Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Surveying - 1 - Assignment
Uploaded by
jojo davidinhoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Surveying - 1 - Assignment
Uploaded by
jojo davidinhoCopyright:
Available Formats
ENGINEERING SURVEY 1 – ASSIGNMENT 1.
GROUP 7.
6.9 Discuss the various options available for defining a north direction on a coordinate
grid.
6.10 What is the fractional linear misclosure for a traverse and how is it calculated?
6.12 Discuss the various sources of error that can occur when measuring traverse angles
and distances.
6.13 How does an intersection differ from a resection?
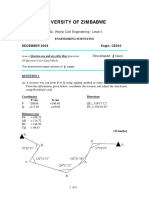
6.15 As they have not been used for some time, the coordinates of three control points A, S
and T are to be checked by measuring the internal angles and lengths of the triangle
AST. Using the coordinates given below, calculate the required angles and distances.
Point mE mN
A 1507.319 632.017
S 1635.904 725.769
T 1738.612 627.301
(Hint: To solve this problem, calculate rectangular polar conversions along each line
of the triangle. This gives the distances. To calculate the internal angles, use the
bearings obtained where angle A = bearing AT – bearing AS and so on)
6.20 A new 100 m × 40 m warehouse is to be set out from four traverse stations A, B, C
and D that were used in the site survey. However, all design coordinates are to be
based on a new structural grid aligned with the warehouse and not the coordinate grid
adopted for the site survey.
Using the data given below, calculate;
i. the transformation parameters to convert coordinates from the site grid to the
structural grid.
ii. the coordinates of B and D on the structural grid.
Station Site survey Structural grid
mE mN mE mN
A 150.000 350.000 109.515 251.780
B 424.887 510.985
C 467.804 288.117 329.456 14.175
D 234.100 128.848
6.23 A distance resection is carried out at point P to two control points A and B. Calculate
the coordinates of P using the data given below.
Point mE mN Measured distances and angle
A 379.588 758.723 PA = 158.635 m PB = 208.272 m
B 411.800 572.850 APB = 60°05'00"
(Note: The approximate position of P is 240 mE, 690 mN)
You might also like
- Orpheus WoD 2 0Document62 pagesOrpheus WoD 2 0Matheus PradoNo ratings yet
- Brand Identity WalmartDocument101 pagesBrand Identity WalmartGuilherme Welter50% (2)
- Conditions For Effective Innovation On The MacroDocument3 pagesConditions For Effective Innovation On The MacroWinesha U. Smith100% (2)
- Eastings and NorthingsDocument34 pagesEastings and NorthingsDarren Hamilton50% (2)
- Field Exercise No. 4Document3 pagesField Exercise No. 4Bambi InjangNo ratings yet
- Due Date: Given in Lecture.: Part I: QuestionsDocument5 pagesDue Date: Given in Lecture.: Part I: QuestionsChristan ChristanNo ratings yet
- Traverse CalculationsDocument6 pagesTraverse CalculationsSteeve SenoNo ratings yet
- Basics On Piping LayoutDocument11 pagesBasics On Piping Layoutpuru55980No ratings yet
- 04-68350A Manual CCN DM01-DI01 PDFDocument47 pages04-68350A Manual CCN DM01-DI01 PDFtaha50% (2)
- SACS TrainingDocument4 pagesSACS Trainingasma100% (1)
- Surveying PDFDocument6 pagesSurveying PDFremster OñateNo ratings yet
- Principles of PaleontologyDocument10 pagesPrinciples of Paleontologyvitrinite50% (2)
- Winone Elevator Connection DiagramDocument40 pagesWinone Elevator Connection DiagramMuhammad Rashid75% (4)
- Test Paper of SurveyingDocument11 pagesTest Paper of Surveyingjhacademyhyd100% (2)
- Remote Sensing GeologyDocument438 pagesRemote Sensing GeologyStalin Bryan100% (2)
- TraversingDocument8 pagesTraversingMarc Dared CagaoanNo ratings yet
- Surveying-II: B.E. (Civil Engineering) Sixth Semester (C.B.S.)Document4 pagesSurveying-II: B.E. (Civil Engineering) Sixth Semester (C.B.S.)Mahesh RamtekeNo ratings yet
- 9 Setting OutDocument4 pages9 Setting OutElisha ThompsonNo ratings yet
- CV2304 Surveying Part 2 Examination: School of Engineering & Mathematical SciencesDocument8 pagesCV2304 Surveying Part 2 Examination: School of Engineering & Mathematical SciencesErnie ErnieNo ratings yet
