Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Engineering and Maintenance Calculations of Mud
Uploaded by
John Severson0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views11 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views11 pagesEngineering and Maintenance Calculations of Mud
Uploaded by
John SeversonCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
PEGN-502 Rest of The Semester
Agenda
Date Subject
03/20 Eng. and Maintenance Calculations of Mud
03/27 Mid Term Exam
04/03 Mid Term Presentations
04/10 Fracture and Fracturing Fluid
04/17 Solid Control Equipments
04/24 Completion and Packer Fluid
05/01 Cementing Operations
Eng. And Maintenance Calculations
Material Balance Equations
V1 D1 + V2 D2 + ..... + Vn Dn = VF DF
and
V1 + V2 + ..... + Vn = VF
Where:
V1= Volume of mud 1, D1= Density of mud 1
V2= Volume of mud 2, D2= Density of mud 2
VF= Final mud volume, DF= Final mud density
Eng. And Maintenance Calculations
• Mix Two Mud Together
Example Problem:
1. Calculate the final density of the mud after
mixing 300 bbl of 14.0 ppg mud with 450 bbl of
11.5 ppg mud.
Eng. And Maintenance Calculations
• Weight up a mud
Example Problem:
2. Calculate how many 100 pound sacks of barite
are required to increase the density of 1200 bbl
of 10.7 ppg to 16.0 ppg.
Eng. And Maintenance Calculations
• Dilute a mud with water
Example Problem:
3. Calculate the volume of water required to
reduce the density of 1500 bbl of 17.4 ppg mud
to 16.7 ppg.
Eng. And Maintenance Calculations
• Make an exact volume of mud
Example Problem:
4. Calculate how many barite and water is required
to mix exactly 900 bbl of 11.5 ppg mud.
Eng. And Maintenance Calculations
• Weight up mud and maintain the same volume.
Example Problem:
5. Weight up 620 bbl of 10.0 ppg and 13.5 ppg
while maintaining a system volume of exactly
620 bbl. How much barite will be needed, and
how much mud must be dumped.
Eng. And Maintenance Calculations
• Dilute a mud and maintain the same volume.
Example Problem:
6. Dilute 1100 bbl of 15.8 ppg mud to 14.0 ppg and
maintain the same volume.
Eng. And Maintenance Calculations
• Make an exact volume oil mud.
Example Problem:
7. Determine how much oil, water and barite will
be required to mix 800 bbl of 16.0 ppg oil mud
with an 85/15 oil/water ratio and oil density of
6.9 ppg.
Calculation Related to Circulation, Hole
and Equipment Volumes
• Annular volume, bbl = 0.000971( DH2 − ODP2 ).L
• Pit volume calculations, bbl L .W . D
=
5 . 615
• Pump output, bbl = 0.000243D 2 .L
• Circulating time calculations
Annu.vol (bbl )
– Bottoms up, min =
POP (bbl / min)
Annu.vol (bbl )
– Hole circulation, min =
POP (bbl / min)
POP
– Annular velocity, ft/min =
Ann.cap
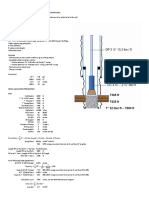
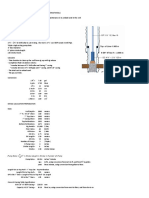
Example Problem
Given the following information: Calculate:
• TVD = 15,000’ – Bottom up, min
• Hole = 8.5” – Kelly to shaker, min
– Total circulation
• Casing: 9 5/8” (N80, 43.5 lb/ft) at
– Annular velocity
10,500’ – ID = 8.625”
• Procedures:
• DP OD = 4.5” (16 lb/ft) @ 14,200’
1. Casing capacity
DP ID = 3.826”
2. Hole capacity
DC OD = 6” (85 lb/ft) @ 800’
3. Total capacity
DC ID = 2”
4. Annular capacity (Casing & DP, OH & DP, OH & DC)
• Pump: Triplex, Liner = 6”, SL.= 16”
5. Drill string displacement
St/min = 80
6. Drill string capacities
Efficiency = 85%
7. Pit volumes
• Pits: 3
8. Pump output + Pump output with efficiency (bbl/st)
Length = 20’
9. Pump output (bbl/min)
Width = 10’
10. Bottom up, min
Depth = 6’
11. Hole circulation
Capacity = 70%
12. Complete circulation
13. Annular velocity
You might also like
- Drilling FormulasDocument87 pagesDrilling Formulaswhydowelove89% (9)
- Reservoir Engineering Exercise Set 1Document9 pagesReservoir Engineering Exercise Set 1Mohammad HaqNo ratings yet
