nadia ShokouhiDocument15 pagesOmega: Mahdi Alinaghian, Nadia ShokouhiMohcine ES-SADQINo ratings yet
- Instant Download Ebook PDF Building Construction Handbook 11th Edition PDF ScribdDocument41 pagesInstant Download Ebook PDF Building Construction Handbook 11th Edition PDF Scribdthomas.bilal255100% (38)
- Strategic Marketing Plan for British American TobaccoDocument31 pagesStrategic Marketing Plan for British American TobaccoAli Abbas50% (2)
- Articulos 2022-2Document11 pagesArticulos 2022-2Nilser Enrique Valle HernandezNo ratings yet
- Asc2104b-T I enDocument21 pagesAsc2104b-T I enELOUNDOU EVARISTE OHANDJANo ratings yet
- HL-1060 User, Parts, and Service Manual 02Document6 pagesHL-1060 User, Parts, and Service Manual 02วรพงษ์ กอชัชวาลNo ratings yet
- DissertationDocument15 pagesDissertationNicole BradyNo ratings yet
- Thermo Safety Cabinets MSC-Advantage - User ManualDocument53 pagesThermo Safety Cabinets MSC-Advantage - User ManualAhmed SalamaNo ratings yet
- LogDocument15 pagesLogandrew_hm925635No ratings yet
- PRESSURE VESSEL Handbook - Eugene F. Megyesy 12th 2001Document501 pagesPRESSURE VESSEL Handbook - Eugene F. Megyesy 12th 2001vamcodong71% (7)
- Junguian PsychotherapyDocument194 pagesJunguian PsychotherapyRene Galvan Heim100% (13)