Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Models of Communication - 8 Major
Uploaded by
Ruben De Asis0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views8 pagesThis document outlines several models of communication: Aristotle's model focuses on the speaker, speech, occasion, audience, and effect. Lasswell's model analyzes communication by asking who said what through which channel to whom with what effects. The Shannon-Weaver model highlights the role of "noise" disrupting messages between sender and receiver. Berlo's S-M-C-R model explains communication through four steps: source, message, channel, and receiver.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document outlines several models of communication: Aristotle's model focuses on the speaker, speech, occasion, audience, and effect. Lasswell's model analyzes communication by asking who said what through which channel to whom with what effects. The Shannon-Weaver model highlights the role of "noise" disrupting messages between sender and receiver. Berlo's S-M-C-R model explains communication through four steps: source, message, channel, and receiver.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views8 pagesModels of Communication - 8 Major
Uploaded by
Ruben De AsisThis document outlines several models of communication: Aristotle's model focuses on the speaker, speech, occasion, audience, and effect. Lasswell's model analyzes communication by asking who said what through which channel to whom with what effects. The Shannon-Weaver model highlights the role of "noise" disrupting messages between sender and receiver. Berlo's S-M-C-R model explains communication through four steps: source, message, channel, and receiver.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 8
Aristotle’s Model
Aristotle argues that we
should look at five elements of
a communication event to
analyze how best to
communicate: speaker,
speech, occasion, target
audience and effect.
Lasswell’s Model
Lasswell’s model is a basic
framework for analyzing one-
way communication by asking
five questions: Who, said what,
through which channel, to
whom, with what effects?
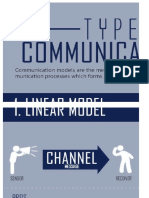
Shannon-Weaver Model
The Shannon-Weaver model
is the first to highlight the role
of ‘noise’ in communication,
which can disrupt or alter a
message between sender and
receiver.
Berlo’s S-M-C-R Model
Berlo’s S-M-C-R model
explains communication in four
steps: Source, Message, Chan
nel, and Receiver.
Osgood-Schramm Model
The Osgood-Schramm model
looks at reciprocal
communication, showing how
we have to encode, decode,
and interpret information in
real-time during a conversation.
Westley and Maclean Model
The Westley and Maclean
model shows that our
communication is influenced by
environmental, cultural and
personal factors.
Barnlund’s Transactional
Model
Barnlund’s Transactional
Model of Communication
highlights the role of private
and public cues that impact our
messages.
Dance’s Helical Model
Dance’s Helical Model sees
communication as a circular
process that gets more and
more complex as
communication occurs, which
can be represented by a helical
spiral.
You might also like
- Models of Communication 1Document11 pagesModels of Communication 1Patrick Luis FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Report On Models of CommunicationDocument38 pagesReport On Models of CommunicationShawn Henry CepedaNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument6 pagesModels of Communicationahsan syedNo ratings yet
- 8 Models of Communication by ProponentsDocument8 pages8 Models of Communication by ProponentsRea TorneaNo ratings yet
- Process of Comunication ModelsDocument23 pagesProcess of Comunication ModelsJahnvi SinghNo ratings yet
- Models of Communication - ExamplesDocument2 pagesModels of Communication - ExamplesRuben De AsisNo ratings yet
- Models CommunicationDocument6 pagesModels CommunicationJames Robert CanlasNo ratings yet
- Linear Models of CommunicationDocument3 pagesLinear Models of CommunicationRay CahayagNo ratings yet
