Professional Documents
Culture Documents
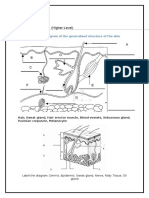
2.2 Organisation in Animals
2.2 Organisation in Animals
Uploaded by
Anais BegueOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.2 Organisation in Animals
2.2 Organisation in Animals
Uploaded by
Anais BegueCopyright:
Available Formats
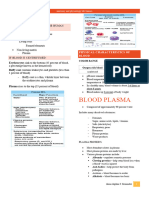
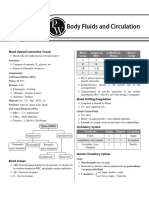
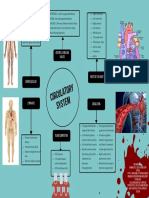
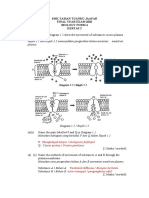
Main blood vessels of the Pacemaker: controls
resting heart rate Main components: plasma, white blood
heart: pulmonary vein, cells, red blood cells, platelets
pulmonary artery, aorta, Blood vessels: arteries,
vena cava, coronary
arteries
veins, capillaries
The heart Diet, exercise, drug/
alcohol consumption,
Alveoli Oxygen enters blood vessels at Double circulatory system: Blood environment, stresses
alveoli and is transported to the right ventricle to lungs, left
heart via the pulmonary vein ventricle to body
The lungs Adapted for exchange: capillary network,
large surface area, thin, moist
Increase the
chance of disease
The circulatory system
The respiratory system Risk factors
2.2 ORGANISATION IN ANIMALS
Diseases are caused by
Function: to break down Animal tissues, organs and organ systems an interaction of
and absorb food different factors
Aids lipid The digestive system e.g. heart disease Health and disease
breakdown
Non-communicable Communicable
Bile ‘Lock and Key’
diseases diseases
Bile is alkaline. It is Enzymes theory
used to neutralise
stomach acid. Allows Carcinogens: chemicals, Cancer
Pathogens:
optimum pH ionising radiation, viruses viral/bacterial
Work best at optimum Carbohydrase (amylase),
protease, lipase Different types of diseases can
temperature and pH interact, e.g. viruses can trigger
cancers
AQA
https://bit.ly/pmt-cc
https://bit.ly/pmt-edu https://bit.ly/pmt-cc
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology Science Olympiad 2024 Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Science Olympiad 2024 Cheat Sheetgfzmrtqj54No ratings yet
- Grabovoi Numbers For Healing CodebookDocument113 pagesGrabovoi Numbers For Healing Codebookmadmaxjune1755797% (36)
- Omaree Autopsy ReportDocument29 pagesOmaree Autopsy ReportKOB4100% (4)
- Blood and Cardiovascular System TransesDocument12 pagesBlood and Cardiovascular System Transeskuroko senpaiNo ratings yet
- Choose Life or Death Rbti Carey Reams PDFDocument176 pagesChoose Life or Death Rbti Carey Reams PDFPatricia Batista Barajas75% (4)
- 7 0 Student WorkbookDocument17 pages7 0 Student Workbookapi-343368893No ratings yet
- 9.6 Introduction To Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument75 pages9.6 Introduction To Human Anatomy and Physiologydmnnfn8hkgNo ratings yet
- c9 Transport in AnimalsDocument8 pagesc9 Transport in Animalsnurhanisa azenanNo ratings yet
- Bioscience 1 NotesDocument21 pagesBioscience 1 NotesLulu0% (1)
- Biology NewDocument63 pagesBiology NewPupun SahooNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Pleural Effusion A Diagnosis Not To BeDocument4 pagesPancreatic Pleural Effusion A Diagnosis Not To BeAmanda TeacaNo ratings yet
- 64eda55a14f460001877b0bc - ## - Body Fluids and Circulation Short NotesDocument2 pages64eda55a14f460001877b0bc - ## - Body Fluids and Circulation Short Notesjai maa Durga aadi parashaktiNo ratings yet
- Body Systems Units 8,9Document8 pagesBody Systems Units 8,9Novalis D’oleoNo ratings yet
- Adventist Medical Center College Activity 3 Group Dynamic: Major Components of Cardiovascular SystemDocument9 pagesAdventist Medical Center College Activity 3 Group Dynamic: Major Components of Cardiovascular SystemAmber Dawn MonteroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Transport: Prepared By: Ling Mei TengDocument21 pagesChapter 1: Transport: Prepared By: Ling Mei TengJuliet LingNo ratings yet
- NUR3517 Critical Care II: SepsisDocument20 pagesNUR3517 Critical Care II: SepsisKELLY RNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DrugsDocument15 pagesCardiovascular DrugsMeilynne Gem C. SonjacoNo ratings yet
- 2 Organisation Biology ChecklistDocument3 pages2 Organisation Biology Checklistu19majli0No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Drugs: D. Hormone DeliveryDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Drugs: D. Hormone DeliveryBelle MakinanoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Plueral Effusion Secondary To Pneumonia: GreenDocument7 pagesPathophysiology Plueral Effusion Secondary To Pneumonia: Greenkuro hanabusaNo ratings yet
