Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COMBINED VARIATION EQUATIONS
Uploaded by
Charlene Grace BronolaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COMBINED VARIATION EQUATIONS
Uploaded by
Charlene Grace BronolaCopyright:
Available Formats
COMBINED VARIATION
Is another concept of variation which involves both the direct and inverse variations.
Examples
1. Translate the following variation statements into mathematical equations using k as the
constant of variation.
a. M varies directly as n and inversely p.
b. A varies directly as b and inversely as c.
2. If z varies directly as x and inversely as y, and z =18 when x = 6 and y = 2, find z when x =
10 and y = 6.
Solution:
a. The relation “z varies directly as x and inversely as y” is translated to
b. Substitute the values to find k.
c. Find z when x = 10 and y = 6.
3. A variable a varies jointly as b and c and inversely as d. If a = 14 when b= 4, c = 7, and d =
6, find the value of c when a = 10, b = 5, and d= 6.
Solution:
a. The relation “a varies jointly as b and c and inversely as d ” is translated to
b. Substitute the values to find k.
c. Find the value of c when a = 10, b = 5, and d = 6.
PRACTICE ANSWERING: (Answer on your notebook)
Activity 1. Using k as the constant of variation, write the equation of variation for each of the
following:
1. W varies jointly as c and the square of a and inversely as b.
2. D varies directly as the square of f and inversely as g.
3. The force F of attraction between two bodies varies directly as the product of their weights
W and inversely as the square of the distance d between them.
4. The time t required for an elevator to lift a weight varies jointly with the weight w and the
distance d through which it is to be lifted and inversely with the power P of the motor.
5. At a given temperature, the electrical resistance R of a piece of copper wire varies directly as
its length l and inversely as the square of its diameter d .
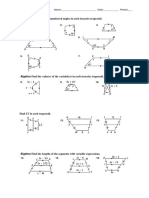
Activity 2. Solve the following:
1. If r varies directly as s and inversely as the square t, and r = 4
when s = 20 and t = 5, find
a. r when t = 2 and s = 48.
b. s when t = 5 and r = 8.
c. t when r = 25 and s = 5
You might also like
- Summative Test on VariationsDocument2 pagesSummative Test on Variationsrotshen casilac100% (1)
- Second Periodical Test in Mathematics 9 S.Y. 2018-2019Document5 pagesSecond Periodical Test in Mathematics 9 S.Y. 2018-2019Maria MaeNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 M1 - W1 Mathematics 9Document50 pagesQuarter 2 M1 - W1 Mathematics 9cutiegab57No ratings yet
- Direct VariationDocument16 pagesDirect VariationGerard Baltazar100% (2)
- Proving Inequalities in A TriangleDocument20 pagesProving Inequalities in A TriangleMichael John LerumNo ratings yet
- 2019 Math9 QuadrilateralsDocument11 pages2019 Math9 QuadrilateralseleonoraNo ratings yet
- Q3 W5 G9 MathematicsDocument5 pagesQ3 W5 G9 MathematicsCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- Math - Lesson2 - Properties of Special ParallelogramDocument9 pagesMath - Lesson2 - Properties of Special ParallelogramFree TemplatesNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Second Quarter Exam - PRINTDocument2 pagesMath 9 Second Quarter Exam - PRINTJustin Martinez50% (2)
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 1 Illustrates Situations That Involve Direct, Inverse, Joint, and Combined VariationsDocument22 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 1 Illustrates Situations That Involve Direct, Inverse, Joint, and Combined VariationsJaneNo ratings yet
- Additional ActivityDocument3 pagesAdditional ActivitySir Jr100% (2)
- 5 Example of Angle of ElevationDocument3 pages5 Example of Angle of ElevationCathyLeePacaldoMelendres100% (1)
- Math9 - Q3 - Mod8 - Problems InvolvingParallelogramsTrapezoidsAndKites - V3Document23 pagesMath9 - Q3 - Mod8 - Problems InvolvingParallelogramsTrapezoidsAndKites - V3Yeoj ParasNo ratings yet
- Dll-Properties of ParallelogramDocument9 pagesDll-Properties of ParallelogramPatrick GuerraNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan-Distance-FormulaDocument12 pagesLesson Plan-Distance-FormulaCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- Gr. 9 Q2 Week 1 Lesson 1 Direct VariationDocument38 pagesGr. 9 Q2 Week 1 Lesson 1 Direct VariationMark A. Soliva100% (2)
