0% found this document useful (0 votes)
444 views31 pagesMath DBOW Final
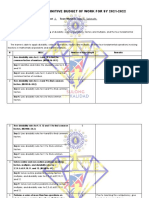
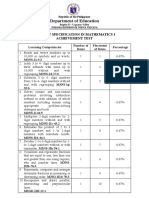
This document contains a Definitive Budget of Work (DBOW) for teaching Mathematics to Grade 3 students in Quarter 1. It outlines 12 key learning competencies (MELCs) to be covered in the quarter related to whole numbers up to 10,000, ordinal numbers up to 100th, and addition of whole numbers including money. Each MELC is assigned a number of teaching days and includes remarks on prerequisites and culminating exercises. The goal is for students to understand and apply skills in visualizing, comparing, ordering, rounding, and adding whole numbers, as well as working with money denominations, through hands-on practice of routine and non-routine word problems.
Uploaded by
Grace RocaporCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
444 views31 pagesMath DBOW Final
This document contains a Definitive Budget of Work (DBOW) for teaching Mathematics to Grade 3 students in Quarter 1. It outlines 12 key learning competencies (MELCs) to be covered in the quarter related to whole numbers up to 10,000, ordinal numbers up to 100th, and addition of whole numbers including money. Each MELC is assigned a number of teaching days and includes remarks on prerequisites and culminating exercises. The goal is for students to understand and apply skills in visualizing, comparing, ordering, rounding, and adding whole numbers, as well as working with money denominations, through hands-on practice of routine and non-routine word problems.
Uploaded by
Grace RocaporCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd