Professional Documents
Culture Documents
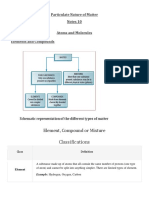
Notes 13 Particulate Nature of Matter
Uploaded by
Naveen Kumar CDOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Notes 13 Particulate Nature of Matter
Uploaded by
Naveen Kumar CDCopyright:
Available Formats
Particulate Nature of Matter
Notes 13
Relative atomic mass:
relative atomic mass (Ar) – the average mass of normally occurring atoms of an
element on a scale where the carbon-12 atom has a mass of exactly 12 units.
One Atomic Mass Unit: One atom of carbon-12 is given the mass of 12 precisely.
From this we get that
1 atomic mass unit (a.m.u.) = 1/12 * mass of one atom of carbon-12.
Chlorine contains two isotopes, chlorine-35 and chlorine-37, in a ratio of 3 : 1 (or
75% : 25%).
Th e relative atomic mass of chlorine can be calculated by finding the total mass
of 100 atoms:
mass of 100 atoms = (35 × 75) + (37 × 25)
= 3550
Q. Calculate the molecular mass of the following substances(relative molecular
mass):
1. Water(H2O)
2. Ammonia(NH3)
3. Calcium carbonate(CaCO3)
4. Ammonium carbonate((NH4)2CO3)
Radioactivity:
• Some elements have unstable isotopes, such as tritium and carbon-14. The
extra neutrons in their nuclei cause them to disintegrate or decay
spontaneously.
• This is radioactivity and takes place through nuclear fission.
• The result of these disintegrations is the release of heat energy and various
forms of radioactive radiation.
• Uranium-235 is a radioactive isotope which is used as a controlled source
of energy in nuclear power stations.
• Radioactive decay is a nuclear process and not a chemical reaction.
The uses of radioactivity:
• Caron-14 is used in Radioactive dating
• An isotope of uranium, 235U, is used in nuclear power stations.
• Cobalt-60 is used to treat internal cancer tumours.
• Skin cancer tumours can be treated with phosphorus-32 or strontium-90.
Page 52.
You might also like
- Novum ETFE Presentation (Master) - WhiteDocument85 pagesNovum ETFE Presentation (Master) - WhiteNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Study Guide: Key Concepts, Problems, and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (10)
- Chemistry Level 4C: (CHM415115) Mole Concept & Stoichiometry Theory Summary & Revision QuestionsDocument29 pagesChemistry Level 4C: (CHM415115) Mole Concept & Stoichiometry Theory Summary & Revision QuestionsS AdiaNo ratings yet
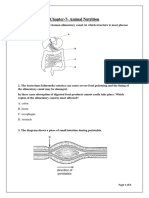
- CH-7 - Animal Nutrition - Revsision Sheet-AKDocument8 pagesCH-7 - Animal Nutrition - Revsision Sheet-AKNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Mass Spectroscopy Module 20094perDocument6 pagesMass Spectroscopy Module 20094perIntan Andrifa Viraya-RnNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules & Stoichiometry RedoxDocument189 pagesAtoms, Molecules & Stoichiometry RedoxPriscilla TjjNo ratings yet
- NSSCAS Chemistry Theme 1 Topic 1.1 - Updated 02 November 2020Document36 pagesNSSCAS Chemistry Theme 1 Topic 1.1 - Updated 02 November 2020Peter Kudumo100% (1)
- Chem. CalculationDocument69 pagesChem. CalculationMaheshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 (Part 1) Fundamentals of Chemistry & Atomic ConceptsDocument88 pagesChapter 1 (Part 1) Fundamentals of Chemistry & Atomic Concepts翁绍棠No ratings yet
- Module 1 - ChemistryDocument48 pagesModule 1 - ChemistryShapnil FinneyNo ratings yet
- Relative Atomic Masses Mass SpectrometryDocument43 pagesRelative Atomic Masses Mass SpectrometryClaytonMitchellJr.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Mole ConceptDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Mole ConceptShari OliverNo ratings yet