- Solving Joint Variation ProblemsDocument2 pagesSolving Joint Variation ProblemsBrendan Lewis DelgadoNo ratings yet
- MATH 9 Q4 Module 2 Trigonometric Ratios of Special Angles 1Document16 pagesMATH 9 Q4 Module 2 Trigonometric Ratios of Special Angles 1Virnalyn S. De SilvaNo ratings yet
- Learners Activity Sheets: Mathematics 8Document11 pagesLearners Activity Sheets: Mathematics 8Amelita TupazNo ratings yet
- Math9 Q3 Mod3 ProvingTheoremsOnTheDifferentKindsOfParallelogram v3Document17 pagesMath9 Q3 Mod3 ProvingTheoremsOnTheDifferentKindsOfParallelogram v3alexablisssNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity SheetDocument10 pagesLearning Activity SheetJasmin Move-RamirezNo ratings yet
- 2021-AIRs-SLM - Math-9 - Q1-Module 1Document19 pages2021-AIRs-SLM - Math-9 - Q1-Module 1Keah Charlene T. DaclanNo ratings yet
- SIM Quadratic Equation by SquareDocument40 pagesSIM Quadratic Equation by SquareRochelle AdlaoNo ratings yet
- Long test in mathematics provides SEO-optimized titleDocument3 pagesLong test in mathematics provides SEO-optimized titleeleonoraNo ratings yet
- Combined VariationDocument8 pagesCombined VariationMarlaFirmalino100% (3)
- Learn Combined Variation in 4 StepsDocument6 pagesLearn Combined Variation in 4 StepsCindy BononoNo ratings yet
- Advance Montessori Education Center of Isabela, Inc.: Mathematics 9 Learner'S Module 3 Second QuarterDocument6 pagesAdvance Montessori Education Center of Isabela, Inc.: Mathematics 9 Learner'S Module 3 Second Quarterchibbs1324No ratings yet
- MATHEMATICS 9 UNIT TEST 1 SOLUTIONSDocument2 pagesMATHEMATICS 9 UNIT TEST 1 SOLUTIONSNeo VillarealNo ratings yet
- Math9 Quarter1 Module5 FINAL-V3-1Document7 pagesMath9 Quarter1 Module5 FINAL-V3-1Rosalie RebayNo ratings yet
- Combined VariationDocument3 pagesCombined VariationRica DespuigNo ratings yet
- Math 9 - Q2 - Week 2 - Module 2 - Variations Joint and Combined Variations - For ReproductionDocument18 pagesMath 9 - Q2 - Week 2 - Module 2 - Variations Joint and Combined Variations - For ReproductionJubilo , Daniella Mae S.100% (1)
- 4 Quarter Writtenwork in Enhanced Mathematics 9 Name: - SectionDocument4 pages4 Quarter Writtenwork in Enhanced Mathematics 9 Name: - SectionKalæ DöNo ratings yet
- Mathgr9q3 Lesson 2Document24 pagesMathgr9q3 Lesson 2Lorenzo Taguinod EsparasNo ratings yet
- Math 9 2nd QE 2017Document3 pagesMath 9 2nd QE 2017Floraville Lamoste-MerencilloNo ratings yet
- Q 1-Math 9 ReviewDocument3 pagesQ 1-Math 9 ReviewFlorita LagramaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 4 - Module 3 Angle of Elevation and DepressionDocument10 pagesMathematics: Quarter 4 - Module 3 Angle of Elevation and DepressionBernaliza CaserNo ratings yet
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 1: Direct VariationDocument16 pagesMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 1: Direct VariationShawee Gucor SaquilabonNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Lesson 4 Supporting Others' AdvocaciesDocument8 pagesModule 2 - Lesson 4 Supporting Others' AdvocaciesMaria BuizonNo ratings yet
- Guess What?: Learning Activity Sheet GRADE 9 MathematicsDocument5 pagesGuess What?: Learning Activity Sheet GRADE 9 MathematicsLea Mae100% (1)
- This Activity Will Be Done After LP3 With TLE, Science, Araling Panlipunan, Math, Filipino, Arts, Physical EducationDocument10 pagesThis Activity Will Be Done After LP3 With TLE, Science, Araling Panlipunan, Math, Filipino, Arts, Physical EducationJanderick DeveraNo ratings yet
- Quadrilaterals and Triangle Similarity Self-Instruction PacketDocument12 pagesQuadrilaterals and Triangle Similarity Self-Instruction PacketJohnlloyd DayritNo ratings yet
- G 8 - 3rd PretestDocument4 pagesG 8 - 3rd PretestHero-name-mo?No ratings yet
- Math 9 Summative Test Indirect VariationDocument1 pageMath 9 Summative Test Indirect VariationMaricris Dizon-MiguelNo ratings yet
- Math Grade9 Quarter3 Week1 Module1Document4 pagesMath Grade9 Quarter3 Week1 Module1ALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- TQ Math 9Document2 pagesTQ Math 9Jestoni AmbrocioNo ratings yet
- Solve Graphically:: X 4Document3 pagesSolve Graphically:: X 4Arturo SierraNo ratings yet
