Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Asexual Reproduction
Uploaded by
Hera ElykaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Asexual Reproduction
Uploaded by
Hera ElykaCopyright:
Available Formats
Asexual Reproduction
It is the mode of reproduction which involves only one organism. The offspring that is produced is
genetically identical to the mother and almost always has the same number of chromosomes. Hence,
they are called clones. Moreover, they are exact copies of their parent cell.
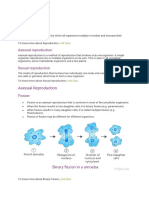
Entities prefer to reproduce asexually by different means. Few asexual methods are budding (e.g.
Hydra), binary fission (e.g. Amoeba, bacteria), spore formation (e.g. ferns), fragmentation (e.g. Planaria),
and vegetative propagation (e.g. Onion).
Also Read: Asexual Reproduction
Asexual Reproduction in Plants
Some plants have the ability to reproduce asexually, that is, without the help of flowers or pollens.
There are different modes of asexual reproduction in plants, both natural and human-induced.
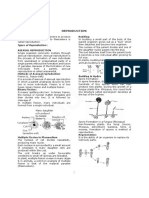
In the natural mode of asexual reproduction, a plant can give rise to an offspring with the help of roots.
Certain plants also use budding and cutting to reproduce asexually.
Human-induced asexual reproduction in plants includes grafting, layering, cutting and micropropagation.
Asexual Reproduction in Animals
Some simple animals, many of which are single-celled, reproduce asexually.
The different modes of asexual reproduction in animals include gemmules (sponges), fragmentation
(planarians), regeneration (echinoderms) and parthenogenesis (ants, wasps)
Living things are wonderful. Wars, poverty, natural disasters, murders, hunting, etc., happen and exist in
the world. But it is still estimated that our earth is the home to around 8 million species. One dies,
another comes. It never ends and is a cycle of life. The secret is within us, it is reproduction in organisms.
It helps organisms to continue their species. It is a life process like nutrition, movement, circulation, etc.
Different modes of reproduction are discussed below.
You might also like
- Animals and Plant ReproductionDocument56 pagesAnimals and Plant ReproductionZyan Subaan VacioNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument14 pagesReproduction in Plantsanjupal100% (2)
- Asexual Sexual ReproductionDocument32 pagesAsexual Sexual ReproductionReymart VillapeñaNo ratings yet
- Pollinator Monitoring for Citizen Scientists: A HandbookFrom EverandPollinator Monitoring for Citizen Scientists: A HandbookNo ratings yet
- Modes of Reproduction in PlantsDocument15 pagesModes of Reproduction in Plantsjudy andrade100% (1)
- Asexual vs. Sexual Reproduction Asexual ReproductionDocument3 pagesAsexual vs. Sexual Reproduction Asexual ReproductionAi LynNo ratings yet
- The Perpetuation of LifeDocument13 pagesThe Perpetuation of LifeJolie BelenNo ratings yet
- Modes of ReproductionDocument4 pagesModes of ReproductionSherilyn ApostolNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument9 pagesBiology ProjectAtharvasheel SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument13 pagesAsexual Reproductionkritishaa8100No ratings yet
- Reproduction: Visit HereDocument5 pagesReproduction: Visit HereSamarth banodiaNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument2 pagesAsexual ReproductionShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument3 pagesAsexual ReproductionmohangeneNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms Reproduce: Reproduction and Its SignificanceDocument3 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduce: Reproduction and Its SignificanceRounak BasuNo ratings yet
- AsexuAL ReproductionDocument21 pagesAsexuAL Reproductionkiller_xd09No ratings yet
- Mode of Reproduction in PlantsDocument3 pagesMode of Reproduction in PlantsBik BokNo ratings yet
- Asexual and Sexual Reproduction (ARA)Document6 pagesAsexual and Sexual Reproduction (ARA)Leonora Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Bio Plant ReproDocument3 pagesBio Plant ReproPriya MalpaniNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Organisms: Hydra and Yeast Chlamydomonas PenicilliumDocument4 pagesReproduction in Organisms: Hydra and Yeast Chlamydomonas PenicilliumRishi Rao ANo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument12 pagesAsexual ReproductionROWELL LEGASNo ratings yet
- Types of Reproductive System 2Document15 pagesTypes of Reproductive System 2cristin ungabNo ratings yet
- Life Science Module 5 Lesson 1 and 2Document69 pagesLife Science Module 5 Lesson 1 and 2Mae AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction - Definition and Examples - Biology Online DictionaryDocument14 pagesAsexual Reproduction - Definition and Examples - Biology Online DictionarysreypichNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument1 pageHow Do Organisms ReproduceRK KreedaNo ratings yet
- How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument4 pagesHow Do Organisms Reproduceamitabnair915No ratings yet
- What Is ReproductionDocument2 pagesWhat Is ReproductionSeptian SitanggangNo ratings yet
- Plants Reproduction: Lesson 7.1Document25 pagesPlants Reproduction: Lesson 7.1Quennie QuiñaNo ratings yet
- VegetativeDocument1 pageVegetativeRaymond LeabresNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproductive SystemsDocument4 pagesPlant Reproductive SystemsFajar HidayantoNo ratings yet
- 8th Guide - Plant Reproduction AsexualDocument3 pages8th Guide - Plant Reproduction AsexualJuanJo ZapataNo ratings yet
- Genbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentDocument9 pagesGenbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentHazel AbitriaNo ratings yet
- Pollination and Reproduction in Crop PlantsDocument66 pagesPollination and Reproduction in Crop PlantsGaurab NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument8 pagesAsexual Reproductionshehzad AhmedNo ratings yet
