Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Gr11 Rev Ch05 04 QnA
Uploaded by
Aidan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesOriginal Title
Gr11_Rev_Ch05_04_QnA
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesGr11 Rev Ch05 04 QnA
Uploaded by
AidanCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
Dr Vince Grade 11 Physics Detailed Revisions [Ch5-02] 1
G11-C05-Q04-A: Fill in the blanks.
1. Most substances can exist in _________ states.
2. The SI unit of specific latent heat is __________.
3. Below the melting point, water can only exist as _________.
4. The direct change from the solid phase to the gas phase is called _________.
5. The process of changing solid into liquid is called _______________.
6. The process of changing liquid into solid is called _______________.
7. The process of changing liquid into vapour is called _______________.
8. The process of changing vapour into liquid is called _______________.
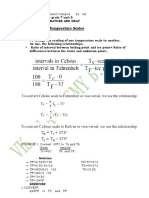
9. If water in a container is heated, the temperature will increase until it reaches _________ °C.
10. At _______ °C at normal pressure, the water boils and begins to vaporize.
11. Under normal pressure, the boiling point of mercury is __________.
12. Under normal pressure, the boiling point of water is ________.
13. If a cup has some water and some ice, its temperature is __________.
14. The melting point for ice under normal pressure is ________.
15. The melting point for ice under normal pressure is ________ K.
16. _____________ is a phase transition from a liquid into a solid
17. ________ is a phase transition from a solid into a liquid.
18. ____________is a phase transition from a liquid into a gas.
19. _________ is a phase transition from a gas into a liquid.
20. ____________ is a phase transition from a solid into a gas.
21. ___________ is a phase transition from a gas into a solid.
22. Increasing the boiling point of water by increasing the pressure is used in ___________.
23. When a pressure cooker is in operation, the pressure inside it is ____ the normal atmospheric pressure.
24. At the pressure of ____ atm, water boils at a higher temperature of 120 C.
G11-C05-Q03-B: Say True (or) False.
1. The change from one phase to another takes place very slowly at a definite temperature.
2. The temperature at which a phase change occurs depends on pressure.
3. The latent heat depends on the mass of the substance.
4. The latent heat depends on the type of the substance.
5. The latent heat for unit mass of a substance is the specific latent heat of that substance.
6. In a phase change, heat may be absorbed or liberated.
7. While ice is melting, the temperature is increasing.
8. During a phase change, heat transferred does not increase kinetic energy of the molecules.
9. During a phase change, the separation between molecules changes.
2 Grade 11 Physics Detailed Revisions [Ch5-02] Dr Vince
10. Temperature is a measure of increase in average kinetic energy of the molecules.
11. The temperature does not change during phase change.
12. Sublimation is used in the freeze-drying process.
13. Heat required to melt 1 g of water at its melting point is less than heat required to vaporize 1 g of water
at its boiling point.
14. Different liquids have different boiling points.
15. If steam at 100 C is cooled at normal atmospheric pressure, it condenses back to water.
16. In condensation, the substance releases heat.
17. In vaporization, the substance absorbs heat.
18. If a certain pieces of ice in a tray are heated, the temperature will increase.
19. The melting point and boiling point vary with pressure.
20. The melting point of ice varies with atmospheric pressure.
21. The melting point of ice decreases as the pressure increases.
22. For an ice skater, the pressure of ice skates lowers the melting point of ice.
23. The boiling point of water varies with the atmospheric pressure.
24. An increase in external pressure will raise the boiling point of water.
25. The hot air and steam contain a lot of heat.
G11-C05-Q04-C: Short Questions.
1. What are the three states of matter?
2. What do you understand by phase change?
3. What do you understand by latent heat?
4. What do you understand by specific latent heat?
5. Can heat be extracted from water at 0 C?
6. What do you understand by vaporization?
7. What do you understand by boiling point?
8. What do you understand by specific latent heat of vaporization?
9. What do you understand by condensation?
10. Why is getting burnt by steam at 100 C worse than that by hot water of the same mass at 100 C?
11. What do you understand by melting point?
12. What do you understand by specific latent heat of fusion?
13. What are the two significant points on the pressure-temperature graph for phase change of water?
14. What do you understand by triple point?
15. What do you understand by critical point?
16. How does the melting point of ice and boiling point of water change with pressure?
17. Compare the molecular distances of ice, water, and steam.
Dr Vince Grade 11 Physics Detailed Revisions [Ch5-02] 3
G11-C05-Q04-D: Calculations.