- 2017 Grade 8 Math Challenge Elimination RoundDocument3 pages2017 Grade 8 Math Challenge Elimination RoundGlenda Tagupa AmbalNo ratings yet
- In The Previous Lesson On It States That TDocument16 pagesIn The Previous Lesson On It States That TNylinam100% (1)
- 2ND Quarter Grade 9Document12 pages2ND Quarter Grade 9Limar Anasco Escaso100% (1)
- Geometry Trapezoid and Kite WorksheetDocument2 pagesGeometry Trapezoid and Kite Worksheetamisamiam2100% (1)
- MATH 9 Module 2 Week 6Document13 pagesMATH 9 Module 2 Week 6Henry Kahal Orio Jr.No ratings yet
- 9 Math LM - U2 m4 v1 0Document75 pages9 Math LM - U2 m4 v1 0'Yoo ShaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics 9 2ndDocument6 pagesMathematics 9 2ndAngelo Morcilla TiquioNo ratings yet
- CNHS Summative Test Title Provides Concise TitleDocument2 pagesCNHS Summative Test Title Provides Concise TitleEdna May Pedong RoblesNo ratings yet
- Notes 6.3 Rectangle, Rhombus, SquareDocument5 pagesNotes 6.3 Rectangle, Rhombus, SquareBrenda Barron0% (1)
- Special Right Triangles: Find The Missing Side Lengths. Leave Your Answers As Radicals in Simplest FormDocument4 pagesSpecial Right Triangles: Find The Missing Side Lengths. Leave Your Answers As Radicals in Simplest FormArron BaranquilNo ratings yet
- 1ST Quarter Grade 9Document12 pages1ST Quarter Grade 9Limar Anasco Escaso100% (2)
- Direct, Inverse, Joint and Combined Variation ExplainedDocument12 pagesDirect, Inverse, Joint and Combined Variation ExplainedGenesisDaquinanNo ratings yet
- School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date and Time QuarterDocument3 pagesSchool Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Teaching Date and Time QuarterJessie OlantigueNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 math explores direct and inverse variationDocument40 pagesGrade 9 math explores direct and inverse variationJo Mai Hann100% (2)
- CLASS NO. EXAM SCOREDocument5 pagesCLASS NO. EXAM SCORELito PepitoNo ratings yet
- Moreh Academy: - Quarter - 2 - Week - 1Document10 pagesMoreh Academy: - Quarter - 2 - Week - 1Bernadeth PlanasNo ratings yet
- Terms Related To Circle-ARChs-g10-MathDocument4 pagesTerms Related To Circle-ARChs-g10-MathCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- Grade 8-ActivtiesDocument6 pagesGrade 8-ActivtiesCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- I. ObjectivesDocument13 pagesI. ObjectivesCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- Grade7 Q2 Week4Document8 pagesGrade7 Q2 Week4Charlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- See Attach Activity SheetDocument12 pagesSee Attach Activity SheetCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- Grade7 Q2 Week7Document13 pagesGrade7 Q2 Week7Charlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- Q3 W4 G9 MathematicsDocument10 pagesQ3 W4 G9 MathematicsCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 - Translating Algebraic Expressions-ActivityDocument10 pagesGrade 7 - Translating Algebraic Expressions-ActivityCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- GRADE 7 MATH MEASUREMENT LESSONDocument19 pagesGRADE 7 MATH MEASUREMENT LESSONCharlene Grace Bronola100% (1)
- Calajatanlynnjohan SinamanisDocument1 pageCalajatanlynnjohan SinamanisCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- Pretest GENMATH FUNCTIONSDocument1 pagePretest GENMATH FUNCTIONSCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- Grade 7-Activity On WeightDocument8 pagesGrade 7-Activity On WeightCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- Address Gaps and Improve Math PracticeDocument2 pagesAddress Gaps and Improve Math PracticeCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- 1st Quarterly Exam-G7Document2 pages1st Quarterly Exam-G7Charlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- Pretest SEQUENCES G10Document2 pagesPretest SEQUENCES G10Charlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- Pretest-FACTORING POLYNOMIALSDocument2 pagesPretest-FACTORING POLYNOMIALSCharlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- PRETEST - Sets-G7-W1Document2 pagesPRETEST - Sets-G7-W1Charlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet
- PRETEST - Sets-G7-W1Document2 pagesPRETEST - Sets-G7-W1Charlene Grace BronolaNo ratings yet