Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cellulose and Its Derivatives
Uploaded by
vzimak2355Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cellulose and Its Derivatives
Uploaded by
vzimak2355Copyright:
Available Formats
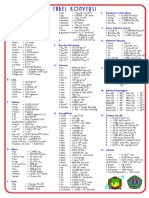
UNITS
This handbook uses the metric system of units. Ultimately, the FE examination will be entirely metric. However, currently some
of the problems use both metric and U.S. Customary System (USCS). In the USCS system of units, both force and mass are
called pounds. Therefore, one must distinguish the pound-force (lbf) from the pound-mass (lbm).
The pound-force is that force which accelerates one pound-mass at 32.174 ft/s2. Thus, 1 lbf = 32.174 lbm-ft/s2. The expression
32.174 lbm-ft/(lbf-s2) is designated as gc and is used to resolve expressions involving both mass and force expressed as pounds.
For instance, in writing Newton's second law, the equation would be written as F = ma/gc, where F is in lbf, m in lbm, and a is
in ft/s2.
Similar expressions exist for other quantities. Kinetic Energy: KE = mv2/2gc, with KE in (ft-lbf); Potential Energy: PE = mgh/gc,
with PE in (ft-lbf); Fluid Pressure: p = ρgh/gc, with p in (lbf/ft2); Specific Weight: SW = ρg/gc, in (lbf/ft3); Shear Stress: τ =
(µ/gc)(dv/dy), with shear stress in (lbf/ft2). In all these examples, gc should be regarded as a unit conversion factor. It is
frequently not written explicitly in engineering equations. However, its use is required to produce a consistent set of units.
Note that the conversion factor gc [lbm-ft/(lbf-s2)] should not be confused with the local acceleration of gravity g, which has
different units (m/s2 or ft/s2)and may be either its standard value (9.807 m/s2 or 32.174 ft/s2) or some other local value.
If the problem is presented in USCS units, it may be necessary to use the constant gc in the equation to have a consistent set of
units.
METRIC PREFIXES
Multiple Prefix Symbol COMMONLY USED EQUIVALENTS
10–18 atto a 1 gallon of water weighs 8.34 lbf
10–15 femto f 1 cubic foot of water weighs 62.4 lbf
10–12 pico p 1 cubic inch of mercury weighs 0.491 lbf
10–9 nano n
The mass of one cubic meter of water is 1,000 kilograms
10–6 micro µ
10–3 milli m
10–2 centi c TEMPERATURE CONVERSIONS
10–1 deci d ºF = 1.8 (ºC) + 32
101 deka da ºC = (ºF – 32)/1.8
102 hecto h ºR = ºF + 459.69
103 kilo k
K = ºC + 273.15
106 mega M
109 giga G
1012 tera T
1015 peta P
1018 exa E
FUNDAMENTAL CONSTANTS
Quantity Symbol Value Units
electron charge e 1.6022 × 10−19 C (coulombs)
Faraday constant 96,485 coulombs/(mol)
gas constant metric R 8,314 J/(kmol·K)
gas constant metric R 8.314 kPa·m3/(kmol·K)
gas constant USCS R 1,545 ft-lbf/(lb mole-ºR)
R 0.08206 L-atm/mole-K
gravitation - newtonian constant G 6.673 × 10–11 m3/(kg·s2)
gravitation - newtonian constant G 6.673 × 10–11 N·m2/kg2
gravity acceleration (standard) metric g 9.807 m/s2
gravity acceleration (standard) USCS g 32.174 ft/s2
molar volume (ideal gas), T = 273.15K, p = 101.3 kPa Vm 22,414 L/kmol
speed of light in vacuum c 299,792,000 m/s
Stephan-Boltzmann constant σ 5.67 × 10–8 W/(m2·K4)
You might also like
- Units: PE in (FT-LBF) Fluid Pressure: P GH/G G/GDocument2 pagesUnits: PE in (FT-LBF) Fluid Pressure: P GH/G G/GElizabeth Cares LiraNo ratings yet
- Common ConstantsDocument3 pagesCommon Constantskristan7No ratings yet
- Tabela de Conversão de UnidadesDocument1 pageTabela de Conversão de UnidadesrobertaNo ratings yet
- Appendix A: Conversion Factors and Constants: Metric Symbols and NamesDocument3 pagesAppendix A: Conversion Factors and Constants: Metric Symbols and NamesNontanan KanmahaNo ratings yet
- 2017 Bookmatter HeatAndMassTransfer PDFDocument44 pages2017 Bookmatter HeatAndMassTransfer PDFZainalAbidinNo ratings yet
- Appendix A: Conversion FactorsDocument44 pagesAppendix A: Conversion FactorsZainalAbidinNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Conversion FactorsDocument2 pagesThermodynamics Conversion FactorsjaiqcooNo ratings yet