1. How much heat is needed to change 5 kg of water at 100 C to steam?
(specific latent beat of vaporization Lv = 2.255 106 J kg-1)
2. A lead bullet at 327 °C melts after striking a steel plate. With what velocity does the bullet strike the
steel plate? (Latent heat of fusion of lead = 24.52 103 J kg-1, the melting point of lead = 327 °C)
(Hint: all of the kinetic energy of the bullet changes into heat energy)
3. How much heat is required to melt 5 kg of ice at 0 °C?
(specific latent heat of fusion of ice is, Lf = 3.335 105 J kg-1)
4. Ice cubes at -10 °C with a total mass of 0.045 kg are mixed with 0.3 kg tea at 30 °C. What is the final
equilibrium temperature? (The specific heat capacity of tea is the same as that of water, the specific
heat capacity of ice is 2089 J kg-1 K-1.)
5. How much heat is needed to melt 10 kg of ice at -10 C?
Specific latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.335 105 J kg-1,
Specific heat capacity of ice = 2089 J kg-1 K-1.
6. Does all the ice melt when 0.15 kg of ice at 0 C is put into 0.25 kg of water at 20 °C? What is the final
temperature?
7. 0.2 kg of water at 0 C is poured into a container having liquid nitrogen at -196 C by mistake. How
much nitrogen vaporizes? The boiling point of nitrogen is -196 C and its latent heat of vaporization is
200 800 J kg-1.
8. A 10 kg mass of copper block is dropped from a height of 50 m. Assume all of the potential energy
change to heat, how much has the temperature increased when the copper block strikes the ground?
(Specific heat capacity of copper = 385 J kg-1 K-1, g = 9.8 m s-2)
You might also like
- Mechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesFrom EverandMechanics of the Household: A Course of Study Devoted to Domestic Machinery and Household Mechanical AppliancesNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Understanding Specific Latent HeatDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Specific Latent HeatNoraidah Harun100% (1)
- Chemistry Investigatory ProjectDocument5 pagesChemistry Investigatory ProjectHarsh Gupta0% (2)
- Heat 3: Class-VIII Physics Question BankDocument28 pagesHeat 3: Class-VIII Physics Question BankSayantan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- HEAT TRANSFERDocument28 pagesHEAT TRANSFERSayantan ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- 3412EM-Physics Study Material Chap-1-7Document85 pages3412EM-Physics Study Material Chap-1-7Karnati Siva rama Swetha ReddyNo ratings yet
- Phase Diagram ActivityDocument8 pagesPhase Diagram ActivityYomiko Danise P. EloresNo ratings yet
- Effect of Impurities On TheDocument6 pagesEffect of Impurities On TheBansal Shivansh100% (1)
- Chemistry Project ReportDocument4 pagesChemistry Project ReportSiddharth Shah100% (1)
- Physics EMDocument38 pagesPhysics EMviswanadapalli anushaNo ratings yet
- Calorimetry SynopsisDocument4 pagesCalorimetry Synopsissreevaishnava01No ratings yet
- Calorimetry 2023Document10 pagesCalorimetry 2023Yatharth TiwariNo ratings yet
- Name: - : Class: F4B Lesson: Date: TimeDocument11 pagesName: - : Class: F4B Lesson: Date: TimeChrise RajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Heat ReviewDocument16 pagesChapter 4 Heat ReviewKurdishNo ratings yet
- CalorimetryDocument5 pagesCalorimetryVenu GopalNo ratings yet
- Temp and Heat Worksheet 1Document6 pagesTemp and Heat Worksheet 1api-328287948100% (1)
- Heat and Temperature Class 3Document5 pagesHeat and Temperature Class 3GopiKrishnaValireddyNo ratings yet
- Melting, Boiling and EvaporationDocument4 pagesMelting, Boiling and Evaporationanwar9602020No ratings yet
- Thermal PhysicsDocument4 pagesThermal PhysicsCheku DorjiNo ratings yet
- PHASE CHANGE Hand OutDocument8 pagesPHASE CHANGE Hand Outjoel rosalNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 1 (Done)Document6 pagesWorksheet 1 (Done)samyak jainNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project Report: Effect of Impurities On The Boiling Point and Freezing Point of A Liquid"Document10 pagesChemistry Project Report: Effect of Impurities On The Boiling Point and Freezing Point of A Liquid"Kaseem ManzerNo ratings yet
- Specific HeatDocument2 pagesSpecific HeatVanessa Christonette SistosoNo ratings yet
- Bridge course-Phy-I PU 78Document5 pagesBridge course-Phy-I PU 78SaputraNo ratings yet
- Pure Substances, Phase-Change Process, Property DiagramsDocument3 pagesPure Substances, Phase-Change Process, Property DiagramsNallely AristaNo ratings yet
- Matter in Our Surroundings: Session 2Document5 pagesMatter in Our Surroundings: Session 2swarup.kadam17No ratings yet
- Section 1 Phy SyllabusDocument3 pagesSection 1 Phy SyllabusSHarves AUdiNo ratings yet
- FKCH 8 HHM BYSJxe F8 ZG 74Document45 pagesFKCH 8 HHM BYSJxe F8 ZG 74MahaNo ratings yet
- Ap 10 Ps em Qa 01 Heat 5Document3 pagesAp 10 Ps em Qa 01 Heat 5VikashNo ratings yet
- Latent HeatDocument32 pagesLatent HeatAbhijit Kar Gupta100% (11)
- Phase Changes GizmoDocument6 pagesPhase Changes GizmoJaylen CarringtonNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Lesson 4 - Specific Latent HeatDocument39 pages3.1 Lesson 4 - Specific Latent HeatMvKhoa Gixer100% (1)
- Topic 3.1 FormativeDocument2 pagesTopic 3.1 FormativeDharmesh Ramnarayan YadavNo ratings yet
- Basic Refrigeration System - MATTERDocument10 pagesBasic Refrigeration System - MATTERCisco StarkNo ratings yet
- LATENT HEAT NotesDocument4 pagesLATENT HEAT NotesSowndaryaNo ratings yet
- Sci-6 Physics Exploratory Test # - CHOICES: Choose The Best Answer. Write The Correct Word/s in Notebook. Nos. 1-10Document3 pagesSci-6 Physics Exploratory Test # - CHOICES: Choose The Best Answer. Write The Correct Word/s in Notebook. Nos. 1-10Ken liamNo ratings yet
- Phase ChangeDocument28 pagesPhase ChangeYomiko Danise P. EloresNo ratings yet
- TP5 - Heat Capacity & Latent Heat 1Document5 pagesTP5 - Heat Capacity & Latent Heat 1wengiemotshegweNo ratings yet
- Pogil - Changes of PhaseDocument4 pagesPogil - Changes of Phaseapi-293306937No ratings yet
- Physics (Autosaved)Document15 pagesPhysics (Autosaved)Jay VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Determine Specific Heats of LiquidsDocument9 pagesDetermine Specific Heats of LiquidsSai Swetha KVNo ratings yet
- In-Class Worksheet AnswersDocument6 pagesIn-Class Worksheet AnswersalgonzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Lesson 3 PDFDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Lesson 3 PDFLOK AI TENG MoeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10. Specific Heat Capacity and Latent HeatDocument27 pagesChapter 10. Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heatbasheer shaikNo ratings yet
- Phase ChangesDocument5 pagesPhase ChangesDavid PopeNo ratings yet
- What We Have Already LearntDocument13 pagesWhat We Have Already Learnt'Shyam SinghNo ratings yet
- Refrigeration Unit-5Document16 pagesRefrigeration Unit-5Mr. P. Ramkumar MECHNo ratings yet
- Latihan Bab Haba FizikDocument16 pagesLatihan Bab Haba FizikNuhaa JamilahNo ratings yet
- Chem - Week - 2Document44 pagesChem - Week - 2cadaxeshpatelNo ratings yet
- Specific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat (4 Files Merged)Document20 pagesSpecific Heat Capacity and Latent Heat (4 Files Merged)Rajesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE 2.0 - Thermal Physics - Test 2018Document9 pagesIGCSE 2.0 - Thermal Physics - Test 2018Brandeice BarrettNo ratings yet
