Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enzymes and Digestive System Mark Scheme
Uploaded by
rkblsistemOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enzymes and Digestive System Mark Scheme
Uploaded by
rkblsistemCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
(a) (i) Energy put in to get reaction started (Look for idea of getting started); 1
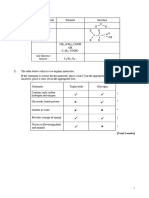
(ii) Curve showing energy levels at start and finish the same;
and lowered activation energy; 2
(b) Benedict’s / Fehling’s reagent and heat;
orange / red / brown / yellow / green; 2
(c) (i) Acid hydrolyses starch / breaks glycosidic bond; 1
(ii) Not specific / forms by–products / alters pH / corrosive; 1
(d) (i) Molecules would have less (kinetic) energy;
move slower;
fewer collisions / fewer E–S complexes form; max 2
(ii) Change in pH alters charge / shape;
distorts active site / tertiary structure of enzyme / denatures enzyme;
substrate will no longer fit active site; 3
[12]
2. (a) (i) Less substrate (molecules) present;
Due to them being used up in reaction;
OR
Product inhibits reaction;
Allosteric / competitive / non-competitive inhibition; 2
(ii) Double;
Increase of 10°C doubles rate of reaction;
OR
Increase;
Increased KE/ increased energy of molecules / increased movement; 2
(b) To show that enzyme was responsible for conversion, (no other factor); 1
[5]
3. (a) (i) Divide amount of product produced by time taken /
calculate gradient / slope of graph;
(R Numerical answer without supporting calculation) 1
(ii) Higher temperatures means molecules have more (kinetic) energy;
(Look for idea of molecules.)
Move faster;
Greater chance of collision (between enzyme and substrate);
More chance of enzyme-substrate complex being formed; max. 3
Groby Community College 1
(b) At 65°C enzyme has been denatured / description of denaturing; 1
(c) To maintain a constant pH; 1
[6]
4. (a) (i) More (kinetic) energy;
(Molecules) moving faster;
R references to vibrating I activation energy
Greater chance of collision
More E-S complexes formed; max 3
(ii) Bonds/specified bonds break; R peptide bond
Tertiary structure disrupted / denatured / active site destroyed;
Substrate no longer fits / binds with active site / ES complex
not formed: 3
(b) Lysosomes contain enzymes / lysozyme;
Break down proteins;
When they burst; max 2
[8]
5. (a) (i) (Polypeptide is) coiled / folded; 1
(ii) Way in which whole molecule is folded / globular shape / folding
of secondary structure / further folding /
Do not accept 3D shape if not further explained.
Structure held by ionic / disulphide bonds; reject hydrogen
bonds / peptide bonds only. 1
(iii) Causes bonds which hold the tertiary structure / named bond;
To break;
Shape no longer maintained / protein denatured; 2 max
(b) (i) 5; 1
(ii) Substrates / active sites with shapes;
Active site / substrate with complementary (shape);
Fitting / binding / forming E-S complex; 3
[8]
Groby Community College 2
6. (a) (Molecules) with little (kinetic) energy;
Move slowly;
Few collisions (between enzyme and substrate)/fewer enzyme-substrate
complexes formed; 3
(Note: Question refers to slow rate at 5°C and answer must be in this
context.)
