Professional Documents
Culture Documents
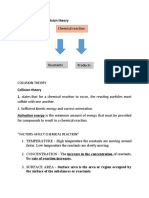
Factors Affecting Chemical Reaction Rates
Uploaded by
Frank SobelOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Factors Affecting Chemical Reaction Rates
Uploaded by
Frank SobelCopyright:
Available Formats
Kinetics
Thermodynamics often can be used to predict whether a reaction will occur spontaneously,
but it gives very little information about the speed at which a reaction occurs
Kinetics is the study of the speed of reactions and is largely an experimental science
Some general qualitative ideas about reaction speed may be developed, but accurate
quantitative relationships require experimental data to be collected
For a chemical reaction to occur, there must be a collision between the reactant particles.
o That collision is necessary to transfer kinetic energy, to break reactant chemical bonds
and form new bonds in the product
o If the collision doesn’t transfer enough energy, no reaction will occur. And the collision
must take place with the proper orientation at the correct place on the molecule, the
reactive site
Five factors affect the rates of a chemical reaction:
1. Nature of the reactants—Large, complex molecules tend to react more slowly than smaller
ones because statistically there is a greater chance of collisions occurring in the wrong place on
the molecule, that is, not at the reactive site
2. The temperature—Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules.
The higher the temperature, the higher the kinetic energy and the greater the chance that
enough energy will be transferred to cause the reaction. Also, the higher the temperature, the
greater the number of collisions and the greater the chance of a collision at the reactive site
3. The concentration of reactants—The higher the concentration of reactants, the greater
the chance of collision and (normally) the greater the reaction rate. For gaseous reactants, the
pressure is directly related to the concentration; the greater the pressure, the greater the reaction
rate
4. Physical state of reactants—When reactants are mixed in the same physical state, the
reaction rates should be higher than if they are in different states, because there is a greater
chance of collision. Also, gases and liquids tend to react faster than solids because of the
increase in surface area. The more chance for collision, the faster the reaction rate
5. Catalysts—A catalyst is a substance that speeds up the reaction rate and is (at least
theoretically) recoverable at the end of the reaction in an unchanged form. Catalysts
accomplish this by reducing the activation energy of the reaction. Activation energy is that
minimum amount of energy that must be supplied to the reactants in order to initiate or start the
reaction. Many times the activation energy is supplied by the kinetic energy of the reactants
You might also like
- Lesson 3 - Factors Affecting Rate of Reaction and Reactions and Molecular CollisionsDocument5 pagesLesson 3 - Factors Affecting Rate of Reaction and Reactions and Molecular CollisionsJeff ValdezNo ratings yet
- Collssion TheoryDocument3 pagesCollssion TheoryJherby TeodoroNo ratings yet
- CHEMISTRYDocument10 pagesCHEMISTRYlifep7417No ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument23 pagesRate of ReactionVirly vcNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentAnsel MercadejasNo ratings yet
- Rates of Reactions 3 5Document1 pageRates of Reactions 3 5api-272358521No ratings yet
- Physci Simple Collision TheoryDocument34 pagesPhysci Simple Collision TheoryLovely benzelNo ratings yet
- Kinetic NotesDocument1 pageKinetic NotesFrank SobelNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument12 pagesRate of ReactionRobin CabralNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 - Chemical Kinetics - Intro To Theories and Boltzmann CurveDocument37 pagesTopic 4 - Chemical Kinetics - Intro To Theories and Boltzmann CurveJoshua LaBordeNo ratings yet
- Phy Sci StudyDocument2 pagesPhy Sci StudyHans Kirby Pacatang DumdumNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Rate of ReactionDocument6 pagesFactors Affecting Rate of Reactionjohnrey_lidres100% (4)
- Chemical Kinetics & RateDocument2 pagesChemical Kinetics & RateMontassar DridiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction Engineering NotesDocument40 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering Noteskrishnaswamy9No ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Collision Theory and Chemical Reaction RateDocument33 pagesLesson 6 Collision Theory and Chemical Reaction Ratealliah nibayNo ratings yet
- Week 5.1 Collision Theory and The RateDocument31 pagesWeek 5.1 Collision Theory and The RatereneicrizaldoNo ratings yet
