Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MOSFET Device Operation and Types
Uploaded by
ALDWIN H. POSTREROOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MOSFET Device Operation and Types
Uploaded by
ALDWIN H. POSTREROCopyright:
Available Formats
Postrero, Aldwin H.
June 16, 2022
BSCPE_II-7 Prof. Elmer Nuñez
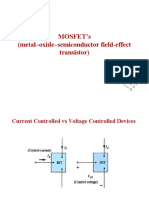
MOSFET
MOSFET is an acronym that stands for metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor.
It has a MOS construction and is a field-effect transistor. MOSFETs are typically three-terminal
devices having gate (G), drain (D), and source (S) connections. A voltage applied to the gate (G)
terminal controls current conduction between the drain (D) and the source (S). MOSFETs
outperform bipolar transistors in terms of relative speed and low-loss operation. By channel
polarity, there are P type and N type, and by control mechanism, there are enhancement type
with normally off (gate voltage 0 V off) and depletion type with normally on (deactivated with
gate voltage 0 V). The enhancement type is widely used.
The main differentiation between FETs and
MOSFETs is that MOSFETs have a Metal Oxide Gate
electrode that is electrically isolated from the main
semiconductor n-channel or p-channel by a thin layer
of Silicon dioxide or glass. The isolation of the
regulating Gate raises the input resistance of the
MOSFET to extreme levels in the Mega-ohms
A MOSFET's most typical use is that of a switch. The circuit below illustrates the
MOSFET acting as a switching device to turn the bulb on and off. The gate input voltage VGS is
applied via an input voltage source. When the applied voltage is positive, the motor is turned on,
and when the applied voltage is zero or negative, the lamp is turned off.
The MOSFET is categorized into two categories depending on the type of operation,
namely Enhancement mode MOSFET (E-MOSFET) and Depletion mode MOSFET (D-
MOSFET). These MOSFETs are further classified as n-channel and p-channel based on the
material used for manufacturing. In general, there are four varieties of MOSFETs.
• MOSFET with N-Channel Depletion Mode
• MOSFET in P-Channel Depletion Mode
• MOSFET with N-Channel Enhancement Mode
• MOSFET with P-Channel Enhancement Mode
MOSFETs require no gate input other than a pulse to charge or discharge their input capacitance.
They have faster switching rates and lower currents than bipolar transistors.
• Diodes of Power
• Bipolar Transistor with Insulated Gate
• Junction Transistor, Bipolar
• Field-Effect Transistor Based on Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor
• SCR, GTO, and MCT thyristors
You might also like
- Cpe Ac 222 - Postrero, Aldwin H. Quiz 4.Document1 pageCpe Ac 222 - Postrero, Aldwin H. Quiz 4.ALDWIN H. POSTRERONo ratings yet
- MOSFET Basics: Working Principles and ApplicationsDocument19 pagesMOSFET Basics: Working Principles and ApplicationsSanyam BajpaiNo ratings yet
- 04 Transistor MOSFETDocument18 pages04 Transistor MOSFETNatalie mirelesNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument4 pagesMOSFETelen19111036 KFUEITNo ratings yet
- What Is A MOSFET - Basics, Working Principle & ApplicationsDocument3 pagesWhat Is A MOSFET - Basics, Working Principle & ApplicationsKimberly Camacho CatubigNo ratings yet
- Debre Markos University Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Computer Engineering (PG)Document10 pagesDebre Markos University Institute of Technology School of Electrical and Computer Engineering Computer Engineering (PG)enidegNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MOSFET.Document4 pagesIntroduction To MOSFET.Akib Hasan NiloyNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 NotesDocument9 pagesUnit 5 NotesShashikant PandeyNo ratings yet
- Back To Basics Introduction To BJTs JFETs MESFETs and MOSFETsDocument28 pagesBack To Basics Introduction To BJTs JFETs MESFETs and MOSFETssonitha alvaNo ratings yet
- Igfet'S Insulated Gate Field Effect TransistorsDocument4 pagesIgfet'S Insulated Gate Field Effect TransistorsAnonymous xzi9LiTNo ratings yet
- ENT251 Special Diodes and FETDocument39 pagesENT251 Special Diodes and FETA76 - shashank agrawalNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument18 pagesMOSFETRajiv RawatNo ratings yet
- The MOSFET - Understanding the Metal Oxide Semiconductor FETDocument11 pagesThe MOSFET - Understanding the Metal Oxide Semiconductor FETAan BeckhsNo ratings yet
- EC302Document15 pagesEC302api-3853441No ratings yet
- MOSFET: A Guide to the Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorDocument21 pagesMOSFET: A Guide to the Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorthesumitsinghNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Guide - Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect TransistorDocument2 pagesMOSFET Guide - Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect TransistorbofshafiqueNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument20 pagesMOSFETBhumika PoriyaNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Seminar: An Introduction to the Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorDocument23 pagesMOSFET Seminar: An Introduction to the Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect TransistorRahulKushwahaNo ratings yet
- SECA1503Document149 pagesSECA1503Thabasum Aara SNo ratings yet
- FET and MOSFETDocument46 pagesFET and MOSFETKULWANT SINGHNo ratings yet
- Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transisitor AssignmentDocument20 pagesMetal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transisitor AssignmentSokoine Hamad DenisNo ratings yet
- Mosfet: Navigation SearchDocument24 pagesMosfet: Navigation SearchAjay KumarNo ratings yet
- MosfetDocument19 pagesMosfetEEE M.AASTHIKANo ratings yet
- L MosfetDocument22 pagesL MosfetBlack spidey GamingNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Basics ExplainedDocument22 pagesMOSFET Basics ExplaineddadadabababaNo ratings yet
- Device Lab Report 8 PDFDocument10 pagesDevice Lab Report 8 PDFScribble RiYaDNo ratings yet
- 510.22E - Lecture - 7Document12 pages510.22E - Lecture - 7SantosNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument18 pagesMOSFETAditya PriyadarshiNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Structure & OperationDocument12 pagesMOSFET Structure & OperationVijay ShankarNo ratings yet
- What Is MOSFET?: Source and Drain. Here, The Drain Current Is Controlled by The Voltage of Gate TerminalDocument1 pageWhat Is MOSFET?: Source and Drain. Here, The Drain Current Is Controlled by The Voltage of Gate TerminalAubrey TolentinoNo ratings yet
- The MOSFET - Metal Oxide FET: Unit-I (Mos Transistor Theory)Document232 pagesThe MOSFET - Metal Oxide FET: Unit-I (Mos Transistor Theory)Manish AgrawalNo ratings yet
- UNIT II (Part 2) PDFDocument7 pagesUNIT II (Part 2) PDFZulkifl KhairoowalaNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument28 pagesMOSFETBck SreedharNo ratings yet
- MOSFET - TutorialspointDocument3 pagesMOSFET - Tutorialspointgunasekaran k100% (1)
- MOSFET GuideDocument5 pagesMOSFET GuideKIT EENo ratings yet
- 3 MosfetDocument16 pages3 MosfetPok NuttapolNo ratings yet
- ETI 2203 Lesson 7Document10 pagesETI 2203 Lesson 7amash.emillyNo ratings yet
- 4 MosfetDocument15 pages4 MosfetUjjwal JhaNo ratings yet
- The Mosfet: Home TransistorsDocument10 pagesThe Mosfet: Home TransistorsPrabashaNo ratings yet