(b) Heating would cause bonds (maintaining tertiary structure)/named
bonds to break:
Denaturing enzyme/ altering tertiary structure;
Altering shape of active site; max 2
(Note: if answers clearly relate to lactose, they are incorrect)
[5]
7. (a) Mauve/ purple/ violet/ lilac;
It is a protein; 2
[Reject: blue or pink colour]
(b) (i) Fell as it was used up/ broken down/ changed; 1
(ii) Substrate becomes limiting/ falls/ gets less;
Fewer collisions/ complexes formed; 2
(iii) 1nitial rate slower;
Levelling out at same value; 2
(c) Enables a comparison to be made;
As the rate/concentration changes as reaction progresses;
Cells/ catalase may become damaged/affected by heat; max 2
[9]
8. (a) (i) Same general structure as all amino acids; = 1 mark
Same general structure as all amino acids and answer making specific
reference
to amino/ NH2 group and carboxyl/ COOH group; 2
(ii) Not normally found in proteins/ polypeptides; 1
[Note: Alternative answers must fit with information provided
in passage]
(b) (i) Protein will have different tertiary structure;
Affecting shape of active site;
Therefore unable to bind to substrate/substrate not able to fit/cannot
form enzyme-substrate complex; 3
(ii) tRNA does not bind with non protein amino acids/ACA;
Groby Community College 3
tRNA will only bring proline / will not bring ACA
ribosome/mRNA;
Enzyme molecules will only contain proline /will not
contain ACA; max 2
(c) Competitive because toxin/ swainsonine has sugar-shaped molecules;
Which will fit into active site of enzyme / mannosidase; 2
(d) Some species can make particular toxins harmless;
Therefore can feed on particular plants;
OR Toxins distributed in different quantities in different parts of plants;
Therefore different species can feed on different parts of plant/
can eat different part of plant at different time; max 2
[12]
9. (a) (i) Curve rising and levelling out; 1
(ii) Substrate becomes limiting/falls/gets less;
Fewer collisions/complexes formed; 2
(b) To keep pH the same / optimum pH / so change in pH does not affect reaction; 1
(c) (i) For temperature up to 40 – 50°C has no effect;
Over temperature (of 40 – 50°C) reduces rate of reaction; 2
Note. Award one mark for general statement about the longer the
incubation time, the slower the rate of reaction.
(ii) Bonds (holding tertiary structure) broken;
More enzyme denatured / tertiary structure destroyed;
Active sites lose shape/no longer fit;
Fewer enzyme-substrate complexes formed; max 3
Note. Award marks if clearly in the context of more denaturation.
Allow credit here for converse relating to exposure for 5 minutes.
Groby Community College 4
(d) 1 Statement about two types, competitive and non-competitive;
Note. Award points 2 –5 only in context of competitive and
non-competitive inhibition
Competitive
2 Similarity of shape of inhibitor and substrate;
3 Inhibitor can enter/bind with active site (of enzyme);
Non-competitive
4 Affect/bind to enzyme other than at active site;
5 Distorts shape of active site;
Inhibitors
6 Prevent entry of/binding of substrate to active site;
7 Therefore fewer/no enzyme-substrate complexes formed; max 6
[15]
10. (a) diagram showing molecule A fitting in inhibition site; distortion of active site; 2
(b) molecules moving less/slower; reduces chance of collision (between enzyme
and substrate)/of enzyme-substrate complexes being formed;
(reject converse) 2
(c) these bonds hold/maintain tertiary/globular structure (of enzyme);
enzyme denatured/tertiary structures destroyed; (shape of) active site
distorted/changes;
substrate no longer fits/enzyme-substrate complex not formed; 3 max
[7]
11. (a) Shape drawn that resembles the active site;
drawn in the active site / clearly going to the active site; 2
(b) Substrate concentration not limiting / enzyme concentration limiting;
all active sites of enzyme full / enzyme at maximum turnover rate; 2
(c) (More substrate than inhibitor so) more likely to form enzyme-substrate
complex;
more likely for substrate to enter the active site: 1
(d) Correctly named bonds broken / water removed;
tertiary / globular shape of enzyme changed;
shape of active site affected; 3
[8]
Groby Community College 5
12. (a) amino acid; 1
(b) violet/purple/mauve/lilac; 1
(c) Amino acid/substrate shape/structure changed;
Active site of enzyme;
No longer fits/ no longer complementary /
enzyme: substrate complex not formed; 3
[5]
13. (a) (i) maltose. 1
(ii) Activation energy reduced;
starch attached to active site / formation of enzyme-substrate complex;
less energy required to bring (substrate) molecules together
/ to break bonds;
reaction occurs in small(er) steps;
change in shape of enzyme molecule (induced fit) brings molecules
together / allows bonds to break / causes overlapping of electron
orbits of substrates. max 3
(b) Enzyme (molecules) denatured at 60°C / high temperature, or description
of denaturing (e.g. vibration disrupts enzymes);
change (in shape) of active site;
change in tertiary/’3D’structure / hydrogen bonds broken;
substrates no longer fit;
loss of activity of enzyme in water bath due to slow denaturing. max 4
[8]
14. (a) Cyanide binds to enzyme molecule away from active site;
shape of active site changed.
OR: cyanide attaches permanently to active site;
active site blocked. 2
(b) (i) Protein (receptors) / antigen / glycoprotein / glycocalyx. 1
(ii) Enzyme + antibody attaches (to membrane);
of cancer cells only;
Enzyme breaks down (injected) linamarin;
Cyanide released disrupts respiration/metabolism of cancer cells. max 3
[6]
15. (a) Active site; 1
Groby Community College 6
(b) Substrate enters active site;
Complimentary shapes / Lock and Key;
(Binding) to form enzyme-substrate complex;
Lowering of activation energy;
Conformational / shape change;
Breaking of bonds in substrate;
Products no longer fit active site and so are released; 4
(c) Molecule A binds at site away from active site / allosteric site;
Causes enzyme / active site to change shape;
Molecule B can enter / competes for active site;
Prevents substrate from entering / no enzyme-substrate
complex formed / active site blocked; 4
(d) (i) Optimum pH is 7 / neutral / between 6 and 8 / between 7 and 8; 1
Dis tan ce 11 11
/ / ;
(ii) Max rate = Time 4 4 60 2
[Correct answer = 2 marks (IGNORE units)
–3
e.g. 2.75 mm / hour, 0.046 mm/min, 4.6 × 10 mm/min
2
1 mm/ 21.8 mins, 23.76mm /hour]
[12]
16. (a) (i) Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen / CHON; 1
(ii) Proteins made up of many monomers / amino acids;
Tryglyceride made of glycerol and fatty acids / few smaller molecules
/not joined in chain; 2
(iii) Different sorts of amino acids;
Only one sort of glucose; 2
(b) They are proteins;
Can be used again / not “used up”;
Bind to other molecules; max 2
(c) (i) Protein has primary structure / amino acid sequence;
Therefore bonds always form in same position; 2
Groby Community College 7
(ii) 1 Active site (of enzyme) has particular shape;
2 (Into which) substrate molecule fits / binds;
3 Appropriate reference linking induced fit and shape;
4 (Competitive inhibitor) has similar shape to substrate;
5 Also fits active sites;
6 Prevents substrate access;
7 (Non-competitive inhibitor) fits at site other than active site;
8 Distorting shape of active site / enzyme;
6 Prevents substrate access; (award once only)
9 Two types identified as competitive and non-competitive; max 6
[15]
17. (a) (i) The receptor / glucagon will have a particular shape / tertiary structure;
The other will fit / bind because of its shape; 2
(ii) Cells in other parts of the body do not have these receptors /
Liver cells have these receptors; 1
(b) Side chains / R-groups are different; 1
(c) Tertiary structure changes / enzyme denatured / bonds broken;
Will affect active site (of enzyme);
Starch cannot bind / fit / form enzyme-substrate complex; 3
(d) Keeps pH constant;
So proteins / enzymes in mitochondria not denatured / affected; 2
(e) 1 Some proteins pass right through membrane;
2 Some proteins associated with one layer;
3 Involved in facilitated diffusion;
4 Involved in active transport;
5 Proteins act as carriers;
6 Carrier changes shape / position;
7 Proteins form channels / pores;
8 Protein allows passage of water soluble molecules /
charged particles / correct named example; 6 max
[15]
18. (a) (i) Biuret / alkali + copper sulphate;
Lilac/purple/mauve/violet; 2
Do not give credit for blue or pink. Ignore references to heating.
(b) R group of phenylalanine copied accurately; 1
Groby Community College 8
(c) (i) Bond shown linking carbon and nitrogen;
OH and H removed, =O and –H remaining; 2
(ii) Peptide bond; 1
(d) Addition of hydroxyl/OH group; 1
Candidate must distinguish clearly between hydroxylation and
hydrolysis
[7]
19. (a) Several/more than one polypeptide chain in molecule; 1
Evidence must only relate to 4º structure
(b) Chemical bonds formed between sulphur-containing groups/
R-groups/form disulphide bonds; Stronger bonds; Bind chain(s)
to each other; max 2
(c) Different number of amino acids; Different sequence of amino
acids; Bonds in different places; Gives different shape; max 2
(d) Outer layer of skin cells are dead; Do not respire/Do not contain
mitochondria; Do not produce ATP/release energy; Cells do not
have required proteins/carriers; max 3
(e) 1 TEM uses (beam of) electrons;
2 These have short wavelength;
3 Allow high resolution/greater resolution/Allow more detail to
be seen/greater useful magnification;
4 Electrons scattered (by molecules in air);
5 Vacuum established;
6 Cannot examine living cells;
7 Lots of preparation/procedures used in preparing specimens
/ fixing/staining/sectioning;
8 May alter appearance/result in artefacts; max 6
[14]
20. (a) Biuret reagent / Add NaOH and CuSO4; (ignore heated)
Positive result = violet/mauve/lilac/purple coloration; (NOT blue) 2
Groby Community College 9
(b) (i) Nitrogen / N; (NOT N2) 1
(ii) Condensation; 1
(iii) Must have box correct (allow HN / NH, but must have C=O correct)
H H O
H 2N C C N C C OH
H O CH 2
SH 1
[5]
21. (a) Add (Benedict’s) reagent (to urine sample) and heat / heat the mixture;
red/ brown/ orange/ green/ yellow; 2
(b) Gives quantitative result/level of glucose/concentration of glucose;
specific (to glucose) / Benedicts not specific;
more sensitive / accurate / precise; max. 2
[4]
22. Quality of written communication should be considered in crediting points in the marking
scheme. In order to gain credit, answers must be expressed logically in clear, scientific terms.
(a) (i) Made up of two sugar units / monosaccharides; R Two glucose units 1
(ii) Correct bond circled; 1
(iii) C12 ;
H22O11 ; 2
(b) A.T. involves carriers / proteins;
Molecules will have a different shape;
(Only those absorbed) will fit; 2
(c) Lactose produces a lower / more negative water potential;
So water moves into the intestine / less water absorbed;
By osmosis / diffusion / down concentration gradient;
Note: concentration gradient must be defined. 3
Groby Community College 10
(d) 1 Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus / have genetic material
in cytoplasm;
2 DNA in loop / ring;
3 Not associated with proteins / do not have chromosomes /
chromatin / do not divide by mitosis;
4 Smaller ribosomes;
5 No membrane-bound organelles;
6 Such as mitochondria / lysosomes / endoplasmic reticulum /
Golgi / chloroplasts;
7 Prokaryotic cells may have mesosomes;
8 Prokaryotic cells smaller;
9 May be enclosed by capsule; max 6
[15]
23. (a) glucose; 1
(reject alpha glucose)
(b) hydrolysis; 1
(accept catabolic)
(c) (long) straight/unbranched chains;
(idea of more than 1) chains lie side by side / form (micro)fibrils;
idea of H bonds holding chains together; 3
[5]
Groby Community College 11
You might also like
- AQA Biology 8 End-Of-Chapter Answers PDFDocument2 pagesAQA Biology 8 End-Of-Chapter Answers PDFAparupa Radhika Devi DasiNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Additional Questions (Cell Transport) AnsDocument8 pagesYear 12 Additional Questions (Cell Transport) Ansdramitrajp9602100% (1)
- Solutions To End-of-Chapter Questions: Erland Stevens Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery - Solutions 1Document78 pagesSolutions To End-of-Chapter Questions: Erland Stevens Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery - Solutions 1Miguel AguilarNo ratings yet
- BIOL 213 - Enzyme Lab IntroDocument4 pagesBIOL 213 - Enzyme Lab IntromariammanutdNo ratings yet
- Jan 2004 U1Document4 pagesJan 2004 U1api-3726022No ratings yet
- Monomers and Polymers MS PDFDocument8 pagesMonomers and Polymers MS PDFRaihanNo ratings yet
- 1.4 Proteins and Enzymes MSDocument11 pages1.4 Proteins and Enzymes MSshahbazhu006No ratings yet
- Biological Moleucles and Enzymes Exam Paper Revision AnswersDocument11 pagesBiological Moleucles and Enzymes Exam Paper Revision AnswersRabia RafiqueNo ratings yet
- B.2 MSDocument3 pagesB.2 MSYuvraj GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lipids MS PDFDocument10 pagesLipids MS PDFRaihanNo ratings yet
- A2AS BIOL Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2013 11881Document8 pagesA2AS BIOL Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2013 118816nht9f65zcNo ratings yet
- Jan 2005 U4aDocument5 pagesJan 2005 U4aapi-3726022No ratings yet
- 1.2 Carbohydrates MSDocument5 pages1.2 Carbohydrates MStrueamerican123196No ratings yet
- GCE Biology Marking Scheme HighlightsDocument29 pagesGCE Biology Marking Scheme Highlightsadam wilsonNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Biological Molecules Ans PDFDocument18 pages2.2 Biological Molecules Ans PDFtess_15No ratings yet
- Proteins and Enzymes MS PDFDocument12 pagesProteins and Enzymes MS PDFRaihanNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure MSDocument5 pagesCell Structure MSsophiaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Biological Molecules Mark Scheme: AQA A-Level BiologyDocument40 pages3.1 Biological Molecules Mark Scheme: AQA A-Level BiologyalinaNo ratings yet
- DNA and Protein Synthesis MS - UpdateDocument5 pagesDNA and Protein Synthesis MS - UpdateAzad AlizadaNo ratings yet
- EPAs Biology B A - Level Ch1Document2 pagesEPAs Biology B A - Level Ch1Simon LecamionNo ratings yet
- MRN AS Biology B - 1Document2 pagesMRN AS Biology B - 1Filsan HusseinNo ratings yet
- Aqa Bya1 Sms Jun09Document7 pagesAqa Bya1 Sms Jun09atbtbtbNo ratings yet
- Atp MSDocument11 pagesAtp MSRaihanNo ratings yet
- FilesDocument5 pagesFilessam miraeeNo ratings yet
- IB BIO Midterm PrepDocument92 pagesIB BIO Midterm Prepptzpwpjk7gNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Digestion and Absorption MSDocument6 pages3.3 Digestion and Absorption MSMunazza SadiaNo ratings yet
- GCE Biology (Salters Nuffield) (6131/01) Mark SchemeDocument9 pagesGCE Biology (Salters Nuffield) (6131/01) Mark SchemeL'Argent DémoiselleNo ratings yet
- Jan 06 E MSDocument6 pagesJan 06 E MSdavid ngNo ratings yet
- Year 11 P4 Test MSDocument11 pagesYear 11 P4 Test MSaditiNo ratings yet
- A2AS BIOL Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2014 13636Document7 pagesA2AS BIOL Past Papers Mark Schemes Standard January Series 2014 136366nht9f65zcNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Part Three Mxed AnswersDocument4 pagesBiochemistry Part Three Mxed AnswersAtulya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Microbiology answers and mark schemesDocument5 pagesMicrobiology answers and mark schemesKajolNo ratings yet
- Bonding Questions Mark SchemeDocument2 pagesBonding Questions Mark SchemeLe Vu nguyenNo ratings yet
- 0653 Combined Science: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2008 Question PaperDocument6 pages0653 Combined Science: MARK SCHEME For The October/November 2008 Question Paperapi-26146498No ratings yet
- 3.2 Cell Transport Ans PDFDocument23 pages3.2 Cell Transport Ans PDFtess_15No ratings yet
- 1.2 Carbohydrates MSDocument4 pages1.2 Carbohydrates MSKate MNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 June 2000Document6 pagesPaper 2 June 2000MSHNo ratings yet
- Y13 January Mock 2021 MarkschemeDocument12 pagesY13 January Mock 2021 Markschemedvvarf xNo ratings yet
- Mark schemes and exam questions on immunologyDocument38 pagesMark schemes and exam questions on immunologyBihandu PigeraNo ratings yet
- 0654 Co-Ordinated Sciences: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of TeachersDocument6 pages0654 Co-Ordinated Sciences: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2009 Question Paper For The Guidance of Teachersapi-26146498No ratings yet
- Jan 2002 U1Document3 pagesJan 2002 U1api-3726022No ratings yet
- 1 GCE Biology Marking Scheme January 2007 2Document21 pages1 GCE Biology Marking Scheme January 2007 2semirah anthonyNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 November 2001Document5 pagesPaper 2 November 2001MSHNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Cell Structure 1B IGCSE9 1 Edexcel Biology MS - LDocument5 pages4.1 Cell Structure 1B IGCSE9 1 Edexcel Biology MS - LMusyoka DanteNo ratings yet
- Number Answer Notes MarksDocument4 pagesNumber Answer Notes MarksJosh DeeNo ratings yet
- AS 2.1.2 Spec Notes AnswersDocument6 pagesAS 2.1.2 Spec Notes Answersmilksheikh2004No ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Paper 1B June 2014Document17 pagesMark Scheme Paper 1B June 2014Shovon MorshedNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme Question OneDocument6 pagesMark Scheme Question OnesulthanramizNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Enzymes MsDocument10 pagesUnit 5 Enzymes MsN. SNo ratings yet
- Year 12 Key Point Document 2021.22Document17 pagesYear 12 Key Point Document 2021.22newNo ratings yet
- OCR A As Biology 3 Practice Question Answers 3Document3 pagesOCR A As Biology 3 Practice Question Answers 3anonuser854No ratings yet
- Paper 6 Nov 2005Document4 pagesPaper 6 Nov 2005MSHNo ratings yet
- S6 Biology P2Document4 pagesS6 Biology P2UV Vïpêr UnïcôrnNo ratings yet
- 0654 Co-Ordinated Sciences: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2007 Question PaperDocument6 pages0654 Co-Ordinated Sciences: MARK SCHEME For The May/June 2007 Question Paperapi-26146498No ratings yet
- Cell Biology Mixed Question Quiz AnswersDocument6 pagesCell Biology Mixed Question Quiz Answersjay prakashNo ratings yet
- Plant Nutrition 4 MSDocument7 pagesPlant Nutrition 4 MSfathimath leeshaNo ratings yet
- Paper 2 November 2000Document5 pagesPaper 2 November 2000MSHNo ratings yet
- Biology exam questions on nitrogen cycle and enzyme functionDocument9 pagesBiology exam questions on nitrogen cycle and enzyme functionCephalic (Nico)No ratings yet
- Biological Molecules 1 MSDocument8 pagesBiological Molecules 1 MSNisha MohdNo ratings yet
- Biological Molecules 1 MSDocument8 pagesBiological Molecules 1 MSRainNo ratings yet
- Block Copolymers: Synthetic Strategies, Physical Properties, and ApplicationsFrom EverandBlock Copolymers: Synthetic Strategies, Physical Properties, and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Renewable Biomaterials: First Principles and ConceptsFrom EverandIntroduction to Renewable Biomaterials: First Principles and ConceptsAli S. AyoubNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Lung Disease QuestionsDocument16 pagesLungs and Lung Disease QuestionsrkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Heart and Heart Disease 1 2 Mark SchemeDocument5 pagesHeart and Heart Disease 1 2 Mark SchemerkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Causes of Disease Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesCauses of Disease Mark SchemerkblsistemNo ratings yet
