Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MATH Rational Roots Theorem
Uploaded by
Ainel Matthew Orbino0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesThe document provides information about sequences, including:
1) An arithmetic sequence has a constant difference between consecutive terms, while a geometric sequence has a common ratio between terms.
2) Formulas are given for finding the nth term, common difference, and first term of an arithmetic sequence, and for finding the common ratio, nth term, geometric mean, first term, and sum of terms of a geometric sequence.
3) An example is worked through of solving a quadratic equation using factoring and setting each factor equal to 0 to find the two values of x.
Original Description:
Original Title
Math 1st Quarter
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document provides information about sequences, including:
1) An arithmetic sequence has a constant difference between consecutive terms, while a geometric sequence has a common ratio between terms.
2) Formulas are given for finding the nth term, common difference, and first term of an arithmetic sequence, and for finding the common ratio, nth term, geometric mean, first term, and sum of terms of a geometric sequence.
3) An example is worked through of solving a quadratic equation using factoring and setting each factor equal to 0 to find the two values of x.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesMATH Rational Roots Theorem
Uploaded by
Ainel Matthew OrbinoThe document provides information about sequences, including:
1) An arithmetic sequence has a constant difference between consecutive terms, while a geometric sequence has a common ratio between terms.
2) Formulas are given for finding the nth term, common difference, and first term of an arithmetic sequence, and for finding the common ratio, nth term, geometric mean, first term, and sum of terms of a geometric sequence.
3) An example is worked through of solving a quadratic equation using factoring and setting each factor equal to 0 to find the two values of x.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
MATH
Sequence : is an arrangement or order of Geometric : What is the value of x?
things (numerical, shapes, etc.) that has a
pattern and it could be finite or infinite. Example :
x + 2 , 5x + 1 , x + 11
an = 4, 7, 10, 13
Divide (Next Previous)
5𝑥 + 1 𝑥 + 11
= } 𝐶𝑟𝑜𝑠𝑠 𝑀𝑢𝑙𝑡𝑖𝑝𝑙𝑖𝑐𝑎𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛
nth term terms 𝑥+2 5𝑥 + 1
(5x + 1)2 = (x + 2)(x + 11) FOIL
Use a + 2ab + b for the left term and
2 2
Arithmetic Sequence : there is a constant FOIL Method for the right term.
difference between two consecutive terms – a 25x2 + 10x + 1 = x2 + 13x + 22
common difference. Subtract the left term and right term.
Formulae : 25x2 – x2 = 24x2
10x – 13x = -3x
For the nth term : an = a1 + (n – 1) d
1 – 22 = -21
𝑎𝑛 − 𝑎1
For common difference : 𝑑 = 24x2 – 3x – 21
𝑛−1
For the first term : a1 = an – [ (n – 1) d ]
Equate to 0.
24x2 – 3x – 21 = 0
Divide the terms by their common
Geometric Sequence : a sequence with multiple.
an inconstant change – a common ratio 24𝑥 2 – 3x – 21
wherein r ≠ 0.
3
Formulae : 8x2 – x – 7 = 0
𝑁𝑒𝑥𝑡 Factor out. If it can’t be factored out,
For common ratio : 𝑟 =
𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑣𝑖𝑜𝑢𝑠 multiply the numerical coefficient of a to
(n – 1) c.
For the nth term : an = a1 (r)
x2 – x – (8)(7) = 0
𝑛−1 𝑎𝑛
For geometric mean : 𝑟 = √𝑎 x2 – x – 56 = 0
1
𝑎𝑛
Factor out and divide both terms by the
For the first term : 𝑎1 = original numerical coefficient of a.
𝑟 (𝑛−1)
𝑎𝑛 (1− 𝑟 𝑛)
(𝑥 − 8)(𝑥 + 7)
For the sum of terms : 𝑆𝑛 =
1−𝑟 8
𝑎1 7
For infinite sum : 𝑆 = (x – 1)(x + 8)
1−𝑟
Equate to 0 and transpose.
7
Arithmetic : What is the value of x? x = -1 x = −8
Example :
x + 2 , 3x – 2 , 7x – 12
Subtract the previous from the next term.
3x – 2 – (x + 2) = 7x – 12 – (3x – 2)
Distribute the – sign to the parentheses.
