Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heart and Heart Disease 1 2 Mark Scheme
Uploaded by
rkblsistemOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heart and Heart Disease 1 2 Mark Scheme
Uploaded by
rkblsistemCopyright:
Available Formats
1.
(a) (i) Filling time stays constant / increases very little /
as heart rate increases;
Decrease in contraction time as heart rate increases;
Allow maximum of 1 mark if no reference to heart rate. 2
(ii) Work out time for one heart beat / one heart beat takes 1 second;
Subtract filling time / 0.38s;
Credit these basic points however determined. If the calculation
has been done, credit any point in method clearly explained.
OR
Plot contraction time against heart rate;
Read off value for 60 beats per minute; 2
(iii) Stroke volume / volume of blood pumped out at each beat; 1
(b) (i) 2
Valve located between Open Closed
Left atrium and left ventricle
Left ventricle and aorta ;
Right atrium and right ventricle
Right ventricle and pulmonary artery ;
(ii) Pressure constant / smooth in vein / only have pressure
surges in artery; 1
(iii) Contraction of ventricle / systole / entry of blood into aorta; 1
[9]
2. (a) (i) B/aorta; 1
(ii) D/pulmonary vein; 1
(b) Filling because valve between artery and ventricle closed;
Valve between atrium and ventricle/ cuspid valve open; 2
[Note: All answers must be in context of filling.
Answers specifically relating to left side are incorrect.]
(c) Pressure increases and volume stays constant; 1
(d) Pressure in ventricle (becomes) higher than pressure in aorta;
[Or converse] 1
Groby Community College 1
(e) ventricle contracts;
Produces increase in pressure;
Blood leaves venticle/ goes into aorta (and volume falls);
Through open valve; max 3
[9]
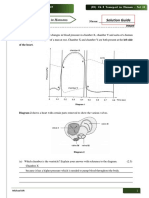
3. (a) (i) Higher pressure in ventricle; 1
(ii) Diagram showing closed valve drawn in appropriate position; 1
(b) Allows blood to leave atria/pass into ventricle;
Before ventricle contracts/empties; 2
(c) Impulses;
Along parasympathetic/vagus;
OR Fewer impulses;
Along sympathetic/(cardiac)accelerator;
Slows activity from SAN/pacemaker; 3
[Reject: decelerator nerve]
[7]
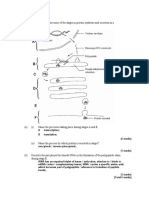
4. (a) Contain different/more than one tissue/type of cell; 1
(b) 0.8 (s) 1
(c) 0.4 (s) as events in right ventricle same as in left; 1
(d) (i) 0 - 0.1/0.4 - 0.9 because the volume increasing/ventricle
filling/blood entering; 1
(ii) from 0.9/0.1 – 0.4 because volume decreasing/ventricle
emptying/blood leaving; 1
In part (d) Accept any two figures from within the range.
(e) Correct answer of 15.75/15.8/16 = 2 marks
3
Incorrect answer but clear understanding that 45cm is 100% = 1 mark 2
[7]
5. (a) 0.1 – 0.6 seconds;
Volume (in left ventricle) increasing / ventricle filling; 2
(b) (i) 2 marks for correct answer of 75 (beats) per minute;
1 mark if heart beat correctly identified as lasting 0.8 seconds; 2
Groby Community College 2
(ii) 70 cm ; 1
(c) Multiply them; 1
(d) 750; 1
Accept a small increase – up to 800 cm
(e) (i) 4 : 1 / 4; 1
Ratio must be expressed in simplest terms
(ii) 18 cm ; 1
[9]
6. (a) (i) Fatty substances/foam cells in artery wall/under endothelium; 1
(ii) Narrows artery;
Turbulence / uneven flow;
Damage to endothelium;
Thromboplastins released; max 2
(b) (i) Correct area shaded (i.e. part supplied by vessels); 1
(ii) Area deprived of oxygen; Accept glucose 1
(c) Muscle in artery walls becomes thicker;
Aneurysm / ballooning of artery walls may occur;
Damage to endothelium (so foam cells enter); max 2
[7]
7. (a) (i) C and D; 1
(ii) left ventricle with thicker wall/more muscle / (muscle in) left ventricle
contracts more forcefully/beats more strongly; 1
(b) higher in atria/lower in ventricles;
atrioventricular valves/valves between atria and ventricles open; 2
(position of valves must be identified. Do not accept
an unqualified reference to valves. Assume pronouns
refer to atria.)
(c) (i) allows blood to pass into ventricles/from atria/so that atria can empty;
Groby Community College 3
before ventricles contract; 2
(ii) ventricle contracts from base /upwards;
blood pushed through B and C/arteries/all blood ejected; 2
[8]
8. (a)
Location of valve Valve open or closed
between chamber C and chamber B closed
between chamber D and chamber A closed
between chamber C and blood vessel Y open
All three correct = 2 marks
Two correct = 1 mark 2
(b) (i) Blood surges/pulsatile;
elastic tissue recoils;
and evens out pressure; Max 2
(ii) Enables one way flow/prevents backflow; 1
[5]
9. (a) correct position of AVN; (at the top of Purkyne tissue) 1
(b) (i) pressure in ventricles increasing (so ventricle contracting);
QRS occurs before pressure increase/ventricle contraction/
contracts after S / 0.14s; 2
(ii) corresponds to time when heart is relaxed/filling with blood/
diastole / not contracting; 1
(c) (i) 0.2s ; 1
(ii) line below left ventricle;
in phase with left ventricle; 2
[7]
10. (a) (i) 60 ÷ 0.72 – 0.76;
79 – 83; (Correct answer = 2 marks) 2
(ii) Ventricular pressure increases above pressure in atrium ; 1
Groby Community College 4
(b) Left ventricle has thicker / more muscle; 1
[4]
11. (a) (i) 0.3 s; 1
(ii) 0.2 - 0.4 s; 1
(b) thicker / more muscle in the left ventricle; 1
(c) Artery
1. thickest wall, enabling it to carry blood at high pressure / withstand
pressure surges;
2. most elastic tissue, which smoothes out flow / maintains pressure;
3. most muscle which maintains pressure;
4. muscle in wall to control blood flow;
Vein
5. thin wall does not have to withstand high pressure;
Capillary
6. thin wall, allowing diffusion/exchange;
7. only endothelium present, allowing short diffusion pathway;
All vessels
8. have endothelium that reduces friction; 6 max
[9]
QWC 1
Groby Community College 5
You might also like
- Cardiac Surgery in The Adult-3rd EditionDocument1,729 pagesCardiac Surgery in The Adult-3rd EditionFlorentina Negoita96% (26)
- Bournemouth School Cardiovascular SystemDocument4 pagesBournemouth School Cardiovascular SystemLesley Boulton100% (2)
- Gcse Biology Answers and Mark Schemes Questionsheet 1: CirculationDocument10 pagesGcse Biology Answers and Mark Schemes Questionsheet 1: CirculationthushyanthNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In HumanFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers Transport In HumanNo ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions Transport In HumansNo ratings yet
- Ergonomics in CarpentryDocument32 pagesErgonomics in CarpentrypsyishNo ratings yet
- CVA Case ClerkingDocument11 pagesCVA Case ClerkingOtaiKatiNo ratings yet
- Groby Community College 1Document5 pagesGroby Community College 1Rubban KunaNo ratings yet
- MYP4 Biology Unit 3 Quiz 1 Answer Key 1Document1 pageMYP4 Biology Unit 3 Quiz 1 Answer Key 1Aref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 3 - MsDocument11 pages3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 3 - MsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 The Lungs MSDocument3 pagesUnit 1 The Lungs MSHassanIsmailNo ratings yet
- ,dand, And, AdnDocument9 pages,dand, And, AdnEuginNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle & Blood Vessels 2022-1Document8 pagesCardiac Cycle & Blood Vessels 2022-1krrish5906No ratings yet
- 3.4 Mass Transport in Animals MSDocument9 pages3.4 Mass Transport in Animals MStzNo ratings yet
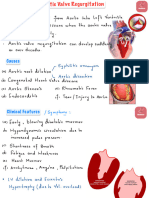
- Aortic Valve RegurgitationDocument3 pagesAortic Valve Regurgitationprakash ramNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Lung Disease Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesLungs and Lung Disease Mark SchemerkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Unit 5-Heart AnswersDocument11 pagesUnit 5-Heart Answersareyouthere92No ratings yet
- Transport of Substances in Humans (MS) PDFDocument6 pagesTransport of Substances in Humans (MS) PDFWan Ching ChanNo ratings yet
- June 2003 U2bDocument3 pagesJune 2003 U2bapi-3726022No ratings yet
- 18.body Fluids and CirculationDocument20 pages18.body Fluids and Circulationg1307No ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Breathing & Respiration RevisionDocument9 pagesGCSE Biology Breathing & Respiration RevisionTamicka Bonnick100% (1)
