Professional Documents
Culture Documents
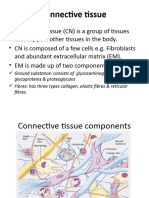
CT Types
Uploaded by
Tarlan SharifiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CT Types
Uploaded by
Tarlan SharifiCopyright:
Available Formats
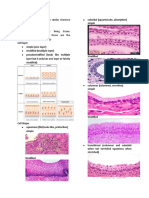
CT type classification cells ECM functions/features locations
ground substance
¯ fibers
cells • lots of ground
• fibroblasts substance and a
• allows the body to move without
connective tissue • mast cells variety of fibers • around muscles. blood vessels, nerves, organs, subcutaneous region
loose overextending and keeps
proper • adipose cells • collagen (thick and • beneath the epithelia of the digestive and respiratory tracts
everything in place
• macrophages wavy)
• plasma cells • elastic (thin, straight,
branching)
• fibers are arranged in densely
packed parallel bundles of • tendons: cord-like structures that attach muscle to bone; surrounded by a CT
¯ cells
collagen to provide strength in capsule (epitendineum), divided into fascicles by CT (peritendineum), and groups of
connective tissue • not a lot of fibers
dense regular one direction fibers surrounded by fibroblasts and very little CT (endotendineum)
proper immune cells ¯ ground substance
• rows of fibroblasts are located • ligaments: short tendon-like structures that attach bone to bone
present
between the bundles of collagen • aponeuroses: broad flat tendon-like structures that attach muscles to bones
fibers
• the collagen fibers are arranged
in large bundles interwoven in • fibrous capsule of organs
¯ cells fibers: some elastic
different directions to provide • deep fascia
connective tissue • mast cells and reticular fibers
dense irregular strength in various directions • dermis
proper • macrophages present
• fibroblasts are scattered • periosteum of bone
• blood vessels ¯ ground substance
between the bundles of collagen • perichondrium of cartilage
fibers
fibers
¯ ground substance • sheets of elastic tissue: ligamentum flava, elastic fibers synthesized by fibroblast
dense regular connective tissue • elastic fibers are arranged
¯ cells • branching elastic • fenestrated membrane: large arteries (tunica media), elastic fibers synthesized by
elastic proper parallel to one another
fibers with sparse smooth muscle cells
collagen
form the framework of:
• type III collagen fibers
• liver
• fibroblasts (reticular fibers) – • need special stain to see the
connective tissue • bone marrow
reticular (reticular cells) thin and branching reticular fibers (silver
proper • lymphatic tissues
• macrophages structure salts/argyrophilic)
• cardiovascular system
• ground substance
• lungs
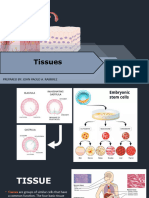
• mesenchymal
cells (stellate • ground substance is
differentiates into
shaped cells rich in hyaluronic acid
• all adult tissue comes from • mucous connective tissue (also embryonic)
mesenchymal embryonic with an oval • reticular fibers
mesenchymal cells • adult CT
nucleus and a scattered ground
• other tissues in the adult
prominent substance
nucleolus)
• ground substance
• some choose to freeze the
(primarily hyaluronic
mucous umbilical cord following birth to
embryonic • fibroblasts acid) • forms substance of the umbilical cord
(wharton’s jelly) preserve the undifferentiated
• type I and III collagen
mesenchymal cells
fibers
You might also like
- Hams Glutes: Seven Days of WorkoutsDocument8 pagesHams Glutes: Seven Days of WorkoutsObsgin Januari17No ratings yet
- Constraints PDFDocument4 pagesConstraints PDFArun Gopal100% (1)
- Connective TissueDocument27 pagesConnective TissueRussel Bob BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy of Neuroendocrine SystemsDocument521 pagesNeuroanatomy of Neuroendocrine SystemsHir100% (2)