- Sagar Institute of Science & Technology (Sistec) Department of Civil EngineeringDocument8 pagesSagar Institute of Science & Technology (Sistec) Department of Civil EngineeringASHISH SINGH SENGARNo ratings yet
- CN106 Engineering Surveying: Semester 2 Examinations 2005-2006Document8 pagesCN106 Engineering Surveying: Semester 2 Examinations 2005-2006H S Vishwanath ShastryNo ratings yet
- 1st Year AssignmentDocument8 pages1st Year AssignmentJigyasaNo ratings yet
- SurveyingDocument63 pagesSurveyingShazrin Yusof100% (1)
- Surveying TutorialDocument3 pagesSurveying Tutoriallangazelamoyo19No ratings yet
- 8 TraverseDocument8 pages8 TraverseSubbu PemmasaniNo ratings yet
- GEOM2015 Traverse Tutorial 2016 PDFDocument2 pagesGEOM2015 Traverse Tutorial 2016 PDFKofi DanielNo ratings yet
- 2962 Bidang Benjamin 2212763Document2 pages2962 Bidang Benjamin 2212763BENJAMIN III BIDANGNo ratings yet
- University of Mauritius Faculty of EngineeringDocument5 pagesUniversity of Mauritius Faculty of EngineeringBhunjun VandanaNo ratings yet
- 10th సోషల్ బిట్స్.జి సైదేశ్వర రావు.Document2 pages10th సోషల్ బిట్స్.జి సైదేశ్వర రావు.Navadeep NavadeepNo ratings yet
- Survey II Assignment: TriangulationDocument2 pagesSurvey II Assignment: TriangulationCharles SnyderNo ratings yet
- SurveyiingDocument11 pagesSurveyiingELEVATED KnowledgeNo ratings yet
- The Mathematics of Engineering Surveying (3) : ScenarioDocument5 pagesThe Mathematics of Engineering Surveying (3) : ScenarioPrimož KozlevčarNo ratings yet
- C1ce02 c1106 Surveying Set1Document2 pagesC1ce02 c1106 Surveying Set1bhkedarNo ratings yet
- B3 G4 210925 Sandipan Lab8Document4 pagesB3 G4 210925 Sandipan Lab8Shishir ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Khan Qasim HW#7Document6 pagesKhan Qasim HW#7Zed ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- SurveyingDocument6 pagesSurveyingMARK KEVIN GUTIERREZNo ratings yet
- SUG413 - Advanced Engineering Survey (Setting-Out Survey)Document17 pagesSUG413 - Advanced Engineering Survey (Setting-Out Survey)mruzainimf92% (37)
- University of Zimbabwe: Engineering Surveying December 2009 Engin. CE203Document4 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe: Engineering Surveying December 2009 Engin. CE203Mercy SimangoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Control SurveyDocument33 pagesChapter 6 Control SurveyGemechis BachaNo ratings yet
- University of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIDocument5 pagesUniversity of Zimbabwe B.Sc. (Engineering) Honours - Level IIMercy SimangoNo ratings yet
- Directions: Answer The Following Questions. Write Your SOLUTION and BOX Your Final Answer in Your NotebookDocument6 pagesDirections: Answer The Following Questions. Write Your SOLUTION and BOX Your Final Answer in Your NotebookKevin Abenojar NamayaNo ratings yet
- nFINAL TUTORIAL FOR ALLDocument12 pagesnFINAL TUTORIAL FOR ALLkefapaul21No ratings yet
- SL105 - 109 Lecture 4 PDFDocument14 pagesSL105 - 109 Lecture 4 PDF18400681menaNo ratings yet
- Surveying I Group AssignmentDocument2 pagesSurveying I Group AssignmentSolomon DanielNo ratings yet
- Report STPP - Group 1Document9 pagesReport STPP - Group 1Ausa RamadhanNo ratings yet
- QPDocument3 pagesQPSuganyashivraj SuganyaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1vine manNo ratings yet
- Revision QuestionDocument3 pagesRevision QuestionKasyage AbubakaliNo ratings yet
- Surveying Model QuestionDocument2 pagesSurveying Model QuestionMahesh Kumar K BNo ratings yet
- r7210105 SurveyingDocument4 pagesr7210105 SurveyingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- NR 220106 Surveying IIDocument8 pagesNR 220106 Surveying IISrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Mste Surv TransDocument25 pagesMste Surv TransMohamed MoralesNo ratings yet
- Lab Report On SurveyingDocument7 pagesLab Report On SurveyingJoycelyn UyNo ratings yet
- Imquestion PaperDocument8 pagesImquestion PaperThulasi Raman KowsiganNo ratings yet
- Ce Integration: DirectionDocument2 pagesCe Integration: DirectionAlthara BaldagoNo ratings yet
- Building 261Document2 pagesBuilding 261OvyeNo ratings yet