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 2 - MsDocument21 pages3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 2 - MsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- Transport 1 MSDocument7 pagesTransport 1 MSAndrew KyawNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals 1 MSDocument7 pagesTransport in Animals 1 MS青木ケイNo ratings yet
- EPAs Biology B A - Level Ch4Document2 pagesEPAs Biology B A - Level Ch4Moha SaadNo ratings yet
- Body fluidsDocument4 pagesBody fluidsShrutheeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory - System - Exam - Ques - 1.rtf BiologyDocument5 pagesCirculatory - System - Exam - Ques - 1.rtf BiologyRekaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument21 pagesCirculatory SystemKumar Sujeet100% (1)
- A2 5.1.5 Spec Notes AnswersDocument3 pagesA2 5.1.5 Spec Notes AnswersjnrjknerNo ratings yet
- As 04 Transport in Animals Ans - BiologyDocument7 pagesAs 04 Transport in Animals Ans - BiologyUncleBulgaria100% (1)
- Tutorial 9 Ciculatory System II 202001 - Self LearningDocument5 pagesTutorial 9 Ciculatory System II 202001 - Self LearningChun Chee LeongNo ratings yet
- Human Heart TransportDocument2 pagesHuman Heart TransportBryantNo ratings yet
- Test 7 XI- Unit5Document9 pagesTest 7 XI- Unit5Tamal NayakNo ratings yet
- 011 - Cardiovascular Physiology) Cardiac Cycle Digital Version @perez Q - ADocument1 page011 - Cardiovascular Physiology) Cardiac Cycle Digital Version @perez Q - Abvxryk29byNo ratings yet
- Biology Task 1 CompleteDocument6 pagesBiology Task 1 Completelauryn morganNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle QuizDocument4 pagesCardiac Cycle QuizkuronokurisatenNo ratings yet
- Coordination & Response 5 MS PDFDocument3 pagesCoordination & Response 5 MS PDFJeffrey PiggottNo ratings yet
- (Board Review Series) Linda S. Costanzo - BRS Physiology, 5th Edition (Board Review Series) - Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (2010)Document7 pages(Board Review Series) Linda S. Costanzo - BRS Physiology, 5th Edition (Board Review Series) - Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (2010)Salifyanji SimpambaNo ratings yet
- Checked - Unit 1 Molecules, Diet, Transport and Health - Exam - MSDocument16 pagesChecked - Unit 1 Molecules, Diet, Transport and Health - Exam - MSEllane leeNo ratings yet
- c00711 SQPDocument54 pagesc00711 SQPSơnSơnNo ratings yet
- 3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 1 MsDocument23 pages3.4 Organisms and Substance Exchange - Mass Transport in Animals 1 MsMaymunah HussainNo ratings yet
- 010 - Cardiovascular Physiology) Cardiovascular Cardiac Cycle @perez Q - ADocument1 page010 - Cardiovascular Physiology) Cardiovascular Cardiac Cycle @perez Q - Abvxryk29byNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and Circulation (1) MMMDocument52 pagesBody Fluids and Circulation (1) MMMRjNo ratings yet
- NEET Important Questions For Biology - Body Fluid and CirculationDocument17 pagesNEET Important Questions For Biology - Body Fluid and Circulationnikkykhanna061No ratings yet
- Aqa Unit 1 June 2002 MsDocument6 pagesAqa Unit 1 June 2002 MsYanahan ParamalingamNo ratings yet
- Transport in Animals 4 MSDocument7 pagesTransport in Animals 4 MSpirateduser666No ratings yet
- Circulatory System 1 MSDocument10 pagesCirculatory System 1 MSAlhaji SowNo ratings yet
- Body FluidsDocument13 pagesBody FluidslixanNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants MSDocument5 pagesTransport in Plants MSOtniel Dita NugrohoNo ratings yet
- Ganong SBADocument13 pagesGanong SBAyuyuarohaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Heart Questions For ASDocument6 pages1 - Heart Questions For ASMohammed AshroffNo ratings yet
- Human Heart - Practice SheetDocument6 pagesHuman Heart - Practice SheetSYEDNo ratings yet
- 20-Feb-2023 at 2 - 11 - 12 PMDocument37 pages20-Feb-2023 at 2 - 11 - 12 PMmihikaNo ratings yet
- Scientific Article For Use With Question 7 - A Red Card For The HeartDocument13 pagesScientific Article For Use With Question 7 - A Red Card For The HeartAmar MuhammedNo ratings yet
- CHF Oral Board SheetDocument2 pagesCHF Oral Board SheetKaitlyn ProbascoNo ratings yet
- ACHAI DLaboratory Actiivty 11 - The HeartDocument6 pagesACHAI DLaboratory Actiivty 11 - The HeartSYDNEY JILL ACHAINo ratings yet
