Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Polygons and Perimeter
Uploaded by
Nicholas Yates100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
1K views2 pagesclass worksheet on perimeter and polygons
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentclass worksheet on perimeter and polygons
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
100%(2)100% found this document useful (2 votes)
1K views2 pagesPolygons and Perimeter
Uploaded by
Nicholas Yatesclass worksheet on perimeter and polygons
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
Polygons & Perimeter
PERIMETER = distance around = add up the distance
along each side
POLYGON = “many-angles” = closed 2-dimensional
shape with line segment edges
From wikipedia tetradecagon (or tetrakaidecagon) 14
( http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Polygon ): pentadecagon (or quindecagon or 15
Polygon names pentakaidecagon)
Name Edges hexadecagon (or hexakaidecagon) 16
henagon (or monogon) 1 heptadecagon (or heptakaidecagon) 17
digon 2 octadecagon (or octakaidecagon) 18
triangle (or trigon) 3 enneadecagon (or enneakaidecagon
19
quadrilateral (or tetragon) 4 or nonadecagon)
pentagon 5 icosagon 20
hexagon 6 No established English name
heptagon (avoid "septagon" = Latin
7
[sept-] + Greek) "hectogon" is the Greek name (see
100
octagon 8 hectometre),
enneagon (or nonagon) 9 "centagon" is a Latin-Greek hybrid;
decagon 10 neither is widely attested.
hendecagon (avoid "undecagon" = chiliagon 1000
11 myriagon 10,000
Latin [un-] + Greek)
dodecagon (avoid "duodecagon" = googolgon 10100
12
Latin [duo-] + Greek)
tridecagon (or triskaidecagon) 13 For large numbers, mathematicians usually
write the numeral itself, e.g. 17-gon.
Classwork
Instructions: Example:
Inside each figure write the number of
sides. Write its name underneath the Perimeter
polygon. Measure its perimeter in 4 1/16 = 4.0625 in
inches, in centimeters, then divide the 11 cm
two (cm ÷ in), and write these three
numbers to the figure’s side. 11 ÷ 4.0625 = 2.71
pentagon
GEOMETRY Mr. Yates Name __________________
Polygons & Perimeters Date _______ Pd _________
You might also like
- 11 Plus Maths RevisionDocument12 pages11 Plus Maths RevisionKhasim100% (3)
- Primary Progression Test - Stage 6 Math Paper 1Document14 pagesPrimary Progression Test - Stage 6 Math Paper 1Erwin Manuzon100% (19)
- Geocity Project Guidelines and RubricDocument3 pagesGeocity Project Guidelines and Rubricapi-111745026100% (1)
- Solid Mensuration Understanding The 3d Space Richard T EarnhartDocument142 pagesSolid Mensuration Understanding The 3d Space Richard T EarnhartKevs SebastianNo ratings yet
- Polygon NamesDocument4 pagesPolygon NamesSAGGITARIUS155No ratings yet
- Plane GeometryDocument24 pagesPlane GeometryEurydiceNo ratings yet
- PolygonsDocument13 pagesPolygonsMs. 37o?sANo ratings yet
- Geometric Shapes and Polygons ExplainedDocument67 pagesGeometric Shapes and Polygons ExplainedJoshua SumillaNo ratings yet
- Polygon Names and Shapes ExplainedDocument2 pagesPolygon Names and Shapes ExplainedPanneer SelvamNo ratings yet
- Types of Polygons: VertexDocument3 pagesTypes of Polygons: VertexRichard TorzarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document25 pagesChapter 2RITCHIE LOU CAGULADANo ratings yet
- CEP SOLID MENSURATION GUIDEDocument26 pagesCEP SOLID MENSURATION GUIDE김나연No ratings yet
- Solid GeometryDocument10 pagesSolid GeometryMark AlvaradoNo ratings yet
- Composite Figures Area and PerimeterDocument18 pagesComposite Figures Area and PerimeterJohn Nikko NicolasNo ratings yet
- L1 Fsolimon PolygonDocument22 pagesL1 Fsolimon Polygonkylegamoso09No ratings yet
- Types of Polygons ChartDocument2 pagesTypes of Polygons ChartJaireNo ratings yet
- Types of PolygonsDocument3 pagesTypes of Polygonsanon-919823100% (9)
- Lesson 2.1 Polygons-Concepts and ApplicationsDocument12 pagesLesson 2.1 Polygons-Concepts and ApplicationsAllan Gabriel LariosaNo ratings yet