- Factors For Unit Conversion 2Document2 pagesFactors For Unit Conversion 2Shereen AminiNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Units and ConstantsDocument3 pagesConversion of Units and ConstantsLopez D NikkoNo ratings yet
- Conversion of UnitsDocument1 pageConversion of UnitsRYAN ABALOSNo ratings yet
- FM Sol Chap12-131Document41 pagesFM Sol Chap12-131CEMONo ratings yet
- Unit Conversion TablesDocument6 pagesUnit Conversion Tablesines.santos.rodriguesNo ratings yet
- Bio Rules and Laws-34-37Document4 pagesBio Rules and Laws-34-37nasser nsoorNo ratings yet
- PIPE Constants and ConversionsDocument2 pagesPIPE Constants and ConversionsJames Joseth ArceoNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors G: For de Common Unit SystemsDocument7 pagesConversion Factors G: For de Common Unit SystemsCintya Stefany Rivadeneyra BurgosNo ratings yet
- Conversion Factors and Constants For Mechanical EngineeringDocument4 pagesConversion Factors and Constants For Mechanical EngineeringElma CruzNo ratings yet
- CH 01Document9 pagesCH 01Mary Lorelyn EscoteNo ratings yet
- Chapter8-Assignment and SolutionDocument6 pagesChapter8-Assignment and SolutionDavid100% (1)
- ConversionDocument1 pageConversionIan KasaiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Intro Problems Set 2 August 2012Document4 pagesFluid Mechanics Intro Problems Set 2 August 2012NoOneNo ratings yet
- Test Supplement 13Document16 pagesTest Supplement 13jimmys45No ratings yet
- Conversions CPCDocument5 pagesConversions CPCVoora GowthamNo ratings yet
- Boiling and Condensation PDFDocument11 pagesBoiling and Condensation PDFYeditha Satyanarayana MurthyNo ratings yet
- First Year Formula SheetsDocument19 pagesFirst Year Formula SheetsIris BenardeteNo ratings yet
- ME ConstantsDocument1 pageME ConstantsOwel CabugawanNo ratings yet
- Useful ConstantsDocument1 pageUseful ConstantsFarhan HalimNo ratings yet
- Tabel Konversi CompressDocument1 pageTabel Konversi CompressNanaNo ratings yet
- Conversion TableDocument2 pagesConversion Tablemahmood0901instaNo ratings yet
- Cnvertion FactorsDocument1 pageCnvertion FactorsOmed. HNo ratings yet
- Mae 261 Dimensions and Units: Standard Sea-Level Values For AirDocument2 pagesMae 261 Dimensions and Units: Standard Sea-Level Values For AirLeilani OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Review Manual PDFDocument509 pagesMechanical Engineering Review Manual PDFKenneth SienaNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument2 pagesReviewerNeo GarceraNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry-5th-Edition Compress RemovePdfPagesDocument59 pagesBiochemistry-5th-Edition Compress RemovePdfPagesWaseem AlnaasNo ratings yet
- Heat Calculation ReferenceDocument5 pagesHeat Calculation ReferenceCham SurendNo ratings yet
- Review Problems 1-85 A Hydraulic Lift Is Used To LiftDocument22 pagesReview Problems 1-85 A Hydraulic Lift Is Used To Liftpanalopee100% (5)
- Basic Units: Quantity Name of Unit SymbolDocument2 pagesBasic Units: Quantity Name of Unit SymbolDhruv AsodariaNo ratings yet
- Tabel Konversi PDFDocument1 pageTabel Konversi PDFsaebanny100% (1)
- Commonly Used Prefixes and Numerical Values For SI Units Prefix Symbol Value ExampleDocument4 pagesCommonly Used Prefixes and Numerical Values For SI Units Prefix Symbol Value ExampleJilliane PascualNo ratings yet
- GasTables ZukerBiblarzDocument72 pagesGasTables ZukerBiblarzArockia FenilNo ratings yet
- Units and Conversion Factors: AppendixDocument2 pagesUnits and Conversion Factors: AppendixAcelora AzulNo ratings yet
- 2016 Bookmatter ThePhysicsOfLivingSystemsDocument11 pages2016 Bookmatter ThePhysicsOfLivingSystemsRihem and Soundosse wordsNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument5 pagesIntroductionJohn Renz RetiroNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Topic 1Document11 pagesThermodynamics Topic 1Sunshine FelongcoNo ratings yet
- ConversionbyEngrProfPH PDFDocument4 pagesConversionbyEngrProfPH PDFCALICA RYAN ANTHONY V.No ratings yet
- Chapter 1,2,3Document64 pagesChapter 1,2,3Faiz Daud100% (1)
- Six Ideas That Shaped Physics - All Units (Thomas A. Moore) (Z-Library)Document1,587 pagesSix Ideas That Shaped Physics - All Units (Thomas A. Moore) (Z-Library)kk72tnbgtj100% (1)
