Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lewis structures and shapes of molecules
Uploaded by
oh khang chiangOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lewis structures and shapes of molecules
Uploaded by
oh khang chiangCopyright:
Available Formats
Tutorial (Shapes of molecules)
1. Draw a Lewis structure for a hydronium ion. Indicate with arrows the different
dipoles present in the ion. Is a hydronium ion polar or non-polar? Explain
briefly. (4 marks)
A hydronium ion is polar because the electrons is pulled towards the
central oxygen atom and the molecule has as trigonal pyramidal shape
Furthermore, the molecules has a net positive charge, increasing its
polarity
2. Nitric acid (HNO3) is mainly used in the production of fertilizers but also has
application in other important areas such as the production of explosives,
purification and extraction of gold, and in chemical synthesis. (7 marks)
a) Draw the Lewis structure of a molecule of nitric acid, HNO3.
b) Describe the electron geometry and shape of the molecule around the
nitrogen atom.
c) What would be the values of the ONO bond angles for this molecule if
they had their “ideal” values.
d) Indicate which of the bond angles are larger or smaller than the ideal
values.
a)
b) Trigonal planar electron geometry and trigonal planar molecular shape
c) 120°
d)
Larger bond angle
Smaller bond angle
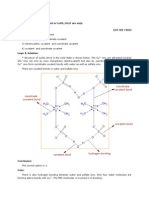
3. Catechin is a common polyphenolic compounds in many plant including tea
(Camellia sinensis). The catechin molecule is made up of three rings as shown
below:
What are the molecular shapes of carbon atoms on the A, B and C ring? What
is the molecular shape of the different oxygen atoms? (4 marks)
A ring: Trigonal planar
B ring: Trigonal planar
C ring: Tetraheral
Oxygen atoms: Bent
4. What is the electron geometry and shape of a molecule with one lone pair and
four bonds? (2 marks)
Electron geometry: Trigonal bipyramidal
Molecular shape: Seesaw shape
5. What is the electron geometry and shape of a molecule with two lone pairs and
two bonds? (2 marks)
Electron geometry: Tetrahedral
Molecular shape: Bent
6. What is the electron geometry and shape of a molecule with one lone pair and
three bonds? (2 marks)
Electron geometry: Tetrahedral
Molecular shape: Trigonal pyramidal
7. Calculate the formal charges for the atoms in both structures and determine the
more prevalent structure: (5 marks)
Formal charge of atom
= No. of valence electrons − (no. of unshared valence electrons
+ ½ no. of shared valence electrons)
You might also like
- Chemical Bonding McqsDocument6 pagesChemical Bonding McqsSumera SarwarNo ratings yet
- Ch-09-Molecular Geometry and Bonding TheoriesDocument104 pagesCh-09-Molecular Geometry and Bonding TheoriesTrọng NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IB CHEMISTRY EXAM REVISION GUIDEDocument19 pagesIB CHEMISTRY EXAM REVISION GUIDEVaida MatulevičiūtėNo ratings yet
- Chemistry HistoryDocument8 pagesChemistry HistorykylianNo ratings yet
- Bulk and Suspenshion Polynerization of MMA Into PMMADocument5 pagesBulk and Suspenshion Polynerization of MMA Into PMMADavid Meza CarbajalNo ratings yet
- Kerboodle StuffDocument4 pagesKerboodle StuffRoshNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Crystalline SolidDocument32 pagesThe Structure of Crystalline SolidRakesh Lingayat100% (2)
- CMC Guidelines On Hazardous Chemicals SpillsDocument8 pagesCMC Guidelines On Hazardous Chemicals Spillskhairul danialNo ratings yet
- Material Balance LNGDocument6 pagesMaterial Balance LNGMichael Robert Gatdula SamarNo ratings yet