- 131431196.H_Polygons_CANDocument46 pages131431196.H_Polygons_CANMaha HumayuneNo ratings yet
- NotesDocument14 pagesNotesKakarotWrldNo ratings yet
- 2D Shapes 3D Shapes: Sides/Faces 2D 3D Example (2D)Document3 pages2D Shapes 3D Shapes: Sides/Faces 2D 3D Example (2D)josephdmeltzer100% (3)
- Name That PolygonDocument6 pagesName That PolygonKuo Garol SarongNo ratings yet
- Learn Key Concepts About Polygons, Tessellations, and Area CalculationsDocument29 pagesLearn Key Concepts About Polygons, Tessellations, and Area CalculationsJohnNo ratings yet
- PolygonDocument2 pagesPolygonJan Maverick TagayongNo ratings yet
- PolygonsDocument23 pagesPolygonsMary Ann TimbalNo ratings yet
- 1ro Sec PPT PoligonosDocument18 pages1ro Sec PPT PoligonosEnrique Espino MaravíNo ratings yet
- Polygon Geometry GuideDocument70 pagesPolygon Geometry GuideAaliyah Jean BelenNo ratings yet
- Geom 8-1Document16 pagesGeom 8-1Ahmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- Project in Mathematics on Properties and Types of QuadrilateralsDocument17 pagesProject in Mathematics on Properties and Types of QuadrilateralsRiz Dadole-GeocadinNo ratings yet
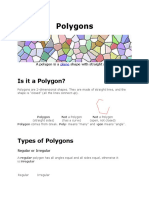
- Polygons: Is It A Polygon?Document7 pagesPolygons: Is It A Polygon?Nilo ValeraNo ratings yet
- Understanding Polygons: Types, Properties, Formulas & MoreDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Polygons: Types, Properties, Formulas & Moregodesus mlNo ratings yet
- Diagonals in Polygons: Number of Diagonals FormulaDocument5 pagesDiagonals in Polygons: Number of Diagonals Formulaगुंजन सिन्हाNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Class 9Document7 pagesEngineering Drawing Class 9GopiKrishnaValireddyNo ratings yet
- Geometry Chapter 7 - Sections 7.1 and 7.2Document2 pagesGeometry Chapter 7 - Sections 7.1 and 7.2Arthur Braga100% (2)
- POLYGONSDocument7 pagesPOLYGONSLuna LedezmaNo ratings yet
- PolygonDocument11 pagesPolygonMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Quiz Solutions With ExplanationDocument23 pagesMath 10 Quiz Solutions With ExplanationBree ElaineNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras MathaleticsDocument36 pagesPythagoras MathaleticsSri Rama100% (5)
- Multiplication - WikipediaDocument22 pagesMultiplication - WikipediaResearch factNo ratings yet
- GE4 - 3506 - Lets AnalyzeDocument4 pagesGE4 - 3506 - Lets AnalyzeKimmy Stix100% (2)
- List of Polygon Shapes Shape Description IllustrationDocument4 pagesList of Polygon Shapes Shape Description IllustrationChelle CabisonNo ratings yet
- ML Geometry 6-1 PolygonsDocument7 pagesML Geometry 6-1 Polygonsmadhuraju778797No ratings yet
- Athematics OR Ngineers: Plate #2Document9 pagesAthematics OR Ngineers: Plate #2Stevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 ULO 1 Wk2 AUSA 2Document5 pagesActivity 1 ULO 1 Wk2 AUSA 2renato tuballaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Theory With ExamplesDocument58 pagesTrigonometry Theory With Examplessushil tripathiNo ratings yet
- Important Fact #1: The Pythagorean Theorem Is True!Document9 pagesImportant Fact #1: The Pythagorean Theorem Is True!Nadzirah SofiaNo ratings yet
- 8-2 Skills Practice: The Pythagorean Theorem and Its ConverseDocument1 page8-2 Skills Practice: The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Conversefatima alarfajNo ratings yet
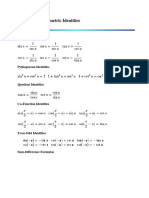
- Trig Identities Cheat SheetDocument15 pagesTrig Identities Cheat SheetEdward EceincoNo ratings yet
- 2015 Calculus Exam 2Document9 pages2015 Calculus Exam 2lllloNo ratings yet
- Names of Polygons from 3 to 999 SidesDocument2 pagesNames of Polygons from 3 to 999 SidesPhil Wilsons MorenoNo ratings yet
- Graphs of Trigonometric FunctionsDocument21 pagesGraphs of Trigonometric FunctionshozipekNo ratings yet
- Pythagoras' Theorem: Learn How to Calculate Sides of Right TrianglesDocument7 pagesPythagoras' Theorem: Learn How to Calculate Sides of Right TrianglesTalha AzanNo ratings yet
- Number:: One Two Three Four Five Six Seven Eight Nine TenDocument5 pagesNumber:: One Two Three Four Five Six Seven Eight Nine TenIndah Chairun AnnisaNo ratings yet
- Polygons Form 3Document45 pagesPolygons Form 3Ateef HatifaNo ratings yet
- Statics 1Document1 pageStatics 1Sheena Abegail LaderaNo ratings yet
- Trig Functions Acute Angles PPDocument6 pagesTrig Functions Acute Angles PPCarmela UrsuaNo ratings yet
- Final Revision 9 C.WDocument3 pagesFinal Revision 9 C.Womarnadermohamedkhairy19No ratings yet
- Lesson 5 PolygonsDocument21 pagesLesson 5 PolygonsAr Jay David100% (1)
- GCSE Mathematics Numerical Crosswords Higher Tier Written for the GCSE 9-1 CourseFrom EverandGCSE Mathematics Numerical Crosswords Higher Tier Written for the GCSE 9-1 CourseNo ratings yet
- Encyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 16, Slice 8 "Logarithm" to "Lord Advocate"From EverandEncyclopaedia Britannica, 11th Edition, Volume 16, Slice 8 "Logarithm" to "Lord Advocate"No ratings yet
- Gini Index Student HandoutDocument8 pagesGini Index Student HandoutNicholas Yates100% (1)
- Phi ProjectDocument4 pagesPhi ProjectNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2T4QuizP3 6 7 8 9Document3 pagesA2T4QuizP3 6 7 8 9Nicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2TQuizP1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6Document2 pagesA2TQuizP1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6Nicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- Green Eggs & Catch: The RulesDocument4 pagesGreen Eggs & Catch: The RulesNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2TQuiz9 10 11 12 13 15 16 17 A2 A3 A4 A5Document4 pagesA2TQuiz9 10 11 12 13 15 16 17 A2 A3 A4 A5Nicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- Big Picture Ideas in A2TDocument1 pageBig Picture Ideas in A2TNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- STEM AnnualChallenge2011Document4 pagesSTEM AnnualChallenge2011Nicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- Bridge GeometryDocument1 pageBridge GeometryNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2T4QuizP5 P6 1 2 A1Document3 pagesA2T4QuizP5 P6 1 2 A1Nicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2TQuizP3 P5 1 2 3 5 6 A1Document2 pagesA2TQuizP3 P5 1 2 3 5 6 A1Nicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- Mr. Yates: 270° Coordinates: (,) 105° Coordinates: (,) A Graph: B GraphDocument3 pagesMr. Yates: 270° Coordinates: (,) 105° Coordinates: (,) A Graph: B GraphNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2TQuiz7 8 9 10 11 12Document2 pagesA2TQuiz7 8 9 10 11 12Nicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2TQuizP1 P2 3 4 5 6Document2 pagesA2TQuizP1 P2 3 4 5 6Nicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2T4QuizP1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6Document3 pagesA2T4QuizP1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6Nicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2T Final Exam 11 FormulaeDocument2 pagesA2T Final Exam 11 FormulaeNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- Mr. Yates: Lgebra With RigonometryDocument3 pagesMr. Yates: Lgebra With RigonometryNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2TQuiz7 8 9 10 11 12Document2 pagesA2TQuiz7 8 9 10 11 12Nicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- Mr. Yates: Lgebra With RigonometryDocument3 pagesMr. Yates: Lgebra With RigonometryNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2T4Quiz1 2 3 4 5Document3 pagesA2T4Quiz1 2 3 4 5Nicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2TSkillsHandout SkillsGradingDocument2 pagesA2TSkillsHandout SkillsGradingNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2T4MiniQuiz10 11Document1 pageA2T4MiniQuiz10 11Nicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2TSkillsHandout Algebra P+ADocument1 pageA2TSkillsHandout Algebra P+ANicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 With Trigonometry SyllabusDocument3 pagesAlgebra 2 With Trigonometry SyllabusNicholas Yates0% (1)
