Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Adobe Scan Dec 09, 2022
Uploaded by
Vijay Raj SinghCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Adobe Scan Dec 09, 2022
Uploaded by
Vijay Raj SinghCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION:
The step response of RC and RLC circuits involves the determination of
the transient and steady-state solutions of the circuit. Energy storage
elements such as inductors or capacifors do not permif an instantaneous
change in energy. Thus a gradual change takes place from some initial
level till the new steady state level is reached.
AIM:
a) To verify KVL and KCL measure input resistance.
b) To study the effect of some modifications in special circuits.
APPARATUS
1. Resistors of value (9.94k2, 6252, 20.82)
2. Capacitor(0.224F)
3. Breadboard
4. Multi-meter
5. Connecting wires
6. DC Power Supply 0-30V
7. DSO(Digital Storage Oscilloscope)
THEORYY
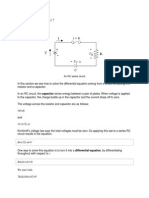
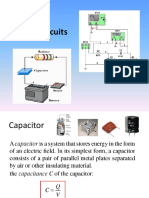
Analysis of the RC circuits can be done as follows:
-
w
ul
Zero-input
C
- +
RC series circurt
CV0
state
To find the total response of an RC series circuit, you need
to find the zero-input response "ZIR" (Natural or free or
transient) and the zero-state response "ZSR" (forced) and then
add them together
For ZIR, the first-order differential equation reduces to:
dve =0
dtR=0
The response(Natural) becomes venlt) =Ae*/RC
The constant term RC in this equation is called the time
constant(t).
Capacitor charging Capacitor discharging
Voltage Voltage
To calculate ZSR, consider the circuit in a steady state (the
capacitor acts as an open circuit). After getting ZSR, Substitute in the
total response to get total response.
v . ) = vt+ Ve
-1
v.0)= Ae /t+V
Analysis of RLC circuit:
R
Blue line= direction of current
RI()+Ld(t)
dt +V(0)+ r)dr =V).
The above equation is just Kirchhoffs Voltage Law applied to the
circuit.
Solving it gives a sinusoidal equation of relation between voltage
and time.
Response Condition Voltage Function
ype
Overdamped woca vt)=V+Ael Axe
You might also like
- What is a VFD? Understanding Variable Frequency DrivesDocument4 pagesWhat is a VFD? Understanding Variable Frequency Driveschandrakanth100% (2)
- 10 October 1960 PDFDocument68 pages10 October 1960 PDFBravo KiloNo ratings yet
- PD CLC TS 50539 12 2013 Low Voltage Surge Protective Devices Surge Protective Devices For Specific Application Including D.C.Document38 pagesPD CLC TS 50539 12 2013 Low Voltage Surge Protective Devices Surge Protective Devices For Specific Application Including D.C.Chang Lee100% (1)
- KITTEN CALIBRATION PROCEDURE STEPSDocument3 pagesKITTEN CALIBRATION PROCEDURE STEPSFlaco Depaulo CarlosNo ratings yet
- Some Applications of Differential Equations in RL-RC Electrical CircuitDocument12 pagesSome Applications of Differential Equations in RL-RC Electrical CircuitArindam MondalNo ratings yet
- 400KV & 220KV DR PanelDocument53 pages400KV & 220KV DR PanelBijaya Kumar MohantyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7-2Document54 pagesChapter 7-2AhmedAlhosaniNo ratings yet
- Transient Excitation of First-Order CircuitsDocument39 pagesTransient Excitation of First-Order CircuitsAakash JainNo ratings yet
- ELL 100 transient response introduction electrical engineeringDocument56 pagesELL 100 transient response introduction electrical engineeringMohamadNo ratings yet
- RL RC CircuitDocument8 pagesRL RC CircuitDavex GwapoNo ratings yet
- ELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: L 9: T R O F O C (N R)Document57 pagesELL 100 Introduction To Electrical Engineering: L 9: T R O F O C (N R)Sasindu DilshanNo ratings yet
- Week 4aDocument39 pagesWeek 4aHari ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ch7-Response of First-Order RL and RC CircuitsDocument34 pagesCh7-Response of First-Order RL and RC CircuitsFakrul HanifNo ratings yet
- EEE 209 Presentation 5 (1st and 2nd Order CCTS)Document88 pagesEEE 209 Presentation 5 (1st and 2nd Order CCTS)Mert YılmazNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit Analysis: Natural Response of RL CircuitsDocument15 pagesElectric Circuit Analysis: Natural Response of RL CircuitsRizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- EE-221-Review of DC CircuitsDocument51 pagesEE-221-Review of DC CircuitsSean Ng100% (1)
- RC CircuitDocument9 pagesRC CircuitRohishkumarReddy MittaNo ratings yet
- Time Domain Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsDocument21 pagesTime Domain Response of First Order RL and RC CircuitsMOHSINALI MOMINNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryDocument6 pagesRC Circuit Response Introduction & TheoryMuhammad FarooqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 - Direct-Current and CircuitsDocument11 pagesChapter 26 - Direct-Current and CircuitsClaire GacayanNo ratings yet
- Thyristor Commutation PDFDocument40 pagesThyristor Commutation PDFalbert agung matondangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2p4p2Document9 pagesChapter 2p4p2Glenn VirreyNo ratings yet
- RL and RC Circuit Time Domain ResponseDocument21 pagesRL and RC Circuit Time Domain ResponseDharamNo ratings yet
- ECS203 2014 ch 10 u4Document23 pagesECS203 2014 ch 10 u4luzmancia0204No ratings yet
- Commutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-I: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth ClassDocument11 pagesCommutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-I: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth Classmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Ii (Eee202)Document19 pagesFundamentals of Electrical & Electronic Engineering Ii (Eee202)ALABI ABIODUNNo ratings yet
- EE 230 Laplace Circuits - 1Document11 pagesEE 230 Laplace Circuits - 1smitaNo ratings yet
- Proof of i=i(1−e−(R/L)t) for an RL circuitDocument6 pagesProof of i=i(1−e−(R/L)t) for an RL circuitNealWhiteNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument28 pagesCourse OutlineIdrisa Mussa ChubwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document77 pagesChapter 7rizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- 7Document36 pages7s2-qx (s2.qx)No ratings yet
- Transistor BJT - 3Document56 pagesTransistor BJT - 3Sinta reinaNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 AC and DC CircuitsDocument35 pagesUnit-2 AC and DC CircuitsAsutosh KumarNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1: RC Circuits: 1.1 Electrical Circuit DefinitionsDocument12 pagesExperiment 1: RC Circuits: 1.1 Electrical Circuit DefinitionsBrice Ekobo AkoaNo ratings yet
- Laplace Circuits PDFDocument11 pagesLaplace Circuits PDFsbosch54No ratings yet
- Bee LabDocument68 pagesBee LabwasimchaspraNo ratings yet
- SOLUTIONS to ELE22EMI 2004 NOVEMBER ExamDocument12 pagesSOLUTIONS to ELE22EMI 2004 NOVEMBER Examسعيد ابوسريعNo ratings yet
- Lect4 RLC CirciuitsDocument13 pagesLect4 RLC CirciuitsbhaveshNo ratings yet
- Power Systems-I: Instructions For Experiment No. 1Document4 pagesPower Systems-I: Instructions For Experiment No. 1Priya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Series Resonance - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument6 pagesSeries Resonance - GATE Study Material in PDFTestbook BlogNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26: Direct-Current Circuits (Part 2)Document23 pagesChapter 26: Direct-Current Circuits (Part 2)ccny07No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Simple Resistive CircuitsDocument45 pagesChapter 3 Simple Resistive CircuitsTony Abi HaidarNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of First-Order RL & RC CircuitsDocument60 pagesFundamentals of First-Order RL & RC CircuitsPhan Phuong NgocNo ratings yet
- Ac Circuits InhouseDocument74 pagesAc Circuits InhouseRenzo GrafiloNo ratings yet
- Experiment-3, Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterDocument2 pagesExperiment-3, Full-Wave Bridge Rectifier Circuit Without and With FilterSudip Kumar KarNo ratings yet
- RC CircuitsDocument34 pagesRC CircuitsFaiz ShbNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 3-BJT Common-Emitter Amplifier Ver3Document41 pagesLECTURE 3-BJT Common-Emitter Amplifier Ver3Sankalp SharmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15BDocument33 pagesChapter 15BVinNo ratings yet
- A18EE2001 - IA2 Sample Questions : Answer Red ColouredDocument6 pagesA18EE2001 - IA2 Sample Questions : Answer Red ColouredanNo ratings yet
- EEL 5245 Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters Effects of Non-IdealitiesDocument8 pagesEEL 5245 Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters Effects of Non-IdealitiesCentvie Joie F. AlbeosNo ratings yet
- Chap 5Document60 pagesChap 5TEH XIAN YOONG STUDENTNo ratings yet
- EE 42/43/100 Introduction To Digital Electronics: Review of Ch. 4-7.3 7/19/13Document43 pagesEE 42/43/100 Introduction To Digital Electronics: Review of Ch. 4-7.3 7/19/13ozanistzNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity: University of Manchester Department of Computer ScienceDocument14 pagesBasic Electricity: University of Manchester Department of Computer Scienceabinash_pattanaik41No ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electric Circuits - First-Order Circuit AnalysisDocument44 pagesFundamentals of Electric Circuits - First-Order Circuit AnalysisLong QuangNo ratings yet