- Design Project 9.3 Lukman Martinus G G 02111540000115Document12 pagesDesign Project 9.3 Lukman Martinus G G 02111540000115Lukman Martinus GunawanNo ratings yet
- 3 - Well Control ExercisesDocument98 pages3 - Well Control ExercisesJoão MayrinkNo ratings yet
- 05 - WellSharp Workover and Completion - Day 4 Pre - Course PDFDocument6 pages05 - WellSharp Workover and Completion - Day 4 Pre - Course PDFMarkus Landington100% (1)
- Design Calculations For Snap Fit Joints in Plastic Parts Ticona PDFDocument30 pagesDesign Calculations For Snap Fit Joints in Plastic Parts Ticona PDFSuteu Ionel100% (1)
- Kill Sheet QuistionsDocument18 pagesKill Sheet Quistionscmrig74No ratings yet
- PETE 355 Rig SelectionDocument68 pagesPETE 355 Rig SelectionNural Muradli100% (1)
- Teori Lag Time + TUGASDocument13 pagesTeori Lag Time + TUGASAndi NovitaNo ratings yet
- Well Clean Up Due To Sand Problem (Engineering System Unit)Document3 pagesWell Clean Up Due To Sand Problem (Engineering System Unit)hilyauliaNo ratings yet
- CT Operations ExerciseDocument20 pagesCT Operations ExerciseMohammed Anis FortasNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4 AnswersDocument12 pagesExercise 4 AnswersadeelsnNo ratings yet
- III. Basic CalculationDocument14 pagesIII. Basic Calculationdidin kenyalNo ratings yet
- 3 Drilling Fluid Volumes - SPDocument25 pages3 Drilling Fluid Volumes - SPmaria del pilar GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Volume and StrokeDocument39 pagesVolume and StrokeHarpreetSinghNo ratings yet
- Answers To WC - SIMULATOR KICK SHEET DATA DrillerlevelDocument4 pagesAnswers To WC - SIMULATOR KICK SHEET DATA DrillerlevelSilveira VictorinoNo ratings yet
- Name: - Student IDDocument11 pagesName: - Student IDMohammad HaqNo ratings yet
- Lag Time CalculationDocument13 pagesLag Time CalculationHasna Afif100% (1)
- Mud Logging: An OverviewDocument103 pagesMud Logging: An OverviewHamid Reza BabaeiNo ratings yet
- @@@@API Technical Data Book Tanques Bombas y Tuberías PDFDocument78 pages@@@@API Technical Data Book Tanques Bombas y Tuberías PDFjorge pajonNo ratings yet
- Formulas For Wait and Weight Well Control MethodDocument5 pagesFormulas For Wait and Weight Well Control MethodHenry Brito100% (1)
- CT Ops Exercise - No AnswersDocument9 pagesCT Ops Exercise - No AnswersMohammed Anis FortasNo ratings yet
- Sand Problem - SIDocument3 pagesSand Problem - SIhilyauliaNo ratings yet
- IWCF Well Control Surface Kick SheetDocument3 pagesIWCF Well Control Surface Kick SheetshaNo ratings yet
- Well Intervention Calculations SpreadsheetDocument5 pagesWell Intervention Calculations SpreadsheetAkol MajookNo ratings yet
- Well Control Exercise 4Document12 pagesWell Control Exercise 4adeelsnNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Ibrahim Bin Noor Alshurdin (133419)Document3 pagesMuhammad Ibrahim Bin Noor Alshurdin (133419)Muhammad IbrahimNo ratings yet
- WF DesignDocument49 pagesWF DesignAviiCaphNo ratings yet
- Rig Maths Presentation on Hydrostatic Pressure, Pump Discharge, Capacity FormulasDocument10 pagesRig Maths Presentation on Hydrostatic Pressure, Pump Discharge, Capacity FormulassubhashNo ratings yet
- Balanced Cement Plug Example CalculationsDocument4 pagesBalanced Cement Plug Example CalculationsJennyNo ratings yet
- PTE-601 Example 1Document3 pagesPTE-601 Example 1Taha AlpolandeNo ratings yet
- RMTUDocument10 pagesRMTUAnyasi UcheNo ratings yet
- Short Course ON Reservoir Management: Tutorial QuestionsDocument10 pagesShort Course ON Reservoir Management: Tutorial QuestionsAnyasi UcheNo ratings yet
- Adsorption PresentationDocument22 pagesAdsorption Presentationapi-457061381No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Onshore DrillingDocument23 pagesFundamentals of Onshore Drillingعبد العزيز مروىNo ratings yet
