Professional Documents
Culture Documents
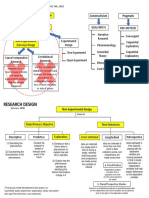
Taxonomy of Research Designs
Uploaded by
Ivy May Dela Cruz0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
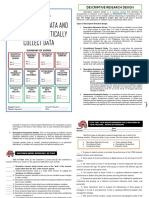
12 views4 pagesThis document provides a taxonomy of different research designs categorized by quantitative and qualitative approaches. It describes the main types of quantitative research as experimental, non-experimental, and descriptive designs. Experimental designs aim to establish causal relationships and include categories such as pre-test post-test, repeated measures, static group comparison, and posttest-only designs. Non-experimental designs are correlational or explanatory in nature. Descriptive designs describe characteristics or trends without inferring causes.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides a taxonomy of different research designs categorized by quantitative and qualitative approaches. It describes the main types of quantitative research as experimental, non-experimental, and descriptive designs. Experimental designs aim to establish causal relationships and include categories such as pre-test post-test, repeated measures, static group comparison, and posttest-only designs. Non-experimental designs are correlational or explanatory in nature. Descriptive designs describe characteristics or trends without inferring causes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views4 pagesTaxonomy of Research Designs
Uploaded by
Ivy May Dela CruzThis document provides a taxonomy of different research designs categorized by quantitative and qualitative approaches. It describes the main types of quantitative research as experimental, non-experimental, and descriptive designs. Experimental designs aim to establish causal relationships and include categories such as pre-test post-test, repeated measures, static group comparison, and posttest-only designs. Non-experimental designs are correlational or explanatory in nature. Descriptive designs describe characteristics or trends without inferring causes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
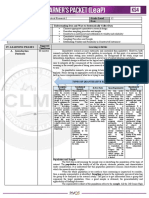
TAXONOMY OF RESEARCH DESIGNS
Research Types of Type of Non- Types of Purpose Purpose Research Design
Approach Quantitative Experimental Descriptive Sub-categories based on Number
Research Research Research of Contacts with
Study Population
To examine the
Correlation relationship between
Research two variables Cross-Sectional
including its direction Design
and magnitude.
To describe the developmental changes brought
about in the population as a function of time and Cross-sectional or
Growth Study age. Longitudinal Design
To describe the status of the development of the
Follow-up subjects going through a particular treatment. Cross-sectional or
Study Longitudinal Design
Quantitative Non-experimental Descriptive To describe the To describe the significant visible trends
Research Research Research Developmental pattern of the Trend Study regarding the development of a particular Longitudinal Design
Research development of a phenomenon.
given population To describe the changes in a population having
across the varying Cohort Study common characteristics over a period of time. Cross-sectional or
ages or life periods. Longitudinal Design
To describe the changes of the same population
Panel Study over a period of time. Longitudinal Design
To describe a Explanatory To explain the cause underlying a phenomenon
Case Study particular individual Case Study or behavior. Case Study Design
unit through in-depth Descriptive To provide a description, or document and Case Study Design
and intensive study. Case Study classify a situation, event or phenomenon.
To describe the Cross-sectional
Survey Study characteristics of the Design
population by using a
survey method.
