Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Raraday'law
Uploaded by
Josmar Herminio Lopez CancheOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Raraday'law
Uploaded by
Josmar Herminio Lopez CancheCopyright:
Available Formats
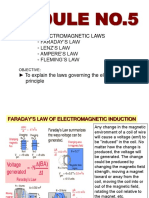
Is a law of physics that states that the magnitude of the
electromotive force induced in a closed circuit is Faraday's law is also based on Lenz's law, which states
proportional to the rate at which the magnetic flux that the direction of the induced e.m.f. is such that it
through that circuit changes. In other words, Faraday's opposes the change that produces it. This means that if
law states that if the magnetic flux through a circuit the magnetic flux through a closed circuit increases, the
changes with time, an electric current is induced in that e.m.f. induced in that circuit is such that it produces a
circuit. current that generates a magnetic field that opposes the
magnetic field that produced it. Similarly, if the magnetic
Faraday's law is one of the fundamental laws of flux decreases, the induced e.m.f. produces a current that
electromagnetics and is essential to understanding how generates a magnetic field that opposes the original
electrical generators and transformers work. Faraday's magnetic field.
law also has applications in industry, medicine and
communication technology, and has been a key part of
the development of modern electronics.
Electromotive force (EMF):
Electromotive force is the amount
of electrical energy produced in a
circuit due to a change in the
Using an alternating current generator: An magnetic flux passing through it. It
alternating current generator is a useful tool WHATS IT'S? is measured in volts (V).
for demonstrating Faraday's law, since it
produces a magnetic flux that changes with Magnetic flux: Magnetic flux is the
time and thus generates an electromotive amount of magnetic field lines
force in a nearby coil. By connecting a coil to passing through a given surface. It
an alternating current generator, the electric is measured in Weber (Wb).
current induced in the coil can be observed.
Electromagnetic induction:
Changing the magnetic field strength: If the FARADAY'S IMPORTANT Electromagnetic induction is the
magnetic field strength across a coil of wire is EXPERIMENTAL LAW DEFINITIONS process by which an electric
changed, it can be observed that the electric CONSIDERATIONS current is generated in a circuit due
current induced in the coil also changes. This to a change in the magnetic flux
shows that the electromotive force is passing through it.
proportional to the rate of change of the
magnetic flux.
Changing the speed of the magnetic field: If a
magnet is moved near a coil of wire at
different speeds, it can be observed that the FUNDAMENTALS
electric current induced in the coil also
changes. This shows that the electromotive
force is proportional to the rate at which the
magnetic flux changes.
Using an oscilloscope: An oscilloscope is an Change in magnetic flux: Faraday's law states that the
instrument that can measure the electric electromotive force (EMF) induced in a circuit is proportional to
current induced in a coil of wire. By connecting the rate of change of magnetic flux through the circuit. This
a coil to an oscilloscope, the waveform of the means that any change in the magnetic flux through a circuit
induced current can be observed and
can induce an electric current in the circuit.
Faraday's law can be demonstrated.
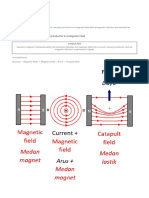
Relationship between magnetic and electric fields: Faraday's law
is based on the close relationship between magnetic and electric
fields. If a magnetic field changes over time, an electric field is
generated, and vice versa. This is known as the law of
electromagnetic induction.
Mathematics of the law: Faraday's law can be expressed
mathematically as EMF = -dΦ/dt, where EMF is the electromotive
force induced in the circuit, Φ is the magnetic flux through the
circuit and dΦ/dt is the rate of change of the magnetic flux. This
means that the induced electromotive force is proportional to
the rate of change of the magnetic flux.