- Comparision of AZF Jacobs TechnologyDocument23 pagesComparision of AZF Jacobs Technologyসাইদুর রহমানNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument29 pagesChapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryNabindra RuwaliNo ratings yet
- S1 Gchem Practical Shapes of MoleculesDocument8 pagesS1 Gchem Practical Shapes of MoleculesNorhadi MohamadNo ratings yet
- Molecular Shapes - SiCl4, BF3, NF3 shapes and bond anglesDocument1 pageMolecular Shapes - SiCl4, BF3, NF3 shapes and bond anglesDaneilla BanksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 11e FinalDocument26 pagesChapter 10 11e Finalmaniz442No ratings yet
- Molecular Geometry - TuesdayDocument45 pagesMolecular Geometry - TuesdayJela AlmonedaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3_Chemical Bonding_ExercisesDocument6 pagesChapter 3_Chemical Bonding_Exercisesphat.nguyendothinhNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Basics and PrinciplesDocument93 pagesOrganic Chemistry Basics and PrinciplesJOHN MVULA IINo ratings yet
- Predicting The Shapes of MoleculesDocument3 pagesPredicting The Shapes of Moleculestommy jimmyNo ratings yet
- Shapes of inorganic molecules explainedDocument23 pagesShapes of inorganic molecules explainedM Shafiq MalikNo ratings yet
- LG 1.1 Hybridization of Carbon and Related Physical PropertiesDocument10 pagesLG 1.1 Hybridization of Carbon and Related Physical PropertieswangmorisNo ratings yet
- INVESTIGORY PROJECTDocument10 pagesINVESTIGORY PROJECTAneek ChakrovartyNo ratings yet
- And Lue ISBN Test BankDocument59 pagesAnd Lue ISBN Test Bankrobert100% (20)
- Chemistry 11th Edition Chang Test BankDocument24 pagesChemistry 11th Edition Chang Test Banklaeliavanfyyqz100% (29)
- Ebook Chemistry 11Th Edition Chang Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument45 pagesEbook Chemistry 11Th Edition Chang Test Bank Full Chapter PDFricinussquabash.46iz9100% (11)
- Molecular Modeling: Isomers, Conformers and StereoisomersDocument17 pagesMolecular Modeling: Isomers, Conformers and StereoisomersGoh Chun KitNo ratings yet
- Practicetopic 4 Paper 1Document10 pagesPracticetopic 4 Paper 1api-312595005No ratings yet
- Chapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument29 pagesChapter 14 - An Introduction To Organic ChemistrySahana KumarNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Biological Science 6th Edition by Freeman Quillin Allison Black Taylor Podgorski Carmichae ISBN 9780321976499 0321976495Document36 pagesSolution Manual For Biological Science 6th Edition by Freeman Quillin Allison Black Taylor Podgorski Carmichae ISBN 9780321976499 0321976495jamesgomezsiztcgnawm100% (21)
- Chem Imp Quest Class 10Document3 pagesChem Imp Quest Class 10Udya KrishnaNo ratings yet
- SMost Repeated Questions of Carbon and It's CompundDocument7 pagesSMost Repeated Questions of Carbon and It's Compundanshchauhan012345No ratings yet
- General Chemistry I - Tutorials 6 and 7Document10 pagesGeneral Chemistry I - Tutorials 6 and 7Duc Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
- 11th Class Chemistry Chapter 12 Study MaterialDocument49 pages11th Class Chemistry Chapter 12 Study MaterialAyushi ShahNo ratings yet
- Neet Chemistry Notes-1Document37 pagesNeet Chemistry Notes-1Abhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Fuel MoleculesDocument3 pagesFuel MoleculesPhillip CookNo ratings yet
- (Trans) Chem 33 1 NomenclatureDocument63 pages(Trans) Chem 33 1 NomenclatureALongNo ratings yet
