Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Truss
Uploaded by
Mordecai de ValoisOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Truss
Uploaded by
Mordecai de ValoisCopyright:
Available Formats
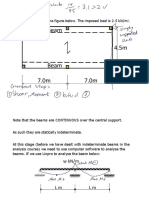
1
Proposal:
• Project: Storehouse.
• Prescription: Single Story Steel Building Roofed by Pitched Truss.
• Location: Port Sudan - Seaport.
• Area: 1300 m2
• Dimensions: length=80m, width=20m, overall height=9.62m.
Design Information:
• Codes: Chapter V-2:1972 and BS 5950-1:2000.
• Truss type: Plane Truss.
• Arrangement of Trusses: transversely.
• Trusses spacing: 4m.
• Basic wind speed: 45m/s.
• Roof Angle: 23o.
• Roof description: Cladding has little corrugations will be use.
• Purling description: 9 purlins will be use at joints and the section of purling will be Unequal Angle.
• Bracing description: Three cross bracing system will be use in roof (at start, middle and end) and the section
of bracing will be equal angle.
• Truss Members: The sections of truss Members will be Single and Double Angle.
Truss Shape :-
[DOCUMENT TITLE] MOHAMED
2
Loads: -
1. Gravity Loads: -
1.1. Dead Loads
1.1.1. Sheeting rails and insulation
• Assuming Weight per unit inclined Area of cladding (D.L 1) =0.17KN/𝑚2
• Assuming Weight per unit inclined Area of Insulation (D.L 2) =0.16KN/𝑚2
1.1.2 Purlins
35.5∗10
• Assuming Mass per unit length = 35.5 kg/m = 1000
= 0.355 KN/m
• Total length of purlins per truss = 4.5*9 = 40.5m
• Total weight of purlins carried by truss = 0.355*40.5 = 14.378 KN
𝟏𝟏.𝟓
• = 12.49 ≈12.5 *2 = 25m
𝒄𝒐𝒔(𝟐𝟑)
𝟏𝟒.𝟑𝟕𝟖
• Weight per unit inclined Area of purlins (D.L 3) = 𝟒.𝟓∗𝟐𝟓 = 0.128 KN/m2
1.1.3 Bracing
20∗10
• Assuming Mass per unit length = 20 kg/m = = 0.2 KN/m.
1000
• 14.378/11.5 = 1.25.
11.5∗2∗√4.52 +1.252
• Total length of bracing per truss = ( 2
) = 53.71m.
• Total weight of bracing carried by truss = 0.2*53.71= 10.742 KN.
10.742
• Weight per unit inclined Area of bracing (D.L 4) = = 0.1 KN/m2.
4.5∗25
1.1.4 Self weight of truss Members
37∗10
• Assuming Mass per unit length = 37 kg/m = = 0.37 KN/m.
1000
• Total length of Members per truss = 92.15m.
• Weight of truss = 0.37*92.15 = 34.1 KN.
34.1
• Weight applied on inclined area of internal truss (D.L 5) = = 0.3031
4.5∗25
Total Dead Load:
D.L Total = D.L 1 +D.L 2 + D.L 3 +D.L 4+ D.L 5
D.L Total = 0.15+ 0.15+ 0.128+ 0.1+ 0.3031 = 0.8611KN/ 𝑚2.
Joint Dead Load:
Force per Middle point = 0.8611*4.5*2.174 = 8.424 KN.
2.174
Force per Edge point = 0.8611*4.5* == 4.212 KN.
2
[DOCUMENT TITLE] MOHAMED
3
1.2. Live Load (from B.S6399 part1)
• Live load per plane Area = 0.75 KN /𝑚2 → (For Maintenance and Repairing)
11.5
• Live load applied on inclined Area of internal truss = 0.75* =0.69 KN/m2.
12.5
Joint Dead Load:
Force per Middle point = 0.69*4.5*2.174 = 6.75KN.
