Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Nucleus - The Control Center of The Cell
Uploaded by
Vinícius SouzaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Nucleus - The Control Center of The Cell
Uploaded by
Vinícius SouzaCopyright:
Available Formats
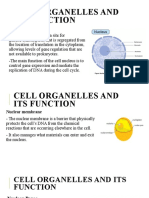
The Nucleus: The Control Center of the Cell
Introduction
The nucleus is a large organelle that is present in eukaryotic cells. It is often
referred to as the control center of the cell, as it contains the cell's genetic
information. In this webpage, we will explore the structure and function of the
nucleus.
Structure of the Nucleus
The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope.
The space between the two membranes is called the perinuclear space. The
nuclear envelope is perforated by nuclear pores, which allow for the exchange
of molecules between the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus also
contains a dense, thread-like material called chromatin, which is composed of
DNA and proteins. During cell division, the chromatin condenses to form visible
structures called chromosomes.
Functions of the Nucleus
The nucleus has several important functions, including:
Containing the cell's genetic information: the nucleus contains the cell's
DNA, which carries the genetic instructions that direct the cell's growth
and function.
Controlling cell division: the nucleus plays a crucial role in the process of
cell division, by organizing the replication and segregation of
chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis.
Regulating gene expression: the nucleus controls the expression of
genes, by turning them on and off as needed.
Conclusion
The nucleus is a vital organelle that plays a central role in the cell. It contains
the cell's genetic information and plays a key role in controlling cell division and
gene expression. Understanding the structure and function of the nucleus
allows us to better understand the inner workings of cells and the organisms
they make up.
You might also like
- Dhannieca I. Solar Bsed Science 1: Centriole DefinitionDocument28 pagesDhannieca I. Solar Bsed Science 1: Centriole DefinitionDhan Nieca SolarNo ratings yet
- ىلوا هلحرم ناونعب ثحب cell nucleus فارشا دبع هبه م.م هذاتسلاا نيسحلاDocument9 pagesىلوا هلحرم ناونعب ثحب cell nucleus فارشا دبع هبه م.م هذاتسلاا نيسحلاعبد اللهNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Mohamad YasinNo ratings yet
- Nucleus: The Head Quarter of CellDocument11 pagesNucleus: The Head Quarter of CellJigarS.MehtaNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusPinak ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- 2-Cell NucleusDocument35 pages2-Cell NucleusAthar Habib ShahaniNo ratings yet
- Distinguishing Characteristics: Cytoplasm Cell Membrane PhospholipidsDocument2 pagesDistinguishing Characteristics: Cytoplasm Cell Membrane PhospholipidsNamra ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Nucleus - Structure and Functions - A-Level Biology Revision Notes PDFDocument2 pagesNucleus - Structure and Functions - A-Level Biology Revision Notes PDFsathya50% (2)
- Human Anatomy and Physiology W1 - EmmanuelaDocument5 pagesHuman Anatomy and Physiology W1 - EmmanuelaRamizNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document28 pagesWeek 4UswaNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument5 pagesNucleussiddharthr954No ratings yet
- Biochemistry PDFDocument2 pagesBiochemistry PDFMuhammad EhsanNo ratings yet
- Elements of Cell: Viral StructureDocument2 pagesElements of Cell: Viral Structurereane_ramirezNo ratings yet
- The Cell NucleusDocument5 pagesThe Cell NucleushutterincNo ratings yet
- 7) 1 - 14 Cell CycleDocument19 pages7) 1 - 14 Cell CycleDawar Aziz MemonNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study of Cellular NucleusDocument25 pagesA Comprehensive Study of Cellular NucleusAnita ShuklaNo ratings yet
- EukaryoticDocument19 pagesEukaryoticwongyikyanNo ratings yet
- Nucleus: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDocument29 pagesNucleus: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleAzifah ZakariaNo ratings yet
- The Cell NucleusDocument3 pagesThe Cell NucleushutterincNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Their Function By. Reyster Pavia 3c Week 3 ReportingDocument24 pagesCell Structure and Their Function By. Reyster Pavia 3c Week 3 ReportingWina MaeNo ratings yet
- General Biology: Lab 3 First Stage Shahad EmadDocument19 pagesGeneral Biology: Lab 3 First Stage Shahad EmadIraqiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1 The CellDocument4 pagesExercise 1 The CellKATHLEEN MAE HERMONo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument2 pagesCell MembraneMaria Morena Cruz BadenasNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM (Exercise 1)Document4 pagesBIOCHEM (Exercise 1)KATHLEEN MAE HERMONo ratings yet
- Cell Definition: "A Cell Is Defined As The Smallest, Basic Unit of Life That Is Responsible For All of Life's Processes."Document5 pagesCell Definition: "A Cell Is Defined As The Smallest, Basic Unit of Life That Is Responsible For All of Life's Processes."shankaram shankaram100% (1)
- Cell NucleusDocument4 pagesCell NucleusrajikrajanNo ratings yet
- CellDocument2 pagesCellTine VagilidadNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument2 pagesCell StructureHR JobsfinderNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 1 The CellsDocument6 pagesExercise No. 1 The CellsHoney June Yvette ArabiaNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept About CELLDocument11 pagesBasic Concept About CELLjack omeNo ratings yet
- Nuclei Nucleus Nuculeus Kernel SeedDocument1 pageNuclei Nucleus Nuculeus Kernel SeedValerie Ann FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Organelles.: Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesOrganelles.: Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisLuzNo ratings yet
- Sample 67Document8 pagesSample 67Rica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Kiera Slideshare PDFDocument9 pagesKiera Slideshare PDFKiera SorianoNo ratings yet
- Module (Cell Nucleus)Document12 pagesModule (Cell Nucleus)Edgie JunelaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Animal CellDocument27 pagesParts of Animal CellJomhel Callueng100% (1)
- CellDocument3 pagesCellShaqueena DanversNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles and Its Function: NucleusDocument15 pagesCell Organelles and Its Function: NucleusRandy AminolaNo ratings yet