Purpose Types of Sub-categories based Purpose & Research Design Characteristics
Experimental on design
Research
Purpose: To attempt to explain a consequent by an 1. Only one group
One-shot Case Study antecedent. 2. No randomization
3. No pretest
Group 1Ex: --- X >> O1 4. Only posttest
Comment: Least reliable of all experimental designs
Purpose: To evaluate the influence of a variable. 1. Only one group
To establish the One Group Pre-test- 2. No randomization
Experimental possible causal Pre- posttest pre- Group 1Ex: O1 >> X >> O2 3. Pretesting
Research relationship Experimental experimental 4. Experimental manipulation (X)
between Research or Comments: Provides a measure of change but can 5. Post-test
variables Within-Subject provide no conclusive results. 6. Note the difference between
through Designs scores (O1-O2)
systematic Purpose: To measure the effect of a treatment over 1. Only one group
observations time. Beneficial for longitudinal studies. 2. Pretest (O1)
carried out in Repeated Measures 3. Repeated measures of posttest
controlled Group 1Ex: O1 X O2 X O3 X O4 X O5 (O2, O3, O4, O5)
conditions. 4. Experimental manipulation of X
at different levels (X1, X2, X3, X4)
5. Note the difference between
scores (O1-O2, O2-O3, O3-O4)
Purpose: To determine the influence of a variable 1. Two groups
Static Group on one group and not on another. 2. Non-equivalent groups
Comparison 3. No pretest
Group 1Ex: -- X >> O1 4. Experimental manipulation of X
Group 2Co: -- -- >> O2
Posttest Only Purpose: To evaluate a situation that cannot be 1. Randomized groups
Equivalent Group pretested. 2. Equivalent groups
Design 3. Different treatments (X1, X2)
Group 1Ex: -- X1 >> O1 4. No pretesting
Group 2Co: -- X2 >> O2 5. Comparison of posttest scores
True Pretest-posttest Purpose: To study the effect of an influence on a 1. Randomized groups
Experiment Equivalent Group carefully controlled sample. 2. Equivalent groups
Research or Design 3. Different treatments (X1, X2)
Between- Group 1Ex: O1 >> X1 >> O2 4. Pretesting
Subject Group 2Co: O3 >> X2 >> O4 5. Comparison of pretest and
Design posttest scores
Solomon Three or Purpose: To minimize the effect of pretesting. 1. Randomized groups
Four Equivalent 2. Four groups
Groups Design Group 1Ex: O1 >> X1 >> O2 3. Two groups: Pretest-Posttest
Group 2Co: O3 >> X2 >> O4 4. Two groups: posttest only
Group 3Ex: -- X1 >> O5 5. Equivalent groups
Group 4Co: -- X2 >> O6
Posttest Only Non- Purpose: To compare the effectiveness of an 1. Non-equivalent groups
equivalent Groups already introduced practice/programme. 2. May not be randomized
Designs 3. No pretesting
Group 1Ex: -- X >> O1 4. Two groups
Group 2Co: -- -- >> O2 5. Post-test scores only
6. Effectiveness is measured by
Comment: Testing is done only once. comparing posttest scores
Experimental To establish the Pretest-posttest Non- Purpose: To compare the effectiveness of a 1. Non-equivalent groups
Research possible causal Quasi- equivalent Groups treatment or intervention. 2. May not be randomized
relationship Experimental Design 3. Two groups
between Research Group 1Ex: O1 >> X1 >> O2 5. Both groups measured twice
variables Group 2Co: O3 >> -- >> O4 6. Effectiveness is measured by
through comparing pretest-posttest scores
systematic Purpose: To determine the influence of a variable 1. Series of repeated observations
observations Time Series Design introduced only after a series of initial observations 2. Pretest observations may reveal
carried out in and only where one group is available. existing trend or fluctuations in
controlled the data.
conditions. Group 1Ex: O1 > O2 > O3 > X > O4 > O5 > O6 3. Posttest observations may
reveal the presence or absence of
any post treatment trend or
fluctuations.
Causal or Co- Purpose: To find relation and association between
relational Research two events, factors or conditions occurring at the
Design same time.
