Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Vectors: MATHEMATICS (Continued)
Uploaded by
ROMIN MANOJ CHITTETTU0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageOriginal Title
a3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageVectors: MATHEMATICS (Continued)
Uploaded by
ROMIN MANOJ CHITTETTUCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
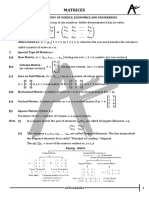
MATHEMATICS (continued)
MATRICES For a third-order determinant:
A matrix is an ordered rectangular array of numbers with m
rows and n columns. The element aij refers to row i and a1 a2 a3
column j. b1 b2 b3 a1b2 c3 a 2b3c1 a3b1c2 a3b2 c1 a2 b1c3 a1b3c2
Multiplication c1 c2 c3
If A = (aik) is an m n matrix and B = (bkj) is an n s
matrix, the matrix product AB is an m s matrix
n VECTORS
C ci j ail blj
l 1
where n is the common integer representing the number of j
columns of A and the number of rows of B (l and k = 1, 2,
, n).
i
Addition k
If A = (aij) and B = (bij) are two matrices of the same size
m n, the sum A + B is the m n matrix C = (cij) where
cij = aij + bij.
Identity
The matrix I = (aij) is a square n n identity matrix where
aii = 1 for i = 1, 2, , n and aij = 0 for i j.
Transpose
The matrix B is the transpose of the matrix A if each entry
bji in B is the same as the entry aij in A and conversely. In
equation form, the transpose is B = AT.
Inverse A = axi + ayj + azk
The inverse B of a square n n matrix A is Addition and subtraction:
adj A A + B = (ax + bx)i + (ay + by)j + (az + bz)k
B A1 , where
A A B = (ax bx)i + (ay by)j + (az bz)k
T
adj(A) = adjoint of A (obtained by replacing A elements The dot product is a scalar product and represents the
with their cofactors, see DETERMINANTS) and projection of B onto A times A . It is given by
A = determinant of A. AB = axbx + ayby + azbz
DETERMINANTS = A B cos = BA
A determinant of order n consists of n2 numbers, called the The cross product is a vector product of magnitude
elements of the determinant, arranged in n rows and n B A sin which is perpendicular to the plane
columns and enclosed by two vertical lines. containing A and B. The product is
In any determinant, the minor of a given element is the i j k
determinant that remains after all of the elements are struck
out that lie in the same row and in the same column as the A B ax a y az B A
given element. Consider an element which lies in the jth
column and the ith row. The cofactor of this element is b x b y bz
the value of the minor of the element (if i + j is even), and
it is the negative of the value of the minor of the element
(if i + j is odd).
If n is greater than 1, the value of a determinant of order n is
the sum of the n products formed by multiplying each
element of some specified row (or column) by its cofactor.
This sum is called the expansion of the determinant
[according to the elements of the specified row (or
column)]. For a second-order determinant:
a1 a2
a1b2 a2 b1
b1 b2
You might also like
- Matrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersFrom EverandMatrix Theory and Applications for Scientists and EngineersNo ratings yet
- Course 2 - Matrix Operations.Document14 pagesCourse 2 - Matrix Operations.boumiasarah4No ratings yet
- Pure Math - Matrix: DefinitionsDocument5 pagesPure Math - Matrix: Definitionsjared liNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Matrix AlgebraDocument86 pagesChapter 2 - Matrix AlgebraBảo NguyễnNo ratings yet
- MHGKJDocument28 pagesMHGKJKarthikesan MakNo ratings yet
- LA - 2. Matrix Algebra - StudentsDocument95 pagesLA - 2. Matrix Algebra - StudentsNhat AnhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Matrix AlgebraDocument89 pagesChapter 2 - Matrix AlgebraCao Bằng Thảo NguyênNo ratings yet
- Matrix DetwrminantsDocument9 pagesMatrix DetwrminantsJared GualonNo ratings yet
- DetermineDocument29 pagesDeterminePragya PanwarNo ratings yet
- SVKM's Narsee Monjee Linear EquationsDocument18 pagesSVKM's Narsee Monjee Linear EquationsNilay ShahNo ratings yet
- Vectors and MatricesDocument8 pagesVectors and MatricesdorathiNo ratings yet
- Matrices and DeterminantDocument13 pagesMatrices and DeterminantAditya NandaNo ratings yet
- Matrices and DeterminantsDocument17 pagesMatrices and Determinantsqtb2z6pqt7No ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapter 4 Maths Important FormulasDocument3 pagesClass 12 Chapter 4 Maths Important FormulasHari omNo ratings yet