- Biology How Life Works 2nd Edition Morris Test BankDocument59 pagesBiology How Life Works 2nd Edition Morris Test Bankkevinbeltranbztxrjdfsy100% (15)
- VSEPR Molecular ShapesDocument7 pagesVSEPR Molecular ShapesIrynaNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper ChemistryDocument7 pagesExam Paper ChemistryalyssatapouhNo ratings yet
- 1.10203 Tutorial 1Document2 pages1.10203 Tutorial 1McAdam TULAPINo ratings yet
- Key Facts about Noble Gases and Their UsesDocument87 pagesKey Facts about Noble Gases and Their UsesNicholas ChenNo ratings yet
- UW CHEM 5100 Homework SolutionDocument11 pagesUW CHEM 5100 Homework Solutionibrahim6muddasserNo ratings yet
- Chemical-Bond NoteDocument9 pagesChemical-Bond NoteDixit GautamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 PDFDocument18 pagesChapter 10 PDFJeong100% (1)
- Hsslive-9. Co-ordination compoundsDocument8 pagesHsslive-9. Co-ordination compoundssindhumv631No ratings yet
- Chem Lec Module 6 Organic Chem NotesDocument7 pagesChem Lec Module 6 Organic Chem NotesPinuela, Kristine AngeliqueNo ratings yet
- Bonding and Molecular Structure ActivityDocument3 pagesBonding and Molecular Structure ActivityMarichu VelascoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 WorksheetsDocument18 pagesChapter 9 WorksheetsShaEshaa100% (1)
- Yasemin Celik Chapter3 2022-2023 Part1Document19 pagesYasemin Celik Chapter3 2022-2023 Part1bastezalteNo ratings yet
- CH 9Document11 pagesCH 9Roxanne Mae VillacoraNo ratings yet
- 4 Chemical BondingDocument63 pages4 Chemical BondingArvin LiangdyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5Document30 pagesLecture 5Md Al AminNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Text Book 111CHEMDocument74 pagesOrganic Chemistry Text Book 111CHEMyyoosafe23No ratings yet
- Biology How Life Works 2nd Edition Morris Test BankDocument58 pagesBiology How Life Works 2nd Edition Morris Test Bankamandablevinsqakymroeiw100% (50)
- SECTION A (15 Marks) Answer ALL Questions in This SectionDocument15 pagesSECTION A (15 Marks) Answer ALL Questions in This SectionFazliawati MahayuddinNo ratings yet
- Q2 M4 General-Chemistry-1 - Geometry-Of-MoleculesDocument16 pagesQ2 M4 General-Chemistry-1 - Geometry-Of-MoleculesElysha Mae RamirezNo ratings yet
- Theories of Bonding in Coordination CompoundsDocument7 pagesTheories of Bonding in Coordination CompoundsDhanush KumarNo ratings yet
- Exp 02 How The Nose Knows - Prelab Bonding HandoutDocument9 pagesExp 02 How The Nose Knows - Prelab Bonding HandoutVanessa WongNo ratings yet
- Class X Chemical BondingDocument4 pagesClass X Chemical BondingvartikasinghNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Organic ChemistryDocument147 pagesIntroduction To Organic ChemistryOrianna SanoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - 4Document5 pagesChapter 3 - 4Sureshkumar DevanNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry Bonding Help Sheet: 2, (Diamond)Document6 pagesAP Chemistry Bonding Help Sheet: 2, (Diamond)Weiyu TongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 QuizDocument2 pagesChapter 1 Quizoh khang chiangNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Structure and Bonding) AnswersDocument3 pagesTutorial (Structure and Bonding) Answersoh khang chiangNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Kinetics) AnswersDocument4 pagesTutorial (Kinetics) Answersoh khang chiangNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry Tutorial on Chiral Carbons, Enantiomers, Diastereomers and Fischer ProjectionsDocument3 pagesStereochemistry Tutorial on Chiral Carbons, Enantiomers, Diastereomers