Ex-post Facto Independent Variable Dependent Variable
Research X Y
Causal-Comparative Group1Ex: IV DV
Design X Y1
Group1Co: -- Y2
Single Subject ABAB Design Purpose: To establish a causal relationship between A – Baseline measurement
Research the variables of the study and/or to evaluate the B – Intervention measurement
effectiveness on the introduced programme to a A – Withdrawal measurement
single study. B – Intervention measurement
You might also like
- Types - of - Quantitative - Research - PPTX Filename - UTF-8''Types of Quantitative ResearchDocument16 pagesTypes - of - Quantitative - Research - PPTX Filename - UTF-8''Types of Quantitative ResearchCris VillarNo ratings yet
- 01-Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument16 pages01-Nature of Inquiry and ResearchRay DomingoNo ratings yet
- PR2 2Document16 pagesPR2 2Nenita GanerNo ratings yet
- IMRAD PresentationDocument37 pagesIMRAD Presentationjeromecaballero0131No ratings yet
- Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument16 pagesNature of Inquiry and ResearchAzeLuceroNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Inquiry and ResearchDocument16 pagesThe Nature of Inquiry and ResearchElenear De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research DesignsDocument16 pagesQuantitative Research Designsapi-339611548100% (15)
- 3 Kinds of Quantitaive Researh DesignDocument30 pages3 Kinds of Quantitaive Researh DesignKitchie Dianne BejarinNo ratings yet
- EPI 3.6 Qualitative ResearchDocument5 pagesEPI 3.6 Qualitative ResearchJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- ResdesDocument15 pagesResdesharsimranNo ratings yet
- Scfull Help YourselfDocument5 pagesScfull Help YourselfMar Jhon CorongNo ratings yet
- Business Research Method Aljamia-1Document2 pagesBusiness Research Method Aljamia-1MNK TALK100% (1)
- Guidelines in Writing Research MethodologyDocument45 pagesGuidelines in Writing Research MethodologyAljon ApigoNo ratings yet
- Unit-1-5 RMMDocument99 pagesUnit-1-5 RMMDharani C KNo ratings yet
- PR2 7thDocument13 pagesPR2 7thtracyNo ratings yet
- Nature of Inquiry and Research Without QuizDocument18 pagesNature of Inquiry and Research Without Quizem-em lafallNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 3rd QuarterDocument5 pagesPractical Research 3rd QuarterSerenity MoonNo ratings yet
- Research Design: Memcha Loitongbam Professor MIMS, Manipur UniversityDocument75 pagesResearch Design: Memcha Loitongbam Professor MIMS, Manipur UniversityWolfie BoNo ratings yet
- Merry Sunshine Montessori School Cauayan City, Isabela Practical Research 2 S.Y. 2020-2021 Quarte R Objectives Duratio N Values Topic Activities References 1st Week 1-3Document3 pagesMerry Sunshine Montessori School Cauayan City, Isabela Practical Research 2 S.Y. 2020-2021 Quarte R Objectives Duratio N Values Topic Activities References 1st Week 1-3mikkaellaNo ratings yet
- LEAP-LINK PR2 Week-1Document6 pagesLEAP-LINK PR2 Week-1RICO HERRERONo ratings yet
- Scfull Help YourselfDocument5 pagesScfull Help YourselfMar Jhon CorongNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Map Practical Research 1Document4 pagesCurriculum Map Practical Research 1Kaneesha Sobreviñas100% (1)
- Research Design HandoutsDocument6 pagesResearch Design HandoutscassseeeyyyNo ratings yet
- 4 - Research DesignsDocument16 pages4 - Research DesignsMarvin Sabesaje DaguploNo ratings yet
- PR2, Week 2Document7 pagesPR2, Week 2Carlos JuanNo ratings yet
- Research Methodology Workshop - 17022021-V2Document34 pagesResearch Methodology Workshop - 17022021-V2nmkanjoo2743No ratings yet
- Research Lec1Document2 pagesResearch Lec1angela verayeNo ratings yet
- Research Design Formulation PowerpointDocument22 pagesResearch Design Formulation PowerpointSamej NaviNo ratings yet
- Quanti DesignsDocument28 pagesQuanti DesignsjamespaulbaternaNo ratings yet
- OBSERVATION SHE-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesOBSERVATION SHE-WPS OfficejavaabbeNo ratings yet
- Research Design: Pragmatic Constructivism Post-PositivismDocument2 pagesResearch Design: Pragmatic Constructivism Post-PositivismMas KudinNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 12 First Sem Ms. Eissa May Villanueva: St. John Fisher School SjfsDocument1 pagePractical Research 2 12 First Sem Ms. Eissa May Villanueva: St. John Fisher School SjfsIssaVillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument14 pagesResearch DesignElenear De OcampoNo ratings yet