3x – 2 – x – 2 = 7x – 12 – 3x + 2
Combine like terms.
2x – 4 = 4x – 10
Transpose like terms.
10 – 4 = 4x – 2x
6 = 2𝑥
2
x = 3
MATH
Division of Polynomials
2
MATH
Rational Roots Theorem
What are the values of x that will make the equation 0?
You might also like
- ACT Math Facts & FormulasDocument8 pagesACT Math Facts & Formulaslslisen100% (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- GraphsDocument1,805 pagesGraphsDinesh Reddy KommeraNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsFrom EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsNo ratings yet
- A Polynomial Function P of Degree N Is A Function That Can Be Written in The FormDocument18 pagesA Polynomial Function P of Degree N Is A Function That Can Be Written in The FormMariano GomazanaNo ratings yet
- Legendre Equation ProblemsDocument2 pagesLegendre Equation ProblemsShahbaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- Midterm Review Spring18 SolsDocument22 pagesMidterm Review Spring18 SolsRobert EdwardsNo ratings yet
- MATH1210 Test1 SolutionsDocument5 pagesMATH1210 Test1 Solutionssukhdeepsukhdeep2903No ratings yet
- Further Mathematics p2 With Recalls ReviewedDocument16 pagesFurther Mathematics p2 With Recalls ReviewedKeng ElsonNo ratings yet
- 1st ClassDocument18 pages1st Classchitl.23bi14075No ratings yet
- مفاهيم 2ث علميDocument2 pagesمفاهيم 2ث علميDomaNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 LinearDocument18 pagesLecture1 LinearNguyễn Minh HoàngNo ratings yet
- Teaching Guide For Problem Solving Involving Rational FunctionsDocument7 pagesTeaching Guide For Problem Solving Involving Rational FunctionsMarie Antoinette Cadorna CadeliñaNo ratings yet
- Solution 1002257Document12 pagesSolution 1002257gulshanprasad510No ratings yet
- Facts and Formulas 0Document6 pagesFacts and Formulas 0mamaNo ratings yet
- Equations in One VariableDocument6 pagesEquations in One VariableAllen Kyle PrielaNo ratings yet
- Pre Final Round Problems 2020 SolutionDocument10 pagesPre Final Round Problems 2020 SolutionK. M. Junayed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Homework 0: Mathematical Background For Machine LearningDocument11 pagesHomework 0: Mathematical Background For Machine Learninganwer fadelNo ratings yet
- LIVE NOTES DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS FOR SL Students of AA and AIDocument26 pagesLIVE NOTES DIFFERENTIAL CALCULUS FOR SL Students of AA and AIsriramaniyerNo ratings yet
- 2022 Mathematics Advanced, Year 11 Marking Guidelines: Callaghan College Jesmond Senior CampusDocument7 pages2022 Mathematics Advanced, Year 11 Marking Guidelines: Callaghan College Jesmond Senior CampusetytytNo ratings yet
- AlgebraicDocument16 pagesAlgebraiczohabnoor63No ratings yet
- 1714methods Unit 1 Exam NotesDocument2 pages1714methods Unit 1 Exam NotesIsaiah KimNo ratings yet
- Differential Equations 1Document9 pagesDifferential Equations 1firas a.sNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Physics PhD Tutor IB DSE IGCSE SAT Integration by Parts GuideDocument9 pagesCambridge Physics PhD Tutor IB DSE IGCSE SAT Integration by Parts GuideHin Wa LeungNo ratings yet
- 122MSE Mathematical Methods 2: May 2015 C 2015 Coventry University 122MSE/12Document8 pages122MSE Mathematical Methods 2: May 2015 C 2015 Coventry University 122MSE/12LexNo ratings yet
- POWER UP 2020 Mathematics EquationsDocument3 pagesPOWER UP 2020 Mathematics EquationsLorniel GraxielNo ratings yet
- 5_6255827558357536259Document27 pages5_6255827558357536259Sanoj KushwahaNo ratings yet
- IYMC Final Solution PDFDocument18 pagesIYMC Final Solution PDFMilad MirzaeeNo ratings yet