2.174
Force per Edge point = 0.69*4.5* 2
= 3.375 KN
1.3. Wind Load.
S1 = 1 , S2 (from Table 3 with interpolation) = 0.96 , S3= 1
V = 45
Vs = V * S1* S2 * S3 V = 45*1*0.96*1 = 43.2m/s
q = k*Vs2 = 0.613*43.22 = 1.14 KN/m2
External pressure coefficient (𝐂𝐏𝐞):
ℎ 9.62
= = 0.481 → roof angle = 23o → from Table 8
𝑤 20
3.3. Force (F):
F= (Cpe – Cpi) max*q
(α = 0): EF= -0.4 GH= -0.4 (α = 90): EG= -0.7 FH= -0.6
Internal pressure coefficient, (Cpi):
• wind normal to permeable face CPi = + 0.2
• wind normal to impermeable face CPi = - 0.3 (Cpe - Cpi) max = -0.9
F = (−0.7 − 0.2) × 1.14 = - 1.03 KN/m2
Joint Wind Load:
Force per Middle point = −1.03 × 4.5 × 2.174 = -10.07 KN
2.174
Force per Edge point = −1.03 × 4.5 × 2
= -5 KN
[DOCUMENT TITLE] MOHAMED
4
Analysis of the Truss: -
Static status:
M+R vs 2*J → 29+3 vs 2*16 → 40 V.S 40
The truss is statically determinate
Figure 1 - length of members
Figure 2 - angels between members
For dead load:
[DOCUMENT TITLE] MOHAMED
5
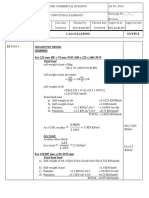
Figure - members, joints and Dead loads
(, 𝑹𝒆𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏𝒔 = 𝟑𝟑. 𝟔𝟗 , 𝑪𝒐𝒎𝒑𝒓𝒊𝒔𝒔𝒊𝒐𝒏 ≡ (−) , 𝑻𝒆𝒏𝒔𝒔𝒊𝒐𝒏 ≡ (+) )
joints Calculations Results
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = 33.7-4.212-M1*sin (23) M1 = -75.46
0
Σ𝑓𝑥 = 0 = 75.46 ∗ Cos(23) − M2 M2 = 69.46
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = −8.424 ∗ sin(67) + M3 ∗ sin(81.4) M3 = -8
1
Σ𝑓𝑥(𝑀1, 𝑀4 𝑎𝑠 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑥) = 0 M4 = -70.1
= −75.46 + 8.424 ∗ cos(67) + 7.84 ∗ cos(81.4)
+ 𝑀4
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = M3*sin(52) +M5*sin(52) M5 = 8
2
Σ𝑓𝑥 = 0 = M3*cos(52) -M5*cos(52)+M2-M6 M6 = 56.76
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = (M10, M4 as stander for x) M7=16.0
= −8.424 ∗ sin(67) + M5 ∗ sin(29) + M9 M10= 66
3 ∗ sin (23) − M7 ∗ sin (67)
Σ𝑓𝑥 = 0 = -M4+M5*cos(29)+M7*cos(67)-M9*cos(23)+M10-
8.424*cos(67)
4 Σ𝑓𝑥 = 0 = −M6 + M14 + M7 ∗ cos(52) + M8 ∗ cos(52) M14 =36.23
5
Σ𝑓𝑦 (𝑀13, 𝑀8 𝑎𝑠 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟(𝑥 𝑑𝑖𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛)) = 0 M9 = 11.36
= M11 ∗ cos(81.4) − 𝑀9 ∗ cos (52 − 23) M8 = 16.5
Σ𝑓𝑦(𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 Σ𝑓𝑦 𝑀3 𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑜𝑓 𝑀3 𝑖𝑛 𝑗𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 (1))𝑀11) M11 = -9.84
6 Σ𝑓𝑥(𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 Σ𝑓𝑥 𝑀1, 𝑀4 𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑜𝑓𝑗𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 (1))𝑀12) M12 = -60
7
8.424 M13=35.17
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = − − 𝑀12 ∗ sin(23) + 𝑀13 ∗ cos (38)
8 2 M15 = 0
M15 = 0
All in (KN)
[DOCUMENT TITLE] MOHAMED
6
For Live load:
Figure - members, joints and Dead loads
(, 𝑹𝒆𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏𝒔 = 𝟐𝟕 , 𝑪𝒐𝒎𝒑𝒓𝒊𝒔𝒔𝒊𝒐𝒏 ≡ (−) , 𝑻𝒆𝒏𝒔𝒔𝒊𝒐𝒏 ≡ (+) )