- MINDMAPGP4Document1 pageMINDMAPGP4farhana yusofNo ratings yet
- Descriptive DesignDocument32 pagesDescriptive DesignAshley Nicole VillegasNo ratings yet
- Qualitative ResearchDocument61 pagesQualitative Researchrmm0415No ratings yet
- Conducting Sas Research: Year 1Document4 pagesConducting Sas Research: Year 1dominique babisNo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument12 pagesResearch DesignDennis S. AgudoNo ratings yet
- Reasearch Design-Exp & Desc-Chapter3Document14 pagesReasearch Design-Exp & Desc-Chapter3Siddhant AggarwalNo ratings yet
- ACID Plan Practical Research 2Document1 pageACID Plan Practical Research 2Zorah Barrera67% (3)
- Types of Research DesignsDocument3 pagesTypes of Research DesignsTrina BolibolNo ratings yet
- AOBTBCResearch 10 Q1 ReviewerDocument8 pagesAOBTBCResearch 10 Q1 ReviewerReizhelle AbisNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Activities With LessonsDocument24 pagesUnit 4 Activities With LessonsAndrea Serrano100% (1)
- St. Augustine's School of Iba Inc.: Subject: Practical ResearchDocument6 pagesSt. Augustine's School of Iba Inc.: Subject: Practical ResearchPatrixia MiclatNo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument53 pagesResearch DesignDaizylie FuerteNo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument14 pagesResearch Designapi-339611548100% (7)
- Understanding Academic Research Its Design and Methods ALUNA March 29 2021Document73 pagesUnderstanding Academic Research Its Design and Methods ALUNA March 29 2021Elmalyn BernarteNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Language Teaching ResearchDocument20 pagesIntroduction To Language Teaching ResearchParlindungan PardedeNo ratings yet
- Answer Causal ComparativeDocument6 pagesAnswer Causal ComparativeBanu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Research DesignDocument37 pagesResearch DesignabachaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Research Approaches and Designs: Learning ObjectivesDocument23 pagesChapter 3: Research Approaches and Designs: Learning ObjectivesGamachu TarikuNo ratings yet
- Descriptive Method of Research MarcosDocument15 pagesDescriptive Method of Research MarcosAntonette FrankeNo ratings yet
- The Approaches in A Qualitiative Research DesignDocument3 pagesThe Approaches in A Qualitiative Research DesignHyde ParkNo ratings yet
- Step 6: Elements of Research DesignDocument21 pagesStep 6: Elements of Research DesignMian SaboorNo ratings yet
- PR2 - Quantitative Research DesignDocument14 pagesPR2 - Quantitative Research DesignSammi ArguelesNo ratings yet
- Qualitative Data Collection - Presentation MaterialDocument15 pagesQualitative Data Collection - Presentation MaterialJudielyn SuaseNo ratings yet
- Quantitative ResearchDocument8 pagesQuantitative ResearchBongato Jahzeel MayNo ratings yet
- Designing and Conducting Ethnographic Research: An IntroductionFrom EverandDesigning and Conducting Ethnographic Research: An IntroductionNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management Notes - Split - 4Document22 pagesIndustrial Management Notes - Split - 4Ivy May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management Notes - Split - 3Document44 pagesIndustrial Management Notes - Split - 3Ivy May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management Notes - Split - 1Document15 pagesIndustrial Management Notes - Split - 1Ivy May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management Notes - Split - 2Document40 pagesIndustrial Management Notes - Split - 2Ivy May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- MAEM 801 Statistics With Computer ApplicationDocument13 pagesMAEM 801 Statistics With Computer ApplicationIvy May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Sample Research Concept PaperDocument4 pagesSample Research Concept PaperIvy May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Research FrameworkDocument11 pagesResearch FrameworkIvy May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Identifying