- Asexual ReproductionDocument2 pagesAsexual ReproductionkiswariazbuttNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction PDFDocument8 pagesAsexual Reproduction PDFLuis IbarrolaNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument10 pagesAsexual Reproduction in PlantsIsmi DahariNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction Differentiation of Plants Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction ParentDocument22 pagesPlant Reproduction Differentiation of Plants Reproduction Sexual Reproduction Asexual Reproduction ParentNix TanNo ratings yet
- Asexual and Sexual Reproduction of Plants PDFDocument18 pagesAsexual and Sexual Reproduction of Plants PDFCatherine Mistiola100% (1)
- Asexual Reproduction: Done By: Christy Cho Class: 3business Date: October 25, 2018Document8 pagesAsexual Reproduction: Done By: Christy Cho Class: 3business Date: October 25, 2018Kristy ChoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Notes XDocument16 pagesReproduction Notes XAarnav JainNo ratings yet
- Summary of All Topics and DiscussionDocument55 pagesSummary of All Topics and Discussionjason balmasNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Spectrum SquareDocument15 pagesReproduction Spectrum SquareAgastya SharmaNo ratings yet
- CH8 Science Notes ReproductionDocument22 pagesCH8 Science Notes ReproductionShaurya MiglaniNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants Notes Mode of Reproduction:: Reproduction Is The Process by Which A Parent Creates OffspringDocument5 pagesReproduction in Plants Notes Mode of Reproduction:: Reproduction Is The Process by Which A Parent Creates OffspringblistedxNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument10 pagesREPRODUCTIONRuth ViernesNo ratings yet
- Thebiologyprimer Com Plant Reproduction - Text Plant 20reproduction 20is 20the 20production Unique 20from 20the 20parent 20plantsDocument4 pagesThebiologyprimer Com Plant Reproduction - Text Plant 20reproduction 20is 20the 20production Unique 20from 20the 20parent 20plantsJayce JaxNo ratings yet
- Plant ReproductionDocument8 pagesPlant ReproductionayanurhidayahNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2Document33 pagesGen Bio 2Rick RhomanNo ratings yet
- Modes of ReproductionDocument5 pagesModes of ReproductionSandeep638No ratings yet
- Repro B21Document33 pagesRepro B21SeptiNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument40 pagesPerpetuation of LifeDionne MagnoNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Plants and AnimalsDocument3 pagesReproduction in Plants and AnimalsJasvinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Asexual Vs Sexual Reproduction FEB 8 12Document33 pagesAsexual Vs Sexual Reproduction FEB 8 12Ysabelle Bea ManaguelodNo ratings yet
- ApomixisDocument3 pagesApomixisPralex Prajapati0% (1)
- Asexual Reproduction: 42.3 Many Plants Can Clone Themselves by Asexual ReproductionDocument1 pageAsexual Reproduction: 42.3 Many Plants Can Clone Themselves by Asexual ReproductionDoni DarimastNo ratings yet
- Pink Lined Illustration Communication Training Talking PresentationDocument14 pagesPink Lined Illustration Communication Training Talking PresentationJimmy Q MadroneroNo ratings yet
- Plant Reproduction Is The Production of New (Offspring) in Plants, Which Can Be Accomplished by SexualDocument3 pagesPlant Reproduction Is The Production of New (Offspring) in Plants, Which Can Be Accomplished by SexualDebbie San PedroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document17 pagesChapter 6sheisbonjing PHNo ratings yet
- A. Abstraction: Sexual ReproductionDocument5 pagesA. Abstraction: Sexual ReproductionJoy MagbutongNo ratings yet
- Organismal BiologyDocument3 pagesOrganismal BiologyOtot DaNo ratings yet
- EDU143 Research 2Document4 pagesEDU143 Research 2Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Edu143 Pset 5Document4 pagesEdu143 Pset 5Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- EDU143 Research 7Document3 pagesEDU143 Research 7Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- EDU143 Soultions 7Document6 pagesEDU143 Soultions 7Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- EDU143 Lecture Notes 1Document4 pagesEDU143 Lecture Notes 1Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- EDU143 Cheat Sheet 9Document6 pagesEDU143 Cheat Sheet 9Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- EDU143 Demonstration 10Document4 pagesEDU143 Demonstration 10Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- EDU143 Handout 7Document2 pagesEDU143 Handout 7Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- EDU143 Soultions 7Document3 pagesEDU143 Soultions 7Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- EDU143 Group Assignment 8Document7 pagesEDU143 Group Assignment 8Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Justify The StatementDocument1 pageJustify The StatementHera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Is A Process by Which One Organism Produces OffspringsDocument2 pagesReproduction Is A Process by Which One Organism Produces OffspringsHera ElykaNo ratings yet
- What Is DNA? Discovery Diagram DNA Structure Chargaff's Rule DNA Replication Function of DNA Why DNA Is Called A Polynucleotide Molecule?Document5 pagesWhat Is DNA? Discovery Diagram DNA Structure Chargaff's Rule DNA Replication Function of DNA Why DNA Is Called A Polynucleotide Molecule?Hera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Apoptosis and NecrosisDocument2 pagesDifference Between Apoptosis and NecrosisHera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Vegetative PropagationDocument4 pagesVegetative PropagationHera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Asexual Reproduction DefinitionDocument3 pagesAsexual Reproduction DefinitionHera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Parthenogenesis Is The Type of Asexual Reproduction Involving The Development of Female Gametes Without Any FertilizationDocument3 pagesParthenogenesis Is The Type of Asexual Reproduction Involving The Development of Female Gametes Without Any FertilizationHera ElykaNo ratings yet
- Apoptosis DefinitionDocument3 pagesApoptosis DefinitionHera ElykaNo ratings yet
- DNA PackagingDocument4 pagesDNA PackagingHera ElykaNo ratings yet