Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Interval Level
Interval Level
Uploaded by
Sanskar KhowalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Interval Level
Interval Level
Uploaded by
Sanskar KhowalCopyright:
Available Formats
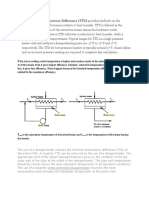
t.3.
3 IN TERVAL LEVEL
Interval-level data measurement is the next to the highest level of data in
which the distances between consecutive numbers have meaning and the data
are always numerical. The distances represented by the differences between
consecutive numbers are equal; that is, interval data have equal intervals.
An example of interval measurement is Fahrenheit temperature. With
Fahrenheit temperature numbers, the temperatures can be ranked, and the
amounts of heat between consecutive readings, such as 20°, 21 °, and 22°, are
the same.
In addition, with interval-level data, the zero point is a matter of GOnvention
or convenience and not a natural or fixed zero point. Zero is just another
point on the scale and does not mean the absence of the phenomenon. For
example, zero degrees Fahrenheit is not the lowest possible temperature.
Some other examples of interval-level data are the percentage change in
employment, the percentage return on a stock and the dollar change in
stock price. '
You might also like
- Mollier DiagramDocument16 pagesMollier DiagramSumeet Khachane100% (3)
- Psychometric ChartDocument9 pagesPsychometric Chartqms1234No ratings yet
- Nominal ScaleDocument2 pagesNominal Scale03454084854No ratings yet
- I Think Ration Scale Is BetterDocument7 pagesI Think Ration Scale Is BetterKiran SohailNo ratings yet
- Calc-Relative Humidity PDFDocument1 pageCalc-Relative Humidity PDFSufian SarwarNo ratings yet
- Scales of Variable Measurement Scales of Variable MeasurementDocument1 pageScales of Variable Measurement Scales of Variable MeasurementA. Saeed KhawajaNo ratings yet
- Role of Dimensionless Numbers in Heat TransferDocument3 pagesRole of Dimensionless Numbers in Heat TransferJCI CilacapNo ratings yet
- Interval Data and Ratio DataDocument1 pageInterval Data and Ratio DataLenkoe GafaneNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19. TemperatureDocument41 pagesChapter 19. TemperatureNguyên Nguyễn SơnNo ratings yet
- Zeroth LawDocument41 pagesZeroth LawYu ErinNo ratings yet
- Discussion 6 - FinalDocument2 pagesDiscussion 6 - FinalMariam DalloulNo ratings yet
- Reading A Psychrometric ChartDocument2 pagesReading A Psychrometric ChartMaulana HidayatNo ratings yet
- Ramey PDFDocument10 pagesRamey PDFvitaxnNo ratings yet
- Data Levels of MeasurementDocument1 pageData Levels of MeasurementRochelle PrieteNo ratings yet
- CalorDocument14 pagesCaloreka123No ratings yet
- Temperature Pressure and Flow Rate MeasurementsDocument78 pagesTemperature Pressure and Flow Rate MeasurementsKing BommNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 HumidifictionDocument20 pagesLecture1 HumidifictionmjunaidNo ratings yet
- Chap 9 TempDocument3 pagesChap 9 TempJacielle Alcain LabialNo ratings yet
- A. Write True If The Statement Is True or False If NotDocument4 pagesA. Write True If The Statement Is True or False If NotAges Teacher 11No ratings yet
- Levels of Measurement: of Measurement Describes The Relationship Among These Three Values. in This Case, WeDocument3 pagesLevels of Measurement: of Measurement Describes The Relationship Among These Three Values. in This Case, WeRochelle PrieteNo ratings yet
- Physics Lab ReportDocument8 pagesPhysics Lab ReportHunter PattonNo ratings yet
- The Four levels-WPS OfficeDocument13 pagesThe Four levels-WPS OfficeDodonGwapo ArnozaNo ratings yet
- Phy 103Document23 pagesPhy 103glorianelson2008No ratings yet
- Lec 13Document14 pagesLec 13Anand KumarNo ratings yet
- P C PDocument5 pagesP C PAli BabaNo ratings yet
- HP Calculators: HP 33S Temperature ConversionsDocument6 pagesHP Calculators: HP 33S Temperature ConversionsMatheus TorresNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 ADocument24 pagesLec 1 Ashah muhammadNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow 15Document2 pagesHeat Flow 15rohitNo ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument2 pagesMeasurementCassandra Kate GuerreroNo ratings yet
- SFG 3023 Chapter 1Document67 pagesSFG 3023 Chapter 1Nik AshrafNo ratings yet
- Chapter Five Measurement and Scaling Techniques Measurement in ResearchDocument10 pagesChapter Five Measurement and Scaling Techniques Measurement in Researchselman AregaNo ratings yet
- L2-Heat and WorkDocument11 pagesL2-Heat and WorkNaveen NaviNo ratings yet
- 05 Ley Cero Escalas TemperaturaDocument32 pages05 Ley Cero Escalas TemperaturaMichelle SerranoNo ratings yet
- Oleh: Dewi Ekawati Indah Dwiphayanti Laelatul Fitriani Juwita Chandra DewiDocument31 pagesOleh: Dewi Ekawati Indah Dwiphayanti Laelatul Fitriani Juwita Chandra DewiNurulWardhani11No ratings yet
- A. Write True If The Statement Is True or False If NotDocument3 pagesA. Write True If The Statement Is True or False If NotAges Teacher 11No ratings yet