- Dimensional AnalysisDocument10 pagesDimensional AnalysisXyra P. KujoNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Conversiones de UnidadesDocument3 pagesTabla de Conversiones de UnidadesChristopher MorenoNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Conversiones de UnidadesDocument3 pagesTabla de Conversiones de UnidadesLuis Fernando Solis CadenaNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Conversiones de Unidades PDFDocument3 pagesTabla de Conversiones de Unidades PDFJavier Hernández RequenaNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Conversiones de UnidadesDocument3 pagesTabla de Conversiones de UnidadesLucas Escudero RamírezNo ratings yet
- Flare Gas Recovery Helpful InformationDocument2 pagesFlare Gas Recovery Helpful InformationKalai SelvanNo ratings yet
- Lamp Konversi DLL Hal 156 SD 160 Rev 2015Document5 pagesLamp Konversi DLL Hal 156 SD 160 Rev 2015Lucky BayanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Examples&SolutionDocument42 pagesChapter 9 Examples&SolutionSami ullahNo ratings yet
- SI - English Unit Conversion Table : Pressure LengthDocument4 pagesSI - English Unit Conversion Table : Pressure LengthVictor Gomez Dy LampadioNo ratings yet
- PROBLEMS With SolutionDocument8 pagesPROBLEMS With Solutionbudoycarino0% (1)
- Practical Units For Fps Mks and Cgs SystDocument2 pagesPractical Units For Fps Mks and Cgs SystRohail HussainNo ratings yet
- Tabla de Conversiones de Unidades-1 PDFDocument3 pagesTabla de Conversiones de Unidades-1 PDFRafael López0% (1)
- ConversionDocument2 pagesConversionHasby AsNo ratings yet
- ABB Green Transformer - Reducing Environmental Impact Without Compromising Reliability (En)Document25 pagesABB Green Transformer - Reducing Environmental Impact Without Compromising Reliability (En)vzimak2355No ratings yet
- Fe School CodesDocument58 pagesFe School Codesvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Fe Mechanical EngineeringDocument5 pagesFe Mechanical Engineeringvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Technical Specification For 24kV Cable Entry Transformers: Ergon Energy Corporation LimitedDocument38 pagesTechnical Specification For 24kV Cable Entry Transformers: Ergon Energy Corporation Limitedvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Mathematics: Ax + by + C 0 y MX + B, y - y M (YDocument12 pagesMathematics: Ax + by + C 0 y MX + B, y - y M (Yvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Fe Engineering Probability StatisticsDocument9 pagesFe Engineering Probability Statisticsvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Fe Environmental EngineeringDocument24 pagesFe Environmental Engineeringvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Fe Industrial EngineeringDocument14 pagesFe Industrial Engineeringvzimak2355No ratings yet
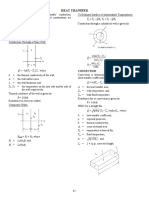
- Fe Heat TransferDocument6 pagesFe Heat Transfervzimak2355No ratings yet
- Fe Fluid Mechanics PDFDocument12 pagesFe Fluid Mechanics PDFvzimak2355No ratings yet
- 10 996e RMDocument14 pages10 996e RMvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Ethics: Model Rules, Section 240.15, Rules of Professional ConductDocument2 pagesEthics: Model Rules, Section 240.15, Rules of Professional Conductvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Fe Mechanical EngineeringDocument16 pagesFe Mechanical Engineeringvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Fe School CodesDocument5 pagesFe School Codesvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Fe School CodesDocument6 pagesFe School Codesvzimak2355No ratings yet
- 10 996e RMDocument14 pages10 996e RMvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Properties of Single-Component Systems NomenclatureDocument11 pagesThermodynamics: Properties of Single-Component Systems Nomenclaturevzimak2355No ratings yet
- Statics: Force Centroids of Masses, Areas, Lengths, and VolumesDocument5 pagesStatics: Force Centroids of Masses, Areas, Lengths, and Volumesvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Research Report 320: Elastomers For Fluid Containment in Offshore Oil and Gas Production: Guidelines and ReviewDocument111 pagesResearch Report 320: Elastomers For Fluid Containment in Offshore Oil and Gas Production: Guidelines and Reviewvzimak2355No ratings yet
- Arai in Ais 066 2008Document26 pagesArai in Ais 066 2008vzimak2355No ratings yet
- Husky Hypet 400Document148 pagesHusky Hypet 400Bir Kamaldeep Singh100% (7)
- HS POLYBAG - NEW FACTORY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 견적서 20190713 (최종)Document11 pagesHS POLYBAG - NEW FACTORY ELECTRICAL SYSTEM 견적서 20190713 (최종)Nhí LêNo ratings yet
- Exam Style Answers 20 Asal Physics CBDocument2 pagesExam Style Answers 20 Asal Physics CBAnshul ShahNo ratings yet
- Transition To Turbopropeller-Powered AirplanesDocument14 pagesTransition To Turbopropeller-Powered AirplanesAditya Sinha100% (1)
- FINAL LAB QUIZ 1 - Attempt ReviewDocument4 pagesFINAL LAB QUIZ 1 - Attempt ReviewjrenceNo ratings yet
- MEROXDocument8 pagesMEROXZubyr AhmedNo ratings yet
- SIPROTEC Compact Protection Systems A1 enDocument168 pagesSIPROTEC Compact Protection Systems A1 enMarcelo MagriNo ratings yet
- Abb Make Hybrid Switchgear PassDocument23 pagesAbb Make Hybrid Switchgear PassAjith AjiNo ratings yet
- Design Check List Viii-1 Rev1Document2 pagesDesign Check List Viii-1 Rev1nirmalNo ratings yet
- @perkins: 4000 Series 4016TAG2 4016TAG2ADocument2 pages@perkins: 4000 Series 4016TAG2 4016TAG2AIman AkbariNo ratings yet
- Bedouin Black TentDocument20 pagesBedouin Black TentKristine Paula Gabrillo TiongNo ratings yet
- Water and Energy Efficient Showers: Project ReportDocument54 pagesWater and Energy Efficient Showers: Project ReportMurali Krishna KakaraparthiNo ratings yet
- Rivulis F3240 English Metric 20191223 WebDocument10 pagesRivulis F3240 English Metric 20191223 WebMehdi BassouNo ratings yet
- Shielding Design GeneralDocument22 pagesShielding Design GeneralAbu OmarNo ratings yet
- 07 Pegasus Ibms v5.2Document4 pages07 Pegasus Ibms v5.2h2odavidNo ratings yet
- 144S... - PCB Series: Signal Conditioned Precision Pressure TransducersDocument4 pages144S... - PCB Series: Signal Conditioned Precision Pressure TransducersAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Residential KitchenBathrooDocument7 pagesResidential KitchenBathrooCarlos Daniel Ayala GonzalezNo ratings yet
- SYS-2020 Owners Manual - EN PDFDocument18 pagesSYS-2020 Owners Manual - EN PDFMunish BajajNo ratings yet
- AMTED398078EN Part2 (Web)Document54 pagesAMTED398078EN Part2 (Web)jobpei2No ratings yet
- Rise & Impact of Crude Oil Price in IndiaDocument10 pagesRise & Impact of Crude Oil Price in IndiaRandal SchroederNo ratings yet
- Instruction Manual For 4 Stroke, 4 Cylinder, Mpfi Petrol Engine Test RIGDocument47 pagesInstruction Manual For 4 Stroke, 4 Cylinder, Mpfi Petrol Engine Test RIGAbhishek ShuklaNo ratings yet
- ExercisesDocument9 pagesExercisesArzum EserNo ratings yet
- Laporan Praktik Mesin ListrikDocument4 pagesLaporan Praktik Mesin ListrikFatimah azzahraNo ratings yet
- Sector:: Automotive/Land Transport SectorDocument20 pagesSector:: Automotive/Land Transport SectorVedin Padilla Pedroso92% (12)
- Two-Stage Ball Milling of Recycled Machining Chips To Create An Alternative Feedstock Powder For Metal Additive ManufacturingDocument40 pagesTwo-Stage Ball Milling of Recycled Machining Chips To Create An Alternative Feedstock Powder For Metal Additive ManufacturingJazmínARNo ratings yet
- 06-DC ChopperDocument26 pages06-DC ChopperTuhin ShahNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Enhanced Flooded Battery For Smart Mild Hybrid Power TrainsDocument29 pagesRecent Advances in Enhanced Flooded Battery For Smart Mild Hybrid Power Trains3 GamerNo ratings yet
- PC-1 Form of SharifDocument3 pagesPC-1 Form of SharifujjancricketNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 LPDocument5 pagesGrade 7 LPMelfe John CerezoNo ratings yet
- Submitted To: Miss Iqra Mujtaba Submitted By: Nuzhat Aslam Roll No 837 Semester: 03Document3 pagesSubmitted To: Miss Iqra Mujtaba Submitted By: Nuzhat Aslam Roll No 837 Semester: 03Nimi MalikNo ratings yet