- (Model Communication) Caole, Aron Joel 11-Abm - ADocument3 pages(Model Communication) Caole, Aron Joel 11-Abm - AAron Joel CaoleNo ratings yet
- Models of Communication, ExplainedDocument7 pagesModels of Communication, ExplainedKVVenkatasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Models of Communication 1Document21 pagesModels of Communication 1Kurt PepitoNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelDocument23 pagesCommunication ModelVenny Rose LmstNo ratings yet
- Intro To Mass Com Models 5 6th Week 15022024 090621pmDocument11 pagesIntro To Mass Com Models 5 6th Week 15022024 090621pmarbab6654No ratings yet
- COMMUNICATIONDocument4 pagesCOMMUNICATIONRoisa JoyNo ratings yet
- Chapter I Communication ModelsDocument8 pagesChapter I Communication ModelsodysonNo ratings yet
- 8 Communication ModelsDocument2 pages8 Communication ModelsJenelou PareraNo ratings yet
- The Various Models of CommunicationDocument36 pagesThe Various Models of CommunicationArmie Salayog100% (1)
- Models of CommunicationDocument13 pagesModels of CommunicationleonwaypNo ratings yet
- Communication Models PDFDocument35 pagesCommunication Models PDFJessmay OlivarNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelDocument19 pagesCommunication ModelApoorva RaviNo ratings yet
- Aspects of Communication A. LinguisticDocument6 pagesAspects of Communication A. LinguisticDaisy UnoNo ratings yet
- Mass Communication ModelsDocument3 pagesMass Communication Modelsbillbishop1947No ratings yet
- Three Main Models of CommunicationDocument8 pagesThree Main Models of Communicationnadir saeedNo ratings yet
- Models and Theories of CommunicationDocument11 pagesModels and Theories of CommunicationaringkinkingNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelsDocument26 pagesCommunication ModelsWu XianNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelsDocument3 pagesCommunication ModelsMary Yvonne AresNo ratings yet
- Mil - Act - Types of CommunicationDocument22 pagesMil - Act - Types of CommunicationSyrah Lou BadaranNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelsDocument10 pagesCommunication ModelsRahib RazaNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument12 pagesModels of CommunicationJea June Petros BaghariNo ratings yet
- Communication Models: Prepared By: Year and Section: BSME 1-B Charles Joshua Areglado Joshua C. Sanchez Russel VitaDocument12 pagesCommunication Models: Prepared By: Year and Section: BSME 1-B Charles Joshua Areglado Joshua C. Sanchez Russel VitaBarbielat0% (1)
- Models of Communication AssignmentDocument5 pagesModels of Communication AssignmentJustine Ann Gonzales0% (1)
- Week 05 - Discussion PaperDocument5 pagesWeek 05 - Discussion PaperShem MacalandaNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument7 pagesModels of CommunicationВіка СобчукNo ratings yet
- The Shannon and Weaver Model of Communication Is ADocument3 pagesThe Shannon and Weaver Model of Communication Is AJOREDSANo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument9 pagesBusiness CommunicationBELENGA GEOFREYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Organizational CommunicationDocument49 pagesChapter 3 Organizational CommunicationJose Marie AnoosNo ratings yet
- Models of Communication: Our Lady of The Pillar College-CauayanDocument3 pagesModels of Communication: Our Lady of The Pillar College-CauayanRyan YdiaNo ratings yet
- Commmunication Proc, Prin, EthicsDocument54 pagesCommmunication Proc, Prin, EthicsMišš HeartNo ratings yet
- Module 3, Activity 1 - COMPLETEDDocument4 pagesModule 3, Activity 1 - COMPLETEDSunnyice SunsunNo ratings yet
- Communication ModelDocument2 pagesCommunication ModelNicole AnngelaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Human Communication 1Document16 pagesUnderstanding Human Communication 1ilantamizh RNo ratings yet
- 02 Handout 2 Oral ComDocument5 pages02 Handout 2 Oral ComEnzo PangilinanNo ratings yet
- ToleraDocument11 pagesToleraRegasa GutemaNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument19 pagesModels of CommunicationPrin CeNo ratings yet
- Asynchronous Task 1 DIOQUINODocument5 pagesAsynchronous Task 1 DIOQUINORm DioquinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Models of CommunicationDocument29 pagesLesson 2 Models of CommunicationIah BelaleNo ratings yet
- Models and Processes of CommunicationDocument5 pagesModels and Processes of CommunicationRAIYYAN COSAINNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument33 pagesModels of CommunicationSaiza JeonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Model of Communications: Linear ModelsDocument13 pagesLesson 3: Model of Communications: Linear ModelsScarlett YuNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument18 pagesModels of CommunicationJoshua Sta AnaNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument26 pagesModels of CommunicationAjay PadhiNo ratings yet
- Linear Model Has Defined Set of Components Required For ADocument5 pagesLinear Model Has Defined Set of Components Required For Aviedos likerNo ratings yet
- Oral ComDocument4 pagesOral ComshinNo ratings yet
- Business CommunicationDocument4 pagesBusiness Communicationbefox87318No ratings yet
- Communication Models and The Tenets of CommunicationDocument20 pagesCommunication Models and The Tenets of CommunicationJealyn ManaloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8 - Communication ModelsDocument11 pagesLesson 8 - Communication ModelsALLIA LOPEZNo ratings yet
- Oral Week5Document2 pagesOral Week5Anika RomeroNo ratings yet
- The Criminal Act: The Role and Influence of Routine Activity TheoryFrom EverandThe Criminal Act: The Role and Influence of Routine Activity TheoryM. AndresenNo ratings yet
- The Ins and Outs of Business and Professional Discourse Research: Reflections on Interacting with the WorkplaceFrom EverandThe Ins and Outs of Business and Professional Discourse Research: Reflections on Interacting with the WorkplaceGlen AlessiNo ratings yet
- Pursuit of Pattern Languages for Societal Change - PURPLSOC: A comprehensive perspective of current pattern research and practiceFrom EverandPursuit of Pattern Languages for Societal Change - PURPLSOC: A comprehensive perspective of current pattern research and practiceNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document47 pagesWeek 2Ruben De AsisNo ratings yet
- Barriers To CommuncationDocument3 pagesBarriers To CommuncationRuben De AsisNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument3 pagesModels of CommunicationRuben De AsisNo ratings yet
- XII. Writ of Habeas Corpus, Writ of Amparo & Habeas DataDocument33 pagesXII. Writ of Habeas Corpus, Writ of Amparo & Habeas DataRuben De Asis100% (1)
- 2.1 The Elements of CommunicationDocument2 pages2.1 The Elements of CommunicationRuben De AsisNo ratings yet
- (Note: Discussions May Change Course (Deviate From The Original Plan) Depending On Students' Responses ToDocument2 pages(Note: Discussions May Change Course (Deviate From The Original Plan) Depending On Students' Responses ToRuben De AsisNo ratings yet
- V. Claims Against The EstateDocument9 pagesV. Claims Against The EstateRuben De AsisNo ratings yet
- 1 RecapDocument15 pages1 RecapRuben De AsisNo ratings yet
- 8 Chapter V.2Document16 pages8 Chapter V.2Ruben De AsisNo ratings yet
- III. Powers and Duties of Probate CourtDocument11 pagesIII. Powers and Duties of Probate CourtRuben De AsisNo ratings yet
- Models of CommunicationDocument14 pagesModels of CommunicationRuben De AsisNo ratings yet
- IV. Allowance and Disallowance of WillDocument28 pagesIV. Allowance and Disallowance of WillRuben De AsisNo ratings yet
- 3 Chapter Iii.2Document17 pages3 Chapter Iii.2Ruben De AsisNo ratings yet
- Pre-Trial - Civil CaseDocument16 pagesPre-Trial - Civil CaseRuben De Asis0% (1)
- Pre-Trial-Script 1.1Document4 pagesPre-Trial-Script 1.1Ruben De Asis100% (1)
- Models of Communication - ExamplesDocument2 pagesModels of Communication - ExamplesRuben De AsisNo ratings yet
- Types of Conversation RepairsDocument1 pageTypes of Conversation RepairsRuben De AsisNo ratings yet
- Intercultural CommunicationDocument14 pagesIntercultural CommunicationRuben De AsisNo ratings yet