- How cells become specialized and change functionDocument2 pagesHow cells become specialized and change functionrkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Lung Disease Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesLungs and Lung Disease Mark SchemerkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Molecules&Cells&Sys (Ja1)Document15 pagesMolecules&Cells&Sys (Ja1)rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Englishlanguage Year4paperii 140518112121 Phpapp02Document6 pagesEnglishlanguage Year4paperii 140518112121 Phpapp02rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- English p2Document5 pagesEnglish p2rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Immunity Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesImmunity Mark SchemeDNo ratings yet
- English Pastpresent TenseDocument2 pagesEnglish Pastpresent TenserkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/03 October/November 2020Document20 pagesCambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/03 October/November 2020rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- SEO-Optimized title for English language evaluation documentDOCUMENT English Language Evaluation Year 4 (Paper 1Document7 pagesSEO-Optimized title for English language evaluation documentDOCUMENT English Language Evaluation Year 4 (Paper 1rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Grade Thresholds - November 2020: Cambridge Pre-U Principal Course Biology (9790)Document1 pageGrade Thresholds - November 2020: Cambridge Pre-U Principal Course Biology (9790)rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Peihwa p2 2015Document7 pagesPeihwa p2 2015rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/04 October/November 2020Document11 pagesCambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/04 October/November 2020rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cell Struc (Q)Document26 pagesCell Struc (Q)rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Biology A: Biology A Unit 3 Ideas in Context Plus B7Document26 pagesBiology A: Biology A Unit 3 Ideas in Context Plus B7rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/02 October/November 2020Document10 pagesCambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/02 October/November 2020rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cell Struc (A)Document13 pagesCell Struc (A)rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- AQA Immunity Booklet AnswersDocument6 pagesAQA Immunity Booklet AnswersrkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/01 October/November 2020Document9 pagesCambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/01 October/November 2020rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Biology A Unit 1 Modules B1, B2, B3Document25 pagesBiology A Unit 1 Modules B1, B2, B3rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- AQA Immunity BookletDocument6 pagesAQA Immunity BookletrkblsistemNo ratings yet
- X Chromo InactivateDocument4 pagesX Chromo InactivaterkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Biology B Unit 2 Modules B4, B5, B6Document23 pagesBiology B Unit 2 Modules B4, B5, B6rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Biology A: Biology A Unit 3 Ideas in Context Plus B7Document28 pagesBiology A: Biology A Unit 3 Ideas in Context Plus B7rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- 5MARK Qs Unit1Document6 pages5MARK Qs Unit1rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Biology A Unit 2 Modules B4, B5, B6Document24 pagesBiology A Unit 2 Modules B4, B5, B6rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Q Examwizard 2018Document112 pagesTopic 1 Q Examwizard 2018rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Influenza virus NA inhibitors block the viral neuraminidase enzyme, so resistance would involve amino acid changes in that enzyme. The correct answer is 1Document61 pagesInfluenza virus NA inhibitors block the viral neuraminidase enzyme, so resistance would involve amino acid changes in that enzyme. The correct answer is 1Alen MehovicNo ratings yet
