Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Breathe
Uploaded by
pancadewisCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Breathe
Uploaded by
pancadewisCopyright:
Available Formats
Just Breathe
By: Joyce Green
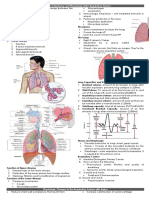
Lung Capacity
When we breathe, we are taking in level, height, and gender, can affect VOCABULARY
oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide lung capacity. You can increase your
Alveoli
into the air. We need oxygen to help lung capacity through regular exercise.
breakdown the food that we eat, to build Bronchi
muscles, and to help us remain active. Today we are going to look at Vital Residual volume
While our cells are performing these Capacity by measuring the amount of Tidal volume
tasks, they are using up the oxygen we air that can be exhaled into a balloon.
breathe in and producing carbon Then we will compare that volume to Total lung capacity
dioxide and water which we exhale. an Expected Vital Capacity which takes Trachea
into account a person’s age and height
Vital capacity
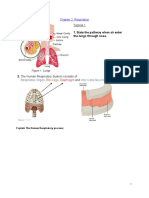
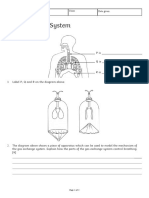
The main job of the Respiratory System to calculate lung volume.
is to bring oxygen to all parts of our
body. Air comes in through the nose and
mouth and travels down the trachea.
The trachea then branches off into two
bronchi, which lead towards our right
and left lungs. The lungs are made up
of tiny sacs called alveoli. The alveoli
help the blood exchange gases, like
oxygen and carbon dioxide.
When we exhale, air flows back through
the bronchi, up the trachea and back Inside This Packet
out into the air. When each breath is Lung Capacity 1
completed, the lung still has some air,
called the residual volume. Activity: Mapping the
Digestive System
2
The amount of air in the lungs can be Activity: Chew It! 5
measured in several different ways:
Information for the
8
Teacher
Tidal Volume is the volume of air that New York State Standards 8
you normally inhale and exhale.
Vital Capacity is the maximum volume New York State Standards
of air that you can inhale and exhale. High School
Living Environment
Residual Volume is the air that remains Key idea 2.4
Key idea 3.1a
in your lungs after you exhale the Use string/metric ruler to measure
maximum amount of air in your lungs. circumference
Intermediate science
Total Lung Capacity is the total volume Standard 1:
Key idea M1
your lungs can hold; vital capacity plus Key idea M2
residual volume. Key idea M3
Standard 4:
Key idea 1: 1.2b, 1.2e
Different factors such as age, activity
Life Sciences - Prior Module 4 High School Page 1
Activity: 1-2-3 Blow!
MATERIALS NEEDED What to do:
1. With a partner to complete the activity. One person will record the
Large balloon
measurements (data collector) and the other will blow up the balloon (test
String subject). If you have asthma or any other lung condition, have your partner
blow up the balloon.
Measuring tape or meter stick
Student Worksheet 2. Test subject - Stretch the balloon and blow it up several times before you begin
taking measurements.
3. Test subject - Take a deep breath and exhale as much air as you can into the
balloon in ONE BREATH. Pinch the opening shut with your fingers.
4. Data collector - Take the string and wrap it around the widest part of the
Students should balloon. Place the string on the meter stick and record the length of the string
be able to: in centimeters. This will give us the circumference of the balloon.
Record this value under Trial 1 in Table 1 on your worksheet.
Calculate their total lung
capacity, vital capacity 5. Repeat this 4 times for a total of 5 trials.
and residual volume.
6. Calculate the average circumference of your 5 trials and record this value in
Table 2.
7. Calculate the diameter of the balloon using the following formula then record
your result in Table 2.
Diameter= circumference / pi pi= 3.14
8. Calculate the radius of the balloon using the following formula then record your
result in Table 2.
Radius= diameter/ 2
9. Calculate the volume of air in the balloon using the following formula then
record your result in Table 2.
Volume = radius3 x pi x ¾
10. Convert the volume of air (mL) to volume of air (L) or Experimental vital
capacity using the following formula then record your results in Table 2.