- How reaction rates are affected by temperature, concentration, and activation energyDocument4 pagesHow reaction rates are affected by temperature, concentration, and activation energypieNo ratings yet
- Collision Theory: Teacher DianneDocument24 pagesCollision Theory: Teacher DianneDianne CofinoNo ratings yet
- Unit - The Periodic TableDocument20 pagesUnit - The Periodic TableMaurya AdeshraNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument3 pagesChemical KineticsSunny RohidaNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument8 pagesChemical KineticsHosam Hasan Abd ElhadyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics & Equilibrium: Froilan Aron S. Faraon, R.PHDocument34 pagesChemical Kinetics & Equilibrium: Froilan Aron S. Faraon, R.PHKenneth TrogonNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics ProjectDocument31 pagesChemical Kinetics ProjectArul VNo ratings yet
- Chemical KineticsDocument25 pagesChemical KineticsAngelo PunzalanNo ratings yet
- Physical Scienc1Document4 pagesPhysical Scienc1Edel MarianoNo ratings yet
- Rate of ReactionDocument6 pagesRate of ReactionDavid ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Collisiontheory: Teacherdia NneDocument24 pagesCollisiontheory: Teacherdia NneDianne CofinoNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rate NotesDocument10 pagesReaction Rate NotesvinaybharadwajbsNo ratings yet
- Chem 3Document103 pagesChem 3César ArenasNo ratings yet
- Rates of Reaction: Factors that Affect Chemical Reaction SpeedsDocument30 pagesRates of Reaction: Factors that Affect Chemical Reaction SpeedsΜαρια ΑνδρεοπουλουNo ratings yet
- CollisionDocument30 pagesCollisionKutoo BayNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rate NOTES HandoutDocument1 pageReaction Rate NOTES HandoutHorizon 99No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Project of Class 12thDocument16 pagesChemical Kinetics Project of Class 12thSubham PrajapatNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics Project of Class 12thDocument16 pagesChemical Kinetics Project of Class 12thDhairya Tamori74% (57)
- I. Introductory Concept: SHS-Physical Science (Rates of Chemical Reaction)Document9 pagesI. Introductory Concept: SHS-Physical Science (Rates of Chemical Reaction)Jane182004No ratings yet
- The Collision Theory and Factors Affecting The Rate of Chemical ReactionDocument28 pagesThe Collision Theory and Factors Affecting The Rate of Chemical ReactionRolan Picones BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics: Factors Affecting Reaction RateDocument4 pagesChemical Kinetics: Factors Affecting Reaction RateMontassar DridiNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceeDocument16 pagesPhysical ScienceejerrylinbermudezNo ratings yet
- Gen_-Chem-2-VELASCO-ENCARNACION-part-2Document12 pagesGen_-Chem-2-VELASCO-ENCARNACION-part-2Edreyan Adong Cortez LimbagaNo ratings yet
- CHEMICAL REACTION AND COLLISION (Autosaved)Document23 pagesCHEMICAL REACTION AND COLLISION (Autosaved)FRANKLYN TRONCONo ratings yet
- Kinetics & Equilibrium: Factors Affecting Reaction RatesDocument2 pagesKinetics & Equilibrium: Factors Affecting Reaction Rateslizaaa333No ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics, Reaction Mechanisms, and Equilibrium (CKRMEDocument4 pagesChemical Kinetics, Reaction Mechanisms, and Equilibrium (CKRMEMesfen MeleseNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting The Rate of ReactionDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting The Rate of ReactionMr GaMeR SMNo ratings yet
- As A Result, The Number of Effective Collisions Increases and The Reaction Proceeds at A Faster RateDocument5 pagesAs A Result, The Number of Effective Collisions Increases and The Reaction Proceeds at A Faster RateJulie MatzaNo ratings yet
- Collision TheoryDocument6 pagesCollision Theoryzayra atreroNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chemical Kinetics: Adnan Chowdhury Chemistry TeacherDocument9 pagesUnit 2 Chemical Kinetics: Adnan Chowdhury Chemistry TeacherZulfikarNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 3 - WEEK 4Document13 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 3 - WEEK 4RODEL AZARESNo ratings yet
- The Collision TheoryDocument5 pagesThe Collision TheoryRhea PardiñasNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Rate of ReactionDocument3 pagesFactors Affecting Rate of ReactionKyle BantaNo ratings yet
- 1126pm - 47.epra Journals 5023Document3 pages1126pm - 47.epra Journals 5023No NameNo ratings yet
- Peter J. NassiffDocument11 pagesPeter J. Nassifflary77No ratings yet
- LAS-2-Rate-of-Chemical-ReactionDocument5 pagesLAS-2-Rate-of-Chemical-Reactiondavemorte20No ratings yet
- Information and Communication Technology in Chemistry: Title: Collision Theory (Simulation)Document10 pagesInformation and Communication Technology in Chemistry: Title: Collision Theory (Simulation)z890% (1)