- Types of Tissues: Lesson 02Document33 pagesTypes of Tissues: Lesson 02DASH100% (2)
- Fascial Manipulation For Internal Dysfunctions FMIDDocument8 pagesFascial Manipulation For Internal Dysfunctions FMIDdavidzhouNo ratings yet
- Urinary Incontinence Nursing ManagementDocument3 pagesUrinary Incontinence Nursing ManagementRnspeakcomNo ratings yet
- LutsDocument35 pagesLutsJulian Eka Putra100% (1)
- Photosynthesis Cellular Respiration (Module 5)Document51 pagesPhotosynthesis Cellular Respiration (Module 5)Trisha DeniseNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue, Ligaments & RapheDocument16 pagesConnective Tissue, Ligaments & Raphedrpankajmaheria100% (1)
- Secondary Progression Test - Stage 8 Science Paper 2 PDFDocument16 pagesSecondary Progression Test - Stage 8 Science Paper 2 PDFstrictlythomas73% (22)
- Million Dollar Exercise BackDocument151 pagesMillion Dollar Exercise BackPablo CruzNo ratings yet
- Clinical Immunology and Serology A Laboratory Perspective 3rd Edition Stevens Test BankDocument12 pagesClinical Immunology and Serology A Laboratory Perspective 3rd Edition Stevens Test Banktracybrownfmaczqejxw100% (16)
- Human Histology 6b Connective TissueDocument2 pagesHuman Histology 6b Connective TissueBlubby BleuNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue NotesDocument6 pagesConnective Tissue Notesferdinand padillaNo ratings yet
- 1 Animal OrganisationDocument29 pages1 Animal OrganisationPERTUNIA KORABINo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument31 pagesConnective Tissuenyashamukamba15No ratings yet
- 5 Connective Tissues 22 July 2021Document46 pages5 Connective Tissues 22 July 2021T KNo ratings yet
- AnapDocument12 pagesAnapJeahn Hazel MontanaNo ratings yet
- Histology - Week 2 - Epithelium TissueDocument8 pagesHistology - Week 2 - Epithelium TissueHIEL MAALIHANNo ratings yet
- BIOL3307 - Unit1Mod1 - Skeletal Basics3Document19 pagesBIOL3307 - Unit1Mod1 - Skeletal Basics3Ren StudyNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 - HistologyDocument25 pagesLab 3 - HistologyRite2summaiya SumiNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 22Document8 pagesAnimal Tissues 22Arleen ColacionNo ratings yet
- Conn. Tissue HemopoiesisDocument14 pagesConn. Tissue HemopoiesischennielafleurNo ratings yet
- Human Tissues PPTDocument40 pagesHuman Tissues PPTKeneth CandidoNo ratings yet
- Hhis Connective TissueDocument5 pagesHhis Connective TissueAbigrael TangcoNo ratings yet
- PDF Document PDFDocument6 pagesPDF Document PDFAhdimer HanapiNo ratings yet
- Human Histology 6b Connective TissueDocument2 pagesHuman Histology 6b Connective TissueBlubby BleuNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue (Proper and Specialized) 2024-01Document32 pagesConnective Tissue (Proper and Specialized) 2024-01jcrosa137No ratings yet
- Animal Organization and HomeostasisDocument2 pagesAnimal Organization and HomeostasisLara CarisaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tissues: Zona Occludens Anchoring JunctionsDocument8 pagesChapter 4 Tissues: Zona Occludens Anchoring JunctionsrenjiniNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY NOTES by Red (Connective)Document2 pagesHISTOLOGY NOTES by Red (Connective)Edzeal Bruan JrNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue, VnaDocument78 pagesConnective Tissue, Vnavaryvira6677No ratings yet
- Cartilage, Bone and Muscle 2021Document69 pagesCartilage, Bone and Muscle 2021PeachybalmnNo ratings yet
- Muskuloskeletal + Tulang (DMS 2)Document53 pagesMuskuloskeletal + Tulang (DMS 2)Ghassani IzlynNo ratings yet