- 3 MatricesDocument19 pages3 MatricesLeonardo TorresNo ratings yet
- MATHS MATRICES & DETERMINANTS FUNDAMENTALSDocument2 pagesMATHS MATRICES & DETERMINANTS FUNDAMENTALSAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis EssentialsDocument13 pagesVector Analysis EssentialsMd Asifuzzaman Khan, 170021005No ratings yet
- Class 12 CH 4 DeterminantsDocument6 pagesClass 12 CH 4 DeterminantsSai Swaroop MandalNo ratings yet
- Intermediate Methods: Matrix AlgebraDocument7 pagesIntermediate Methods: Matrix AlgebrahishamsaukNo ratings yet
- LinearAlgebra2000 Bookmatter ModellingAndControlOfRobotManiDocument41 pagesLinearAlgebra2000 Bookmatter ModellingAndControlOfRobotManidoudikidNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument7 pagesMatricesPriti DixitNo ratings yet
- Matrix AlgebraDocument21 pagesMatrix AlgebraivanmrnNo ratings yet
- Engineering Mathematics IIIDocument17 pagesEngineering Mathematics IIIbethuyegoNo ratings yet
- Electrodynamics - Week 1 - Lecture MaterialsDocument11 pagesElectrodynamics - Week 1 - Lecture MaterialsatififpNo ratings yet
- Mathematics II-matricesDocument52 pagesMathematics II-matricesBagus RizalNo ratings yet
- Matrices and Determinants EssentialsDocument60 pagesMatrices and Determinants Essentialsvenu duggineniNo ratings yet
- MatricesDocument19 pagesMatricesExperimental ViveNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument14 pagesChapter OneBiruk YidnekachewNo ratings yet
- Unit Six (10) ECON 1003 MATRICESDocument27 pagesUnit Six (10) ECON 1003 MATRICESFitzmore PetersNo ratings yet
- 19vectors 3d PDFDocument8 pages19vectors 3d PDFSunita MauryaNo ratings yet
- Vectors and MatricesDocument8 pagesVectors and MatricesdorathiNo ratings yet
- BAB 3 BA501 Vector Dan ScalarDocument29 pagesBAB 3 BA501 Vector Dan ScalarAriez AriantoNo ratings yet
- Leep204 PDFDocument21 pagesLeep204 PDFchankit vashishtNo ratings yet
- Appendix B Matrix AlgebraDocument11 pagesAppendix B Matrix Algebrama yeningNo ratings yet
- UEE507 Engineering Electromagnetics Vector AnalysisDocument34 pagesUEE507 Engineering Electromagnetics Vector AnalysisAniket BabutaNo ratings yet
- 20 Matrices Formula Sheets QuizrrDocument8 pages20 Matrices Formula Sheets Quizrrbharasha mahantaNo ratings yet
- 20 Matrices Formula Sheets Getmarks AppDocument9 pages20 Matrices Formula Sheets Getmarks AppAashrith PemmarajuNo ratings yet
- 20 FRDocument7 pages20 FRyellaiahNo ratings yet
- Matrices Determinants MathongoDocument12 pagesMatrices Determinants MathongoArya NairNo ratings yet
- 19matrices DeterminantsDocument5 pages19matrices DeterminantssatyahbhatNo ratings yet
- Matrices & DeterminantsDocument60 pagesMatrices & DeterminantsPradeep SinglaNo ratings yet
- Vector SynopsisDocument9 pagesVector Synopsisbulu30No ratings yet
- Vectors and Their Representation:: Vector & Three Dimensional GeometryDocument223 pagesVectors and Their Representation:: Vector & Three Dimensional GeometryAnony PrevailsNo ratings yet
- EGR2013 Tutorial 8: Z Powers of A Matrix and Matrix Polynomial Z Vector Algebra Z Vector SpacesDocument6 pagesEGR2013 Tutorial 8: Z Powers of A Matrix and Matrix Polynomial Z Vector Algebra Z Vector SpacesKaneki KenNo ratings yet
- Matematika Teknik Kimia I: Siswo SumardionoDocument28 pagesMatematika Teknik Kimia I: Siswo SumardionodakrezniaNo ratings yet
- Scalars and Vectors ExplainedDocument32 pagesScalars and Vectors ExplainedMuhammad AfzalNo ratings yet
- Matrix Math TutorialDocument6 pagesMatrix Math TutorialToby ChengNo ratings yet
- matrixAlgebraReview PDFDocument16 pagesmatrixAlgebraReview PDFRocket FireNo ratings yet
- 02A-Vector Calculus Part1Document18 pages02A-Vector Calculus Part1JDR JDRNo ratings yet
- LinearAlgebraI 2023 MatrdetsDocument27 pagesLinearAlgebraI 2023 Matrdetsguilhermeab2008No ratings yet
- Maths Synopsis 075648Document40 pagesMaths Synopsis 075648ateefjodamani67No ratings yet
- 12 Math Notes CHP 10Document15 pages12 Math Notes CHP 10Shah KavishNo ratings yet
- Matrix Algebra: By:Ansh Garg Xii-CDocument26 pagesMatrix Algebra: By:Ansh Garg Xii-CAnsh GargNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 LinearAlgebra ECDocument21 pagesChap 1 LinearAlgebra ECMidhun BabuNo ratings yet
- ES 21 First Exam NotesDocument13 pagesES 21 First Exam NotesGil Kenneth San MiguelNo ratings yet