Volume (L)= Volume (mL) / 1000
The volume of air you calculated is your Experimental Lung Capacity, or the
amount of air your lungs actually held.
We can also calculate your Vital Capacity, or the amount of air your lungs
should hold when based on your height and age.
11. Calculate your height in cm using the following formula then record your
results in Table 3.
Height in cm= height in inches x 2.54
12. Calculate your expected vital capacity using the following formula then
record your result in Table 3.
Vital Capacity = 0.041 x height (in cm) – 0.018 x your age – 2.69
Life Sciences - Prior Module 4 High School Page 2
Activity: 1-2-3 Blow! Student Worksheet
Name: _______________________________ Date: ________________
Name: _______________________________
Table 1: Circumference of the Balloon
Trial 1 Trial 2 Trial 3 Trial 4 Trial 5
Table 2: Calculated Values
Average Diameter of Radius of Volume of Air Volume of Air
Circumference the Balloon the Balloon in ML in L
Table 3: Expected Vital Capacity
Expected Vital Experimental Vital
Age in Years Height in Inches Height in CM Capacity in L Capacity (from Table 2)
Questions
1. How does your expected vital capacity compare to your calculated vital capacity?
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
2. Why might the experimental vital capacity be different than the calculated vital capacity?
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
3. Compare your experimental vital capacity with other students in your class. Are they the same or different
Explain your answer.
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________
Life Sciences - Prior Module 4 High School Page 3
You might also like
- Human Excretory System WorksheetDocument2 pagesHuman Excretory System WorksheetpancadewisNo ratings yet
- John PFTDocument231 pagesJohn PFTAlexander Santiago ParelNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument15 pagesThe Human Respiratory SystemNandita Halder100% (1)
- Science6 Q2 Mod2 TheHumanBodySystemsDocument31 pagesScience6 Q2 Mod2 TheHumanBodySystemsKneight riduzNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Biology A2 Core Practical WorkbookDocument39 pagesEdexcel Biology A2 Core Practical WorkbookTim Filtness80% (20)
- Pathophysiology Respiratory SystemDocument63 pagesPathophysiology Respiratory SystemAli Basha QudahNo ratings yet
- Oriental Breathing Terapy NakamuraDocument146 pagesOriental Breathing Terapy Nakamurahcorzo100% (2)
- Detailed Lesson Plan Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan Respiratory Systemjane91% (11)
- Science 8 Learner Book AnswersDocument35 pagesScience 8 Learner Book AnswersVanished Man95% (269)
- Measure Your Lung Capacity with Fun Science ActivitiesDocument15 pagesMeasure Your Lung Capacity with Fun Science ActivitiesSthephen MarquezNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument39 pagesRespiratory SystemJesstine Famatiga100% (2)
- The Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessFrom EverandThe Basic Breathwork Book: A Fundamental Guide to Enhancing Health, Performance and MindfulnessNo ratings yet
- Science-Form 3-Chapter 1 Respiration by KelvinDocument14 pagesScience-Form 3-Chapter 1 Respiration by KelvinKelvinNo ratings yet
- Science 9 q1 Week 1 - Respiratory System at WorkDocument30 pagesScience 9 q1 Week 1 - Respiratory System at WorkJanet Brigida CatiponNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Respiratory and Circulatory System Working Together!Document5 pagesChapter 1: Respiratory and Circulatory System Working Together!Precious Aiverose EspinaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Lung Capacity Using Portable SpirometerDocument11 pagesMeasuring Lung Capacity Using Portable SpirometerTootsie88% (16)