- EEE102L: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Semiconductor Devices and ApplicationsDocument16 pagesEEE102L: Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Semiconductor Devices and ApplicationsKavi Rohith M 22BEC0147No ratings yet
- What Are MOSFETDocument2 pagesWhat Are MOSFETAngelica DiazNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics Lecture-3 MosfetDocument13 pagesIndustrial Electronics Lecture-3 MosfetHamza TariqNo ratings yet
- Power Beyond Mosfet Vs BJT Whats The Difference 909006Document4 pagesPower Beyond Mosfet Vs BJT Whats The Difference 9090062RtiNo ratings yet
- Untitled 4Document13 pagesUntitled 4maria.rehmanNo ratings yet
- The Metal Oxide FETDocument7 pagesThe Metal Oxide FETSitty GuNo ratings yet
- Lect 4,5,6,7 MOSFET Construction, Working Principle SND ChsrscteridticsDocument26 pagesLect 4,5,6,7 MOSFET Construction, Working Principle SND Chsrscteridticsshashikala kotiNo ratings yet
- The MosfetDocument10 pagesThe MosfetRene100% (2)
- Difference Between D-MOSFET and E-MOSFETDocument25 pagesDifference Between D-MOSFET and E-MOSFETgezahegnNo ratings yet
- Course Name: Basic Electronics Engineering Course Code: EC101 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Document37 pagesCourse Name: Basic Electronics Engineering Course Code: EC101 Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)Dr Sunipa RoyNo ratings yet
- Lab - 12 Transistor MOSFETDocument11 pagesLab - 12 Transistor MOSFETNecotNo ratings yet
- MOSFETDocument11 pagesMOSFETpaupauganda7No ratings yet
- Mosfet: By: Mohamed Ahmed EL - Maghawry Mohamed Adel Yomna MohammedDocument16 pagesMosfet: By: Mohamed Ahmed EL - Maghawry Mohamed Adel Yomna MohammedAhmed Mahmoud AhmedNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Guide: Understanding Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect TransistorsDocument6 pagesMOSFET Guide: Understanding Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect TransistorsYasir KhanNo ratings yet
- Transistor: What Is A Transistor and How Does It WorkDocument7 pagesTransistor: What Is A Transistor and How Does It WorkmonalisaNo ratings yet
- EEE111+ (Exp+7) +Study+of+Switching+CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesEEE111+ (Exp+7) +Study+of+Switching+CharacteristicsFaria SharifNo ratings yet
- 7.1 The MOSFET - Introduction: 7.1.1 Basic Structure and Principle of OperationDocument4 pages7.1 The MOSFET - Introduction: 7.1.1 Basic Structure and Principle of OperationManoj VatsNo ratings yet
- BE Finals 10Document2 pagesBE Finals 10Somebody NobodyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (MOSFET)Document47 pagesChapter 4 Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (MOSFET)redhataNo ratings yet
- MOSFET GUIDEDocument52 pagesMOSFET GUIDEKAMARUDHEEN KP100% (1)
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (7)
- Postrero - Notes 2 - Final QuizDocument9 pagesPostrero - Notes 2 - Final QuizALDWIN H. POSTRERONo ratings yet
- Postrero Quiz2Document2 pagesPostrero Quiz2ALDWIN H. POSTRERONo ratings yet
- BSCPE_II-7 Report on PPT PictureDocument2 pagesBSCPE_II-7 Report on PPT PictureALDWIN H. POSTRERONo ratings yet
- DCElectrical Circuit AnalysisDocument374 pagesDCElectrical Circuit AnalysisNNo ratings yet
- Cpe Ac 222 - Postrero, Aldwin H. Transistors.Document1 pageCpe Ac 222 - Postrero, Aldwin H. Transistors.ALDWIN H. POSTRERONo ratings yet
- Cpe Ac 222 - Postrero, Aldwin H.quiz 3.Document1 pageCpe Ac 222 - Postrero, Aldwin H.quiz 3.ALDWIN H. POSTRERONo ratings yet
- Cpe Ac 222 - Postrero, Aldwin H. Transistors.Document1 pageCpe Ac 222 - Postrero, Aldwin H. Transistors.ALDWIN H. POSTRERONo ratings yet
- Cpe Ac 222 - Postrero, Aldwin H.quiz 3.Document1 pageCpe Ac 222 - Postrero, Aldwin H.quiz 3.ALDWIN H. POSTRERONo ratings yet
- BASIC ELEX SendDocument28 pagesBASIC ELEX SendALDWIN H. POSTRERONo ratings yet
- Cpe Ac 222 - Postrero, Aldwin H. Transistors.Document1 pageCpe Ac 222 - Postrero, Aldwin H. Transistors.ALDWIN H. POSTRERONo ratings yet
- Hardware Components Inside a Computer CaseDocument33 pagesHardware Components Inside a Computer CaseRIZALDY CANTONo ratings yet
- Silicon NPN Power Transistors: Savantic Semiconductor Product SpecificationDocument3 pagesSilicon NPN Power Transistors: Savantic Semiconductor Product Specificationvali2daduicaNo ratings yet
- TMS320F28004x Real-Time Microcontroller - Technical Reference ManualDocument2,745 pagesTMS320F28004x Real-Time Microcontroller - Technical Reference ManualmsnNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document6 pagesAssignment 2bevan678No ratings yet
- 5.AD and DA ConvertersDocument7 pages5.AD and DA ConvertersAkram TahaNo ratings yet
- Introd To LtspiceDocument37 pagesIntrod To LtspiceNando HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Combinational Logic Circuits Experiment 4Document11 pagesCombinational Logic Circuits Experiment 4Vince abcdNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design Combinational Circuits and AnalysisDocument74 pagesDigital Logic Design Combinational Circuits and AnalysisHusnain GhaffarNo ratings yet
- Antipona, Clarence A. - Chapter 5-1, 5-2, 5-3 SummaryDocument3 pagesAntipona, Clarence A. - Chapter 5-1, 5-2, 5-3 Summaryclarence antiponaNo ratings yet
- The 8051 Microcontroller Based Embedded Systems PDFDocument45 pagesThe 8051 Microcontroller Based Embedded Systems PDFvarshi0% (3)
- Bannari Amman Institute of Technology: Regulation: 2018Document2 pagesBannari Amman Institute of Technology: Regulation: 2018veerakumarsNo ratings yet
- ATMEL AVR DatasheetDocument31 pagesATMEL AVR DatasheetmiperrorufoNo ratings yet
- Ec5554 Microcontroller Module: Product InformationDocument7 pagesEc5554 Microcontroller Module: Product InformationABDUL QADIRNo ratings yet
- BCD To 7segement Design Lecture NotesDocument11 pagesBCD To 7segement Design Lecture Notesraul gironellaNo ratings yet
- Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70Document3 pagesTime: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 70Syed MoinNo ratings yet
- EE Digital Logic Design Latches and Flip-FlopsDocument24 pagesEE Digital Logic Design Latches and Flip-FlopsSana NazirNo ratings yet
- DSP TMS320C2812 DatasheetDocument177 pagesDSP TMS320C2812 DatasheetJosé Ramón MezaNo ratings yet
- 3-Channel PC Power Supply SupervisorDocument7 pages3-Channel PC Power Supply SupervisorU DemNo ratings yet
- Systolic ArchitectureDocument9 pagesSystolic ArchitectureRohini ShahNo ratings yet
- Bo Lym In: 6. Option: LED B/L EL B/L & EL InverterDocument1 pageBo Lym In: 6. Option: LED B/L EL B/L & EL InverterAgus BrewsNo ratings yet
- Xilinx Chipscope Tutori PDFDocument16 pagesXilinx Chipscope Tutori PDFGarrett CainNo ratings yet
- Z80 Microprocessor Kit Construction ManualDocument31 pagesZ80 Microprocessor Kit Construction ManualAlfredo Meurer JuniorNo ratings yet
- 8086Document54 pages8086Pavankumar KalliNo ratings yet
- MOSFET Chapter - 5Document73 pagesMOSFET Chapter - 5田佳生No ratings yet
- PCF 8583Document28 pagesPCF 8583Wassim ZouchNo ratings yet
- 3.4-TESTER DE PULSOS DIGITALES 1-0-PULSOS Fabricado Con NANDDocument2 pages3.4-TESTER DE PULSOS DIGITALES 1-0-PULSOS Fabricado Con NANDDavid molinaNo ratings yet
- True USB GQ Universal Programmer Supported EPROM Device ListDocument63 pagesTrue USB GQ Universal Programmer Supported EPROM Device ListHallisson RogerNo ratings yet
- FPGADocument16 pagesFPGAAnshuman VyasNo ratings yet
- EE6301 DLC Unit 2 Part A Q&ADocument6 pagesEE6301 DLC Unit 2 Part A Q&AVigneswaran VigneshNo ratings yet