- Hand Made Slides For TeachersDocument79 pagesHand Made Slides For TeachersMuhammad Modood AbbasiNo ratings yet
- ANALOGYDocument1 pageANALOGYaathiraNo ratings yet
- Four Different Levels of MeasurementDocument2 pagesFour Different Levels of MeasurementMaria Isabella RuaYanaNo ratings yet
- Week1 StatsDocument5 pagesWeek1 StatsAditya SinghNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric ChartDocument1 pagePsychrometric ChartMike LassaNo ratings yet
- Natural ConvectionDocument7 pagesNatural ConvectionLuthfy AditiarNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer: Lecture 23: Internal Flow ConvectionDocument9 pagesHeat Transfer: Lecture 23: Internal Flow ConvectionDavico MartinezNo ratings yet
- Terminal Temperature DifferenceDocument3 pagesTerminal Temperature DifferenceKhawaja Muhammad MoinNo ratings yet
- Specific Volume, Density and Specific Weight: Sample ProblemDocument13 pagesSpecific Volume, Density and Specific Weight: Sample ProblemRoderick VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Error Analysis LectureDocument60 pagesError Analysis LectureCHERUYIOT IANNo ratings yet
- PsychrometryDocument27 pagesPsychrometryBienNo ratings yet
- Lecture-02 - PHY101 (BBA) - 51KA+52KB - PHY101.KC-22-05-2021Document39 pagesLecture-02 - PHY101 (BBA) - 51KA+52KB - PHY101.KC-22-05-2021KRZ. Arpon Root HackerNo ratings yet
- Psychrometric Chart UseDocument7 pagesPsychrometric Chart UseMohammed Azher100% (1)
- Disscusion 7Document1 pageDisscusion 7Mariam DalloulNo ratings yet
- Dew Point and Wet Bulb TemperatureDocument8 pagesDew Point and Wet Bulb TemperatureDileep S NairNo ratings yet
- 12 TemperatureDocument34 pages12 Temperaturelc1999227No ratings yet
- Dew PointDocument6 pagesDew PointtipusemuaNo ratings yet
- Thermal AnalysisDocument37 pagesThermal AnalysisZaid Majed100% (1)
- Heat ExchangerDocument3 pagesHeat ExchangermasukuhlelokuhleNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of MatterDocument26 pagesThermal Properties of MatterDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Chapter Two PDFDocument86 pagesHeat Transfer Chapter Two PDFteddiyfentawNo ratings yet
- Disscusion 7Document1 pageDisscusion 7Mariam DalloulNo ratings yet
- The Number Concept, True its Definition and The Division by ZeroFrom EverandThe Number Concept, True its Definition and The Division by ZeroNo ratings yet
- International Business Assignment June 2023Document10 pagesInternational Business Assignment June 2023Sanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Cost & Management Accounting Assignment June 2023Document15 pagesCost & Management Accounting Assignment June 2023Sanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument11 pagesConsumer BehaviourSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Organizational Theory Structure and Design Assiognment June 2023Document9 pagesOrganizational Theory Structure and Design Assiognment June 2023Sanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Traval - Exp - Format FINAL APRILDocument1 pageTraval - Exp - Format FINAL APRILSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Project Management Assignment 2023Document12 pagesProject Management Assignment 2023Sanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Financial AccountingDocument5 pagesFinancial AccountingSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Data MeasurmentDocument1 pageData MeasurmentSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- V A H A N - National Register E-Services - Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, Government of IndiaDocument1 pageV A H A N - National Register E-Services - Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, Government of IndiaSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Digital MarketingDocument13 pagesDigital MarketingSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Solutions For Discriptive LevelDocument1 pageSolutions For Discriptive LevelSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument6 pagesStrategic ManagementSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Essentials of HRMDocument7 pagesEssentials of HRMSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Short Notes On InsuranceDocument1 pageShort Notes On InsuranceSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Agreement of Sale and Agreement To SellDocument1 pageDifference Between Agreement of Sale and Agreement To SellSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Formation of ContractDocument1 pageFormation of ContractSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument6 pagesBusiness CommunicationSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Operations Management Set - 3Document7 pagesOperations Management Set - 3Sanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Decision ScienceDocument8 pagesDecision ScienceSanskar KhowalNo ratings yet
- Decision Science Set - 3Document8 pagesDecision Science Set - 3Sanskar KhowalNo ratings yet