- A2TSkillsHandout Analysis P+ADocument1 pageA2TSkillsHandout Analysis P+ANicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- POE FMP The Paper Tower BlankDocument1 pagePOE FMP The Paper Tower BlankNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2TSkillsHandout AllDocument4 pagesA2TSkillsHandout AllNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2TSkillsHandout Analysis CoreDocument1 pageA2TSkillsHandout Analysis CoreNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- A2TSkillsHandout Algebra CoreDocument1 pageA2TSkillsHandout Algebra CoreNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- WindmillDocument1 pageWindmillNicholas YatesNo ratings yet
- Calculate the area of composite shapesDocument6 pagesCalculate the area of composite shapesAbhinav SinghNo ratings yet
- Guidelines for solving projection of planes problemsDocument2 pagesGuidelines for solving projection of planes problemsreddy rajaNo ratings yet
- Licensure For LET Major in MathDocument91 pagesLicensure For LET Major in MathNilo ValeraNo ratings yet
- 11 Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines Solutions: Q P P Q P 6Document3 pages11 Coordinate Geometry of Straight Lines Solutions: Q P P Q P 6(4C27) Wong Ching Tung, Zoey 20181D043spss.hkNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry TestDocument2 pagesTrigonometry TestJeff BuenoNo ratings yet
- Exercise Solution of Coordinate Geometry WatermarkedDocument33 pagesExercise Solution of Coordinate Geometry WatermarkediTutor Classes BapiNo ratings yet
- How To Create A NUT Using CATIADocument15 pagesHow To Create A NUT Using CATIASuresh Sheel100% (1)
- Unit NDocument34 pagesUnit NASHOK SINHA KARANAMNo ratings yet
- Areas Related To CirclesDocument33 pagesAreas Related To CirclesDkuaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Geometric Construction New - ppt1Document29 pagesChapter 2 Geometric Construction New - ppt1NSBMRNo ratings yet
- Preview Qadi 2Document8 pagesPreview Qadi 2api-238188038No ratings yet
- Perimeter and Area: Exercise 11.1Document30 pagesPerimeter and Area: Exercise 11.1Pravat TiadiNo ratings yet
- ISMC 2016 Primary 4 Answer SheetDocument2 pagesISMC 2016 Primary 4 Answer SheetAileen MimeryNo ratings yet
- GTM Special Meeting NotesDocument12 pagesGTM Special Meeting NotesbhartiyaanujNo ratings yet
- S Puiching01 f3Document7 pagesS Puiching01 f3Llosemi LsNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Vii Ya QPDocument2 pagesMathematics Vii Ya QPTechnetNo ratings yet
- Identifying Triangles by SidesDocument2 pagesIdentifying Triangles by SidesJames KeruNo ratings yet
- Maths Workbook 8 SolutionsDocument57 pagesMaths Workbook 8 SolutionsHassan Alsharqawi100% (1)
- Section of Solids PDFDocument56 pagesSection of Solids PDFpadmanabanNo ratings yet
- Final - Math 9 - Q3 - Module 3Document10 pagesFinal - Math 9 - Q3 - Module 3Yeoj ParasNo ratings yet
- Math 4th QuarterDocument129 pagesMath 4th QuarterJannahNo ratings yet
- Integrative Course QuizDocument2 pagesIntegrative Course QuizAndrei AlidoNo ratings yet
- Graphics Notes 3Document200 pagesGraphics Notes 3m.No ratings yet
- Diagnostic Test in Mathematics IVDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Test in Mathematics IVFlorecita CabañogNo ratings yet
- The Construction of Equations: Introductio in Analysin Infinitorum Vol. 2Document31 pagesThe Construction of Equations: Introductio in Analysin Infinitorum Vol. 2david.contatos4308No ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing by Sakthi PDFDocument238 pagesEngineering Drawing by Sakthi PDFSakthi RoyalhunterNo ratings yet
- Smith KJ Student Mathematics Handbook and Integral Table ForDocument328 pagesSmith KJ Student Mathematics Handbook and Integral Table ForStrahinja DonicNo ratings yet
- Geometry - Olympiad Material BY DR SHYAM SUNDAR AGRAWALDocument67 pagesGeometry - Olympiad Material BY DR SHYAM SUNDAR AGRAWALdrssagrawalNo ratings yet