- Capacities and Annular Volumes and Pump OutputsDocument7 pagesCapacities and Annular Volumes and Pump OutputsBen BieberNo ratings yet
- Contoh Soal LagtimeDocument6 pagesContoh Soal LagtimenyimasNo ratings yet
- Latihan HitunganDocument9 pagesLatihan HitunganMuhamad FadilahNo ratings yet
- Latihan HitunganDocument9 pagesLatihan HitunganMuhamad FadilahNo ratings yet
- Faizan Naikwadi PA 12 IWCF L3 & 4 Day 1 HomeworkDocument16 pagesFaizan Naikwadi PA 12 IWCF L3 & 4 Day 1 Homeworkparesh pawarNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Pressure: Assignment #2 PE313 Drilling and Well DesignDocument3 pagesHydrostatic Pressure: Assignment #2 PE313 Drilling and Well Designعلي عباس جاسم غليمNo ratings yet
- 1.basic Formulas PDFDocument30 pages1.basic Formulas PDFKevin AtochaNo ratings yet
- Basic Drilling FormulasDocument30 pagesBasic Drilling FormulasKevin AtochaNo ratings yet
- Causes of KickDocument8 pagesCauses of KickSZ EccvNo ratings yet
- P and P Calc. AnDocument19 pagesP and P Calc. AnJaber AlbaajNo ratings yet
- 6) Iwcf l3 & 4 Surface Kick Sheet 2Document4 pages6) Iwcf l3 & 4 Surface Kick Sheet 2shaNo ratings yet
- MOGE-3 Study - Ideas R UsDocument16 pagesMOGE-3 Study - Ideas R UsSARTHAK BAPATNo ratings yet
- SLB WCS Homework Balanced PlugDocument10 pagesSLB WCS Homework Balanced PlugMohsen AndishgarNo ratings yet
- 3.3 - Circulating System - Hole Volume, Hydrostatic and SlugsDocument26 pages3.3 - Circulating System - Hole Volume, Hydrostatic and Slugsrabiu nuhuNo ratings yet
- PumpDocument3 pagesPumpfazila fauziNo ratings yet
- 1) Anusha A/P Nagaih 2) Melinda Mallini A/P Loudersamy 3) Sangeetha A/P Balaram 4) Vinohthinii A/P R Tamilselvan 5) Youssif SamiDocument17 pages1) Anusha A/P Nagaih 2) Melinda Mallini A/P Loudersamy 3) Sangeetha A/P Balaram 4) Vinohthinii A/P R Tamilselvan 5) Youssif Samitashh raoNo ratings yet
- Southern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume IFrom EverandSouthern Marine Engineering Desk Reference: Second Edition Volume INo ratings yet
- Handbook of Heating, Ventilating and Air ConditioningFrom EverandHandbook of Heating, Ventilating and Air ConditioningRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Formulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsFrom EverandFormulas and Calculations for Drilling, Production, and Workover: All the Formulas You Need to Solve Drilling and Production ProblemsNo ratings yet
- Pares 60.11Document633 pagesPares 60.11John SeversonNo ratings yet
- SolidsDocument135 pagesSolidsapi-3714673100% (4)
- BHI Screen SelectionDocument54 pagesBHI Screen SelectionJohn SeversonNo ratings yet
- Rheology-Hydraulics OverviewDocument6 pagesRheology-Hydraulics OverviewJohn SeversonNo ratings yet
- BHI Screen TechnologyDocument113 pagesBHI Screen TechnologyJohn SeversonNo ratings yet
- Perforating 101Document152 pagesPerforating 101John SeversonNo ratings yet
- Shavandi and Thodla DNV Bsee HPHTDocument23 pagesShavandi and Thodla DNV Bsee HPHTJohn SeversonNo ratings yet
- NAG-Product Selection Chart - 21Document1 pageNAG-Product Selection Chart - 21John SeversonNo ratings yet
- 8059 Pricing of DelayDocument31 pages8059 Pricing of DelayJohn SeversonNo ratings yet
- Geobrugg TECCO Product ManualDocument59 pagesGeobrugg TECCO Product ManualJohn SeversonNo ratings yet
- ApproachesToGroutingInKarst ARCHIVEDDocument40 pagesApproachesToGroutingInKarst ARCHIVEDJohn SeversonNo ratings yet
- Hoshman HPHT Guidance 4 17 15Document27 pagesHoshman HPHT Guidance 4 17 15John SeversonNo ratings yet
- ASCE - Avoiding Ethical Pitfalls in Failure InvestigationsDocument46 pagesASCE - Avoiding Ethical Pitfalls in Failure InvestigationsJohn SeversonNo ratings yet
