Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Factor Affecting Standard Electrode Potential
Uploaded by
sumathi0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pages1. The document discusses how changes in concentration affect electrode potential and cell potential. Increasing the concentration of the oxidized form of a half-reaction increases electrode potential while increasing the reduced form decreases it.
2. It also provides examples of half-reactions and predicts how changing concentrations would affect electrode potential. For a cell, increasing the concentration of the oxidized species increases cell potential while decreasing the reduced species concentration has the same effect.
3. Factors that can increase cell potential at constant temperature include increasing the concentration of the oxidized species or decreasing the concentration of the reduced species in either half-cell reaction.
Original Description:
Original Title
FACTOR AFFECTING STANDARD ELECTRODE POTENTIAL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document discusses how changes in concentration affect electrode potential and cell potential. Increasing the concentration of the oxidized form of a half-reaction increases electrode potential while increasing the reduced form decreases it.
2. It also provides examples of half-reactions and predicts how changing concentrations would affect electrode potential. For a cell, increasing the concentration of the oxidized species increases cell potential while decreasing the reduced species concentration has the same effect.
3. Factors that can increase cell potential at constant temperature include increasing the concentration of the oxidized species or decreasing the concentration of the reduced species in either half-cell reaction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views2 pagesFactor Affecting Standard Electrode Potential
Uploaded by
sumathi1. The document discusses how changes in concentration affect electrode potential and cell potential. Increasing the concentration of the oxidized form of a half-reaction increases electrode potential while increasing the reduced form decreases it.
2. It also provides examples of half-reactions and predicts how changing concentrations would affect electrode potential. For a cell, increasing the concentration of the oxidized species increases cell potential while decreasing the reduced species concentration has the same effect.
3. Factors that can increase cell potential at constant temperature include increasing the concentration of the oxidized species or decreasing the concentration of the reduced species in either half-cell reaction.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
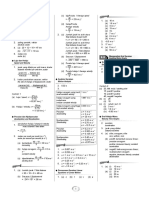
FACTOR AFFECTING STANDARD ELECTRODE POTENTIAL
A. Effect of concentration on electrode potential
1. Fe3+ (aq) + e Fe2+ Eo = +0.77V
Predict the change in the electrode potential of the above half-cell if
(a) The concentration of Fe3+ increased
(b) The concentration of Fe3+ decreased
(c) The concentration of Fe2+ increased
2. VO2+ + 2H+ + e V3+ + H2O Eo = +0.34V
Predict the change in the electrode potential of the above half cell if
(a) The concentration of H+ decreased
(b) The concentration of V3+ decreased
(c ) The concentration of VO2+ increased
3. Sn4+ + 2e Sn2+ Eo = +0.15 V
Predict the change in the electrode potential of the above half cell if the
(a) The concentration of Sn4+ is increased
(b) The concentration of Sn4+ is decreased
(c) The concentration of Sn4+ and Sn2+ are increased by the same factor
B. Effect of Concentration on the emf of the cell
1. An electrochemical cell is constructed from the following two half cell
Zn 2+ + 2e Zn
Fe 3+ + e Fe2+
(a) Write the cell diagaram for the electrochemical cell
(b) Calculate the e.m.f of the cell under standard condition
( c) Write an equation for the overall cell reaction
(c) Predict the changes (if any) in the e.m.f if,
(i) The concentration of Fe3+ is increased
(ii) The concentration of Fe2+ is decreased
(iii) The concentration of Zn2+ is decreased
(iv) The concentration of Zn2+ is increased
2. Consider the following electrochemical cell
Pt(s)/Fe2+(aq), Fe3+ (aq) // Ag2+ (aq) /Ag (s)
(a) Name the two half-cells that are involved in the construction of the cell
(b) Indcate the direction of the flow of electrons in the external circuit
(c) Name the anode and cathode of the cell
(d) Calculate the e.m.f of the cell under standard condition
(e) Suggest two ways whereby the e.m.f of the cell can be increased at contant
temperature
You might also like
- Exam 3-1 KeyDocument10 pagesExam 3-1 Keyraw4rillNo ratings yet
- 05 Extra Problems Recap KEYDocument5 pages05 Extra Problems Recap KEYUday Prakash SahuNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit2 Worksheet AnswersDocument7 pagesAp Unit2 Worksheet Answersburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Questions On ElectrochemistryDocument5 pagesTutorial Questions On ElectrochemistrycpliamNo ratings yet
- C3 TutoDocument2 pagesC3 TutoaliesyaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry - 2 AssignmentsDocument4 pagesElectrochemistry - 2 AssignmentsPritish Dutta100% (1)
- Adobe Scan 02 Sept 2023Document3 pagesAdobe Scan 02 Sept 2023Negi DeepakNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry 8.2Document12 pagesElectrochemistry 8.2sumathiNo ratings yet