- X Physics emDocument116 pagesX Physics emPhani KumarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Calorimetry and Joule's LawDocument4 pagesThermodynamics: Calorimetry and Joule's LawbigaNo ratings yet
- Heat and Phase Changes ExplainedDocument13 pagesHeat and Phase Changes ExplainedMaliq MorrisNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Temperature Scales: ExerciseDocument6 pagesConversion of Temperature Scales: Exercisekidanemariam HabtemariamNo ratings yet
- Experiment 11 Specific Heat and Heat of Fusion: PreparationDocument5 pagesExperiment 11 Specific Heat and Heat of Fusion: PreparationMae Joy PalmaNo ratings yet
- Heating and Phase ChangesDocument4 pagesHeating and Phase ChangesMark ProchaskaNo ratings yet
- Thermal Properties of Matter - 23-24Document9 pagesThermal Properties of Matter - 23-24smodi6545No ratings yet
- Dr Vince's Grade 10 Physics Revision Notes on Gravitational ForceDocument3 pagesDr Vince's Grade 10 Physics Revision Notes on Gravitational ForceAidanNo ratings yet
- GRFP01 Gr11 Ch03 AllDocument22 pagesGRFP01 Gr11 Ch03 AllAidanNo ratings yet
- GRFP01 Gr11 Ch01toCh06Document126 pagesGRFP01 Gr11 Ch01toCh06AidanNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Physics Power and Efficiency NotesDocument22 pagesGrade 11 Physics Power and Efficiency NotesAidanNo ratings yet
- GRFP01 Gr11 Ch09 ALLDocument37 pagesGRFP01 Gr11 Ch09 ALLAidanNo ratings yet
- Functions Assignment3Document7 pagesFunctions Assignment3AidanNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics ForcesDocument1 pageGrade 10 Physics ForcesAidanNo ratings yet
- G11 Rev Ch01 01Document1 pageG11 Rev Ch01 01AidanNo ratings yet
- Functions Assignment1Document3 pagesFunctions Assignment1AidanNo ratings yet
- G10 New Ch06 Test 2023 01 HeatDocument1 pageG10 New Ch06 Test 2023 01 HeatAidanNo ratings yet
- Functions Assignment4Document6 pagesFunctions Assignment4AidanNo ratings yet
- Remainder Theorem ProblemsDocument4 pagesRemainder Theorem ProblemsAidanNo ratings yet
- The Factor TheoremDocument4 pagesThe Factor TheoremAidanNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics Forces Revision NotesDocument2 pagesGrade 10 Physics Forces Revision NotesAidanNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Rev Ch03 05 WA SQDocument1 pageGr10 Rev Ch03 05 WA SQAidanNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Physics Revision: Mass vs Weight Concepts ExplainedDocument2 pagesGrade 10 Physics Revision: Mass vs Weight Concepts ExplainedAidanNo ratings yet
- Gr11 Rev Ch03 05 QDocument3 pagesGr11 Rev Ch03 05 QAidanNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Rev Ch04 02 WADocument1 pageGr10 Rev Ch04 02 WAAidanNo ratings yet
- G10 New Ch08 2023 01 RayDocument1 pageG10 New Ch08 2023 01 RayAidanNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Rev Ch03 05Document2 pagesGr10 Rev Ch03 05AidanNo ratings yet
- Gr11 Rev Ch05 01 QnADocument2 pagesGr11 Rev Ch05 01 QnAAidanNo ratings yet
- G10 New Ch08 2023 01 Ray AnsDocument3 pagesG10 New Ch08 2023 01 Ray AnsAidanNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Rev Ch03 05 WADocument3 pagesGr10 Rev Ch03 05 WAAidanNo ratings yet
- Gr11 Rev Ch05 02 QnADocument2 pagesGr11 Rev Ch05 02 QnAAidanNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Rev Ch04 01 WADocument2 pagesGr10 Rev Ch04 01 WAAidanNo ratings yet
- Gr11 Rev Ch05 03 QnADocument2 pagesGr11 Rev Ch05 03 QnAAidanNo ratings yet
- GRFP01 - Gr10 - Ch10 - 05 - MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF IRON AND STEELDocument7 pagesGRFP01 - Gr10 - Ch10 - 05 - MAGNETIC PROPERTIES OF IRON AND STEELAidanNo ratings yet
- Gr10 Rev Ch04 03 WADocument1 pageGr10 Rev Ch04 03 WAAidanNo ratings yet
- Gr11 Rev Ch06 01 QnADocument3 pagesGr11 Rev Ch06 01 QnAAidanNo ratings yet