- Histology and Microtechniques Biology 160 Prof. Maria Luisa J. LandinginDocument2 pagesHistology and Microtechniques Biology 160 Prof. Maria Luisa J. LandinginDavid YapNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument52 pagesConnective TissueMaxamed Faarax XaashiNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument8 pagesMuscle TissueMiyuki MeyNo ratings yet
- Structural Organisation in Animals: Connective Tissue - Bones, Cartilage, Blood, Muscular TissueDocument10 pagesStructural Organisation in Animals: Connective Tissue - Bones, Cartilage, Blood, Muscular TissueKali Shankar SinghNo ratings yet
- Written Work 1 (SW 3.1) : Animal Structure: 3. MascularDocument1 pageWritten Work 1 (SW 3.1) : Animal Structure: 3. MascularHannah Lynn EllisNo ratings yet
- Definition and Types of Connective Tissue - KenhubDocument19 pagesDefinition and Types of Connective Tissue - Kenhubyigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- Theme #1: Histology of Supporting-Motor SystemDocument34 pagesTheme #1: Histology of Supporting-Motor SystemKhurshidbuyamayumNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument37 pagesAnimal Tissueshero samilinNo ratings yet
- The Connective Tissue ReviewerDocument4 pagesThe Connective Tissue ReviewerSasukeNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures & Functions: Biology Unit Perak Matriculation CollegeDocument50 pagesCell Structures & Functions: Biology Unit Perak Matriculation CollegeMarjorie DenorogNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - BIOSCI2Document30 pagesModule 3 - BIOSCI2Jahzel JacaNo ratings yet
- B.pharm-Connective Tissue & SkinDocument73 pagesB.pharm-Connective Tissue & Skin安 娜 胡No ratings yet
- 08.30 2021 IA Histology S1T4 Cartilage and BoneDocument11 pages08.30 2021 IA Histology S1T4 Cartilage and BoneAman SinghNo ratings yet
- التشريح نظري م 2 غير مترجمةDocument10 pagesالتشريح نظري م 2 غير مترجمةبايNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Cell Biology and Organisation: 2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular OrganismsDocument47 pages2.0 Cell Biology and Organisation: 2.3 Living Processes in Multicellular OrganismsFHATIN AMIRA BINTI MUSA MoeNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 (Tissues and Oragnismal Biology)Document10 pagesGen Bio 2 (Tissues and Oragnismal Biology)Yenyen C. BagtasosNo ratings yet
- Structural OrganizationDocument119 pagesStructural OrganizationAVS CONo ratings yet
- Muscletissue 2. CardiacDocument8 pagesMuscletissue 2. CardiacAloha I. SarolNo ratings yet
- 96 (1) Tissue and OrgansDocument81 pages96 (1) Tissue and OrgansbillNo ratings yet
- N HistologyDocument26 pagesN HistologyHohai ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Prática Cartilagem Osso HistologiaDocument9 pagesPrática Cartilagem Osso HistologiamiguelfilipegralhaalmeidaNo ratings yet
- Reviewr Tissue CompleteDocument4 pagesReviewr Tissue CompleteJomar ManalangNo ratings yet
- 3 Intro To Skeletal MusclesDocument3 pages3 Intro To Skeletal MusclesKimberlee Ced NoolNo ratings yet
- Tissues 1Document42 pagesTissues 1Patricia JalbanNo ratings yet
- 4.the Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument49 pages4.the Tissue Level of OrganizationKojo Yeboah EnchillNo ratings yet
- Awdal College Department of Health: General HistologyDocument24 pagesAwdal College Department of Health: General HistologyAyro Business CenterNo ratings yet
- Anatomy All in One?Document244 pagesAnatomy All in One?hp9zgxv7tgNo ratings yet
- Objectives: at The End of This Lecture, Student Will Be Able ToDocument19 pagesObjectives: at The End of This Lecture, Student Will Be Able Tohjjhh6596No ratings yet