- Circulaotry System Solved.Document10 pagesCirculaotry System Solved.Methyl OrangeNo ratings yet
- 2022 Sec 4IP Bio EOY Paper 2 - Mark Scheme - Updated 131022Document14 pages2022 Sec 4IP Bio EOY Paper 2 - Mark Scheme - Updated 131022anya de silvaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesCirculatory SystemKushagra jaiswalNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Pathology - 025) Valvular Heart Diseases Overview (Notes)Document18 pagesCardiovascular Pathology - 025) Valvular Heart Diseases Overview (Notes)Geraldine HernandezNo ratings yet
- Biology Weekly Worksheet g7s2pb Transport in HumansDocument5 pagesBiology Weekly Worksheet g7s2pb Transport in HumansD'ferti AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- MCQ Unit 7 Answers: TYS Unit 7 (Science Biology)Document3 pagesMCQ Unit 7 Answers: TYS Unit 7 (Science Biology)prameetaNo ratings yet
- New PaperDocument12 pagesNew PaperkajuNo ratings yet
- Molecules&Cells&Sys (Ja1)Document15 pagesMolecules&Cells&Sys (Ja1)rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Causes of Disease Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesCauses of Disease Mark SchemerkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Enzymes and Digestive System Mark SchemeDocument11 pagesEnzymes and Digestive System Mark SchemerkblsistemNo ratings yet
- How cells become specialized and change functionDocument2 pagesHow cells become specialized and change functionrkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Immunity Mark SchemeDocument6 pagesImmunity Mark SchemeDNo ratings yet
- English Pastpresent TenseDocument2 pagesEnglish Pastpresent TenserkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Lung Disease QuestionsDocument16 pagesLungs and Lung Disease QuestionsrkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Lungs and Lung Disease Mark SchemeDocument3 pagesLungs and Lung Disease Mark SchemerkblsistemNo ratings yet
- SEO-Optimized title for English language evaluation documentDOCUMENT English Language Evaluation Year 4 (Paper 1Document7 pagesSEO-Optimized title for English language evaluation documentDOCUMENT English Language Evaluation Year 4 (Paper 1rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/01 October/November 2020Document9 pagesCambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/01 October/November 2020rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- English p2Document5 pagesEnglish p2rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Englishlanguage Year4paperii 140518112121 Phpapp02Document6 pagesEnglishlanguage Year4paperii 140518112121 Phpapp02rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Peihwa p2 2015Document7 pagesPeihwa p2 2015rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/03 October/November 2020Document20 pagesCambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/03 October/November 2020rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/04 October/November 2020Document11 pagesCambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/04 October/November 2020rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/02 October/November 2020Document10 pagesCambridge Pre-U: Biology 9790/02 October/November 2020rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Grade Thresholds - November 2020: Cambridge Pre-U Principal Course Biology (9790)Document1 pageGrade Thresholds - November 2020: Cambridge Pre-U Principal Course Biology (9790)rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Biology A Unit 1 Modules B1, B2, B3Document25 pagesBiology A Unit 1 Modules B1, B2, B3rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cell Struc (Q)Document26 pagesCell Struc (Q)rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- 5MARK Qs Unit1Document6 pages5MARK Qs Unit1rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- AQA Immunity Booklet AnswersDocument6 pagesAQA Immunity Booklet AnswersrkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Cell Struc (A)Document13 pagesCell Struc (A)rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Biology A: Biology A Unit 3 Ideas in Context Plus B7Document26 pagesBiology A: Biology A Unit 3 Ideas in Context Plus B7rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- AQA