A Research Topic (Extract From Mertler, 2017)Document9 pagesIdentifying A Research Topic (Extract From Mertler, 2017)Ivy May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research DesignsDocument26 pagesQuantitative Research DesignsIvy May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To ResearchDocument9 pages1 - Introduction To ResearchIvy May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Biostat Principle-Of-Sampling GolesDocument1 pageBiostat Principle-Of-Sampling GolesTrisha GolesNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 - Q4 - SLM5Document14 pagesPractical Research 2 - Q4 - SLM5Simplicity FajardoNo ratings yet
- One-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test: Npar TestsDocument25 pagesOne-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test: Npar TestsНiкOлa MиlИЋNo ratings yet
- Random and Fixed Factor ANOVA Models - Gauge R&R StudiesDocument14 pagesRandom and Fixed Factor ANOVA Models - Gauge R&R StudiesleovenceNo ratings yet
- Nferential StatisticsDocument6 pagesNferential StatisticsUnissNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics Final ExamDocument7 pagesBiostatistics Final ExamMALIK MANASRAHNo ratings yet
- 1 - 8617 - Autumn 2018Document18 pages1 - 8617 - Autumn 2018Atif RehmanNo ratings yet
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Weight Measured in Pounds Is An Example of Which Scale of Measurement?Document5 pagesMultiple-Choice Questions: Weight Measured in Pounds Is An Example of Which Scale of Measurement?khanzamanshahNo ratings yet
- Kesahan Dan Kebolehpercayaan Dalam Kajian Kualitatif: January 2012Document38 pagesKesahan Dan Kebolehpercayaan Dalam Kajian Kualitatif: January 2012Shalini A/P SurianarayananNo ratings yet
- Stat130 A3Document4 pagesStat130 A3UsmanNo ratings yet
- Business Data Analysis and Interpretation Notes Lecture Notes Lectures 1 13Document20 pagesBusiness Data Analysis and Interpretation Notes Lecture Notes Lectures 1 13Justin Paul VallinanNo ratings yet
- Task 4 - Final Exam. Angie SantamariaDocument4 pagesTask 4 - Final Exam. Angie SantamariaRicardo RottaNo ratings yet
- ANOVA ExampleDocument6 pagesANOVA ExampleLuis ValensNo ratings yet
- HypotestDocument14 pagesHypotestMadhukar SamathamNo ratings yet
- Balance Dan Budaya Kerja Terhadap Kepuasan KerjaDocument17 pagesBalance Dan Budaya Kerja Terhadap Kepuasan KerjaFerio Lambang PutraNo ratings yet
- The T Test For Independent Means: Prepared By: Jhunar John M. Tauy, RPMDocument47 pagesThe T Test For Independent Means: Prepared By: Jhunar John M. Tauy, RPMChin Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Q1. A Manufacturer Would Like To Survey Users To Determine The DemandDocument2 pagesQ1. A Manufacturer Would Like To Survey Users To Determine The DemandAvinash Ingole100% (1)
- 2 5 - SwiggyDocument81 pages2 5 - SwiggyMubeen67% (9)
- Business Research 1Document98 pagesBusiness Research 1vansha_mehra1990No ratings yet
- Surinder Singh - Final Capstone PresentationDocument24 pagesSurinder Singh - Final Capstone PresentationSurinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Multivariate Analysis-MRDocument8 pagesMultivariate Analysis-MRhemalichawlaNo ratings yet
- RM0102 - Research Methodology - SyllabusDocument5 pagesRM0102 - Research Methodology - SyllabuskapilNo ratings yet
- DISC 203-Probability & Statistics-Muhammad AsimDocument4 pagesDISC 203-Probability & Statistics-Muhammad AsimSarmadNo ratings yet
- Practice of Social Research 14th Edition Babbie Test BankDocument20 pagesPractice of Social Research 14th Edition Babbie Test Banktauriddiastyleon6100% (33)
- Penilaian Efektivitas Implementasi Building InformationDocument14 pagesPenilaian Efektivitas Implementasi Building InformationelyaNo ratings yet
- CGPA Calculator: Cumulative GPADocument18 pagesCGPA Calculator: Cumulative GPARana Awais0% (1)
- LargeScaleInference PDFDocument273 pagesLargeScaleInference PDFJchitPNo ratings yet
- Guidelines MEd Masters ProjectDocument27 pagesGuidelines MEd Masters ProjectKAMALLA KUNJU RAMANNo ratings yet
- Q1E Presentation PDFDocument22 pagesQ1E Presentation PDFIsmailNo ratings yet
- Legal Method and Reasoning Project PDFDocument14 pagesLegal Method and Reasoning Project PDFTanushree Gupta100% (1)