Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Integumentary System
Uploaded by
Ella PanesOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Integumentary System
Uploaded by
Ella PanesCopyright:
Available Formats
October 20, 2021
Anatomy and Physiology ANAPH111
Leoncia Daniela F. Panes
BSN 1-A-16
Ms. Girlie Doza
Integumentary
Lab Report #4
System
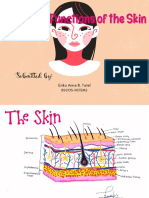
1. Epidermis - The outermost layer of the skin, provides a waterproof barrier and creates our skin tone.
2. Dermis (corium) - to support and protect the skin and deeper layers, assist in thermoregulation, and aid
in sensation.
3. Subcutaneous layer - It provides the main structural support for the skin, as well as insulating the body
from cold and aiding shock absorption.
4. Nerve - To sense and transmit heat, pain, and other noxious sensations.
5. Hair follicle - Produce hair fibers in a regular cycle. As part of their hair-producing role, hair follicles retain
stem cells, promote cell growth and tissue invasion and induce angiogenesis.
6.Pressure receptor - Sense pressure and vibration changes deep in the skin. Skin receptors don’t only
respond to touch. They also register pain as well as warmth and cold.
7. Artery - Vasoconstriction by arterioles (small arteries) in the dermis layer provides a smaller surface area in
the blood vessels, resulting in less heat loss. Vasodilatation by arterioles in the dermis layer provides a larger
surface area in the blood vessels, resulting in greater heat loss.
8. Vein -Vessels of the circulatory system that support circulation by conveying blood to the heart. Blood
flowing through the circulatory system transports nutrients, oxygen, and water to cells throughout the
body.
9. Adipose (fat) cells - Connective-tissue cell specialized to synthesize and contain large globules of fat.
10. Fibrous connective tissue - To provide support and shock absorption to our bones and organs.
11. Sudoriferous (sweat) gland - Are sweat producing glands. These are important to help maintain body
temperature.
12. Muscle (arector pili) - This is a tiny muscle that attaches to the base of a hair follicle at one end and
to dermal tissue on the other end. In order to generate heat when the body is cold, the arrector pili muscles
contract all at once, causing the hair to "stand up straight" on the skin.
13. Stratum corneum - The barrier that prevents unwanted materials from entering, and excessive loss of
water from exiting the body.
14. Pore (opening of sweat gland) - Allow sweat and oil to escape through your skin, cooling you off and
keeping your skin healthy while getting rid of toxins. Pores are also the openings of hair follicles.
15. Stratum basale (growing layer) - This layer contains column-shaped basal cells that are constantly dividing
and being pushed toward the surface. The stratum basale is also home to melanocytes that produce
melanin(the pigment responsible for skin color).
16. Sebaceous (oil gland) - To produce and secrete sebum, a group of complex oils including triglycerides and
fatty acid breakdown products, wax esters, squalene, cholesterol esters and cholesterol. Sebum lubricates the
skin to protect against friction and makes it more impervious to moisture.
17. Nerve Endings - Are the millions of points on the surface of your body and inside it which send messages to
your brain when you feel sensations such as heat, cold, and pain.
You might also like
- The Skin NotesDocument7 pagesThe Skin NotesSafeer SefiNo ratings yet
- Anatomical TermsDocument8 pagesAnatomical TermsDAGUMAN, FIONA DEI L.No ratings yet
- Seven MetalsDocument40 pagesSeven MetalsMaik Moura100% (1)
- NUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityDocument5 pagesNUR11O1 Integrated Human Anatomy and Physiology Department of Biology Institute of Arts and Sciences Far Eastern UniversityPrancheska Abigayle Peneyra SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Medical Lab Technician PDFDocument50 pagesMedical Lab Technician PDFMd Ozair Ahmad80% (5)
- Activity 3 Midterm LaboratoryDocument4 pagesActivity 3 Midterm LaboratoryRej CosainNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument19 pagesThe Integumentary SystemInigo Galima SusanNo ratings yet
- M2 - Check-In Activity 2Document5 pagesM2 - Check-In Activity 2Erika TatelNo ratings yet