- Integumentary TransesDocument8 pagesIntegumentary TransesanaodtohanNo ratings yet
- The Fundamental Unit of Life & Tissues - NotesDocument25 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life & Tissues - NotesNaman VatsNo ratings yet
- Body Tissues: DR Fadel Naim Ass. Prof. Faculty of Medicine IUGDocument54 pagesBody Tissues: DR Fadel Naim Ass. Prof. Faculty of Medicine IUGأمال داودNo ratings yet
- Muscles and Muscle Tissue: Functional Anatomy, Excitation-Contraction CouplingDocument46 pagesMuscles and Muscle Tissue: Functional Anatomy, Excitation-Contraction CouplingRevanth VejjuNo ratings yet
- Human TissuesDocument41 pagesHuman TissuesMae Ann Mejico EspirituNo ratings yet
- Module3 Bio - Sci.2 GenaralZoologyDocument11 pagesModule3 Bio - Sci.2 GenaralZoologyJahzel JacaNo ratings yet
- S:F Exam 2Document11 pagesS:F Exam 2Tarlan SharifiNo ratings yet
- Histology Lab 1.keyDocument36 pagesHistology Lab 1.keyTarlan SharifiNo ratings yet
- CT CellsDocument1 pageCT CellsTarlan SharifiNo ratings yet
- CartilageDocument1 pageCartilageTarlan SharifiNo ratings yet
- Annual CEW User Update 2019 V21Document43 pagesAnnual CEW User Update 2019 V21GESTA RADARNo ratings yet
- To Study The Effect of K+, Ca++, Acetylcholine and Adrenaline On Frog's Heart PDFDocument4 pagesTo Study The Effect of K+, Ca++, Acetylcholine and Adrenaline On Frog's Heart PDFJoshita VeeramachaneniNo ratings yet
- Truscope Elite - A8: Modulbaserad Multiparameter MonitorDocument2 pagesTruscope Elite - A8: Modulbaserad Multiparameter MonitorDaniel GuillenNo ratings yet
- Increased Body Temperature Related To Decrease in Urine Output As Evidenced by The Client's Body Temperature Which Is 38Document3 pagesIncreased Body Temperature Related To Decrease in Urine Output As Evidenced by The Client's Body Temperature Which Is 38Senyorita KHayeNo ratings yet
- Grand Test 36Document65 pagesGrand Test 36NikhilBhattNo ratings yet
- WrwerDocument251 pagesWrwerRaheelNo ratings yet
- TracheostomyDocument11 pagesTracheostomyBryan DorosanNo ratings yet
- #Davidson - Review #HematologyDocument23 pages#Davidson - Review #Hematologyemtiaz zamanNo ratings yet
- Topic 8 Transport in Mammals - CAIE Biology A-LevelDocument77 pagesTopic 8 Transport in Mammals - CAIE Biology A-LevelElisaNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound Contrast AgentsDocument40 pagesUltrasound Contrast AgentsAndrócki AndreaNo ratings yet
- Porth - Pathophysiology Concepts of AlteDocument20 pagesPorth - Pathophysiology Concepts of AlteHina liaquatNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles Webquest Day 2 With Notes Filled inDocument3 pagesCell Organelles Webquest Day 2 With Notes Filled inJustin TisNo ratings yet
- MEHU130 - U2 - T43 - Nefropatia DiabeticaDocument110 pagesMEHU130 - U2 - T43 - Nefropatia DiabeticaStefani AtlleNo ratings yet
- Homework Marking Scheme 16.1: Inherited ChangeDocument2 pagesHomework Marking Scheme 16.1: Inherited ChangeMikeNo ratings yet
- Acute Coronary SyndromesDocument3 pagesAcute Coronary SyndromesbedogdelongeNo ratings yet
- Absorption and The Products of Digestion1Document55 pagesAbsorption and The Products of Digestion1Abbie WhileyNo ratings yet
- 9700 m19 QP 22 PDFDocument16 pages9700 m19 QP 22 PDFIG UnionNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Case Analysis OnDocument70 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia: A Case Analysis OnAngelica RelanaNo ratings yet
- Angiology Lecture 2Document5 pagesAngiology Lecture 2আহানাফ তাহমিদ শব্দNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The ArmDocument31 pagesAnatomy of The ArmAlexNo ratings yet