- Perencanaan Instalasi Penangkal Petir Pada Bangunan Industri FurnitureDocument6 pagesPerencanaan Instalasi Penangkal Petir Pada Bangunan Industri Furniture4rtanto DedyNo ratings yet
- Heat Energy WorksheetDocument3 pagesHeat Energy Worksheetfakhar.0917No ratings yet
- Study Questions (Chapter - 3) PDFDocument6 pagesStudy Questions (Chapter - 3) PDFefeln1No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure Class 11thDocument168 pagesAtomic Structure Class 11thAnand JhaNo ratings yet
- 92Document8 pages92Yabisira ayeleNo ratings yet
- Module - Engineering Vibration1Document29 pagesModule - Engineering Vibration1Romeo LloverasNo ratings yet
- 7 2 Optical Waves in Crystals Cap-3 e 5 YarivDocument25 pages7 2 Optical Waves in Crystals Cap-3 e 5 YarivOmar Yair López RicoNo ratings yet
- 4a's LESSON PLAN-MadiaDocument3 pages4a's LESSON PLAN-MadiaDerlyn Aganan MadiaNo ratings yet
- LMDTDocument6 pagesLMDThassnainiqbal11No ratings yet
- 1.8.1 Distance Time Graph Set 1 QP Ms p4Document5 pages1.8.1 Distance Time Graph Set 1 QP Ms p4HuyenThanhNguyenNo ratings yet
- Prandtl Number Effects On Laminar Mixed Convection Heat Transfer in A Lid-Driven CavityDocument12 pagesPrandtl Number Effects On Laminar Mixed Convection Heat Transfer in A Lid-Driven CavityNamanNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1698314208316 7123246077197692067Document27 pagesOrca Share Media1698314208316 7123246077197692067ClaiireNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Sulphur Melting Steam RequirementDocument2 pagesCalculation of Sulphur Melting Steam RequirementAnonymous jAQnoacHcNo ratings yet
- Physics - WavesDocument21 pagesPhysics - WavesMemory SitambuliNo ratings yet
- Physics HSSC-I According To KPK BookDocument4 pagesPhysics HSSC-I According To KPK BookM ARHAM AAMIR100% (1)
- CLL-251 Heat Transfer (Conduction) : Dr. Manojkumar C. RamtekeDocument53 pagesCLL-251 Heat Transfer (Conduction) : Dr. Manojkumar C. RamtekeHriday GoelNo ratings yet
- Experiments Proving That Light and Electron Behave As Wave Christian HuygensDocument2 pagesExperiments Proving That Light and Electron Behave As Wave Christian HuygensRubin RubinNo ratings yet
- Position-Time and Velocity-Time GraphsDocument29 pagesPosition-Time and Velocity-Time GraphsKrislyn Con-Ek DumulagNo ratings yet
- Science-Grade 8Document45 pagesScience-Grade 8Rosiro100% (1)
- 134 519 1 PB PDFDocument8 pages134 519 1 PB PDFL Fattih Diwa ModeonNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic WavesririkgopeNo ratings yet
- Revised G7-Test-QuestionsDocument6 pagesRevised G7-Test-Questionsapi-668289592No ratings yet
- Physics Updated Neet 2024 SyllubusDocument6 pagesPhysics Updated Neet 2024 SyllubusAbhinave SNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 - Module 1: Different Forms of EM Waves: Grade Level 10 Week 1 Page NoDocument11 pagesQuarter 2 - Module 1: Different Forms of EM Waves: Grade Level 10 Week 1 Page NoMarivic Salvame Amper100% (1)
- Heat Exchanger Design: Key Concepts and CalculationsDocument5 pagesHeat Exchanger Design: Key Concepts and CalculationsSunil KumarNo ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument4 pagesWave OpticsJayanth100% (1)
- Themodynamics1 3Document13 pagesThemodynamics1 3Miko Anderson YjaresNo ratings yet
- Progress in Entransy Theory and Its Applications: Chen LingenDocument23 pagesProgress in Entransy Theory and Its Applications: Chen Lingenhassan zohairNo ratings yet
- Heat Transfer Video Course Dr. GhoshalDocument2 pagesHeat Transfer Video Course Dr. GhoshalMerrelNo ratings yet
- FUNDAMENTALS OF HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER 7th EDITION BY FRANK P. INCROPERA-458Document1 pageFUNDAMENTALS OF HEAT AND MASS TRANSFER 7th EDITION BY FRANK P. INCROPERA-458Endru MourishioNo ratings yet