- DermisDocument1 pageDermisChloe RiddleNo ratings yet
- Body SystemsDocument16 pagesBody Systemsapolinario mabini elementary schoolNo ratings yet
- Integumentary & Skeletal SystemsDocument21 pagesIntegumentary & Skeletal SystemsRachelle Anne TanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Angcahan2021 1Document53 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Angcahan2021 1G E MNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument25 pagesSkinDJ DannyNo ratings yet
- Bio2 M2-3Document4 pagesBio2 M2-3Ako ToNo ratings yet
- Compare and Contrast The Epidermis and DermisDocument3 pagesCompare and Contrast The Epidermis and DermisClark Vincent PabloNo ratings yet
- Homeostasis: by Afshan HassanDocument19 pagesHomeostasis: by Afshan HassanZulnorain IrfanNo ratings yet
- Organ System Nat Sci2Document98 pagesOrgan System Nat Sci2alowinaNo ratings yet
- Nursing AnaPhy Integumentary SystemDocument22 pagesNursing AnaPhy Integumentary SystemGail Chantel Spring PerlasNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesThe Integumentary System Lecture NotesEdric CantilloNo ratings yet
- Integumentary LectureDocument10 pagesIntegumentary LectureTheAsylumLetterNo ratings yet
- TUGAS Agus SusantoDocument3 pagesTUGAS Agus SusantoAgus Tiwansyah AbunasibNo ratings yet
- Science Human Body SystemDocument9 pagesScience Human Body SystemJOSE RENE CASILINo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Lab Report 1Document12 pagesIntegumentary System Lab Report 1api-374265257No ratings yet
- IntegumentaryDocument6 pagesIntegumentarytrisha anne uberasNo ratings yet
- Skin Model LegendDocument1 pageSkin Model Legendapi-300485063No ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument32 pagesIntegumentary Systemherlygail9No ratings yet
- Presentation About Skin PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPresentation About Skin PhysiologyWalaa Bani IrheadNo ratings yet
- 8 Human SystemDocument23 pages8 Human SystemMarkLesterEstrellaMabagosNo ratings yet
- Organs Systems of The BodyDocument12 pagesOrgans Systems of The BodyJan Michael SalomonNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The SkinDocument4 pagesAnatomy of The SkinRae DaWn VaLesNo ratings yet
- The Skin PDFDocument3 pagesThe Skin PDFThomas KurtzNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument1 pageSkinamy28stewartNo ratings yet
- Zoology 100 Notes 1Document8 pagesZoology 100 Notes 1Bethany Jane Ravelo IsidroNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument12 pagesIntegumentary Systemapi-263280953No ratings yet
- Diaphragm - Divides The Thoracic From TheDocument7 pagesDiaphragm - Divides The Thoracic From TheRizzalyn OrtizNo ratings yet
- Science Week 1 and 2Document67 pagesScience Week 1 and 2Monica BanzueloNo ratings yet
- Science 1Document28 pagesScience 1hirosakinagashima14No ratings yet
- Pragyan College of Nusing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Integumentary System/The SkinDocument4 pagesPragyan College of Nusing-Bhopal BSC Nursing 1 Year Subject-Anatomy and Physiology Topic-Integumentary System/The SkinNeelofur Ibran AliNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.3Document6 pagesAnatomy Lec.3aminqasm111No ratings yet
- MODULE 4 Ana PhysioDocument11 pagesMODULE 4 Ana Physiojoshua ordenaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesIntegumentary Systemrosalyn gaboniNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System - The Dermis: T. RickDocument17 pagesThe Integumentary System - The Dermis: T. Rickapi-464344582No ratings yet
- The Physiology of The SkinDocument39 pagesThe Physiology of The SkinElvisNo ratings yet
- BIO 11 Module 3-L1 PDFDocument10 pagesBIO 11 Module 3-L1 PDFZulqarnain TampogaoNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System (Skin) : HistologyDocument6 pagesThe Integumentary System (Skin) : HistologyNurani AtikasariNo ratings yet
- Lab Report #4 Integumentary SystemDocument3 pagesLab Report #4 Integumentary SystemBb. JayNo ratings yet
- Skin Vertebrate Epidermis HypodermisDocument3 pagesSkin Vertebrate Epidermis Hypodermise sNo ratings yet
- 03 The Integumentary SystemDocument48 pages03 The Integumentary SystemLucy Kare100% (1)
- Solution Manual For Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy Physiology 14th Edition Charles WelshDocument5 pagesSolution Manual For Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy Physiology 14th Edition Charles WelshCristianRodriguezpawry100% (80)