- Science ResumeDocument1 pageScience ResumenadhirahBTEamranNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell: and Converts It To Chemical Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell: and Converts It To Chemical Energy by The Process of PhotosynthesisNicole CatolicoNo ratings yet
- What Is The Function of Nucleus in A Eukaryotic CellDocument1 pageWhat Is The Function of Nucleus in A Eukaryotic CellDon King FernandoNo ratings yet
- Cell Parts and Their FunctionsDocument9 pagesCell Parts and Their FunctionsMlshin LaoNo ratings yet
- Notes Plant Cell 21Document2 pagesNotes Plant Cell 21Samantha JerezNo ratings yet
- Diagram of Plant CellDocument4 pagesDiagram of Plant CellekongNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument31 pagesCellsPranav ShindeNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues and Membranes-FinaDocument12 pagesCells, Tissues and Membranes-FinaDerrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- Cell Definition: "A Cell Is Defined As The Smallest, Basic Unit of Life That Is Responsible For All of Life's Processes."Document6 pagesCell Definition: "A Cell Is Defined As The Smallest, Basic Unit of Life That Is Responsible For All of Life's Processes."Woobin Real100% (1)
- Infografia de BiologiaDocument4 pagesInfografia de BiologiafrancosebastianbcNo ratings yet
- Nucleus 161221143029Document12 pagesNucleus 161221143029Lemuel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Module 1-2Document21 pagesModule 1-2Edel Ruth Pal-Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1.1cell ConceptDocument10 pages1.1cell ConceptMokariya SanjayNo ratings yet
- CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapDocument17 pagesCELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS RecapSonakshi Chavan100% (1)
- Parts of A Typical Cell and Their FunctionsDocument2 pagesParts of A Typical Cell and Their FunctionsMaria Sahara FregilNo ratings yet
- Found-1 Science NotesDocument15 pagesFound-1 Science NotesSonakshi ChavanNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue Cells::: Neurons NeurogliaDocument7 pagesNervous Tissue Cells::: Neurons NeurogliaSonakshi KumarNo ratings yet
- The Cell Nucleus: Chromatin and ChromosomesDocument34 pagesThe Cell Nucleus: Chromatin and ChromosomesMary SolomonNo ratings yet
- CELL Are The Small Living Units of An OrganismDocument6 pagesCELL Are The Small Living Units of An Organismsweet michaela paduaNo ratings yet
- About Cell Membrane: CellsDocument2 pagesAbout Cell Membrane: CellsRaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument8 pagesCell StructurePallabi ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Mitochondria - The Powerhouses of The CellDocument1 pageMitochondria - The Powerhouses of The CellVinícius SouzaNo ratings yet
- Basic Math QuizDocument1 pageBasic Math QuizVinícius SouzaNo ratings yet
- Cells - The Building Blocks of LifeDocument2 pagesCells - The Building Blocks of LifeVinícius SouzaNo ratings yet
- Endoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Apparatus - Organelles That Help Transport and Process Molecules Within The CellDocument1 pageEndoplasmic Reticulum and Golgi Apparatus - Organelles That Help Transport and Process Molecules Within The CellVinícius SouzaNo ratings yet
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (397)
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (6)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (517)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)From EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (378)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Tales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceFrom EverandTales from Both Sides of the Brain: A Life in NeuroscienceRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (18)
- The Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionFrom EverandThe Ancestor's Tale: A Pilgrimage to the Dawn of EvolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (812)
- Fast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperFrom EverandFast Asleep: Improve Brain Function, Lose Weight, Boost Your Mood, Reduce Stress, and Become a Better SleeperRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (15)
- Good Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveFrom EverandGood Without God: What a Billion Nonreligious People Do BelieveRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (66)
- A Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouFrom EverandA Series of Fortunate Events: Chance and the Making of the Planet, Life, and YouRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (62)
- Seven and a Half Lessons About the BrainFrom EverandSeven and a Half Lessons About the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (109)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Who's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainFrom EverandWho's in Charge?: Free Will and the Science of the BrainRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (65)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- Human: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueFrom EverandHuman: The Science Behind What Makes Your Brain UniqueRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (38)
- The Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldFrom EverandThe Rise and Fall of the Dinosaurs: A New History of a Lost WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (595)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- Moral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemFrom EverandMoral Tribes: Emotion, Reason, and the Gap Between Us and ThemRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (115)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Why We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsFrom EverandWhy We Sleep: Unlocking the Power of Sleep and DreamsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2083)
- The Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineFrom EverandThe Second Brain: A Groundbreaking New Understanding of Nervous Disorders of the Stomach and IntestineRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Buddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomFrom EverandBuddha's Brain: The Practical Neuroscience of Happiness, Love & WisdomRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (216)