Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Discovery of Neutrons
Uploaded by
Emnet Solomon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views12 pagesDiscovery of neutrons
Original Title
Discovery of neutrons
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentDiscovery of neutrons
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views12 pagesDiscovery of Neutrons
Uploaded by
Emnet SolomonDiscovery of neutrons
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
DISCOVERY OF NEUTRONES
JAMES CHAD WICK ( English scientist 1932)
Who Discovered Neutrons?
• Neutrons were first theorized by the New Zealand born British physicist
Ernest Rutherford in the year 1920.
• The discovery of neutrons is credited to the British physicist James Chadwick in the
year 1932.
• He was awarded the Nobel prize in physics for this discovery in the year 1935.
• In the year 1931, two German nuclear physicists observed that when the alpha
particle radiation that is emitted by polonium is made incident on beryllium,
lithium, or boron, it resulted in the production of an unusually penetrating
form of radiation.
• Later, it was proven by James Chadwick through a series of
experiments that these particles that constituted the
unusually penetrating radiation were neutrons.
• Polonium is a radioactive material that occurs naturally in
the earth's crust at very low levels. Po-210 is a product of
the radioactive decay of uranium, which decays to radon
and then to polonium.
• If the neutron's mass was less than the combined masses of a
proton and an electron (1.0078 u), then the neutron could be a
proton-electron composite because of the mass defect from the
nuclear binding energy. If greater than the combined masses, then
the neutron was elementary like the proton.
• The question was challenging to answer because the electron's
mass is only 0.05% of the proton's, hence exceptionally precise
measurements were required
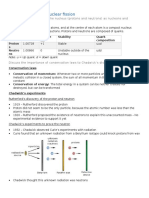
Charge and Mass of Neutrons
The electric charge that is associated with a neutron is 0. Therefore,
neutrons are neutrally charged subatomic particles.
The mass of a neutron is roughly equal to 1.008 atomic mass units.
When converted into kilograms, the mass of the neutron can be
approximated to 1.674*10 10-27kg.
Since neutrons lack electric charge, their mass cannot be directly
determined via the analytical technique of mass spectrometry.
Isotopes
• Thomson is also credited with the discovery of the isotope in 1912.
• An isotope has the same number of protons and electrons as the
original element, but it has a different number of neutrons.
• Every element has isotopes
• Isotopes of an element have the same atomic number, but
different mass number.
• For example, Carbon has 3 main isotopes: Carbon-12, Carbon-13, and
Carbon-14
• Nuclear Symbol or Isotopic symbol shows number of protons,
neutrons and electrons in an atom
ISOTOPE CHART
Atomic mass
• The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of the atoms of an
element measured in atomic mass unit (amu, also known as Daltons, D).
• The atomic mass is a weighted average of all of the isotopes of that
element, in which the mass of each isotope is multiplied by the
abundance of that particular isotope. (Atomic mass is also referred to as
atomic weight, but the term "mass" is more accurate.)
• Atomic number (Ζ) of an element is equal to the number of protons in
the nucleus of atom. And it also equal to the number of electrons in
neutral atom. {Ζ = p+ 𝑜𝑟 Ζ = e_}
• Mass number (𝜜)= is the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the
nucleus of an atom. {𝜜=p+ + n𝝄 }
• Relative atomic mass (Αr) or r.a.m.) also known by the deprecated
synonym atomic weight, is a dimensionless physical quantity defined as the
ratio of the average mass of atoms of a chemical element in a given
sample to the atomic mass constant.
• Relative atomic mass is determined by the average atomic mass, or the
weighted mean of the atomic masses of all the atoms of a particular
chemical element found in a particular sample, which is then compared to
the atomic mass of carbon-12.
• This comparison is the quotient of the two weights, which makes the value
dimensionless (having no unit). This quotient also explains the word relative
the sample mass value is considered relative to that of carbon-12
#Questions
1. Gallium has two stable isotopes, and the mases of Gallium-69 (60.11 %
abundant ) and Gallium-71(39.89% abundant) are 68.926 amu and 70.925
amu, respectively. Calculate the average atomic mass.