You might also like
- ParagraphDocument8 pagesParagraphPatel BhavyaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Flux, Induction, and Faraday's Law - Boundless PhysicsDocument40 pagesMagnetic Flux, Induction, and Faraday's Law - Boundless PhysicsFen XiaNo ratings yet
- Phy PRJDocument9 pagesPhy PRJStudies 123No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument3 pagesPhysics Investigatory Projectsivansh shuklaNo ratings yet
- KN Phy Project 12Document13 pagesKN Phy Project 12Mariappan NatarajanNo ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument8 pagesPhysics ProjectVanshika DariraNo ratings yet
- Faraday's LawDocument9 pagesFaraday's LawaliNo ratings yet
- Kashish Physics ProjectDocument6 pagesKashish Physics ProjectNirmit JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Faraday's Law of InductionDocument2 pagesFaraday's Law of InductionCirceSheetNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - DC MachDocument8 pagesModule 5 - DC MachNoel BactonNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical MachinesDocument61 pagesBasics of Electrical MachinesZubair IqbalNo ratings yet
- FaradayDocument14 pagesFaradayVarad KakodkarNo ratings yet
- Physics Faraday ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics Faraday ProjectAlviya Rizwan100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Induction: Name: Abhist Kamle Class: XII A (PCM) Subject: Physics Roll No: Year: 2021-22Document44 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Name: Abhist Kamle Class: XII A (PCM) Subject: Physics Roll No: Year: 2021-22Abhist KamleNo ratings yet
- Faraday's Law of Induction - WikipediaDocument11 pagesFaraday's Law of Induction - WikipediaKiran KarthikNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 - LessonsDocument24 pagesGeneral Physics 2 - LessonsAshley NicoleNo ratings yet
- Dheeraj 1Document16 pagesDheeraj 1dheeraj singhrajputNo ratings yet
- Faraday's LawDocument5 pagesFaraday's LawSyeda Rutab AzizNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Electrical MeasurmentDocument16 pagesPhysics Project On Electrical Measurmentujjwalmamgain9No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction PDFDocument9 pagesElectromagnetic Induction PDFShahnaj ParvinNo ratings yet
- Physics Project: Reliance Foundation School KoparkhairaneDocument18 pagesPhysics Project: Reliance Foundation School KoparkhairanePrerana PorechaNo ratings yet
- RestatedDocument1 pageRestatedvienzbengNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument15 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectSreenath ParameswaranNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument5 pagesElectromagnetic InductionGreetings HoomanNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction - 0Document14 pagesElectromagnetic Induction - 0Micah PañaNo ratings yet
- ELECTRICALMICROPROJECTDocument6 pagesELECTRICALMICROPROJECTshaikhnumn22No ratings yet
- Index Faraday's Law ConceptsDocument4 pagesIndex Faraday's Law ConceptsRajesh SharmaNo ratings yet
- Submitted By:-Name: - Mandeep Dhiman ROLL NO.: - 24 SECTION: - B4802 Course: - B.Tech (Me) - MbaDocument7 pagesSubmitted By:-Name: - Mandeep Dhiman ROLL NO.: - 24 SECTION: - B4802 Course: - B.Tech (Me) - Mbashailesh singhNo ratings yet
- PHYSICSDocument11 pagesPHYSICSNatalie SheelamNo ratings yet
- Physics Sample ProjectDocument19 pagesPhysics Sample ProjectRishi Kumar AryaNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument18 pagesElectromagnetic Inductionwakki 10No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument25 pagesElectromagnetic Inductionnivasan aNo ratings yet
- ALCANTARA, JESSIE - Assignment #3 (Finals)Document3 pagesALCANTARA, JESSIE - Assignment #3 (Finals)sweet wobsNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetism: 4.1 Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic FieldDocument7 pagesElectromagnetism: 4.1 Force On A Current-Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic FieldEv LamNo ratings yet
- 4th General Physics 2 (Week 3-4)Document56 pages4th General Physics 2 (Week 3-4)Darious PenillaNo ratings yet
- Phy-EMI-Shreya ProjectDocument20 pagesPhy-EMI-Shreya Projectshreyaaa1104No ratings yet
- Physics AbhinavDocument22 pagesPhysics AbhinavabhinavNo ratings yet
- Aniruddh RaghuwanshiDocument15 pagesAniruddh Raghuwanshiatharvsolanki.11No ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Induction: Name - Kunal Agrawal Roll No. - 20Document22 pagesElectromagnetic Induction: Name - Kunal Agrawal Roll No. - 20Kunal AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Electricity and MagnetismDocument12 pagesElectricity and MagnetismTrisha Bonita Restauro100% (1)
- Faraday Law of Electromagnetic InductionDocument5 pagesFaraday Law of Electromagnetic Inductionantex nebyuNo ratings yet
- Electrical Machines 3rd Sem AsgnmntDocument95 pagesElectrical Machines 3rd Sem AsgnmntNivedNo ratings yet
- Physics Investogatory Project 2023Document17 pagesPhysics Investogatory Project 2023revNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Abhishek CDocument19 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Abhishek CKrupa SindhuNo ratings yet