- Lung Volumes Alveolar VentilationDocument30 pagesLung Volumes Alveolar Ventilationz nameNo ratings yet
- 250 Questions For The MRCPCH Part 2Document250 pages250 Questions For The MRCPCH Part 2doctor aabiNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDDocument7 pagesScience 9 Worktext, Sketchnote, Face Mask Activity and Assessment L1 PRINTEDClarice Jenn MaltoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Respiratory System LessonsDocument19 pagesGrade 7 Respiratory System LessonsclaireNo ratings yet
- Activity 17 The Respiratory System and Pulmonary VentilationDocument5 pagesActivity 17 The Respiratory System and Pulmonary VentilationarmandNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange and Pulmonary Disorders AssessmentDocument7 pagesGas Exchange and Pulmonary Disorders AssessmentTrisha Faye OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Lung Capacity PDFDocument5 pagesMeasuring Lung Capacity PDFSip BioNo ratings yet
- Activity 2.2.1b_ Oxygen _ Human RespirationDocument4 pagesActivity 2.2.1b_ Oxygen _ Human RespirationVictoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- WEEK 11 ANPH 111Document6 pagesWEEK 11 ANPH 111itsmearonsupanNo ratings yet
- Activity 3.3.2 - Measuring Lung Capacity - Human Body SystemsDocument13 pagesActivity 3.3.2 - Measuring Lung Capacity - Human Body SystemsHerman Henson [Northwest CTA]No ratings yet
- MODULE 4 2ND QUARTER Science 6 EDITDocument6 pagesMODULE 4 2ND QUARTER Science 6 EDITEmie PonceNo ratings yet
- Measuring Lung Capacity at HomeDocument12 pagesMeasuring Lung Capacity at HomeRita CheungNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11. Gas ExchangeDocument11 pagesChapter 11. Gas Exchangerep.0mar13No ratings yet
- Science 9: LessonDocument9 pagesScience 9: LessonJellyn Rose Panganiban RamosNo ratings yet
- The Triple B: Breath andDocument12 pagesThe Triple B: Breath andChristian FarofaldaneNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesRespiratory System Anatomy and PhysiologyEricka ElloNo ratings yet
- Sas 15 (Respiratory)Document7 pagesSas 15 (Respiratory)Julie YahnNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan in Science 9: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of TheDocument7 pagesDaily Lesson Plan in Science 9: The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of TheChelsea Quinn MesaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Respiratory SystemMark Jerome CifraNo ratings yet
- HSCI 103 Lab 4 HandoutDocument4 pagesHSCI 103 Lab 4 HandoutMatthewFlecknoeNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledRafsan HossainNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System E-Notes on Aerobic vs Anaerobic RespirationDocument5 pagesRespiratory System E-Notes on Aerobic vs Anaerobic RespirationAarav AroraNo ratings yet
- 8Cb Gas Exchange (Part 1)Document19 pages8Cb Gas Exchange (Part 1)maryamNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in Humans Grade 9Document49 pagesGas Exchange in Humans Grade 9harliv2.5chandhokNo ratings yet
- ME Sci 9 Q1 0101 PSDocument29 pagesME Sci 9 Q1 0101 PScassiopeia bianca sartigaNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document2 pagesTask 1pancadewisNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 ReportDocument19 pagesLab 6 Reportapi-311215267100% (2)
- Respiratory System ExplainedDocument2 pagesRespiratory System ExplainedBryanAngelo Laguilles100% (1)
- Act 2 Mechanisms of Gas ExchangeDocument7 pagesAct 2 Mechanisms of Gas ExchangeTyrone Dave BalitaNo ratings yet
- LabDocument6 pagesLabapi-462581208No ratings yet
- Week 8 Respiratory System Weekly Workbook 2022Document22 pagesWeek 8 Respiratory System Weekly Workbook 2022rishabhvasisht03No ratings yet
- PRAYER SCIENCE 9 QUARTER 1 Week 1-DAY 2 LESSON 2: PROCESS OF RESPIRATIONDocument24 pagesPRAYER SCIENCE 9 QUARTER 1 Week 1-DAY 2 LESSON 2: PROCESS OF RESPIRATIONKRISTA MAE BALANAYNo ratings yet