- Chemistry Chapter 17 NotesDocument3 pagesChemistry Chapter 17 NotesMario V LopezNo ratings yet
- Collision Theory and The Factors Affecting The RateDocument17 pagesCollision Theory and The Factors Affecting The RatePeter MorenoNo ratings yet
- Kinetics DR JagadishDocument37 pagesKinetics DR JagadishVikas KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Kinetics (Pt. 1) Introduction and Factors Affecting Reaction RatesDocument13 pagesChemical Kinetics (Pt. 1) Introduction and Factors Affecting Reaction RatesRida akhtarNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Kinetics and Equilibrium with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Reaction Kinetics: Reactions in SolutionFrom EverandReaction Kinetics: Reactions in SolutionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- V5750maintance ManualDocument114 pagesV5750maintance ManualJoe Gozinia100% (2)
- Nota Ringkas KimiaDocument2 pagesNota Ringkas KimiaZulhilmil Zul100% (7)
- Construction and Building Materials: Banana Leaves Ashes As Pozzolan For Concrete and Mortar of Portland CementDocument7 pagesConstruction and Building Materials: Banana Leaves Ashes As Pozzolan For Concrete and Mortar of Portland CementSWAPNILNo ratings yet
- Activities Class VI Month Prepared by RK SinghDocument4 pagesActivities Class VI Month Prepared by RK SinghcuriousnavinNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Report 4 - Colorimetric Titration of VinegarDocument8 pagesChemistry Report 4 - Colorimetric Titration of VinegarsmarakNo ratings yet
- Khaki X-Wind - Instruction ManualDocument98 pagesKhaki X-Wind - Instruction Manualmeor_ayobNo ratings yet
- Gravity Light - Homemade - DIY PDFDocument3 pagesGravity Light - Homemade - DIY PDFvromikoNo ratings yet
- HPLC - GCDocument28 pagesHPLC - GCTayyaba SadaqNo ratings yet
- Acr 1 Final 2021Document5 pagesAcr 1 Final 2021CAROLYN RhoeNo ratings yet
- Open Test Series - Paper-1 - (21-09-2021)Document31 pagesOpen Test Series - Paper-1 - (21-09-2021)Yogesh KhatriNo ratings yet
- PDF Updated Class 11 Physics Formula Sheet CompressDocument22 pagesPDF Updated Class 11 Physics Formula Sheet CompressdrjbjpNo ratings yet
- Masibus 8208 User ManualDocument42 pagesMasibus 8208 User ManualMẫn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Combe and Hartig 2006Document10 pagesCombe and Hartig 2006Komathi MuruganNo ratings yet
- Fatigue Life Estimation of An Engine Rubber Mount: W.D. Kim, H.J. Lee, J.Y. Kim, S.-K. KohDocument8 pagesFatigue Life Estimation of An Engine Rubber Mount: W.D. Kim, H.J. Lee, J.Y. Kim, S.-K. KohhadiNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School, Digboi: Biology Project ON Calculatiion of Human Horse PowerDocument12 pagesDelhi Public School, Digboi: Biology Project ON Calculatiion of Human Horse PowerSakshi GiriNo ratings yet
- Design a sensory center for food industryDocument3 pagesDesign a sensory center for food industryNguyễn ThuNo ratings yet
- Lecture Planner - Maths - Lakshya JEE 2024Document3 pagesLecture Planner - Maths - Lakshya JEE 2024tejinderNo ratings yet
- Sub Module 3.9 Capacitance FinalDocument26 pagesSub Module 3.9 Capacitance FinalInterogator5No ratings yet
- FSTEM, CTD, Philippine Normal University, Taft Avenue, Malate, ManilaDocument12 pagesFSTEM, CTD, Philippine Normal University, Taft Avenue, Malate, ManilaRENYRICK MANALOTONo ratings yet
- Introduction to Natural UnitsDocument4 pagesIntroduction to Natural UnitsMohamed ElsayedNo ratings yet
- FS 4009 Lighting Transformer, Rev - 0Document14 pagesFS 4009 Lighting Transformer, Rev - 0Dinesh RajNo ratings yet
- Science: Quarter 1 - Module 2 Changes in MaterialsDocument33 pagesScience: Quarter 1 - Module 2 Changes in MaterialsYoshidaNo ratings yet
- HMP7 Relative Humidity and Temperature Probe: For High HumiditiesDocument3 pagesHMP7 Relative Humidity and Temperature Probe: For High HumiditiesRODRIGONo ratings yet
- MDR 2 DRH 4189340300i Uk 6852 Taptin0Document26 pagesMDR 2 DRH 4189340300i Uk 6852 Taptin0wan jspNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Thermal Contacts With Heat Generation: Application To Electrothermal ProblemsDocument20 pagesModeling of Thermal Contacts With Heat Generation: Application To Electrothermal ProblemsThouraya HbsNo ratings yet
- Questions Bank On ElectrostaticsDocument2 pagesQuestions Bank On Electrostaticsashok PradhanNo ratings yet
- Physics 1345Document24 pagesPhysics 1345Barney ParadoxNo ratings yet
- Voltage Regulation by MMFDocument4 pagesVoltage Regulation by MMFKrushna PisalNo ratings yet
- Curiculum Vitae Iyere Faith-1Document5 pagesCuriculum Vitae Iyere Faith-1Halleluyah HalleluyahNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Fundamentals: MEE 341 Chap 2Document20 pagesKinematics Fundamentals: MEE 341 Chap 2Memeber JNo ratings yet