joints Calculations Results
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = 27-3.375-M1*sin (23) M1 = -60.46
0
Σ𝑓𝑥 = 0 = M1 ∗ Cos(23) − M2 M2 = 55.65
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = −6.75 ∗ sin(67) + M3 ∗ sin(81.4) M3 = -6.42
1 Σ𝑓𝑥(𝑀1, 𝑀4 𝑎𝑠 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑥) = 0 M4 = -56.18
= −M1 + 6.75 ∗ cos(67) + 6.42 ∗ cos(81.4) + 𝑀4
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = M3*sin(52) +M5*sin(52) M5 = 6.47
2
Σ𝑓𝑥 = 0 = M3*cos(52) -M5*cos(52)+M2-M6 M6 = 47.5
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = (M10, M4 as stander for x) M7=16.0
= −6.75 ∗ sin(67) + M5 ∗ sin(29) + M9 M10= -52.8
3 ∗ sin (23) − M7 ∗ sin (67)
Σ𝑓𝑥 = 0 = -M4+M5*cos(29)+M7*cos(67)-M9*cos(23)+M10-
6.75*cos(67)
4 Σ𝑓𝑥 = 0 = −M6 + M14 + M7 ∗ cos(52) + M8 ∗ cos(52) M14 =31.23
5
Σ𝑓𝑦 (𝑀13, 𝑀8 𝑎𝑠 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟(𝑥 𝑑𝑖𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛)) = 0 M9 = 9.1
= M11 ∗ cos(81.4) − 𝑀9 ∗ cos (52 − 23) M8 = 13.4
Σ𝑓𝑦(𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 Σ𝑓𝑦 𝑀3 𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑜𝑓 𝑀3 𝑖𝑛 𝑗𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 (1))𝑀11) M11 = -7.91
6 Σ𝑓𝑥(𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 Σ𝑓𝑥 𝑀1, 𝑀4 𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑜𝑓𝑗𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 (1))𝑀12) M12 = -48.21
7
6.75 M13=21
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = − − 𝑀12 ∗ sin(23) + 𝑀13 ∗ cos (38)
8 2 M15 = 0
M15 = 0
All in (KN)
[DOCUMENT TITLE] MOHAMED
7
For Live load:
Figure - members, joints and Dead loads
(, 𝑹𝒆𝒂𝒄𝒕𝒊𝒐𝒏𝒔 = −𝟑𝟔. 𝟖𝟐 , 𝑪𝒐𝒎𝒑𝒓𝒊𝒔𝒔𝒊𝒐𝒏 ≡ (−) , 𝑻𝒆𝒏𝒔𝒔𝒊𝒐𝒏 ≡ (+) )
joints Calculations Results
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = 27+5-M1*sin (23) M1 = 82.45
0
Σ𝑓𝑥 = 0 = M1 ∗ Cos(23) + M2 M2 = -74
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = 10 ∗ sin(67) − M3 ∗ sin(81.4) M3 = 10.3
1 Σ𝑓𝑥(𝑀1, 𝑀4 𝑎𝑠 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟𝑑 𝑓𝑜𝑟 𝑥) = 0 M4 = 79.81
= +M1 − 10 ∗ cos(67) − 10 cos(81.4) + 𝑀4
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = -M3*sin(52) -M5*sin(52) M5 = -10.423
2
Σ𝑓𝑥 = 0 = −M3*cos(52) +M5*cos(52)-M2+M6 M6 = -61.14
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = (M10, M4 as stander for x) M7=21.39
= 10 ∗ sin(67) − M5 ∗ sin(29) − M9 ∗ sin(23) M10= 78.62
3 + M7 ∗ sin (67)
Σ𝑓𝑥 = 0 = +M4-M5*cos(29)-M7*cos(67)-M9*cos(23)-
M10+10*cos(67)
4 Σ𝑓𝑥 = 0 = M6 − M14 − M7 ∗ cos(52) − M8 ∗ cos(52) M14 =-34.677
5
Σ𝑓𝑦 (𝑀13, 𝑀8 𝑎𝑠 𝑆𝑡𝑎𝑛𝑑𝑎𝑟(𝑥 𝑑𝑖𝑟𝑒𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛)) = 0 M9 = -14.56
= −M11 ∗ cos(81.4) + 𝑀9 ∗ cos (52 − 23) M8 = -21.55
Σ𝑓𝑦(𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 Σ𝑓𝑦 𝑀3 𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑜𝑓 𝑀3 𝑖𝑛 𝑗𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 (1))𝑀11) M11 = 12.67