- Induced EMFDocument21 pagesInduced EMFJaica Mangurali TumulakNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Document43 pagesMagnetic Induction and Faradays Law in General Physics 2Heidi QuiranteNo ratings yet
- Elmachi1 - Lecture6 (Electrical Machines - Part 1)Document17 pagesElmachi1 - Lecture6 (Electrical Machines - Part 1)Trisha SARMIENTONo ratings yet
- Faraday's Law: TransformersDocument9 pagesFaraday's Law: Transformersmyscribd1209No ratings yet
- Physics - Kashvi - Electromagnetic InductionDocument16 pagesPhysics - Kashvi - Electromagnetic InductionKashvi ShriNo ratings yet
- InducelecDocument9 pagesInducelecrenNo ratings yet
- Presentation (Autosaved)Document17 pagesPresentation (Autosaved)Muhammad Hamza Mujeeb AhmadNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory ProjectDocument18 pagesPhysics Investigatory ProjectVINIT MALLICKNo ratings yet
- EMO Project Perposal 062 055 079Document4 pagesEMO Project Perposal 062 055 079Nassr KhanNo ratings yet
- INDEXDocument12 pagesINDEXK GhatageNo ratings yet
- Chittaranjan Dutta FinalDocument19 pagesChittaranjan Dutta Finalchitta5828No ratings yet
- Technical ReportDocument23 pagesTechnical ReportLaxman Kiran0% (1)
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument1 pageElectromagnetic WavesKfalNo ratings yet
- Phy ProjectDocument18 pagesPhy ProjectRohit rajaNo ratings yet
- Resume GLM 8 Juni 2023Document10 pagesResume GLM 8 Juni 2023badry shidiqNo ratings yet
- Gallagher 2021 Price List USADocument54 pagesGallagher 2021 Price List USADarrylNo ratings yet
- SABUERO-ME62-Board Exam AssignmentDocument39 pagesSABUERO-ME62-Board Exam AssignmentJohn Westly S. SabueroNo ratings yet
- How Roller Coasters Work ARTICLEDocument6 pagesHow Roller Coasters Work ARTICLEmarie.tl.naarNo ratings yet
- CG Power and Industrial Solutions Limited: LT Motors Division AhmednagarDocument1 pageCG Power and Industrial Solutions Limited: LT Motors Division AhmednagarMohan BabuNo ratings yet
- EEE Guidance BookletDocument120 pagesEEE Guidance BookletNicolau Nechita IulianNo ratings yet
- Tenderdocument 142Document38 pagesTenderdocument 142rajabharath12No ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Combined Science 0653/22Sarah KKCNo ratings yet
- Gilian HFS513 - Fpro2105 - CDocument32 pagesGilian HFS513 - Fpro2105 - CEDERSON GUIMARÃES SILVANo ratings yet
- Mitigation of Voltage Swells by Static Series Compensator: MemberDocument7 pagesMitigation of Voltage Swells by Static Series Compensator: MemberKevin MacancelaNo ratings yet
- 18th Edition Solutions: Circuit ProtectionDocument5 pages18th Edition Solutions: Circuit ProtectionThiago LobatoNo ratings yet
- Dokumen - Tips Cfm56 7 B AnswerbookDocument75 pagesDokumen - Tips Cfm56 7 B AnswerbookOnur YayNo ratings yet
- Transport Geo CHapter1Document26 pagesTransport Geo CHapter1Habib NuredinNo ratings yet
- An Autonomous Wave-Powered Desalination System - 21Document14 pagesAn Autonomous Wave-Powered Desalination System - 21abci jorginNo ratings yet
- Romero-Lankao 2021 Prog. Energy 3 032002Document16 pagesRomero-Lankao 2021 Prog. Energy 3 032002Abu AzwaNo ratings yet
- Accumulator EHVDocument19 pagesAccumulator EHVRobert PradanaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet - Thermostat Type MBC 8000 and MBC 8100Document9 pagesData Sheet - Thermostat Type MBC 8000 and MBC 8100Fabiola barriosNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Comparisons (Flooded Tubular vs. GEL)Document1 pageCatalogue Comparisons (Flooded Tubular vs. GEL)Jean Claude EidNo ratings yet
- PS276740 50 5 610Document10 pagesPS276740 50 5 610Kh AhmedNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual: Microprocessor Controlled Constant Current Regulator Type MCR 2.5 kVA To 30kVADocument118 pagesInstallation Manual: Microprocessor Controlled Constant Current Regulator Type MCR 2.5 kVA To 30kVABramindo Niaga PratamaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Personal DataDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Personal DataTyasTriJuliansyahNo ratings yet
- BU1-AC-230 VAC - Sinar Elektrindo PerkasaDocument1 pageBU1-AC-230 VAC - Sinar Elektrindo Perkasafarazali2919No ratings yet
- McqsDocument15 pagesMcqsPriyansu Singh100% (2)
- Unit-5 Speed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorDocument16 pagesUnit-5 Speed Control of Three Phase Induction MotorAshok P100% (1)
- ScienceClinic Grade12 DBE SmartPrep-Eng V2.2Document75 pagesScienceClinic Grade12 DBE SmartPrep-Eng V2.2Malale KgaogeloNo ratings yet
- Oman Sustainability Week 2023Document112 pagesOman Sustainability Week 2023Firas BoubesNo ratings yet
- D1435-13 Intemprismno NaturalDocument5 pagesD1435-13 Intemprismno Naturalmarcos moranNo ratings yet
- 539 Grease-Interchange Feb10Document1 page539 Grease-Interchange Feb10SamtakoiNo ratings yet
- Gns 311 by Plato (Modified) - 1Document102 pagesGns 311 by Plato (Modified) - 1Ibiwoye JoshuaNo ratings yet
- Bulkweighing Installation Manual 2004Document99 pagesBulkweighing Installation Manual 2004Oscar Giovani SosaNo ratings yet
- AFL Substation Bus ConductorsDocument24 pagesAFL Substation Bus ConductorsHilbert FloresNo ratings yet