Immunity BookletDocument6 pagesAQA Immunity BookletrkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Biology A: Biology A Unit 3 Ideas in Context Plus B7Document28 pagesBiology A: Biology A Unit 3 Ideas in Context Plus B7rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- X Chromo InactivateDocument4 pagesX Chromo InactivaterkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Biology A Unit 2 Modules B4, B5, B6Document24 pagesBiology A Unit 2 Modules B4, B5, B6rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Biology B Unit 2 Modules B4, B5, B6Document23 pagesBiology B Unit 2 Modules B4, B5, B6rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 Q Examwizard 2018Document112 pagesTopic 1 Q Examwizard 2018rkblsistemNo ratings yet
- Professor Devendra Kumar Chhabra: TH THDocument2 pagesProfessor Devendra Kumar Chhabra: TH THVineet UttamNo ratings yet
- Preventing Urinary Tract Infections: X X X XDocument10 pagesPreventing Urinary Tract Infections: X X X XLia Ayu Nur'ainiNo ratings yet
- SPECT brain imaging for blood flowDocument2 pagesSPECT brain imaging for blood flowissaiahnicolleNo ratings yet
- Sanofi Just Got Its First Cancer Drug Approved in A Decade.Document7 pagesSanofi Just Got Its First Cancer Drug Approved in A Decade.Antonietta BlacconeriNo ratings yet
- Drug Discovery and Development Lecture NotesDocument75 pagesDrug Discovery and Development Lecture NotesJameel BakhshNo ratings yet
- Cad NCPDocument1 pageCad NCPKrizzia Mae F. MayoresNo ratings yet
- Public Health Surveillance TrainingDocument51 pagesPublic Health Surveillance TrainingSalihu MustaphaNo ratings yet
- Artificial HeartDocument17 pagesArtificial HeartRAKESHKANNAN100% (1)
- JUNE 2008 NP1 BOARD EXAM QUESTIONSDocument70 pagesJUNE 2008 NP1 BOARD EXAM QUESTIONSPrecious Nidua100% (1)
- JURNAL GonoreDocument20 pagesJURNAL GonoreRuni Arumndari100% (1)
- What Are The Signs of Autism in GirlsDocument8 pagesWhat Are The Signs of Autism in GirlsAna Sofia Nunes JorgeNo ratings yet
- Consideraciones Practicas en La Administracion y Dosis de Cannabis MedicinalDocument8 pagesConsideraciones Practicas en La Administracion y Dosis de Cannabis MedicinalGerardo QGNo ratings yet
- HallucinogensDocument18 pagesHallucinogensDavyne Nioore Gabriel100% (1)
- Journal Heptojugular RefluxDocument5 pagesJournal Heptojugular RefluxFarhan RezaNo ratings yet
- Cocaine's Journey from Medicine to Deadly AddictionDocument6 pagesCocaine's Journey from Medicine to Deadly AddictionDoniele DalorNo ratings yet
- Medical AbbreviationsDocument6 pagesMedical AbbreviationsEina CarmonaNo ratings yet
- NAMA BARANG LIST AND PRICESDocument51 pagesNAMA BARANG LIST AND PRICESlevely rizkiNo ratings yet
- CPR First Aid SyllabusDocument2 pagesCPR First Aid Syllabusapi-3704804No ratings yet
- G6PD Deficiency Associated With Hearing Loss in Malaria FalciparumDocument2 pagesG6PD Deficiency Associated With Hearing Loss in Malaria FalciparumCagar Irwin TaufanNo ratings yet
- Abs, Dis, Met, Excretion, Routesof Drug AdministrationDocument46 pagesAbs, Dis, Met, Excretion, Routesof Drug Administrationzarairahad486No ratings yet
- DiethylcarbamazineDocument8 pagesDiethylcarbamazinePrakob GikokNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Relationship Between Anxiety Levels and Panic Attacks Among The Youth in ShimlaDocument52 pagesAssessing The Relationship Between Anxiety Levels and Panic Attacks Among The Youth in ShimlaAni RudhNo ratings yet
- MnemonicS in OphthaDocument22 pagesMnemonicS in Ophthaabuahmed&janaNo ratings yet
- Injectable Bone Graft and Allograft Bone Chips in The Treatment of Benign Bone LesionDocument8 pagesInjectable Bone Graft and Allograft Bone Chips in The Treatment of Benign Bone LesionIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- AlbuminDocument16 pagesAlbuminMaroofAliNo ratings yet
- 16 Natural Ways To Manage Meniere's Disease SymptomsDocument16 pages16 Natural Ways To Manage Meniere's Disease SymptomsMeseret NegashNo ratings yet
- Health and Disease Status of Thai Pangas, Bangladesh: Pangasius Hypophthalmus Cultured in Rural Ponds of MymensinghDocument3 pagesHealth and Disease Status of Thai Pangas, Bangladesh: Pangasius Hypophthalmus Cultured in Rural Ponds of MymensinghgooedliaNo ratings yet