Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SSLM-OC-Q1-WEEK-3 Oral Com
Uploaded by
Doane NadongOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SSLM-OC-Q1-WEEK-3 Oral Com
Uploaded by
Doane NadongCopyright:
Available Formats
ORAL COMMUNICATION IN CONTEXT - GRADE 11
Name: ____________________________________ Date: ____________________
Grade: ______________________________ Section: ___________________
Quarter: 1 Week: 3 SSLM No. 3 MELC(s): Differentiate the various models of
communication (EN11/12OC-Ia-3)
Objectives:
1. Compare and Contrast models of communication in context.
2. Illustrate the three models of communication.
Title of Textbook/LM to Study: Oral Communication in Context
Chapter: 1 Pages: 5-6 Topic: Various Models of Communication
Let Us Discover
COMMUNICATION MODELS
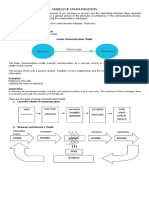
I. LINEAR COMMUNICATION MODEL
Communication is considered as a one-way process.
The message signal is encoded and transmitted through the channel in presence of
noise.
The sender is more prominent in a linear model of communication.
It is applied in mass communication like television, radio, etc.
Linear Communication Model
There are different types of communication models based on the Linear Model of
Communication. These are the following:
1. Aristotle’s Model of Communication
It is considered as the first model of communication.
It is most widely accepted among all communication models.
It is mainly focused on speaker and speech. It can be broadly divided into 5
primary elements: Speaker, Speech, Occasion, Audience and Effect.
It is considered as a speaker-centered model.
1 GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 03.00, Effective June 9, 2021
Aristotle’s Model of Communication
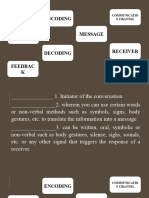
2. Lasswell’s Model of Communication
It is also known as “action model”.
Lasswell’s Model of Communication
COMPONENTS MEANING ANALYSIS
The communicator or sender or source of
WHO Control Analysis
message
SAYS WHAT The content of the message Content Analysis
IN WHICH CHANNEL The medium/media Media Analysis
The receiver of the message or an
TO WHOM Audience Analysis
audience
WITH WHAT EFFECT The feedback of the receiver to the sender Effect Analysis
3. Berlo’s SMCR Model
SMCR refers to Sender-Message-Channel-Receiver.
It focuses on encoding and decoding which happen before the sender sends the
message and before the receiver receives the message respectively.
2 GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 03.00, Effective June 9, 2021
II. TRANSACTIONAL MODEL OF COMMUNICATION
It is the exchange of messages between sender and receiver where each takes turns
to send or receive messages.
Both sender and receiver are known as communicators.
It is mostly used for interpersonal communication and is also called a circular model
of communication.
One of the most common types of communication models based on the
Transactional Model of Communication is the Shannon-Weaver’s Model of Communication.
1. Shannon-Weaver’s Model of Communication (Information Theory)
It is considered as “Mother of all models”.
Concepts of Shannon-Weaver Model:
Sender – (source) the person who makes the message.
Encoder – (transmitter) the sender who uses the machine which converts message
into signals.
Channel – medium used to send message
Decoder – (receiver) machine used to convert signals into message
Receiver – (destination) the person who gets the message or the place where the
message must reach.
Noise - (barrier) the physical disturbances like environment, people, etc. which does
not let the message get to the receiver as what is sent.
Shannon-Weaver’s Model of Communication
III. INTERACTIVE MODEL OF COMMUNICATION
It is also known as the “convergence model”.
It deals with the exchange of ideas and messages taking place in both ways from
sender to receiver and vice-versa.
1. Schramm’s Model of Communication
It is built on the theory that communication is a two-way street, with a sender and a
receiver as shown in the illustration below:
3 GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 03.00, Effective June 9, 2021
MESSAGE
DECODER
INTERPRETER
DECODER
MESSAGE
It is a Circular model, so that communication is something circular in nature.
ENCODER INTERPRETER DECODER
Encoder – One who sends the message and where the message originates
Decoder – One who receives the message
Interpreter – A person trying to understand (analyzes, perceives)
Let Us Try
Read the following statements carefully. Write True if the idea is correct and replace
the underlined statement if False.