2. Magnesium has three stable isotopes. Calculate its average atomic mass.
Using the information in chat below.
3. There are two stable isotopes of chlorine cl-35 (which weighs 34.97 amu),
and Cl-37 (36.97amu). If the relative atomic mass of chlorine is 35.45 amu,
what is the abduce of each isotopes
4. There are two naturally occurring isotopes of lithium Li-6(6.015 amu) and Li-7
(7.016 amu). What is the abundance of each?
You might also like
- 5 Early Atomic TheoryDocument55 pages5 Early Atomic TheoryGlen Mangali100% (1)
- 6B Atomic StructureDocument137 pages6B Atomic StructureOrane CassanovaNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Atoms ExplainedDocument168 pagesThe Structure of Atoms ExplainedBlaize Aurellius B. CordeneteNo ratings yet
- Chem 101 Chapter 2: Faculty of Engineering and Natural SciencesDocument80 pagesChem 101 Chapter 2: Faculty of Engineering and Natural SciencesNora Zor-elNo ratings yet
- CHAP4 AtomicStructureDocument34 pagesCHAP4 AtomicStructureJex AsupardoNo ratings yet
- PM1 and Prepharm. CHEMISTRY Course OverviewDocument225 pagesPM1 and Prepharm. CHEMISTRY Course OverviewMary KallonNo ratings yet
- L2-Atoms and Atomic StructureDocument49 pagesL2-Atoms and Atomic Structurekoladejoy49No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument17 pagesAtomic StructureAvel Xyphus N. MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, ElectronsDocument9 pagesAtomic Structure: Protons, Neutrons, ElectronshenryNo ratings yet
- Elements and MoleculesDocument26 pagesElements and MoleculesTrevor NamalawaNo ratings yet
- a) La secuencia correcta es la (I) Be2+ < Li+ < F- < N3- ya que a medida que aumenta el número atómico disminuye el radio iónico. b) El orden de mayor a menor radio es: N3- > F- > Li+ > Be2Document44 pagesa) La secuencia correcta es la (I) Be2+ < Li+ < F- < N3- ya que a medida que aumenta el número atómico disminuye el radio iónico. b) El orden de mayor a menor radio es: N3- > F- > Li+ > Be2Andrea PomboNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Note-1Document27 pagesChemistry Note-1mematugoldahmunu21No ratings yet
- The Structure of AtomsDocument159 pagesThe Structure of Atomsallendale123No ratings yet
- Additional MathematicsDocument6 pagesAdditional Mathematicslonydon23No ratings yet
- Atomic Structure PDFDocument59 pagesAtomic Structure PDFNashraat BukhoryNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory of Matter: Tufts University - Chem 1 - Fall 2011 Lecture 3 - AtomsDocument4 pagesAtomic Theory of Matter: Tufts University - Chem 1 - Fall 2011 Lecture 3 - AtomsAaron WishnickNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyDocument28 pagesAtomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyJerry De Leon LptNo ratings yet
- Electronic Structure of Atoms: General ChemistryDocument52 pagesElectronic Structure of Atoms: General ChemistryNAM TRƯƠNG HOÀINo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: The Structure of The Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation EnergiesDocument22 pagesAtomic Structure: The Structure of The Atom Mass Spectrometry Electronic Structure Ionisation EnergiesVijithaNo ratings yet
- Democritus' Atomic TheoryDocument13 pagesDemocritus' Atomic TheoryAnthony BasantaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One ChemistryDocument28 pagesChapter One Chemistryclarethomas1994No ratings yet
- 1.1 The Nature of Atoms Jan 2019Document37 pages1.1 The Nature of Atoms Jan 2019Dima SabeehNo ratings yet
- Physics of The Atom Grade11Document36 pagesPhysics of The Atom Grade11Jodell CampbellNo ratings yet
- Chem ModuleDocument20 pagesChem Modulekeeno manzanoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory of MatterDocument36 pagesAtomic Theory of MatterngvkietNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyDocument28 pagesAtomic Structure: Vinay Desai M.SC Radiation Physics Kidwai Memorial Institute of OncologyJerry De Leon LptNo ratings yet