6 Σ𝑓𝑥(𝑠𝑎𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 Σ𝑓𝑥 𝑀1, 𝑀4 𝑐𝑎𝑙𝑐𝑢𝑙𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛 𝑜𝑓𝑗𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 (1))𝑀12) M12 = 75.42
7
10 M13= -33.639
Σ𝑓𝑦 = 0 = + 𝑀12 ∗ sin(23) − 𝑀13 ∗ cos (38)
8 2 M15 = 0
M15 = 0
All in (KN)
End of task 1 !
[DOCUMENT TITLE] MOHAMED
You might also like
- Z-Purlin DesignDocument6 pagesZ-Purlin DesignrammohanNo ratings yet
- Purlin and RunnerDocument8 pagesPurlin and RunnerBabu Sundararaman0% (1)
- Reinforced Concrete Slab Design CalculationsDocument9 pagesReinforced Concrete Slab Design Calculationstawas20No ratings yet
- Design of Purlin (Rectangular Sections Only)Document3 pagesDesign of Purlin (Rectangular Sections Only)Amit Parikh100% (1)
- Design of Slab: Ly/lx 2. So This Is Two Way SlabDocument6 pagesDesign of Slab: Ly/lx 2. So This Is Two Way SlabSudip ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Design of Abutment For BridgeDocument28 pagesDesign of Abutment For BridgeMuhammad Wazim Akram100% (1)
- Venkats Interpretation On Configuration of MORTHDocument29 pagesVenkats Interpretation On Configuration of MORTHV Venkata Narayana100% (3)
- Wind Load Analysis For Open StructureDocument3 pagesWind Load Analysis For Open Structurehitesh gandhiNo ratings yet
- Boundary Wall Design - Final For RFCDocument10 pagesBoundary Wall Design - Final For RFCShubham KhareNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Simply Supported Beam V.2Document7 pages2.2 Simply Supported Beam V.2Hafiz95 ReactsNo ratings yet
- Design of Steel Truss MembersDocument6 pagesDesign of Steel Truss MembersSaim WaqarNo ratings yet
- Slab Design To BS 8110Document11 pagesSlab Design To BS 8110Samuel Antobam100% (2)
- Example 6.2 - Slab-Continuous (One-Way)Document7 pagesExample 6.2 - Slab-Continuous (One-Way)nnsNo ratings yet
- Lifting CalculationDocument7 pagesLifting CalculationAsaru DeenNo ratings yet
- Example: Design The Beams in The Figure Below. The Imposed Load Is 2.5 KN/MDocument32 pagesExample: Design The Beams in The Figure Below. The Imposed Load Is 2.5 KN/MSarah HaiderNo ratings yet
- Fence Type-3: Design Calculation Sheet HYD-121 FenceDocument18 pagesFence Type-3: Design Calculation Sheet HYD-121 FenceAbhilash KowndinyaNo ratings yet
- 10 TON - GantryDocument4 pages10 TON - GantryPraveen Jose100% (1)
- Design of RCC SlabDocument8 pagesDesign of RCC Slabrajseema_n2180% (5)
- IRC Conc Bridge DesignDocument16 pagesIRC Conc Bridge Designovikbasu100% (1)
- Design of Curtain WallDocument2 pagesDesign of Curtain WallRaju Saini100% (1)
- Design of BridgeDocument24 pagesDesign of BridgeSabin MaharjanNo ratings yet
- Design of Precast SlabDocument3 pagesDesign of Precast SlabarvnndNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Structural Design Lab - 2 Submitted by PRADYUT ANAND/ MT/CE/10016/19Document15 pagesAssignment On Structural Design Lab - 2 Submitted by PRADYUT ANAND/ MT/CE/10016/19Pradyut AnandNo ratings yet
- Deck Design Calculation - R1 20210627Document8 pagesDeck Design Calculation - R1 20210627Kwan Shing ChanNo ratings yet
- Slab and StaircaseDocument8 pagesSlab and StaircaseSamikshya ShahNo ratings yet
- Nef N67 Ent M45 450Document212 pagesNef N67 Ent M45 450jvega_534120100% (7)
- Lifting A Pressure Vessel With Two Main Lift Cranes and One Tail CraneDocument12 pagesLifting A Pressure Vessel With Two Main Lift Cranes and One Tail Cranezeusvares100% (1)
- Form Aktivitas 5RDocument4 pagesForm Aktivitas 5RNanang FA0% (1)
- Design of Boundary Column & FoundationDocument7 pagesDesign of Boundary Column & FoundationAmarjit KulkarniNo ratings yet
- 24 M Span Pre Stressed BridgeDocument350 pages24 M Span Pre Stressed Bridgekathir1956100% (2)
- IRC Conc Bridge DesignDocument16 pagesIRC Conc Bridge DesignovikbasuNo ratings yet
- Bridge Supper Structure DesignDocument25 pagesBridge Supper Structure DesignskumaraNo ratings yet
- Technical Catalogue: Curtain - Wall SystemDocument285 pagesTechnical Catalogue: Curtain - Wall Systemtudor-72No ratings yet
- Timber DesignDocument17 pagesTimber Designshaina mae omandacNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis Critical MachineryDocument19 pagesVibration Analysis Critical Machineryatif majeedNo ratings yet
- Buried Box Design Example To BD 31Document32 pagesBuried Box Design Example To BD 31Nizeyimana Jean BoscoNo ratings yet
- RC StructureDocument14 pagesRC StructureCupid PhungNo ratings yet
- Turret Calm BuoyDocument6 pagesTurret Calm BuoyMikiRoniWijayaNo ratings yet
- Gorakhpur Bypass RobDocument9 pagesGorakhpur Bypass RobvivekNo ratings yet
- QF1500, QF2500 & QF2500S HCQF Sprayer: Parts Lists SERIAL NOS. 75000 - PresentDocument47 pagesQF1500, QF2500 & QF2500S HCQF Sprayer: Parts Lists SERIAL NOS. 75000 - PresentDmytroNo ratings yet
- Porumamilla 220kV SS & Line-Reach II-BOQDocument58 pagesPorumamilla 220kV SS & Line-Reach II-BOQzakir242100% (1)
- PSC Bridge Girder Design To bs5400 by D ChildsDocument321 pagesPSC Bridge Girder Design To bs5400 by D ChildsRABAH MESLOUBNo ratings yet
- Hollow Pot Design WorksheetDocument7 pagesHollow Pot Design Worksheetpatrick chegeNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresFrom EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- RC Precast Slab Bridge: Institute of Technology of Cambodia Bridge Assignment Professor: KAING SaosereyDocument46 pagesRC Precast Slab Bridge: Institute of Technology of Cambodia Bridge Assignment Professor: KAING SaosereyPiseyNo ratings yet
- TASK 1 MergedDocument19 pagesTASK 1 MergedMordecai de ValoisNo ratings yet
- RC DesignDocument11 pagesRC DesignZul FadzliNo ratings yet
- Kenyatta University: Cat IiDocument9 pagesKenyatta University: Cat IiCarolineMwitaMoseregaNo ratings yet