- 5 Early Atomic TheoryDocument55 pages5 Early Atomic TheoryGlen Mangali100% (1)
- Chemistry: Is A Whole Branch of Science About Matter, Which Is Anything ThatDocument11 pagesChemistry: Is A Whole Branch of Science About Matter, Which Is Anything Thatmalzaben001No ratings yet
- Chemistry Calculations ADocument8 pagesChemistry Calculations AKasunDilshanNo ratings yet
- Chemistry STPM Chapter 1 by STUDY SMART WWW - Studysmart.page - TLDocument8 pagesChemistry STPM Chapter 1 by STUDY SMART WWW - Studysmart.page - TLAcyl Chloride Hariprem95% (40)
- Relative Masses of Atoms and MoleculesDocument23 pagesRelative Masses of Atoms and MoleculesKris DookharanNo ratings yet
- Amount of Substance Atomic Mass Unit (A.M.U)Document6 pagesAmount of Substance Atomic Mass Unit (A.M.U)primalNo ratings yet
- SGCH 03Document25 pagesSGCH 03kalloliNo ratings yet
- What Controls The Rate of ElectrolysisDocument11 pagesWhat Controls The Rate of ElectrolysisSalem GarrabNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Unit 1Document26 pagesChemistry Unit 1Muneer LallasNo ratings yet
- 2 Ar, MR and MolesDocument11 pages2 Ar, MR and MoleslfcluishoughtonNo ratings yet
- 2nd Day HandoutDocument67 pages2nd Day HandoutIsabel Velan ViernesNo ratings yet
- As Chemistry Note1 FinalDocument56 pagesAs Chemistry Note1 Finaltej786No ratings yet
- The Relative Atomic MassDocument42 pagesThe Relative Atomic MassMorris KariukiNo ratings yet
- Redox ReactionDocument52 pagesRedox ReactionChauhan DharmendraNo ratings yet
- The Structure of The Atom - PortalDocument50 pagesThe Structure of The Atom - Portaldhruvini100% (1)
- s1.4 The MoleDocument88 pagess1.4 The Molelettybadran2007No ratings yet
- Chemistry 2Document2 pagesChemistry 2Kriezhel Kim TadleNo ratings yet
- 1b - The MoleDocument16 pages1b - The Moleapi-227549282No ratings yet
- A1951-194df-F4-Kimia-Chapter-3-Note - (Bi) - Edited - Compressed StudentDocument15 pagesA1951-194df-F4-Kimia-Chapter-3-Note - (Bi) - Edited - Compressed Studentforyourhonour wongNo ratings yet
- GR12 (1sem) Pri - StoichiomestryDocument6 pagesGR12 (1sem) Pri - StoichiomestryKiller KnightNo ratings yet
- 03 Chemical Formulae & EquationDocument15 pages03 Chemical Formulae & EquationSathya RauNo ratings yet
- Notes On AtomDocument7 pagesNotes On Atomprincefresh853No ratings yet
- Presentation How The Elements Are Formed Part 3a.pdf 1Document30 pagesPresentation How The Elements Are Formed Part 3a.pdf 1ceriolaieahmarie09No ratings yet
- Atoms Molecules Stoch 1Document31 pagesAtoms Molecules Stoch 1jakelakerNo ratings yet
- 1.060 Notes - Relative Mass - MoleDocument10 pages1.060 Notes - Relative Mass - MolelyliasahiliNo ratings yet
- 4 Chapter 3 0Document59 pages4 Chapter 3 0azizNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 Mole Concept TheoryDocument25 pagesTopic 3 Mole Concept TheoryMr. XNo ratings yet
- Atomic MassDocument2 pagesAtomic MasscrazynupNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of Materials Lec 6Document42 pagesChemistry of Materials Lec 6sanjunaNo ratings yet
- Elements and MoleculesDocument26 pagesElements and MoleculesTrevor NamalawaNo ratings yet
- Topic 1bDocument5 pagesTopic 1bapi-336093393No ratings yet
- Topic 1bDocument5 pagesTopic 1bapi-336093393No ratings yet
- MATTER (1.1 Atoms and Molecules) 2Document46 pagesMATTER (1.1 Atoms and Molecules) 2Eroll MirulNo ratings yet