- Structure of AtomDocument5 pagesStructure of AtomSaurabh DhyaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document31 pagesChapter 2sabhari_ramNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Physics NotesDocument14 pagesNuclear Physics NotesJonathan ThomasNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument55 pagesAtomic StructureNikolai Matthew BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Atomic Structure and Electrons in The AtomDocument75 pagesUnit 3 Atomic Structure and Electrons in The Atomapi-327076063No ratings yet
- II. ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONSDocument18 pagesII. ATOMS, MOLECULES and IONSHania ABDULNo ratings yet
- Concept of Atomic StructureDocument24 pagesConcept of Atomic StructureNoor Mohammad NofaerNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 05 Structure of AtomsDocument146 pagesCHAPTER 05 Structure of AtomsRogelio Arellano LawayanNo ratings yet
- (General Chemistry) : Kimia Umum (TKK 134)Document25 pages(General Chemistry) : Kimia Umum (TKK 134)metromini44No ratings yet
- Mass Relationship in Chemical Reaction - Atomic MassDocument5 pagesMass Relationship in Chemical Reaction - Atomic MassLovely RamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 For OnlineDocument35 pagesChapter 2 For OnlineKarina Roxana Marquez TumeNo ratings yet
- Welcome!: M H M Mubassir (MNS, Bracu)Document29 pagesWelcome!: M H M Mubassir (MNS, Bracu)raven ravenNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument58 pagesAtomic Structurecipet imphalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11Document44 pagesChapter 11swezinomg2002No ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument55 pagesAtomic StructureBhuwan GhimireNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Atomic StructureDocument47 pagesChapter 4 Atomic StructureJulius Erick EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Physics AssignmentDocument22 pagesPhysics AssignmentanessnabelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter-4: Structure of An AtomDocument20 pagesChapter-4: Structure of An AtomTanisha JainNo ratings yet
- 2nd Day HandoutDocument67 pages2nd Day HandoutIsabel Velan ViernesNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Atomic Mass Atomic Number and Isotopes PDFDocument23 pages1.3 Atomic Mass Atomic Number and Isotopes PDFMARVIN DELA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Lecture 04 - Atoms, Molecules & IonsDocument69 pagesLecture 04 - Atoms, Molecules & IonsmytiensakuraNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1 Atomic Structures and Theory-FinalDocument138 pagesChapter-1 Atomic Structures and Theory-FinalJATIN DALMIANo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory 1Document48 pagesAtomic Theory 1Liz EvermoreNo ratings yet
- CHEM100Lec Atomic-StructureDocument52 pagesCHEM100Lec Atomic-StructureLady Edzelle AliadoNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure: Name: Mr. Burnett Date: 03/05/2021 Class: 6A PhysicsDocument50 pagesAtomic Structure: Name: Mr. Burnett Date: 03/05/2021 Class: 6A PhysicsACSVNo ratings yet
- Hukum-Hukum Dasar KimiaDocument55 pagesHukum-Hukum Dasar KimiaOkta Abdul ChoirNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Atoms, Molecules, and IonsDocument70 pagesTopic 1 Atoms, Molecules, and IonsRendysaputraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Atomic Structure Snr1Document50 pagesChapter 5 Atomic Structure Snr1Abdul HaseebNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure and the Periodic TableDocument8 pagesAtomic Structure and the Periodic TableVishal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mole and Atomic ModelDocument73 pagesMole and Atomic ModelApeksha MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1From EverandConcepts of Nuclear Medicine Volume I: Concepts of Nuclear Medicine, #1No ratings yet