______________1. According to the Transactional Model, people are both sender and
receiver at the same time.
______________2. The best model to explain the complexities of face-to-face
communication is the Interactive Model.
______________3. The content of the message is called the noise.
______________4. To convert a message into groups of words, symbols, gestures, or
sounds that present ideas or concepts is called encoding.
______________5. Any communication that conveys a message consisting of words is
called nonverbal communication.
______________6. Decoding is the process by which the receiver interprets the symbols
used by the source of the message by converting them into concepts
and ideas.
______________7. Noise is the interference within the communication process.
______________8. Context is any medium within the communication process.
______________9. Shannon & Weaver Model is an example of a Linear Communication
Model.
______________10. An interpreter is the one who analyzes or perceives the message.
4 GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 03.00, Effective June 9, 2021
Let Us Do
Fill in the chart below with useful information about the various models of
communication. Write your answers in complete sentence.
Model of Illustration of the
Description Examples
Communication Model
1. 1.
2. 2.
Linear
3. 3.
1. 1.
2. 2.
Transactional
1. 1.
Interactive
5 GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 03.00, Effective June 9, 2021
Let Us Apply
Choose one model of communication to illustrate. Modify by labeling it with actual
people, events and place. Then, briefly explain the illustration. Use the space below the box
for your explanation.
Model of Communication: ________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________
6 GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 03.00, Effective June 9, 2021
Rubrics
Category 3 2 1
The content is not
The content is relevant The content is not so
Content relevant and accurate at
and accurate. relevant and accurate.
all.
The explanation is free The explanation has
The explanation has few
of errors on many errors on
errors on capitalization,
Mechanics capitalization, spelling, capitalization, spelling,
spelling, grammar and
grammar and grammar and
punctuation.
punctuation. punctuation.
The illustration is The illustration is not so The illustration is not
Illustration creative, neat and creative, neat and creative, neat and
colorful. colorful. colorful.
TOTAL
References
Flores, R., (2016). Oral Communication in Context. Rex Printing Company, Inc. Sta. Mesa
Heights, Quezon City.
Self - Learning Module, Quarter 1- Module 2
http://cm.bell-labs.com/cm/ms/what/shannonday/paper.html A Mathematical Theory of
Communication
SSLM Development Team
Writer: Pearl Joy L. Jakar
Content Editor: Margie T. Javier
LR Evaluators: Jocelyn P. Abing, Louie Mark G. Garvida
Illustrator:
Creative Arts Designer: Reggie D. Galindez
Education Program Supervisor:
Education Program Supervisor – Learning Resources: Sally A. Palomo
Curriculum Implementation Division Chief: Juliet F. Lastimosa
Asst. Schools Division Superintendent: Carlos G. Susarno, Ph. D.
Schools Division Superintendent: Romelito G. Flores, CESO V
7 GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 03.00, Effective June 9, 2021
GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, v.r. 03.00, Effective June 9, 2021
You might also like
- Communication ModelsDocument3 pagesCommunication ModelsMary Yvonne AresNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument20 pagesModels of CommunicationTrisha Ray60% (5)
- Models of CommunicationDocument33 pagesModels of Communicationishana kalra100% (6)
- Lesson Plan in Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in 21st CenturyDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in 21st CenturyDoane Nadong0% (1)
- M.tech Colleges Karnataka DetailsDocument6 pagesM.tech Colleges Karnataka DetailsAshish BharatNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument20 pagesModels of CommunicationKAREN75% (4)
- Introduction to LLMs for Business Leaders: Responsible AI Strategy Beyond Fear and Hype: Byte-Sized Learning SeriesFrom EverandIntroduction to LLMs for Business Leaders: Responsible AI Strategy Beyond Fear and Hype: Byte-Sized Learning SeriesNo ratings yet
- Let Us Discover: GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, V.R. 03.00, Effective June 9, 2021Document8 pagesLet Us Discover: GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, V.R. 03.00, Effective June 9, 2021Margie JavierNo ratings yet
- Let Us Discover: GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, V.R. 03.00, Effective June 9, 2021Document8 pagesLet Us Discover: GSC-CID-LRMS-ESSLM, V.R. 03.00, Effective June 9, 2021James Libo-onNo ratings yet
- Name: Grade Level: Section: Date: Worksheet No. 2 Title: Models of CommunicationDocument13 pagesName: Grade Level: Section: Date: Worksheet No. 2 Title: Models of CommunicationLeigh AfableNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument9 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesGIETRIN CALALIN100% (1)
- ModelsDocument34 pagesModelsClaire SingsonNo ratings yet
- Compilation of Activity in EC05Document16 pagesCompilation of Activity in EC05Jiann CapiralNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Communication ModelsDocument3 pagesLESSON 3 Communication ModelsSheryl S. DumangengNo ratings yet
- Activities For Module 3: ActivityDocument5 pagesActivities For Module 3: ActivityKenleinard ParafinaNo ratings yet
- Alviola Ge Comm Activity 1Document2 pagesAlviola Ge Comm Activity 1Michael D. DicenNo ratings yet
- English: Influence of MediaDocument12 pagesEnglish: Influence of MediaJuren Andrew Nieves100% (2)
- Communication TheoryDocument5 pagesCommunication TheoryJulie Ann GernaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Oral CommmDocument4 pagesLesson 2 Oral Commmja imamNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument3 pagesModels of Communication123 456No ratings yet
- Module 3 - Models of CommunictionDocument8 pagesModule 3 - Models of CommunictionMarcus Henry Acoymo HabanaNo ratings yet
- Ws 2Document5 pagesWs 2rhen reluyaNo ratings yet
- 1 2 MergedDocument8 pages1 2 MergedAira CorderoNo ratings yet
- OCC Module 2Document5 pagesOCC Module 2Jessa Mae Neri SardanNo ratings yet
- ED111 - Comm Skills Module Latest 2014 - Run2016Document48 pagesED111 - Comm Skills Module Latest 2014 - Run2016Sydney ChilesheNo ratings yet
- 1.2 The Communication Process - Communication in The Real WorldDocument15 pages1.2 The Communication Process - Communication in The Real WorldKimberly MagtalasNo ratings yet
- Oralcom Module 2 Week 2 Models of CommunicationDocument9 pagesOralcom Module 2 Week 2 Models of CommunicationCesarNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument5 pagesModels of Communicationrhen reluyaNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelDocument14 pagesCommunication Modelananyabhardwaj3663No ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 1-Edited 2Document4 pagesModule 1 Lesson 1-Edited 2Chloe Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument25 pagesModels of CommunicationkateNo ratings yet
- Oral Comm. HandoutDocument4 pagesOral Comm. HandoutshannenkrishagwapaNo ratings yet
- Oral Comunication Q1 Module 2Document10 pagesOral Comunication Q1 Module 2Stephanie DilloNo ratings yet
- 2 - Models of Communication-NotesDocument13 pages2 - Models of Communication-NotesJESSA NOQUILLANo ratings yet
- P CPDF FormatDocument165 pagesP CPDF FormatShyrie Keydel A. PrimeroNo ratings yet
- PurCom FINALS Reviewer 2Document74 pagesPurCom FINALS Reviewer 2Renalyn Ps MewagNo ratings yet
- San Jose Community College College of EducationDocument6 pagesSan Jose Community College College of EducationRica BioNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Q1 Oral Com. SHS Module 2Document16 pagesWeek 3 - Q1 Oral Com. SHS Module 2John John BidonNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper: What Do We Share? What Do We Impart? Why Do We Participate?Document21 pagesLesson Proper: What Do We Share? What Do We Impart? Why Do We Participate?BeaNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication Mod2 Week 2Document5 pagesOral Communication Mod2 Week 2Josie EscalaNo ratings yet