- Project: Assignment On Structural Design Lab - 2 Submitted by PRADYUT ANAND/ MT/CE/10016/19Document15 pagesProject: Assignment On Structural Design Lab - 2 Submitted by PRADYUT ANAND/ MT/CE/10016/19Pradyut Anand100% (1)
- Wall Tie 1Document4 pagesWall Tie 1John SmithNo ratings yet
- Steel Member Deflection CheckDocument12 pagesSteel Member Deflection CheckProlay MannaNo ratings yet
- Composite Slab For Proposed Residential House-1Document7 pagesComposite Slab For Proposed Residential House-1JosephNo ratings yet
- I6325571 170713065236 PDFDocument17 pagesI6325571 170713065236 PDFshoebNo ratings yet
- Rohini 61347201776Document13 pagesRohini 61347201776soumyadeba04No ratings yet
- Rohini 84851395706Document14 pagesRohini 84851395706pankajNo ratings yet
- Structural Analysis For A Composite Parallel Beam Structures Using QSE 7 Staad Pro Software in Accordance To BS 5950 - 1 Advanced UK BeamsDocument6 pagesStructural Analysis For A Composite Parallel Beam Structures Using QSE 7 Staad Pro Software in Accordance To BS 5950 - 1 Advanced UK BeamsKhalid Abdel Naser Abdel RahimNo ratings yet
- Beam Design ProcedueresDocument14 pagesBeam Design ProcedueresKarim SayedNo ratings yet
- Wind Load Calculation For Hoarding BoardDocument9 pagesWind Load Calculation For Hoarding BoardSohail ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Expt 4-1Document5 pagesExpt 4-1PARVATHY ANILNo ratings yet
- StaticaculationrDocument8 pagesStaticaculationrEngineeri TadiyosNo ratings yet
- Strut Analysis and Design at - 0.5Document4 pagesStrut Analysis and Design at - 0.5SGOCTNo ratings yet
- Decathlon Udl CheckDocument3 pagesDecathlon Udl CheckAnonymous Clm40C1No ratings yet
- The Hashemite University Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument31 pagesThe Hashemite University Faculty of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentengsalamNo ratings yet
- Design of BeamsDocument21 pagesDesign of Beamsxxnur100% (1)
- Triangular PurlinsDocument1 pageTriangular PurlinsKrishnaraj Cnt.No ratings yet
- Design of Longitudinal Girders: Exterior GirderDocument9 pagesDesign of Longitudinal Girders: Exterior GirderteweldeNo ratings yet
- Naseer Al JihadmeDocument33 pagesNaseer Al JihadmeMuhammad ImranNo ratings yet
- Strut Analysis and Design at - 10.00Document4 pagesStrut Analysis and Design at - 10.00SGOCTNo ratings yet
- CBD - SAMPLE Calculation SheetDocument14 pagesCBD - SAMPLE Calculation Sheetاحمد على احمدNo ratings yet
- 1 Final Design, Development and Performance Evaluation of Onion Storage StructureDocument17 pages1 Final Design, Development and Performance Evaluation of Onion Storage StructuredipakNo ratings yet
- Dead Liad AnalysisDocument3 pagesDead Liad AnalysisMordecai de ValoisNo ratings yet
- Specifications of Dell G15 5511: Dimensions and WeightDocument9 pagesSpecifications of Dell G15 5511: Dimensions and WeightMordecai de ValoisNo ratings yet
- Task 2Document13 pagesTask 2Mordecai de ValoisNo ratings yet
- Task 2.2Document15 pagesTask 2.2Mordecai de ValoisNo ratings yet
