Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Precal M1
Uploaded by
Eme Rose0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
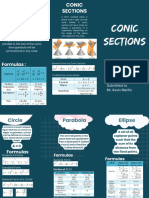
11 views1 pageThe document discusses conic sections and circles. There are four types of conic sections: circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas, which are formed by the intersection of a plane with one or two cones. A circle is a special type of conic section that is formed when the plane is parallel to the base of the cone. It is the set of all points equidistant from a fixed central point, called the center. The standard equations of a circle with center at the origin or a point (h,k) are provided.
Original Description:
Original Title
PRECAL-M1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses conic sections and circles. There are four types of conic sections: circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas, which are formed by the intersection of a plane with one or two cones. A circle is a special type of conic section that is formed when the plane is parallel to the base of the cone. It is the set of all points equidistant from a fixed central point, called the center. The standard equations of a circle with center at the origin or a point (h,k) are provided.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pagePrecal M1
Uploaded by
Eme RoseThe document discusses conic sections and circles. There are four types of conic sections: circles, parabolas, ellipses, and hyperbolas, which are formed by the intersection of a plane with one or two cones. A circle is a special type of conic section that is formed when the plane is parallel to the base of the cone. It is the set of all points equidistant from a fixed central point, called the center. The standard equations of a circle with center at the origin or a point (h,k) are provided.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Conic Section:
Circle Galvan, Emelane Rose A.
Conics Four Types
00
CIRCLE: is formed if the plane is parallel to
➢ Also known as Conic Section the base of the cone.
➢ Particular class of curves which
can be found in nature and can
be nab-made. PARABOLA: is formed when the plane
intersects only one cone to form an
➢ Generated by the intersection
unbounded curve.
of a plane with one or two
nappes of a cone.
ELLIPSE: is formed when the tilted plane
Application: architecture, engineering, physics, intersects only one cone to form a bounded
astronomy and navigation. curve.
Circle HYPERBOLA: is formed when the plane (not
necessarily vertical) intersects both
cones to form an unbounded curve.
➢ Is the set of all points in a plane
that are at a constant distance, Equations of a Circle
the radius from the fixed point.
➢ Is a special kind of ellipse. Standard Equations of a Circle
FIXED POINT: is also called as the center of the
circle. (Circles are usually named according to Center at the origin
its fixed point)
C (0,0)
x2 + y 2 = r 2
CENTER
RADIUS
DIAMETER
Center at the (h,k) (x-h)2 + (y-k)2 = r2
You might also like
- Conic Sections: By: Jovic G. Rullepa SST - Iii, PnhsDocument45 pagesConic Sections: By: Jovic G. Rullepa SST - Iii, PnhsMykhaela Louize Gumban100% (1)
- Introduction To Conic Sections and CirclesDocument5 pagesIntroduction To Conic Sections and CirclesJanexx DioNo ratings yet
- 1.1.introduction To Conic SectionsDocument11 pages1.1.introduction To Conic Sectionscharlene quiambaoNo ratings yet
- CONIC SECTIONS and Circles Grade 11Document7 pagesCONIC SECTIONS and Circles Grade 11ha hakdogNo ratings yet
- Notes (Intro To Conic Sections)Document1 pageNotes (Intro To Conic Sections)Not MeNo ratings yet
- Blue White Geometric Modern Sea Travel BrochureDocument2 pagesBlue White Geometric Modern Sea Travel Brochurenightmarehappy142No ratings yet
- 1 Semester: Cag - Edu.Gt/11Th-Grade-Precalculus/ - /RSRC/ 1413568039105/config/ Customlogo - Gif?Revision 24Document12 pages1 Semester: Cag - Edu.Gt/11Th-Grade-Precalculus/ - /RSRC/ 1413568039105/config/ Customlogo - Gif?Revision 24Coulline DamoNo ratings yet
- CONIC SECTIONS - Grade 11Document5 pagesCONIC SECTIONS - Grade 11ha hakdogNo ratings yet
- Assignment - Mendoza, Jillea RDocument4 pagesAssignment - Mendoza, Jillea Rjillea mendozaNo ratings yet
- For NotesDocument1 pageFor NotesAzeleah Nosil VilladiegoNo ratings yet
- To Conic Sections: Prepared By: Miss Carizza BatacDocument24 pagesTo Conic Sections: Prepared By: Miss Carizza BatacBruceNo ratings yet
- SLK Precalculus Quarter 1 Unit 1Document55 pagesSLK Precalculus Quarter 1 Unit 1Nikkaa XOX100% (1)
- Lesson1 Introduction To Conic SectionsDocument51 pagesLesson1 Introduction To Conic SectionsKrissa Mae PenalosaNo ratings yet
- What Is Circle? What Is Circle?Document2 pagesWhat Is Circle? What Is Circle?Alexa Jill MirandaNo ratings yet
- Pre CalDocument5 pagesPre CalCristina Astrero BisqueraNo ratings yet