- Assignment Namba 1Document7 pagesAssignment Namba 1Loki PagcorNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6.1: Find The Coordinates of Point C GivenDocument4 pagesExercise 6.1: Find The Coordinates of Point C GivenWaled HantashNo ratings yet
- (Join AICTE Telegram Group) ASU 22301 Question Paper (1) Ce3iDocument4 pages(Join AICTE Telegram Group) ASU 22301 Question Paper (1) Ce3iVivek SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bearings. Also Determine The Included Angles at A, B, C, D and EDocument6 pagesBearings. Also Determine The Included Angles at A, B, C, D and EHari HarishkumarNo ratings yet
- AQS2102200507 Engineering Surveying IDocument4 pagesAQS2102200507 Engineering Surveying ITatenda PaduzeNo ratings yet
- B.Tech II Year (Civil) BCE-18 Advanced Surveying Tutorial Sheet 1-4Document3 pagesB.Tech II Year (Civil) BCE-18 Advanced Surveying Tutorial Sheet 1-4Rahul SinghNo ratings yet
- Surveying Lec2Document6 pagesSurveying Lec2hazelNo ratings yet
- C1ce02 c1106 Surveying Set1Document2 pagesC1ce02 c1106 Surveying Set1bhkedarNo ratings yet
- Lab 5Document4 pagesLab 5Joamy Mark AbellaNo ratings yet
- Ce-1254 - Surveying IiDocument9 pagesCe-1254 - Surveying IiMix TubeNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: InstructionsDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological University: Instructionsvarunsingh214761No ratings yet
- The Good Governance Concept Revisited PDFDocument16 pagesThe Good Governance Concept Revisited PDFPritam AnantaNo ratings yet
- Qualities of A Good PresenterDocument2 pagesQualities of A Good PresenterMuhammad Umair KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations Research 11E Ise 11Th Ise Edition Frederick S Hillier Full ChapterDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Operations Research 11E Ise 11Th Ise Edition Frederick S Hillier Full Chapterrobin.mccomb793No ratings yet
- Pallet Truck wp3000 Spec1 GBDocument6 pagesPallet Truck wp3000 Spec1 GBEjaz EjazNo ratings yet
- Bituminous Construction TypesDocument3 pagesBituminous Construction TypesSiya Fal DesaiNo ratings yet
- Aurelia Vallier SlidesDocument42 pagesAurelia Vallier SlidesSaddy KhanNo ratings yet
- Vilta-S: Stabilizer For SmartphoneDocument28 pagesVilta-S: Stabilizer For SmartphoneNivin KumarNo ratings yet
- tf00001054 WacDocument22 pagestf00001054 WacHritik RawatNo ratings yet
- Ascend P7: Huawei SchematicDocument51 pagesAscend P7: Huawei SchematicCarlos Andres EscamillaNo ratings yet
- Schlosser Distillation SSCHI 2011 256Document14 pagesSchlosser Distillation SSCHI 2011 256Brandon LizardoNo ratings yet
- Product Manual 26205 (Revision B) : IC-100 CD Ignition SystemDocument60 pagesProduct Manual 26205 (Revision B) : IC-100 CD Ignition SystemSyed Mohammad NaveedNo ratings yet
- Linear Analysis and Effective Length MethodDocument4 pagesLinear Analysis and Effective Length MethodmnagasandeepNo ratings yet
- Progresive DPKDocument7 pagesProgresive DPKAmol WalunjNo ratings yet
- TÀI LIỆU - Tính toán thông gió phòng máy động cơ (Engine room ventilation calculation)Document2 pagesTÀI LIỆU - Tính toán thông gió phòng máy động cơ (Engine room ventilation calculation)Thành TháiNo ratings yet
- Political Discourse A Critical Discourse Discourse A Critical Discourse AnalysisDocument13 pagesPolitical Discourse A Critical Discourse Discourse A Critical Discourse AnalysisJennina MazoNo ratings yet
- Urban Bias in Community Development: Student: Tiongson Yvonne P. Instructor: Ar. Irene G. FlorendoDocument9 pagesUrban Bias in Community Development: Student: Tiongson Yvonne P. Instructor: Ar. Irene G. FlorendoYvonne TiongsonNo ratings yet
- Catalog of Replacement Parts: Model D300 Series MixersDocument24 pagesCatalog of Replacement Parts: Model D300 Series Mixersanto starlinNo ratings yet
- Micro SplatDocument17 pagesMicro SplatCarlosAndresGarnicaSalazarNo ratings yet
- GAP Guidelines: Management Programs (Overview)Document27 pagesGAP Guidelines: Management Programs (Overview)LleiLlei100% (1)
- Heat Transfer EquipmentDocument28 pagesHeat Transfer Equipmentdeepak.dce.meNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map in Introduction To The World ReligionDocument7 pagesCurriculum Map in Introduction To The World ReligionRaizza Vanizza SiguenzaNo ratings yet