- TASK 2 MergedDocument14 pagesTASK 2 MergedMordecai de ValoisNo ratings yet
- Kömmerling 76: The Window For Explorers!Document2 pagesKömmerling 76: The Window For Explorers!treborNo ratings yet
- Elastic-Plastic Behaviour of A Nuclear Pipe Elbow With Axial Through Wall Crack at Crown Under In-Plane BendingDocument9 pagesElastic-Plastic Behaviour of A Nuclear Pipe Elbow With Axial Through Wall Crack at Crown Under In-Plane BendingPeto FoteNo ratings yet
- Process Analyzer Sample Systems: Home BlogDocument8 pagesProcess Analyzer Sample Systems: Home BlograhulNo ratings yet
- z11125 Cadet 340 Solid Gris 2006 3456Document3 pagesz11125 Cadet 340 Solid Gris 2006 3456ideaslabsofiaNo ratings yet
- SC Judgment On Condition of Construction WorkersDocument57 pagesSC Judgment On Condition of Construction WorkersLatest Laws TeamNo ratings yet
- ThrdsDocument47 pagesThrdsfrancisdimeNo ratings yet
- Lost Circulation:: Thief Zone To Be Equal To 0.465 Psi/ft. Mud Level Inside Casing After Loss CirculationDocument22 pagesLost Circulation:: Thief Zone To Be Equal To 0.465 Psi/ft. Mud Level Inside Casing After Loss CirculationbeautybdNo ratings yet
- Outline of Building Survey For SE - ASE - TOT Myanmar 1108 PDFDocument16 pagesOutline of Building Survey For SE - ASE - TOT Myanmar 1108 PDFrogerw06No ratings yet
- My Published PaperDocument11 pagesMy Published PaperAhmet TukenNo ratings yet
- NEW - MERGED Capital Procurement Checklist FINAL - 2007-12-11Document20 pagesNEW - MERGED Capital Procurement Checklist FINAL - 2007-12-11yaredNo ratings yet
- MS13 Part 2 Rev 00 Spillway Concrete ReinforcementDocument64 pagesMS13 Part 2 Rev 00 Spillway Concrete ReinforcementRelu MititeluNo ratings yet
- 4Document1 page4Veronica NayahNo ratings yet
- 69 2685ES (HE280 Installation)Document40 pages69 2685ES (HE280 Installation)David ChungNo ratings yet
- PCAB List of Licensed Contractors For CFY 2018-2019 As of 24 Sep 2018 - WebDocument69 pagesPCAB List of Licensed Contractors For CFY 2018-2019 As of 24 Sep 2018 - WebedisonNo ratings yet
- Greener Blocks Towards A Sustainable Future. Greener Blocks To Make Sturdier Homes. Greener Blocks Towards A Sturdier FutureDocument4 pagesGreener Blocks Towards A Sustainable Future. Greener Blocks To Make Sturdier Homes. Greener Blocks Towards A Sturdier FutureNiel Bartolome100% (1)
- FBDocument5 pagesFBbimal bhandariNo ratings yet
- Coliseum Presentation - 8.13.2020Document13 pagesColiseum Presentation - 8.13.2020Helen BennettNo ratings yet
- The Project For Improvement of Magway General Hospital & Dawei General HospitalDocument154 pagesThe Project For Improvement of Magway General Hospital & Dawei General Hospitallwin_oo2435No ratings yet
- Swms NPG Rev2 Smeg WarehouseDocument9 pagesSwms NPG Rev2 Smeg WarehousemhwjgcnsnzNo ratings yet
- BOQ GP RHD Bridge 883542 (Barshapara)Document2 pagesBOQ GP RHD Bridge 883542 (Barshapara)kazisajib2021No ratings yet