- Integrity Assessment of Deep FoundationsDocument47 pagesIntegrity Assessment of Deep FoundationsJohn SeversonNo ratings yet
- Desktop Guide To Aggregate Pier Ground ImprovementDocument17 pagesDesktop Guide To Aggregate Pier Ground ImprovementJohn SeversonNo ratings yet
- Topic 3.3 - Energy Systems: 3.3.1 Draw A Diagram To Show The Ultrastructure of A Generalized Animal CellDocument8 pagesTopic 3.3 - Energy Systems: 3.3.1 Draw A Diagram To Show The Ultrastructure of A Generalized Animal CellTiago José ReisNo ratings yet
- Camille Pissarro Paintings For ReproductionDocument827 pagesCamille Pissarro Paintings For ReproductionPaintingZ100% (1)
- GFT 4 Rail Installation Guide 20171219 1Document31 pagesGFT 4 Rail Installation Guide 20171219 1Comsip400No ratings yet
- NASPUBDOKDocument14 pagesNASPUBDOKmakan yogsNo ratings yet
- Drilling Fluid Processing System BrochureDocument20 pagesDrilling Fluid Processing System BrochureazkNo ratings yet
- 20 Rules of Parenting (Specific To Mothers)Document2 pages20 Rules of Parenting (Specific To Mothers)Karen KitchellNo ratings yet
- Parte 2 Segundo ParcialDocument23 pagesParte 2 Segundo ParcialJose Luis Rasilla GonzalezNo ratings yet
- PowerStop Shock Absorber CatalogDocument24 pagesPowerStop Shock Absorber CatalogAfiyat Nur100% (1)
- Clear ViewDocument6 pagesClear ViewJamieNo ratings yet
- Pre-Job Hazard AnalysisDocument4 pagesPre-Job Hazard AnalysisFiras HamanNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document29 pagesModule 2Melody SorianoNo ratings yet
- B.Sc CHARTS (OTHER PARAMEDICALS) Electrolyte ImbalancesDocument20 pagesB.Sc CHARTS (OTHER PARAMEDICALS) Electrolyte ImbalancesKiruba HaranNo ratings yet
- Foreign Bodies of Air Passages and Food PassageDocument20 pagesForeign Bodies of Air Passages and Food PassageRamli HassanNo ratings yet
- Mole Calculation Worksheet: Practice & SolutionsDocument3 pagesMole Calculation Worksheet: Practice & SolutionsQurrat Ul AinNo ratings yet
- Gualberto Vs GualbertoDocument16 pagesGualberto Vs GualbertoTalina BinondoNo ratings yet
- AppendicesDocument6 pagesAppendicesMark James Bugarin BarayugaNo ratings yet
- Performance Checklist On Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocument3 pagesPerformance Checklist On Cranial Nerve AssessmentSolsona Natl HS Maananteng100% (1)
- Periodontal IndicesDocument29 pagesPeriodontal IndicesFachrul Latif DentistNo ratings yet
- Imogene Martina KingDocument7 pagesImogene Martina KingJoanna Marie TulioNo ratings yet
- Health10 q3 Mod1 Healthtrendsissues v5Document27 pagesHealth10 q3 Mod1 Healthtrendsissues v5Wensyl Mae De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Pest Management Practices of Farmers in PambujanDocument13 pagesPest Management Practices of Farmers in PambujanLucille MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cancer Treatment HomeopathyDocument121 pagesCancer Treatment Homeopathykshahulhameed100% (1)
- Radial UnoDocument5 pagesRadial Unobhupi dagarNo ratings yet
- Bio-Diesel Production From Waste Cooking OilDocument51 pagesBio-Diesel Production From Waste Cooking OilDemostenes DeceoNo ratings yet
- Cause: Lymphatic System Oriental Rat Flea Human Flea Septicemic PlagueDocument3 pagesCause: Lymphatic System Oriental Rat Flea Human Flea Septicemic PlagueMattNo ratings yet
- What is Special EducationDocument2 pagesWhat is Special EducationImelda Nantin GarciaNo ratings yet
- JnaDocument34 pagesJnaDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- LEC 5 Elements of An Offence and Their QualificationsDocument27 pagesLEC 5 Elements of An Offence and Their QualificationsEliezer Charles Ngahyoma67% (3)
- Network Marketing BusinessesDocument1 pageNetwork Marketing BusinessessukhberNo ratings yet