- Unit 5. Respiratory SystemDocument10 pagesUnit 5. Respiratory SystemRaquelNo ratings yet
- Lung Capacity Study of Teens and AdultsDocument23 pagesLung Capacity Study of Teens and AdultsjyotiNo ratings yet
- Measuring Lung Capacity LabDocument2 pagesMeasuring Lung Capacity Labapi-301939115No ratings yet
- 112 NotesDocument9 pages112 NotesDawnmurph Dharlene Wag-eNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - Human Anatomy and Physiology IIDocument23 pagesLab Manual - Human Anatomy and Physiology IIosm paglaNo ratings yet
- Lab 07 Respiratory SystemsDocument5 pagesLab 07 Respiratory SystemsameeschwittersNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology Lab ReportDocument15 pagesRespiratory Physiology Lab ReportThalia PacamalanNo ratings yet
- 0 - CSBC-321 Assignment 2 CHCS-2017-045Document13 pages0 - CSBC-321 Assignment 2 CHCS-2017-045JessieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Tutorial 1Document4 pagesChapter 2 Tutorial 1Tanisa SaminNo ratings yet
- Science 9 W AnswerDocument62 pagesScience 9 W AnswerAstrande KevinNo ratings yet
- Science9 Q1Document50 pagesScience9 Q1AILEEN LUZONNo ratings yet
- 6 Human Respiration 2Document10 pages6 Human Respiration 2Harlee QuizzaganNo ratings yet
- ENGLISHDocument5 pagesENGLISHArmida SisonNo ratings yet
- Expt. 26 Lung Volumes and Capacities (A)Document5 pagesExpt. 26 Lung Volumes and Capacities (A)api-3769252100% (2)
- Biology WE g8 s1 PB - Respiration Part 1 Kunci JawabanDocument3 pagesBiology WE g8 s1 PB - Respiration Part 1 Kunci JawabannoorlailyNo ratings yet
- Physiology Practical Simple and Dynamic Spirometry.Document18 pagesPhysiology Practical Simple and Dynamic Spirometry.Abhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Activity 2-Respiratory SystemSabrosoDocument2 pagesActivity 2-Respiratory SystemSabrosoJean SabrosoNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Ventilatory System PPT EMSDocument77 pages2.1 Ventilatory System PPT EMShdhshNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Qtr1 Lesson 3Document2 pagesGrade 9 Qtr1 Lesson 3Niña Catubig - TangcalaganNo ratings yet
- Human Heart Blood Flow Path in 39 CharactersDocument1 pageHuman Heart Blood Flow Path in 39 CharacterspancadewisNo ratings yet
- FitterDocument1 pageFitterpancadewisNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document2 pagesTask 1pancadewisNo ratings yet
- Exercise InvestigationDocument3 pagesExercise InvestigationpancadewisNo ratings yet
- Wave WorksheetDocument3 pagesWave WorksheetpancadewisNo ratings yet
- Activity1 Worksheet 2Document2 pagesActivity1 Worksheet 2pancadewisNo ratings yet
- Model the Lungs with Bottles and BalloonsDocument3 pagesModel the Lungs with Bottles and BalloonspancadewisNo ratings yet
- DTL LabelYourKidneyDocument2 pagesDTL LabelYourKidneypancadewisNo ratings yet
- Dying To Live The Urinary System Science Year 9-Student WorksheetDocument4 pagesDying To Live The Urinary System Science Year 9-Student WorksheetpancadewisNo ratings yet
- Woody's life before and after kidney transplantDocument1 pageWoody's life before and after kidney transplantpancadewisNo ratings yet
- Dying To Live The Urinary System Science Year 9-Teacher WorksheetDocument11 pagesDying To Live The Urinary System Science Year 9-Teacher WorksheetpancadewisNo ratings yet
- Westbury High School Science Lesson on Thermodynamics & WavesDocument12 pagesWestbury High School Science Lesson on Thermodynamics & WavespancadewisNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange System: Pis QisDocument4 pagesGas Exchange System: Pis QispancadewisNo ratings yet
- Modelling The Mechanism of Breathing Worksheet SupportDocument4 pagesModelling The Mechanism of Breathing Worksheet SupportpancadewisNo ratings yet
- Ingenuity, Inventing, and Creative Learning: ©ed Sobey, PH.DDocument20 pagesIngenuity, Inventing, and Creative Learning: ©ed Sobey, PH.DpancadewisNo ratings yet
- Expansion: Note The Particles (Atoms or Molecules) THEY DO NOT EXPANDDocument1 pageExpansion: Note The Particles (Atoms or Molecules) THEY DO NOT EXPANDpancadewisNo ratings yet
- Westbury High School Science Lesson on Thermodynamics & WavesDocument12 pagesWestbury High School Science Lesson on Thermodynamics & WavespancadewisNo ratings yet
- WatershedDocument22 pagesWatershedpancadewisNo ratings yet
- Test 1Document6 pagesTest 1pancadewisNo ratings yet
- Messing Around With Model Boats: Northwest Invention CenterDocument6 pagesMessing Around With Model Boats: Northwest Invention CenterpancadewisNo ratings yet
- PembukaanDocument1 pagePembukaanpancadewisNo ratings yet
- Water PollutionDocument2 pagesWater PollutionpancadewisNo ratings yet
- 2nd Semester Grade 7Document3 pages2nd Semester Grade 7pancadewisNo ratings yet
- Cover BelakangDocument1 pageCover BelakangpancadewisNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Physiology & NeurobiologyDocument14 pagesRespiratory Physiology & NeurobiologyRaul DoctoNo ratings yet
- On Study Of: Dr.A.K.RastogiDocument73 pagesOn Study Of: Dr.A.K.RastogiMudit MisraNo ratings yet
- Definition:: Maternal Physiology During PregnancyDocument139 pagesDefinition:: Maternal Physiology During PregnancygibreilNo ratings yet
- Pneumo Tot MergedDocument103 pagesPneumo Tot MergedAndra BauerNo ratings yet
- Lung Volumes and CapacitiesDocument16 pagesLung Volumes and CapacitiesMoses DumbuyaNo ratings yet
- Simple SpirometerDocument11 pagesSimple SpirometerKumutha ChelliahNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Ventilation ModuleDocument5 pagesPulmonary Ventilation ModulejunquelalaNo ratings yet
- Pathologycal PhysiologyDocument29 pagesPathologycal PhysiologyArsilan Aziz LoneNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Sports Health and Exercise Science GuideDocument27 pagesThe Ultimate Sports Health and Exercise Science GuideTiago José ReisNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Cardiovascular and Respiratory System of GymnastDocument19 pagesGroup 2 Cardiovascular and Respiratory System of GymnastSariephine Grace ArasNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Function TestsDocument38 pagesPulmonary Function TestsMohamedSalahNo ratings yet
- Measuring Lung CapacityDocument6 pagesMeasuring Lung CapacitydrockriotNo ratings yet
- Scan 17-Nov-2021Document6 pagesScan 17-Nov-2021Savita AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Medical PhysicsDocument24 pagesMedical PhysicsgeethaNo ratings yet
- PP Lung VolumesDocument30 pagesPP Lung VolumesAdam PrabowoNo ratings yet
- AdvDocument215 pagesAdvTousif Haider100% (1)
- Glossary and Acronyms of FreedivingDocument2 pagesGlossary and Acronyms of FreedivingIvo XNo ratings yet
- Zanki Respiratory Physiology: Complete Guide to Lung FunctionDocument19 pagesZanki Respiratory Physiology: Complete Guide to Lung Functionsmian08No ratings yet
- Lung Volumes: DescriptionDocument4 pagesLung Volumes: DescriptionWyn AgustinNo ratings yet
- Revision QuestionsDocument11 pagesRevision QuestionsxilcomNo ratings yet
- Answer Discussion Share: (A) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)Document8 pagesAnswer Discussion Share: (A) Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)gopeabhijit85No ratings yet
- Worksheet-Breathing and Exchange of GasesDocument8 pagesWorksheet-Breathing and Exchange of Gasessaravanan.kavinilaNo ratings yet
- I. Anatomy, Physiology, and Functions of The Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesI. Anatomy, Physiology, and Functions of The Respiratory SystemYAMINIPRIYANNo ratings yet