and Fischer Projectionsoh khang chiangNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Organic) AnswersDocument5 pagesTutorial (Organic) Answersoh khang chiangNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Carbohydrate) AnswersDocument3 pagesTutorial (Carbohydrate) Answersoh khang chiangNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Equlibrium) AnswersDocument4 pagesTutorial (Equlibrium) Answersoh khang chiangNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Biomolecules) AnswersDocument2 pagesTutorial (Biomolecules) Answersoh khang chiangNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Atomic Nature) AnswersDocument3 pagesTutorial (Atomic Nature) Answersoh khang chiangNo ratings yet
- Physics XII Chapter# 12 Practice SheetDocument4 pagesPhysics XII Chapter# 12 Practice SheetGhulam NabiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Chemical Bond Stability of Noble GasesDocument20 pagesChapter 5: Chemical Bond Stability of Noble GasesLuna LatisyaNo ratings yet
- 2020.09.24 OLV & MSV Lead Piping DiscussionDocument11 pages2020.09.24 OLV & MSV Lead Piping DiscussionAswindana Ibnu SenaNo ratings yet
- Cycle-III Expt 9 ESR - Lande G FactorDocument6 pagesCycle-III Expt 9 ESR - Lande G FactorSwapnil BabeleNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing of Acrylonitrile Internship ReportDocument33 pagesManufacturing of Acrylonitrile Internship ReportHirenNo ratings yet
- (Topics in Chemical Engineering) Martyn S. Ray, David W. Johnston - Chemical Engineering Design Project - A Case Study Approach Topics in Chemical Engineering - Volume 6-Routledge (1989)Document2 pages(Topics in Chemical Engineering) Martyn S. Ray, David W. Johnston - Chemical Engineering Design Project - A Case Study Approach Topics in Chemical Engineering - Volume 6-Routledge (1989)Pratiwi Puji Ajeng LestariNo ratings yet
- Us3479310 PDFDocument7 pagesUs3479310 PDFKhoi Nguyen DangNo ratings yet
- Catalog Metal RotameterDocument12 pagesCatalog Metal RotameterNibinNo ratings yet
- Question BankDocument4 pagesQuestion BankNagaraj PeriasamyNo ratings yet
- Sizing and Design of Utilities For Chemical ProcessDocument13 pagesSizing and Design of Utilities For Chemical Processpavanchem610% (1)
- Geohellas Aglevsi300 Tds 1.87.3 4Document1 pageGeohellas Aglevsi300 Tds 1.87.3 4aliNo ratings yet
- 5061 10023 1 SMDocument7 pages5061 10023 1 SMNadya Rahmawati PutriNo ratings yet
- Improving Separation of Basic Compounds by Reversed-Phase HPLC Using Chaotropic AgentsDocument7 pagesImproving Separation of Basic Compounds by Reversed-Phase HPLC Using Chaotropic AgentsKriti TyagiNo ratings yet
- Colleen Samantha Dioquino, Christopher Jay RobidilloDocument5 pagesColleen Samantha Dioquino, Christopher Jay RobidilloLohith HRNo ratings yet
- Data 568320Document1 pageData 568320Waqas AhmadNo ratings yet
- Anuj AgrawalDocument15 pagesAnuj AgrawalSAVITRI GURJARNo ratings yet
- Parofluor PTD3026 enDocument16 pagesParofluor PTD3026 enVictor Flores ResendizNo ratings yet
- Biology Yearly Lesson Plan Form 4Document4 pagesBiology Yearly Lesson Plan Form 4Hisyam Deraman100% (1)
- Ideal Gas and Rankine CycleDocument12 pagesIdeal Gas and Rankine CycleAkshay A KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Answer Key PDFDocument1 pageChemistry Answer Key PDFMark FuentesNo ratings yet
- C Colours-Merged PDFDocument90 pagesC Colours-Merged PDFvinodhiniNo ratings yet
- Msds Mepoxe MDocument5 pagesMsds Mepoxe MAhmad HidayatNo ratings yet
- Kaise Kbl12550Document2 pagesKaise Kbl12550Seba LopezNo ratings yet