- Worked SolutionsDocument17 pagesWorked SolutionsanuNo ratings yet
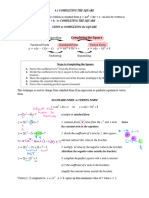
- 6.3completingsquare(a) 2022Document3 pages6.3completingsquare(a) 2022juan.hernandez.500No ratings yet
- MathEcon18 FinalExam SolutionDocument13 pagesMathEcon18 FinalExam SolutionCours HECNo ratings yet
- Elements of H2 A Level MathDocument13 pagesElements of H2 A Level MathnicNo ratings yet
- Partial Fractions: Syllabus RequirementsDocument9 pagesPartial Fractions: Syllabus RequirementsChandini ManoharanNo ratings yet
- Numerical PDFDocument19 pagesNumerical PDFDharmapaljungNo ratings yet
- Hermite Polynomials RecursionDocument4 pagesHermite Polynomials RecursionShailendra SinghNo ratings yet
- Math 10 Formula SheetDocument1 pageMath 10 Formula SheetAdrienNo ratings yet
- HKDSE 2012 Math M2 MSDocument13 pagesHKDSE 2012 Math M2 MSTW ChanNo ratings yet
- Feb 2007 SolutionsDocument3 pagesFeb 2007 Solutionspaul taniwanNo ratings yet
- Calc 2 Spring Study Guide Real Yes Its DoneDocument23 pagesCalc 2 Spring Study Guide Real Yes Its DoneDefault AccountNo ratings yet
- 1.1. Real Numbers, Intervals, and InequalitiesDocument12 pages1.1. Real Numbers, Intervals, and InequalitiesTearlëşşSufíåñNo ratings yet
- XII ClassDocument3 pagesXII Classpremsempire100% (1)
- Power SeriesDocument8 pagesPower SeriescOrekernNo ratings yet
- 9.04 Partial FractionsDocument10 pages9.04 Partial FractionsFarab Saleem BhuttoNo ratings yet
- Notes 24 6382 Legendre FunctionsDocument30 pagesNotes 24 6382 Legendre FunctionsMohamed Al-OdatNo ratings yet
- Facts and Formulas 2aDocument9 pagesFacts and Formulas 2aamc994No ratings yet
- Maths Practicesheet-02 (Code-A) SolDocument9 pagesMaths Practicesheet-02 (Code-A) Solksanthosh29112006No ratings yet
- JC1 EOY Solutions (For Students)Document23 pagesJC1 EOY Solutions (For Students)BooNo ratings yet
- Boyce & DiPrima ODE Section 5.4 Problem 3Document2 pagesBoyce & DiPrima ODE Section 5.4 Problem 3shivamNo ratings yet
- Calculus Test12 Sol 20191015Document7 pagesCalculus Test12 Sol 20191015Mạc Hải LongNo ratings yet
- ACTMathFormulaSheet2Document2 pagesACTMathFormulaSheet2Stu PotNo ratings yet
- 1653 List 10 AnswersDocument5 pages1653 List 10 Answerscs17plNo ratings yet
- 2017-2-Sar-St Thomas-Q&aDocument8 pages2017-2-Sar-St Thomas-Q&aMuhammad IzzuanNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Systems of Linear EquationsDocument39 pagesCH 1 Systems of Linear EquationsMaeriel AggabaoNo ratings yet
- FODE 4 LecturesDocument32 pagesFODE 4 LecturesZaid PeroNo ratings yet
- Student Generating Functions Relation LatticeDocument3 pagesStudent Generating Functions Relation LatticeBadshah KazmiNo ratings yet
- 1C-4 Schaum's Partial FractionsDocument9 pages1C-4 Schaum's Partial FractionsPhelisaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 201/1/2017: Calculus ADocument10 pagesTutorial Letter 201/1/2017: Calculus AKhathutshelo KharivheNo ratings yet
- Rational Expressions SimplifiedDocument5 pagesRational Expressions SimplifiedRyan SorianoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 201/1/2017: Calculus ADocument10 pagesTutorial Letter 201/1/2017: Calculus AKhathutshelo KharivheNo ratings yet
- CALCULUS 1 RATESDocument24 pagesCALCULUS 1 RATESDindo HiocoNo ratings yet
- Rakshit Maths M&DDocument4 pagesRakshit Maths M&DRida SamreenNo ratings yet
- Exercises On LU FactorizationDocument1 pageExercises On LU FactorizationanaperturescienceNo ratings yet
- Nonlinear Programming: Applicability Possible Types of Constraint Set Methods For Solving The Problem ExamplesDocument4 pagesNonlinear Programming: Applicability Possible Types of Constraint Set Methods For Solving The Problem ExamplesLewis SitorusNo ratings yet