- Cacl Cuso (NH) So MG (No) 6H O: Relative Molecular Mass (Document3 pagesCacl Cuso (NH) So MG (No) 6H O: Relative Molecular Mass (Bijoy SalahuddinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Relative Masses and Mole CalculationsDocument9 pagesChapter 7 - Relative Masses and Mole CalculationsAdrawa NorwelNo ratings yet
- Atoms & Isotopes: Mrs. Page Chemistry10Document24 pagesAtoms & Isotopes: Mrs. Page Chemistry10RENE N. RAMILONo ratings yet
- Solution 938396Document7 pagesSolution 938396Unsinkable GamingNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Molecules and StoichiometryDocument19 pagesAtoms, Molecules and StoichiometryMohammed ZakeeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesDocument17 pagesChapter 3 Atoms and MoleculesParas NathNo ratings yet
- KSJ SpectroaDocument12 pagesKSJ SpectroaNAMENo ratings yet
- Masses of Particles: Unit 1 Chemistry Chapter 4 Notes Relative Isotopic MassDocument4 pagesMasses of Particles: Unit 1 Chemistry Chapter 4 Notes Relative Isotopic Masssmeethadeep.kaurNo ratings yet
- Form 4 Chemistry Chapter 3 NoteDocument21 pagesForm 4 Chemistry Chapter 3 NoteSF CHENGNo ratings yet
- Mass Spectrometry and IsotopesDocument13 pagesMass Spectrometry and IsotopesMaysaa El HarakehNo ratings yet
- Chemical Stoichiometry CHEM 107Document43 pagesChemical Stoichiometry CHEM 107AhmedAdelIbrahimNo ratings yet
- 18 Quantitative Aspects of Chemical ChangeDocument30 pages18 Quantitative Aspects of Chemical Changeapi-235269401No ratings yet
- STPM Chem Chp1 NotesDocument29 pagesSTPM Chem Chp1 Noteskpew100% (4)
- Concepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1From EverandConcepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1No ratings yet
- Che - Periodic TableDocument19 pagesChe - Periodic TableNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- Notes 12 Particulate Nature of MatterDocument3 pagesNotes 12 Particulate Nature of MatterNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- ECO Part1 ActivitiesDocument5 pagesECO Part1 ActivitiesNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- Cash Book and Petty Cash Book - Answer KeyDocument6 pagesCash Book and Petty Cash Book - Answer KeyNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- Notes 9 - Particulate Nature of MatterDocument3 pagesNotes 9 - Particulate Nature of MatterNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- Notes 10 - Particulate Nature of MatterDocument4 pagesNotes 10 - Particulate Nature of MatterNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- reply-RFS-Alsabah-HVAC-00001 (Rev 0) Source Approval of Galvanized Steel Sheet DuctDocument2 pagesreply-RFS-Alsabah-HVAC-00001 (Rev 0) Source Approval of Galvanized Steel Sheet DuctNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- CH-8 - Transport in Plants (Assignmnet) - AKDocument7 pagesCH-8 - Transport in Plants (Assignmnet) - AKNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- Notes 11 Particulate Nature of MatterDocument3 pagesNotes 11 Particulate Nature of MatterNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- CH-6 - Plant Nutrition - Revision Sheet-AKDocument6 pagesCH-6 - Plant Nutrition - Revision Sheet-AKNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- Part A 9Th Floor ACTUAL LEVEL 56.030Document6 pagesPart A 9Th Floor ACTUAL LEVEL 56.030Naveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet
- Operation Guide 5229: Daylight Saving Time (DST) 12-Hour and 24-Hour TimekeepingDocument6 pagesOperation Guide 5229: Daylight Saving Time (DST) 12-Hour and 24-Hour TimekeepingNaveen Kumar CDNo ratings yet