- EE42 100 Wb-Lecture16 073113-FDocument42 pagesEE42 100 Wb-Lecture16 073113-FozanistzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3Document33 pagesChapter 3Pratik KumarNo ratings yet
- RC CircuitsDocument37 pagesRC CircuitsNoviNo ratings yet
- EEE 104 All Lab Sheet (Department of EEE, NSTU)Document28 pagesEEE 104 All Lab Sheet (Department of EEE, NSTU)Sakif IrtizaNo ratings yet
- Ac Circuit Experiment: EquipmentDocument4 pagesAc Circuit Experiment: EquipmentBien BasbasNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit: Natural Response Complex Impedance Series CircuitDocument12 pagesRC Circuit: Natural Response Complex Impedance Series CircuitKrishanu ModakNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICAL SCIENCES - IDocument39 pagesELECTRICAL SCIENCES - IGanesh DharmireddyNo ratings yet
- RL TransientDocument35 pagesRL Transientkrish104411No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Oct 22, 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan Oct 22, 2022Vijay Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Nov 15, 2022Document1 pageAdobe Scan Nov 15, 2022Vijay Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Dec 01, 2022Document4 pagesAdobe Scan Dec 01, 2022Vijay Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Feb 06, 2023Document15 pagesAdobe Scan Feb 06, 2023Vijay Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- Three-phase load analysis: power, voltage, current and power factor calculationsDocument1 pageThree-phase load analysis: power, voltage, current and power factor calculationsVijay Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- instaPDF - in Jee Advanced 2021 Toppers List With Marks 408Document1 pageinstaPDF - in Jee Advanced 2021 Toppers List With Marks 408Vijay Raj SinghNo ratings yet
- Maths Matrix LN 1634830491948Document56 pagesMaths Matrix LN 1634830491948Tanmay SagarNo ratings yet
- Method of Calculating Energy Losses in Distribution NetworksDocument6 pagesMethod of Calculating Energy Losses in Distribution NetworksAdoos KhalidNo ratings yet
- Filterpro Design Report: SchematicDocument4 pagesFilterpro Design Report: SchematicLuis-mi Champi GutierrezNo ratings yet
- SK 3239.118 Toptherm Fan-And-Filter UnitsDocument5 pagesSK 3239.118 Toptherm Fan-And-Filter UnitsLOI HONo ratings yet
- Marine FlexenDocument67 pagesMarine FlexenpayaljeevaNo ratings yet
- Brochure Commerciale Studer Next 3Document12 pagesBrochure Commerciale Studer Next 3SINES FranceNo ratings yet
- Study of The Variation of Power Loss With Frequency Along A RectangularDocument6 pagesStudy of The Variation of Power Loss With Frequency Along A RectangularIAEME PublicationNo ratings yet
- TMS819Document496 pagesTMS819NISHANNo ratings yet
- Exp - 2 Second LPF PDFDocument15 pagesExp - 2 Second LPF PDFJuma AryNo ratings yet
- Auto 210 CableDocument1 pageAuto 210 CableVijay KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- CM8600A CcmicDocument16 pagesCM8600A CcmicGheorghe MihaiNo ratings yet
- Government College of Engineering, Yavatmal: 1. EmailDocument9 pagesGovernment College of Engineering, Yavatmal: 1. EmailKim D'souzaNo ratings yet
- RP-04 + SDM-1 PDFDocument4 pagesRP-04 + SDM-1 PDFIrwing MoranNo ratings yet
- Field Strength MeterDocument9 pagesField Strength MeterVinod JagdaleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Optical AmplifiersDocument40 pagesChapter 6 Optical AmplifiersThasnimFathimaNo ratings yet
- PARAMAGNETISM LECTUREDocument12 pagesPARAMAGNETISM LECTUREawaisaNo ratings yet
- MCQ On Crystal StructureDocument6 pagesMCQ On Crystal StructureJamilur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Eee150 Chapter 3 (Electrical Safety) PDFDocument52 pagesEee150 Chapter 3 (Electrical Safety) PDFMUHAMMAD LUKMAN ARSHADNo ratings yet
- Microwave BenchDocument32 pagesMicrowave Benchghadei_debasishNo ratings yet
- EMC Power Quality Web14Document169 pagesEMC Power Quality Web14Lammie Sing Yew Lam100% (1)
- Elettronica Pratica 1972 - 01Document10 pagesElettronica Pratica 1972 - 01rikyNo ratings yet
- CR306Document3 pagesCR306josé fernando sotelo ventosillaNo ratings yet
- U-3 BJTDocument56 pagesU-3 BJTGloryNo ratings yet
- Bridge Rectifier: FeaturesDocument3 pagesBridge Rectifier: FeaturesEdgar DauzonNo ratings yet
- t420 ThinkpadDocument11 pagest420 ThinkpadDwi RachmatNo ratings yet