- Avegno2016Document18 pagesAvegno2016Indah95No ratings yet
- Human Digestive System Has Two Key FunctionsDocument36 pagesHuman Digestive System Has Two Key FunctionssaqibNo ratings yet
- Body PhysiologyDocument19 pagesBody PhysiologydrmfhNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationNelly CruzNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Parts and FunctionDocument14 pagesCardiovascular System: Parts and FunctionkeykeepNo ratings yet
- Chap# 9 / IGCSE Biology/ 0610 Animal TransportDocument6 pagesChap# 9 / IGCSE Biology/ 0610 Animal TransportAtif MohammadNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System-2Document7 pagesCardiovascular System-2Muhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriNo ratings yet
- 06.15.1 Liver Pathology Final PDFDocument60 pages06.15.1 Liver Pathology Final PDFAkbar TaufikNo ratings yet
- The Human BodyDocument17 pagesThe Human Bodyapi-552691119No ratings yet
- Organisation of The Human Pancreas in Health and in DiabetesDocument8 pagesOrganisation of The Human Pancreas in Health and in DiabetesCARMEN EMILIA RODRIGUEZ SEMINARIONo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument95 pagesCirculatory SystemAj MirandaNo ratings yet
- Case Study 3 - HCVDDocument12 pagesCase Study 3 - HCVDJilkiah Mae Alfoja CampomanesNo ratings yet
- How Do I Carry Out A Resonance Test?Document1 pageHow Do I Carry Out A Resonance Test?Inayattullah KhamkerNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument38 pagesHuman Anatomy & PhysiologyDeva ChiruNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument16 pagesCirculatory SystemHarinder KaurNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument3 pagesLymphatic SystemKuldeep Monga100% (1)
- 4511/2 Sulit: Transfer The Information From The Text Above Into The Graphic Organizer BelowDocument42 pages4511/2 Sulit: Transfer The Information From The Text Above Into The Graphic Organizer BelowCheong Kang JieNo ratings yet
- Right-Sided Heart Failure: College of NursingDocument30 pagesRight-Sided Heart Failure: College of NursingMatelyn OargaNo ratings yet
- Circul Atory System: Arteries, Veins and ValvesDocument1 pageCircul Atory System: Arteries, Veins and ValvesRenata Hernández PiñeyroNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument2 pagesEndocrine SystemSheinny RodriguezNo ratings yet
- 16circulatory Istudent - 611629985pdf - 211102 - 105416Document8 pages16circulatory Istudent - 611629985pdf - 211102 - 105416Leslie CuevasNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion DraftDocument8 pagesBlood Transfusion DraftVivian Jean TapayaNo ratings yet
- 11 Organ SystemsDocument12 pages11 Organ Systemsprincessfarah hussinNo ratings yet
- MRSM Biology Notes TransportDocument16 pagesMRSM Biology Notes TransportAhmad Hafize100% (2)
- Biology Notes.Document8 pagesBiology Notes.Mohith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocument12 pagesBody Fluids and Circulationadityaaggarwal821No ratings yet
- Health Teaching PlanDocument6 pagesHealth Teaching PlanLay YoungNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Blood Blood VesselsDocument8 pagesCardiovascular System: Blood Blood VesselsmmdadnanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemDocument48 pagesLesson 1 - Circulatory SystemJhon Excell SanoNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia Pathophysiology (Book Based) : Non-Modifiable: ModifiableDocument2 pagesPneumonia Pathophysiology (Book Based) : Non-Modifiable: ModifiableYVETTE CLAIRE BORRESNo ratings yet
- Practice Session 8.: 1. Liver Function 2. Hepatitis 3. CirrhosisDocument30 pagesPractice Session 8.: 1. Liver Function 2. Hepatitis 3. CirrhosisVishtasb KhaliliNo ratings yet
- HCP MODULE 12 - Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesHCP MODULE 12 - Circulatory SystemAvea RiveraNo ratings yet
- Estanislao, H., Midterm, LaboratoryDocument25 pagesEstanislao, H., Midterm, LaboratoryCris Adrey Reyes AdrianoNo ratings yet
- Biology 2020 SPM Crash Course Form5Document15 pagesBiology 2020 SPM Crash Course Form5Zhuan ZuneNo ratings yet
- NCP - Dela CruzDocument4 pagesNCP - Dela CruzChristine Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Untitled NotebookDocument1 pageUntitled Notebookmuhammadkhalid030520No ratings yet