- 2 Enzymes & Enzyme KineticsDocument37 pages2 Enzymes & Enzyme KineticsNovVie VietTha Sccor IINo ratings yet
- Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd PolymerDocument339 pagesAcademic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd PolymerBLUECOMANCHE100% (1)
- Utami 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1563 012024Document9 pagesUtami 2020 J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1563 012024Whaler PausNo ratings yet
- Chapter Outline: I Ntrod Uction The Nature of Enzymes LsoenzymesDocument16 pagesChapter Outline: I Ntrod Uction The Nature of Enzymes LsoenzymesfjkgldjfNo ratings yet
- Composite RepairDocument9 pagesComposite RepairFelipe Perissé Duarte LopesNo ratings yet
- ITC ExplainedDocument6 pagesITC ExplainedShahil AlamNo ratings yet
- Drug Designing, Discovery and Development Techniques: Elvis A. Martis and Rakesh R. SomaniDocument19 pagesDrug Designing, Discovery and Development Techniques: Elvis A. Martis and Rakesh R. SomanitahafeNo ratings yet
- NIPER MEMORY BASED QUESTIONSDocument8 pagesNIPER MEMORY BASED QUESTIONSSwaroopSinghJakharNo ratings yet
- Rose Pharmacy JaipurDocument6 pagesRose Pharmacy JaipurAmit KochharNo ratings yet
- Chicken LiverDocument10 pagesChicken LiverZoran MiladinovićNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of SHMP and Advanced Scale Inhibitors For Control of and Scales in RO DesalinationDocument10 pagesEvaluation of SHMP and Advanced Scale Inhibitors For Control of and Scales in RO DesalinationKool LokeshNo ratings yet
- Mbbs BiochemistryDocument12 pagesMbbs BiochemistryKumar KPNo ratings yet
- Acidification of Purple Sweet Potato Long-Life NoodlesDocument16 pagesAcidification of Purple Sweet Potato Long-Life NoodlesPhuong NguyenNo ratings yet
- Date palm resistance to Bayoud diseaseDocument8 pagesDate palm resistance to Bayoud diseasemekaekNo ratings yet
- Biochem Pre-Lab 3bDocument2 pagesBiochem Pre-Lab 3bOla Anna GamutinNo ratings yet
- Tranylcypromine in Mind Part I - Review of P - 2017 - European Neuropsychopharm PDFDocument17 pagesTranylcypromine in Mind Part I - Review of P - 2017 - European Neuropsychopharm PDFdanilomarandolaNo ratings yet
- Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters: A A B C A D e B ADocument30 pagesBioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters: A A B C A D e B ABi LouNo ratings yet
- 2023-08-18 Enzymes KineticsDocument52 pages2023-08-18 Enzymes KineticsAjay MahalkaNo ratings yet
- McKee Chapter8 Sample PDFDocument44 pagesMcKee Chapter8 Sample PDFMustafa Kırca100% (1)
- BIOL 409 Quiz #8 KEYDocument2 pagesBIOL 409 Quiz #8 KEYBellony SandersNo ratings yet
- Detoxifying Cancer Causing Agents To Prevent CancerDocument7 pagesDetoxifying Cancer Causing Agents To Prevent CancerFedoxyzNo ratings yet
- Assessment Report Hamamelis Virginiana L Cortex Hamamelis Virginiana L Folium Hamamelis Virginiana L - en PDFDocument47 pagesAssessment Report Hamamelis Virginiana L Cortex Hamamelis Virginiana L Folium Hamamelis Virginiana L - en PDFvera GaborNo ratings yet
- Potency of Medicinal Leaves in The Growth Performance of Broiler ChicksDocument11 pagesPotency of Medicinal Leaves in The Growth Performance of Broiler ChicksJohn Michael RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall SynthesisDocument46 pagesAntibiotics That Inhibit Cell Wall SynthesisFadli Fadil Ramadhan RNo ratings yet
- MCQ in BiochemistryDocument6 pagesMCQ in Biochemistryvmshanes100% (1)
- Yeast MetabolismDocument60 pagesYeast MetabolismLina Marcela Reyes Solis100% (1)
- Enzymes and VitaminsDocument102 pagesEnzymes and VitaminsHey itsJamNo ratings yet