- G-10 Physics Unit 2 Note - 07-08-14E.CDocument35 pagesG-10 Physics Unit 2 Note - 07-08-14E.CEmnet SolomonNo ratings yet
- Generation of MobileDocument10 pagesGeneration of MobileEmnet SolomonNo ratings yet
- AtomDocument24 pagesAtomEmnet SolomonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 G 11Document4 pagesChapter 3 G 11Emnet SolomonNo ratings yet
- IGCSE O Level Essential Chemistry Third Edition Answer Key by OxfordDocument40 pagesIGCSE O Level Essential Chemistry Third Edition Answer Key by OxfordHninn Aye WaiNo ratings yet
- Exercises NarayanaDocument34 pagesExercises NarayanaTanishqNo ratings yet
- 3.6.2 Radiation 00-10Document16 pages3.6.2 Radiation 00-10Murray PhysicsNo ratings yet
- L2 BIO 101 Chemical Foundations For CellsDocument45 pagesL2 BIO 101 Chemical Foundations For CellsAhamadul Islam OnonnoNo ratings yet
- Radioactivity 1 QPDocument9 pagesRadioactivity 1 QPAnonymous N3VvjVSTATNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - Synthesis of Elements in The LaboratoryDocument62 pagesLesson 3 - Synthesis of Elements in The Laboratorytheresa balatico100% (1)
- Class IX Vistaar ExpertDocument100 pagesClass IX Vistaar ExpertSrinivas VenkataramanNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Saturation ToolDocument50 pagesReservoir Saturation Toolroshan01100% (1)
- 2.3.5 Practice - Atomic Structure (Practice)Document11 pages2.3.5 Practice - Atomic Structure (Practice)damarionbryant46No ratings yet
- Arc Reactor THEORYDocument32 pagesArc Reactor THEORYAbhay Tiwari100% (1)
- DPP - Structure of Atom - Chemistry - Victory PDFDocument5 pagesDPP - Structure of Atom - Chemistry - Victory PDFAnshul VermaNo ratings yet
- Transmutation and Nuclear Fission - NotesDocument6 pagesTransmutation and Nuclear Fission - Notesapi-327272079No ratings yet
- Assignment Topic:: Use of RadioisotopesDocument6 pagesAssignment Topic:: Use of RadioisotopesSSEFSDNo ratings yet
- Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons Practice WorksheetDocument3 pagesProtons, Neutrons, and Electrons Practice WorksheetAnthony Gio L. AndayaNo ratings yet
- Homework 37Document7 pagesHomework 37Socdal AbdiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Nuclear RadiationDocument164 pagesChapter 3 Nuclear RadiationJoseph MabajenNo ratings yet
- Heinrich Päs - The One - How An Ancient Idea Holds The Future of PhysicsDocument337 pagesHeinrich Päs - The One - How An Ancient Idea Holds The Future of PhysicsAnonymous tp9Xatf3UNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Electron Structure and Periodicity HWDocument10 pagesAtoms, Electron Structure and Periodicity HWMuhandiramalageNo ratings yet
- Atoms, Elements and CompoundsDocument20 pagesAtoms, Elements and CompoundsMenaga Ilangkovan100% (1)
- IB Physics Definitions GuideDocument13 pagesIB Physics Definitions Guidegloria11111No ratings yet
- Crossword Nuclear Physics CrosswordDocument2 pagesCrossword Nuclear Physics CrosswordashokNo ratings yet
- Ajc H2 Chem P2 QPDocument20 pagesAjc H2 Chem P2 QPclarissa yeoNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chapter SolutionsDocument34 pagesNuclear Chapter SolutionslvnarsingaraoNo ratings yet
- Atomic StructureDocument6 pagesAtomic StructureAttiqueNo ratings yet
- ST. MICHAEl'S INsTlnmoN, IPOH STPM Trial Examination PhysicsDocument10 pagesST. MICHAEl'S INsTlnmoN, IPOH STPM Trial Examination PhysicsHaRry ChgNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan IsotopesDocument11 pagesLesson Plan Isotopescekgu yayangdevtiarani100% (1)
- Atomic StructureDocument55 pagesAtomic StructureNikolai Matthew BaltazarNo ratings yet
- WEEK2Document26 pagesWEEK2Krishia Rhey “Shang” DulaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Theory and Structure QuizDocument3 pagesAtomic Theory and Structure QuizPradeep PatilNo ratings yet
- M2 ATOMS NewnewDocument11 pagesM2 ATOMS NewnewsittienaharamotalibNo ratings yet