- Various Models of CommunicationDocument4 pagesVarious Models of CommunicationJana BalisalisaNo ratings yet
- Nature of CommunicationDocument4 pagesNature of CommunicationStephanie Joyce TejadaNo ratings yet
- Models of Communication PDFDocument33 pagesModels of Communication PDFvmukadamNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document23 pagesModule 2Mariah Divina VillasurNo ratings yet
- Modules in Grade 12: Schools Division of Pasay CityDocument28 pagesModules in Grade 12: Schools Division of Pasay CityDaylyn GomezNo ratings yet
- SW2 AsuncionDocument2 pagesSW2 Asuncionvanicole916No ratings yet
- Communication Process, Mass Communication Models and PerceptionDocument15 pagesCommunication Process, Mass Communication Models and PerceptionJen PhoebeNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelsDocument32 pagesCommunication ModelsTimNo ratings yet
- Models of Communication: Alviola - Cabusao - de La Torre - Mercado - Plaza - Ravelo - SyDocument13 pagesModels of Communication: Alviola - Cabusao - de La Torre - Mercado - Plaza - Ravelo - SyChelseaT.VillavendaNo ratings yet
- Various Models of CommunicationDocument13 pagesVarious Models of CommunicationTsej IsaacNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Communication ModelsDocument3 pagesLesson 2 Communication Modelswinstone arradazaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Nature of Language and CommunicationDocument9 pagesLesson 1: Nature of Language and CommunicationJehada AbdukadilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: Nature of Language and CommunicationDocument9 pagesLesson 1: Nature of Language and CommunicationJehada AbdukadilNo ratings yet
- Finals1 Purposive CommunicationDocument3 pagesFinals1 Purposive CommunicationShen ShenNo ratings yet
- Oral Communication in Context Module 2 - Week 2: Topics: Communication Models Melc: I. Learning ObjectivesDocument13 pagesOral Communication in Context Module 2 - Week 2: Topics: Communication Models Melc: I. Learning ObjectivesJan MykaNo ratings yet
- The Communication ProcessDocument9 pagesThe Communication ProcessVanessaNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument20 pagesModels of CommunicationNiro MadlusNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument5 pagesModels of CommunicationSudarsan SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2: Types of Communication ModelsDocument7 pagesLesson 2: Types of Communication ModelsScarlett YuNo ratings yet
- Oral Com. 11 Q1 W2Document10 pagesOral Com. 11 Q1 W2Gino Dijeto SolesNo ratings yet
- Communication Models: Lindo - Oralcomm - Sem1Document16 pagesCommunication Models: Lindo - Oralcomm - Sem1rjule2023000519No ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets Oral CommunicationDocument2 pagesLearning Activity Sheets Oral CommunicationDoane NadongNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Oral Communication in ContextDocument3 pagesLesson Plan in Oral Communication in ContextDoane NadongNo ratings yet
- SSLM-OC-Q1-WEEK 8 - Types of Speech Acts - Oral ComDocument6 pagesSSLM-OC-Q1-WEEK 8 - Types of Speech Acts - Oral ComDoane NadongNo ratings yet
- SSLM-OC-Q1-WEEK-4 - Oral ComDocument7 pagesSSLM-OC-Q1-WEEK-4 - Oral ComDoane NadongNo ratings yet
- SSLM Q2 Week 6 Oral ComDocument6 pagesSSLM Q2 Week 6 Oral ComDoane NadongNo ratings yet
- SSLM Q2 Week 5 Oral ComDocument8 pagesSSLM Q2 Week 5 Oral ComDoane NadongNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week1Document8 pagesQ2 Week1Doane NadongNo ratings yet
- SSLM Q1 Oral ComDocument8 pagesSSLM Q1 Oral ComDoane NadongNo ratings yet
- Q2 Week 2 Oral ComDocument7 pagesQ2 Week 2 Oral ComDoane NadongNo ratings yet
- Math Bcs 1,2,3 Finl BcsDocument8 pagesMath Bcs 1,2,3 Finl BcsHibha MoosaNo ratings yet
- CS 301 Theory of Automata Fall 2018Document4 pagesCS 301 Theory of Automata Fall 2018i201757 Khawaja Razzi Ul IslamNo ratings yet
- Februrary-2-2024 Catch UpDocument4 pagesFebrurary-2-2024 Catch UpMarinel BayronNo ratings yet
- Script For COC 1Document9 pagesScript For COC 1louiced reno2129No ratings yet
- Mathematics 4 - Weekly Learning Plan (Week 4)Document4 pagesMathematics 4 - Weekly Learning Plan (Week 4)mei rose puyatNo ratings yet
- White Elegant Minimalist About Article Page Layout A4 DocumentDocument3 pagesWhite Elegant Minimalist About Article Page Layout A4 Documentapi-670910177No ratings yet
- Problems of Education in The 21st Century, Vol. 24, 2010Document141 pagesProblems of Education in The 21st Century, Vol. 24, 2010Scientia Socialis, Ltd.No ratings yet
- Cs8494 Software Engineering: Course Instructor Mrs.A.Tamizharasi, AP/CSE, RMDEC Mrs. Remya Rose S, AP/CSE, RMDECDocument23 pagesCs8494 Software Engineering: Course Instructor Mrs.A.Tamizharasi, AP/CSE, RMDEC Mrs. Remya Rose S, AP/CSE, RMDECTamizharasi ANo ratings yet
- JW 1 StgrclassactivityDocument6 pagesJW 1 Stgrclassactivityapi-632123997No ratings yet
- The Relationship of Faculty Development On Employee Productivity of DLSUDDocument52 pagesThe Relationship of Faculty Development On Employee Productivity of DLSUDLorenz GenidoNo ratings yet
- Truera Slides LLM Workshop Session 2Document38 pagesTruera Slides LLM Workshop Session 2uday samalaNo ratings yet
- L4 M4 Learning Principles and Events of Instruction ModifiedDocument10 pagesL4 M4 Learning Principles and Events of Instruction ModifiedSom cNo ratings yet
- Chat GPT Final SpeechDocument2 pagesChat GPT Final SpeechPrativaNo ratings yet
- About The Agency of Things of Objects AnDocument13 pagesAbout The Agency of Things of Objects AnCarlos AfonsoNo ratings yet
- Students Perceptions On The Use of Project BasedDocument12 pagesStudents Perceptions On The Use of Project BasedraneeNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter QA - Final Research ManuscriptDocument23 pages4th Quarter QA - Final Research ManuscriptariNo ratings yet
- The Policy Research Proposal DescriptorDocument5 pagesThe Policy Research Proposal DescriptorNescire NescireNo ratings yet
- Oral ScriptDocument7 pagesOral ScriptArdent BautistaNo ratings yet
- How To Choose The Right Machine Learning AlgorithmDocument10 pagesHow To Choose The Right Machine Learning Algorithmtanvir anwarNo ratings yet
- Retooling Beginning Literacy Instruction For The Brigada Pagbasa Program-ReflectionDocument2 pagesRetooling Beginning Literacy Instruction For The Brigada Pagbasa Program-ReflectionCarmela BancaNo ratings yet
- Annisa Salsa Fitri - J0314201166 - BIB - TM 11 - A Praktikum 2Document2 pagesAnnisa Salsa Fitri - J0314201166 - BIB - TM 11 - A Praktikum 2Annisa Salsa FitriNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Organizational Behavior and Organizational PsychologyDocument56 pagesDifference Between Organizational Behavior and Organizational PsychologyMokshit JainNo ratings yet
- Null 2 PDFDocument5 pagesNull 2 PDFPerez InokobaNo ratings yet
- Ejemplo de La Actividad 5. Mtra Miriam Torres Bermudez. Analisis Del DiscursoDocument2 pagesEjemplo de La Actividad 5. Mtra Miriam Torres Bermudez. Analisis Del DiscursoHilda VillagranNo ratings yet
- A1932408349 - 26090 - 7 - 2021 - Ca 3 QTT 201Document4 pagesA1932408349 - 26090 - 7 - 2021 - Ca 3 QTT 201Pankaj MahantaNo ratings yet
- Ipd Online - Changes To Ice Attributes From October 2021Document16 pagesIpd Online - Changes To Ice Attributes From October 2021sri TEMKARNo ratings yet
- Digital Prescription and Disease Prediction Using Machine LearningDocument8 pagesDigital Prescription and Disease Prediction Using Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Holy Name University: Master of Arts in Education Major in Science Education Effective Year - 1998Document1 pageHoly Name University: Master of Arts in Education Major in Science Education Effective Year - 1998Ruel PerochoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 What Is Technical WritingDocument7 pagesLesson 1 What Is Technical WritingMichaella Portugal FloridaNo ratings yet