- Pre CalDocument6 pagesPre CalPaul Mikko MolonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - An Overview of Conic SectionsDocument2 pagesLesson 1 - An Overview of Conic SectionsIresh Gail DoriaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections: Conics or Conic Sections Were Studied by Greek Mathematicians, With ApolloniusDocument18 pagesConic Sections: Conics or Conic Sections Were Studied by Greek Mathematicians, With ApolloniusS P ECIALISENo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 An Overview of Conic SectionsDocument2 pagesLesson 1 An Overview of Conic SectionsIresh Gail DoriaNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4-5 Curve-1Document28 pagesLecture-4-5 Curve-1nameNo ratings yet
- 11.2 Circles and Ellipses Conic SectionsDocument24 pages11.2 Circles and Ellipses Conic SectionsNiña Marie BachoNo ratings yet
- Pre Cal W1Document31 pagesPre Cal W1Dianne Marie Crisol PerezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Conic SectionDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Conic SectionEJ ARREZANo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument1 pagePre Calculuskiellaus6127No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Conic SectionsDocument7 pagesLesson 1 Conic SectionsJojo OcampoNo ratings yet
- Conic Section Discussion RoughDocument8 pagesConic Section Discussion RoughSamantha BaldovinoNo ratings yet
- L1 Intro To Conic SectionDocument36 pagesL1 Intro To Conic Sectionjinnie kimNo ratings yet
- Polar Coordinates Conics And: Learning OutcomesDocument43 pagesPolar Coordinates Conics And: Learning OutcomesAnkur GuptaNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument14 pagesConic SectionsjbdliganNo ratings yet
- 11 ConicsDocument9 pages11 Conicsshubhamdalal.anmNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Conic SectionsDocument4 pagesConcepts of Conic SectionsMario AnacletoNo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document20 pagesUnit 3cooooool1927No ratings yet
- Prec Cal Week 1Document30 pagesPrec Cal Week 1Lenard JamesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 PrecalculusDocument47 pagesLesson 1 PrecalculusBrightTiger 123No ratings yet
- SS2 PresentationDocument16 pagesSS2 PresentationAdoga EdwinNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionDocument14 pagesConic SectionIsha GoelNo ratings yet
- A Brief Introduction To Pre-Calculus and Non-Linear EquationsDocument6 pagesA Brief Introduction To Pre-Calculus and Non-Linear EquationsPat ChuNo ratings yet
- Module 1Document15 pagesModule 1ruth torzarNo ratings yet
- Ewald ConstructionDocument22 pagesEwald Constructionabhinay sreeramNo ratings yet
- Think of Set of Planes Reflecting in X-Ray Beam: Ewald ConstructionDocument22 pagesThink of Set of Planes Reflecting in X-Ray Beam: Ewald ConstructionmunseongNo ratings yet
- Parabola Notes HNDocument158 pagesParabola Notes HNadityavaish739No ratings yet
- Pre Cal W1Document31 pagesPre Cal W1Dianne Marie Crisol PerezNo ratings yet
- Engineering Curves: ConicsDocument37 pagesEngineering Curves: ConicsKirtan PatelNo ratings yet
- PRECAL - Lesson 1 - Introduction To Conic SectionDocument23 pagesPRECAL - Lesson 1 - Introduction To Conic SectionmanansalastarringNo ratings yet
- SS2 Tech Drawing 1st Term E-NoteDocument48 pagesSS2 Tech Drawing 1st Term E-NoteJesseNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections - Ellipses Jordan Stephen Samantha Liam ColeDocument10 pagesConic Sections - Ellipses Jordan Stephen Samantha Liam Coleapi-358928099No ratings yet
- (PreCal 11) Conic Section - Ellipse PDFDocument49 pages(PreCal 11) Conic Section - Ellipse PDFTeacher Len EnoyNo ratings yet
- The Conic SectionsDocument2 pagesThe Conic SectionsDominic RagoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer PrecalDocument3 pagesReviewer PrecalErwin Ranel ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Conic SectionsDocument10 pagesConic SectionsJunna Mae GimongalaNo ratings yet
- The Parabola Conic SectionDocument11 pagesThe Parabola Conic SectionRiza Mae BayoNo ratings yet
- The Parabola Conic SectionDocument11 pagesThe Parabola Conic SectionJohn Anthony Bersabe ChavezNo ratings yet
- q1 Precal Notes (In Progress)Document20 pagesq1 Precal Notes (In Progress)saturosjuliaclarisseNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1: Introduction To Conic Sections and CirclesDocument5 pagesLesson 1.1: Introduction To Conic Sections and CirclesAerl XuanNo ratings yet
- Parabola PDF SK GOYAL - CompressedDocument97 pagesParabola PDF SK GOYAL - CompressedDarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Conic Sections: Ellipses: EllipseDocument20 pagesConic Sections: Ellipses: EllipseClaire GumahinNo ratings yet
- Conic SectinsDocument12 pagesConic SectinsintendencialuigiNo ratings yet
- Aayusip Aayusip: Conic SectionsDocument3 pagesAayusip Aayusip: Conic SectionsShnle CansebNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1a. Standard Equation of A CircleDocument5 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1a. Standard Equation of A CircleJarkos BarrilNo ratings yet
- Performance Task No. 2Document2 pagesPerformance Task No. 2Eme RoseNo ratings yet
- ENTREP NOTES EmeDocument4 pagesENTREP NOTES EmeEme RoseNo ratings yet
- Prose - Short Story GalvanDocument3 pagesProse - Short Story GalvanEme RoseNo ratings yet
- Ucsp Gender InequalityDocument3 pagesUcsp Gender InequalityEme RoseNo ratings yet
- Groupings Assigned ColorDocument5 pagesGroupings Assigned ColorEme RoseNo ratings yet
- Choral Reading 2Document8 pagesChoral Reading 2Eme RoseNo ratings yet