- Biology Research AssignmentDocument5 pagesBiology Research AssignmentPriyanshi ChoksiNo ratings yet
- Science HelpDocument5 pagesScience HelpDena AL-SHOWALINo ratings yet
- Biology - Circulatory SystemDocument13 pagesBiology - Circulatory SystemEnkoujo KairiNo ratings yet
- Case Study (Preeclampsia)Document6 pagesCase Study (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendDocument3 pagesPredisposing Factors Disease Precipitating Factors: LegendSOPHIA LOISE TEJANO FULACHENo ratings yet
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineFrom EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineNo ratings yet
- 3.5. Use of Amount of Substance in Relation To Volumes of Gases - 20220609 - 061315Document1 page3.5. Use of Amount of Substance in Relation To Volumes of Gases - 20220609 - 061315Anais BegueNo ratings yet
- 4.2. Reactions of AcidsDocument1 page4.2. Reactions of AcidsAnais BegueNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument2 pagesDefinitionsAnais BegueNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument3 pagesDefinitionsAnais BegueNo ratings yet
- Best Basic Circulatory SystemDocument44 pagesBest Basic Circulatory SystemJerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System-ELSDocument44 pagesCirculatory System-ELSJomer CasimNo ratings yet
- Fred Kummerow Cholesterol April 2014 Transcript2Document11 pagesFred Kummerow Cholesterol April 2014 Transcript2scribd2learn100% (1)
- Science 7th PaperDocument2 pagesScience 7th PaperArshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Edexcel International GCSE (9-1) Biology Student Book-41Document1 pageEdexcel International GCSE (9-1) Biology Student Book-41Mominul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 08 - Transport in HumansDocument84 pagesChapter 08 - Transport in Humanshussaini polackNo ratings yet
- UW Notes - 7 - Cardiology ArrangedDocument84 pagesUW Notes - 7 - Cardiology ArrangedAaquib AmirNo ratings yet
- The Nclex-Rn Cram Sheet: General Test InformationDocument2 pagesThe Nclex-Rn Cram Sheet: General Test InformationMikaela Angeles NazarNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis: (Takayasu's Arteritis & Giant Cell Arteritis)Document3 pagesVasculitis: (Takayasu's Arteritis & Giant Cell Arteritis)nivraeNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Kevin Farina - CirculatorySystemSEDocument4 pagesKami Export - Kevin Farina - CirculatorySystemSEKevin FarinaNo ratings yet
- Biology 5090 12 Paper 1 Question Paper Mayjue 2013Document16 pagesBiology 5090 12 Paper 1 Question Paper Mayjue 2013Raja Muda Raja NgahNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System NotesDocument31 pagesCirculatory System NotesJMHenry0% (1)
- Biology Notes For O LevelDocument36 pagesBiology Notes For O LevelAhmad Barrun Nidhom92% (158)
- The HeartDocument86 pagesThe HeartBlackHerbalsNo ratings yet
- Bio Kertas 2 - SkemaDocument11 pagesBio Kertas 2 - SkemaHaslinda SheikhNo ratings yet
- ANGIOLOGYDocument32 pagesANGIOLOGYFaisal IqbalNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition EllisDocument8 pagesTest Bank For Ekg Plain and Simple 3rd Edition Elliscanebrutalfniy66No ratings yet
- 0610 s17 Ms 41Document12 pages0610 s17 Ms 41pkrajenpillaygmailcomNo ratings yet
- Presented by Rasgas Medical Centre: Lowering Your CholesterolDocument22 pagesPresented by Rasgas Medical Centre: Lowering Your CholesterolNarasimhan PNo ratings yet
- 10 - Blood Flow To The LungsDocument20 pages10 - Blood Flow To The Lungsf3er3No ratings yet
- Circulation and Gas ExchangeDocument164 pagesCirculation and Gas ExchangeZuliyanto ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Test 5 & 6 BDSDocument19 pagesTest 5 & 6 BDSrababNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30 Assessment and Management of Patients With Vascular Disorders and Problems of Peripheral CirculationDocument23 pagesChapter 30 Assessment and Management of Patients With Vascular Disorders and Problems of Peripheral CirculationAbel C. Idusma Jr.No ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pathology IDocument37 pagesCardiovascular Pathology IOyuka OyukNo ratings yet
- LIFE PROCESSES - Question BankDocument15 pagesLIFE PROCESSES - Question BankMISHKA KHANDELWALNo ratings yet
- Highschool Department: Neville Learning SchoolDocument29 pagesHighschool Department: Neville Learning SchoolJeuel RobiatoNo ratings yet