- Vector Analysis: Multivector Review and Training CenterDocument10 pagesVector Analysis: Multivector Review and Training CenterMark FrancisNo ratings yet
- كتاب المقرر الاستاتيكاDocument105 pagesكتاب المقرر الاستاتيكاEbrahem BarakaNo ratings yet
- JR Linear Algebra (Pgs-359)Document359 pagesJR Linear Algebra (Pgs-359)Rohit Mandal100% (2)
- MATRIX ALGEBRADocument21 pagesMATRIX ALGEBRA洪梓沛No ratings yet
- Cellulose and Its DerivativesDocument1 pageCellulose and Its Derivativesvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Engineering Probability and Statistics: Dispersion, Mean, Median, and Mode Values Permutations and CombinationsDocument1 pageEngineering Probability and Statistics: Dispersion, Mean, Median, and Mode Values Permutations and CombinationsROMIN MANOJ CHITTETTUNo ratings yet
- Numerical MethodsDocument1 pageNumerical MethodsROMIN MANOJ CHITTETTUNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Engineering Upplied-Eference Andbook: Eventh DitionDocument1 pageFundamentals of Engineering Upplied-Eference Andbook: Eventh DitionROMIN MANOJ CHITTETTUNo ratings yet
- SYMMETRIC AND ALTERNATING GROUPSDocument366 pagesSYMMETRIC AND ALTERNATING GROUPSWidya DwiyantiNo ratings yet
- PDEDocument39 pagesPDEchandra kantNo ratings yet
- Mathematics & Statistics 11th Part 2Document224 pagesMathematics & Statistics 11th Part 2Amit MeshramNo ratings yet
- Linear Programming Through Solver Tool in ExcelDocument16 pagesLinear Programming Through Solver Tool in Excelami402t0% (1)
- Ratio and Proportion, RaviDocument85 pagesRatio and Proportion, RaviShrishailamalikarjunNo ratings yet
- Cee 101 Sim PDFDocument135 pagesCee 101 Sim PDFNovelyn AppillanesNo ratings yet
- MEP Y9 Practice Book A: Index Notation and Standard FormDocument32 pagesMEP Y9 Practice Book A: Index Notation and Standard FormWei yet ChuNo ratings yet
- NumericalMethods Part1Document321 pagesNumericalMethods Part1محمد العراقيNo ratings yet
- NUET 2022 Mathematics Specimen PaperDocument26 pagesNUET 2022 Mathematics Specimen Papernyry2005No ratings yet
- TitleDocument18 pagesTitleAaditya BaidNo ratings yet
- TrigDocument33 pagesTrigHappybabyNo ratings yet
- ABAQUS NumericalMethods PDFDocument53 pagesABAQUS NumericalMethods PDFwoongs73No ratings yet
- The Word Problem and Cayley GraphsDocument13 pagesThe Word Problem and Cayley GraphsramNo ratings yet
- GMAT Quant Topic 4 - Numbers SolutionsDocument73 pagesGMAT Quant Topic 4 - Numbers SolutionsJuan Carlos PatricioNo ratings yet
- Math 1 Week 5 Frequently Asked Questions PDFDocument3 pagesMath 1 Week 5 Frequently Asked Questions PDFGirindhra A NairNo ratings yet
- Matrix Differentiation GuideDocument34 pagesMatrix Differentiation Guidetake shoboNo ratings yet
- W8 - Laplace Transform (Part 1)Document46 pagesW8 - Laplace Transform (Part 1)HermyraJ RobertNo ratings yet
- Trig Exam 2 Review F07Document6 pagesTrig Exam 2 Review F07Rodion Romanovich RaskolnikovNo ratings yet
- Graph vertex degree and path/circuit identificationDocument1 pageGraph vertex degree and path/circuit identificationWeStan LegendsNo ratings yet
- A Level PMMS P2 2021Document3 pagesA Level PMMS P2 2021Labssen FaithNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Maths Deleted Syllabus Portion For 2020 21 PDFDocument2 pagesCBSE Class 11 Maths Deleted Syllabus Portion For 2020 21 PDFSweta chaturvediNo ratings yet
- CosineDocument10 pagesCosineSohaib AslamNo ratings yet
- Mathematics - IVDocument4 pagesMathematics - IVAtish GhoshNo ratings yet
- Indefinite integrals of basic functionsDocument17 pagesIndefinite integrals of basic functionsVincent DL TngNo ratings yet
- Chap5C 4pDocument10 pagesChap5C 4pMingdreamerNo ratings yet
- Chandan Mandal 11.Document14 pagesChandan Mandal 11.jefferson sarmientoNo ratings yet
- Inverse Trig Functions ExamplesDocument4 pagesInverse Trig Functions ExamplesAbdirazak Mohamed Haaji OmarNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Matrices Index:: Please Click On The Question Number You WantDocument17 pagesIGCSE Matrices Index:: Please Click On The Question Number You WantNad HsNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 On WednesdayDocument46 pagesQuiz 1 On WednesdayAmitava KansabanikNo ratings yet
- DGT Pair of St. LinesDocument39 pagesDGT Pair of St. Linesvardhan prakashNo ratings yet