- Integumentary System PT 1Document16 pagesIntegumentary System PT 1Widjaya HS TeacherNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Notes Handbook of Medical inDocument22 pagesDermatology Notes Handbook of Medical inMian BazanNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument22 pagesUntitledclaireNo ratings yet
- The Mammalian Skin and LiverDocument7 pagesThe Mammalian Skin and LiverHarun IbrahimNo ratings yet
- A & P Chapter 5: The Integumentary System Review and OutlineDocument7 pagesA & P Chapter 5: The Integumentary System Review and OutlineAngelica GrossNo ratings yet
- Biological Science, An IntroductionDocument25 pagesBiological Science, An IntroductionTristan BabaylanNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 3 AnaphysDocument5 pagesACTIVITY 3 Anaphys리아No ratings yet
- TissuesDocument33 pagesTissuesAnonymous imF0MCd9UNo ratings yet
- HumanbodyDocument6 pagesHumanbodyapi-318703645No ratings yet
- Human Anatomy I: Tissues, Skin & BonesDocument23 pagesHuman Anatomy I: Tissues, Skin & BonessuhaibqaisarNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 IntegumentaryDocument5 pagesActivity 6 Integumentaryhanna castueraNo ratings yet
- DermatologyDocument42 pagesDermatologyJonalynCollodChewacheoNo ratings yet
- Math ???Document1 pageMath ???Ella PanesNo ratings yet
- MoodDocument1 pageMoodElla PanesNo ratings yet
- Social Media Is The Real Cause of Teenage DepressionDocument6 pagesSocial Media Is The Real Cause of Teenage DepressionElla PanesNo ratings yet
- October 6, 2021Document1 pageOctober 6, 2021Ella PanesNo ratings yet
- Ex Ophtalmo Eng 1Document4 pagesEx Ophtalmo Eng 1Roxana PascalNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 21 Sylvia Mader ModifiedDocument29 pagesBiology Chapter 21 Sylvia Mader ModifiedabdallahNo ratings yet
- 9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 SeriesDocument7 pages9700 BIOLOGY: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2013 Seriesyeelin96No ratings yet
- Breathing WsDocument10 pagesBreathing Wssalahuddin_md5935No ratings yet
- PermlDocument11 pagesPermlFayeNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue SystemsDocument3 pagesPlant Tissue Systemselizabeth shaw gonzalez100% (1)
- Digestive System: Arba P. RamadaniDocument28 pagesDigestive System: Arba P. RamadaniQd Vella QnozesDanteNo ratings yet
- Format Usulan Reagen 2016Document3 pagesFormat Usulan Reagen 2016Puskesmas Secang1No ratings yet
- Anterior Abdominal Wall PDFDocument57 pagesAnterior Abdominal Wall PDFShivaprasad J PatilNo ratings yet
- Occupational Therapy - Play, SIs and BMTsDocument3 pagesOccupational Therapy - Play, SIs and BMTsAnnbe Barte100% (1)
- Practical 3: Photosynthesis & Transpiration: Pre-Labs BiologyDocument4 pagesPractical 3: Photosynthesis & Transpiration: Pre-Labs BiologyThu AnhNo ratings yet
- Thesis Statement and OutlinesDocument3 pagesThesis Statement and OutlinesShane DistorNo ratings yet
- PAT Interoception Paper For Submission FINALDocument23 pagesPAT Interoception Paper For Submission FINALDavid PlansNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/11Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/11andrea dyanne AzoresNo ratings yet
- Remote Viewing - Part 2 - Sex MagicDocument2 pagesRemote Viewing - Part 2 - Sex Magicstop-organized-crime50% (2)
- Glossary of EMTDocument5 pagesGlossary of EMTErnan BaldomeroNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Music Video ProjectDocument2 pagesMitosis Music Video Projectapi-237316144No ratings yet
- Phylum ArthopodaDocument17 pagesPhylum ArthopodaIsaacNo ratings yet
- ANTIPSYCHOTICSDocument16 pagesANTIPSYCHOTICSGelah DacanayNo ratings yet
- 2020 MedicalCertificate ATHLETEDocument1 page2020 MedicalCertificate ATHLETEJohn Cyrill manubaNo ratings yet
- MCB 169 Lecture 1 NotesDocument2 pagesMCB 169 Lecture 1 NotesLiz PaigeNo ratings yet
- Survival MDDocument206 pagesSurvival MDEddie Kluss III100% (11)
- Endo Pancrease ElhDocument27 pagesEndo Pancrease Elhodiodi57No ratings yet
- Guided NotesDocument4 pagesGuided NotesMahlodi LamolaNo ratings yet
- Morfologi DaunDocument34 pagesMorfologi DaunTasyaChNo ratings yet
- Daly Cluttering 2006 RDocument35 pagesDaly Cluttering 2006 RMinkushNo ratings yet