0% found this document useful (0 votes)
183 views6 pagesBarton Chart
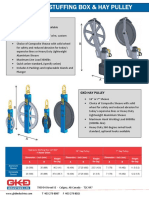
Chart recorders are electromechanical devices that record electrical or mechanical inputs on paper charts. They have various components like pressure and temperature elements, recording mechanisms, chart drives, and cases. Periodic maintenance includes cleaning elements, checking components, and calibrating the static pressure pen. Chart recorders require replacement of charts, pens, and occasional calibration to ensure accurate readings.
Uploaded by
Dwi Agung AriyonoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
183 views6 pagesBarton Chart
Chart recorders are electromechanical devices that record electrical or mechanical inputs on paper charts. They have various components like pressure and temperature elements, recording mechanisms, chart drives, and cases. Periodic maintenance includes cleaning elements, checking components, and calibrating the static pressure pen. Chart recorders require replacement of charts, pens, and occasional calibration to ensure accurate readings.
Uploaded by
Dwi Agung AriyonoCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd