0% found this document useful (0 votes)
536 views3 pagesHydrostatic Drive System Guide
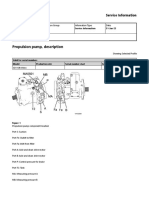
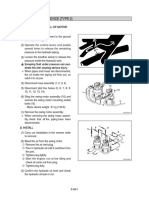
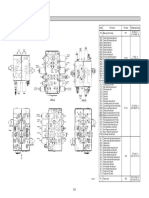
The hydrostatic drive system uses a bidirectional variable pump to drive bidirectional axle and drum motors. Propulsion depends on the parking brake being off, engine rpm, the position of the propulsion lever, and the selection of work or travel speed mode. In low travel speed with traction control activated, a flow divider maintains a fixed oil volume to the drum and axle motors.
Uploaded by
Noor RahmanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
536 views3 pagesHydrostatic Drive System Guide
The hydrostatic drive system uses a bidirectional variable pump to drive bidirectional axle and drum motors. Propulsion depends on the parking brake being off, engine rpm, the position of the propulsion lever, and the selection of work or travel speed mode. In low travel speed with traction control activated, a flow divider maintains a fixed oil volume to the drum and axle motors.
Uploaded by
Noor RahmanCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
- Hydrostatic Drive System Description: An overview of the hydrostatic drive system, detailing its features and function diagram.
- Basic Hydraulic Drive System: Describes the operation of a basic hydraulic drive system and its components, such as the propulsion pump and drive motor.
- Hydrostatic Drive System with Flow Divider: Explains the integration of a flow divider in the hydrostatic drive system, highlighting diagrams and control systems.
- Supplementary Information: Provides additional information including references to diagrams and function checks for system maintenance.