- Transmitter Simulink StudyDocument38 pagesTransmitter Simulink StudyLucky Asr AwaisNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3.1 K Means Clustering in Python PART 1Document7 pagesAssignment 3.1 K Means Clustering in Python PART 1Paul RJ GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Data Structures BST OperationsDocument39 pagesData Structures BST OperationscooldudeNo ratings yet
- 5 - Lesson (Frequency Domain Image Processing)Document58 pages5 - Lesson (Frequency Domain Image Processing)Abdataa waaqaaNo ratings yet
- Realization of FSK Modem in Matlab AND TI's TMS320C5510 DSP: Project MentorDocument19 pagesRealization of FSK Modem in Matlab AND TI's TMS320C5510 DSP: Project MentorRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Signal Transmission Over Communication Channel: Lesson 03 EE352 Analog Communication Systems Mansoor KhanDocument27 pagesSignal Transmission Over Communication Channel: Lesson 03 EE352 Analog Communication Systems Mansoor Khanali_rehman87No ratings yet
- Lagrange Interpolation ExplainedDocument2 pagesLagrange Interpolation ExplainedKundan KumarNo ratings yet
- Fontes WimpplBDocument1 pageFontes WimpplBRafael RamosNo ratings yet
- Mining Frequent Itemsets Without Candidate GenerationDocument17 pagesMining Frequent Itemsets Without Candidate GenerationmaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Interpolation and Data FittingDocument16 pagesLecture Notes Interpolation and Data FittingAmbreen KhanNo ratings yet
- Numerical DifferentiationDocument10 pagesNumerical DifferentiationAmlan ShomeNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To E1 2mbit/s PCM SystemsDocument28 pagesAn Introduction To E1 2mbit/s PCM Systemsangelo_lopez1993No ratings yet
- EAB 2113 NUMERICAL METHOD SOLUTIONSDocument20 pagesEAB 2113 NUMERICAL METHOD SOLUTIONSAngel Ngo100% (1)
- Chapter 18 Polynomial Division and The Factor and Remainder TheoremsDocument9 pagesChapter 18 Polynomial Division and The Factor and Remainder TheoremsFritz FatigaNo ratings yet
- MLP Algorithm Overview: Feedforward Neural NetworkDocument3 pagesMLP Algorithm Overview: Feedforward Neural NetworkHari hara Sudhan .MNo ratings yet
- Edge DetectionDocument21 pagesEdge Detectionسميحة سميحةNo ratings yet
- Nlp Basic 03-N-gram Language Model: Nguyễn Quốc TháiDocument31 pagesNlp Basic 03-N-gram Language Model: Nguyễn Quốc TháiY NguyenNo ratings yet
- BST Menu DrivenDocument17 pagesBST Menu Driven025Md ShadNo ratings yet
- Brain Tumor Detection Based On Machine Learning Algorithms: Komal Sharma Akwinder Kaur Shruti GujralDocument5 pagesBrain Tumor Detection Based On Machine Learning Algorithms: Komal Sharma Akwinder Kaur Shruti GujralAmany MorseyNo ratings yet
- Winnow Algorithm for Learning Monotone DisjunctionsDocument4 pagesWinnow Algorithm for Learning Monotone DisjunctionsCNSNo ratings yet
- Solution Problemset 4Document5 pagesSolution Problemset 4Usiel VelaNo ratings yet
- Lorch Filter DiplexersDocument4 pagesLorch Filter DiplexersYung SangNo ratings yet
- Non-Recursive Predictive Parsing - LL (1) ParserDocument1 pageNon-Recursive Predictive Parsing - LL (1) ParserSudama KhatriNo ratings yet
- Pattern Recoginition Assignment - 1 PDFDocument31 pagesPattern Recoginition Assignment - 1 PDFAnirudh KrishnanNo ratings yet
- SQT Q - BankDocument5 pagesSQT Q - Banksomya singhNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing ExplainedDocument24 pagesDigital Signal Processing ExplainedözlemArtukNo ratings yet