- Ap Unit10 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAp Unit10 Worksheetburcak gecNo ratings yet
- Redox Review - IB-Short QuestionsDocument8 pagesRedox Review - IB-Short QuestionsStephanie LeeNo ratings yet
- 8.6 Factors Affecting Standard Electrode Potential (SEP)Document8 pages8.6 Factors Affecting Standard Electrode Potential (SEP)cintiaNo ratings yet
- ElectroChemistry NEET PYQDocument6 pagesElectroChemistry NEET PYQJENGNo ratings yet
- Electro Chemistry Assignment For Iitjee PDFDocument19 pagesElectro Chemistry Assignment For Iitjee PDFggk20130% (2)
- HL9Q&ADocument28 pagesHL9Q&ABrianNo ratings yet
- AP Electrochemistry Problem Set 2021Document7 pagesAP Electrochemistry Problem Set 2021Vineeth SendilrajNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Assignment-3Document1 pageElectrochemistry Assignment-3Akshara SreeNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: E° (Cathode) - E° (Anode) G - nFE F 96,485J/ V X Mols G GDocument15 pagesElectrochemistry: E° (Cathode) - E° (Anode) G - nFE F 96,485J/ V X Mols G GandrewNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 Electrochemistry: General Chemistry, 10e CDN (Petrucci)Document17 pagesChapter 20 Electrochemistry: General Chemistry, 10e CDN (Petrucci)ChemistNo ratings yet
- Topic 3 - ElectrochemistryDocument7 pagesTopic 3 - ElectrochemistryMutasimNo ratings yet
- Unit 13 Practice Free ResponseDocument10 pagesUnit 13 Practice Free Responseapi-182809945No ratings yet
- Unit 8B AP Chem - ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesUnit 8B AP Chem - ElectrochemistryAnivia12100% (1)
- Galvanic (Voltaic) Cells Problems: 2 (G) - (Aq) - (Aq) 2 (S)Document2 pagesGalvanic (Voltaic) Cells Problems: 2 (G) - (Aq) - (Aq) 2 (S)Rose Belle A. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Predicting Redox Reactions (No MS)Document1 pagePredicting Redox Reactions (No MS)AsadNo ratings yet
- Quiz (Two Half Cells System With Inert Electrodes)Document8 pagesQuiz (Two Half Cells System With Inert Electrodes)Matt MattNo ratings yet
- Voltaic Cells and ElectrollysisDocument2 pagesVoltaic Cells and ElectrollysisRolyn Mae CariñoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 BQDocument10 pagesChapter 18 BQTarek GhaddarNo ratings yet
- L.S.F. CHM201 Exam 2 L.S.F.: Always Ready To Help!Document0 pagesL.S.F. CHM201 Exam 2 L.S.F.: Always Ready To Help!Alysson Vany ClochetteNo ratings yet
- Topical Test Echem 2014Document1 pageTopical Test Echem 2014irnihafizan6812No ratings yet
- Electrochemistry TestDocument3 pagesElectrochemistry TesttusharNo ratings yet
- Nanyang Technological University Singapore Entrance Examination CHEMISTRY (Sample) InstructionsDocument8 pagesNanyang Technological University Singapore Entrance Examination CHEMISTRY (Sample) InstructionsAriny Lastarya PutriNo ratings yet
- Electrochem Question NewDocument9 pagesElectrochem Question NewrjakrithiNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Final RevisionDocument2 pagesElectrochemistry Final RevisionROWA new year CelebrationNo ratings yet
- Tutorial (Electrochemistry)Document4 pagesTutorial (Electrochemistry)Amir Aiman AniqNo ratings yet
- 4-Chem 1A Exam 2 Review ProblemsDocument7 pages4-Chem 1A Exam 2 Review ProblemsNesrine LaradjiNo ratings yet
- Xi - ChemistryDocument4 pagesXi - Chemistrybinodxyz0No ratings yet
- Periodic Table Q BANK RESODocument11 pagesPeriodic Table Q BANK RESOHarsh TyagiNo ratings yet
- 8.5 S.E.P and Electrochemical CellsDocument8 pages8.5 S.E.P and Electrochemical CellscintiaNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chemistry Ch-2.ElectrochemistryDocument37 pagesClass 12 Chemistry Ch-2.Electrochemistrykarnan karupiahNo ratings yet
- Question Chapter Test - 1 Atomic StructureDocument3 pagesQuestion Chapter Test - 1 Atomic StructureAryanNo ratings yet
- GT Group of Institutions CHEMISTRY-Revision Worksheet Class 11 Chemistry Worksheet 12/02/2021Document6 pagesGT Group of Institutions CHEMISTRY-Revision Worksheet Class 11 Chemistry Worksheet 12/02/2021jayashree krishnaNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Tut 2008Document3 pagesElectrochemistry Tut 2008DubistWhiteNo ratings yet
- ElectrochemistryDocument5 pagesElectrochemistryDhanush SNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 02 PDFDocument9 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 02 PDFamanNo ratings yet
- 12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 02 PDFDocument9 pages12 Chemistry Impq CH03 Electro Chemistry 02 PDFamanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 DmsDocument2 pagesTutorial 2 DmsCik ApaiNo ratings yet
- 12 ChemistryDocument4 pages12 ChemistryUnwantedNo ratings yet
- CHEM1300 Fall 2011 With SolutionsDocument13 pagesCHEM1300 Fall 2011 With SolutionsImtiaz MohammedNo ratings yet
- JEE-MAIN - Part Test - 1 - PaperDocument12 pagesJEE-MAIN - Part Test - 1 - PaperApex Institute100% (1)
- Sample Questions - Chapter 15Document6 pagesSample Questions - Chapter 15Rasel IslamNo ratings yet
- Test 2: State of Matter (Gas) and ElectrochemistryDocument4 pagesTest 2: State of Matter (Gas) and ElectrochemistryDai Fei PohNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Questions Paper (Clear Version)Document6 pagesChemistry Questions Paper (Clear Version)Aditi ThakurNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry: WWW - Crackjee.xyzDocument8 pagesElectrochemistry: WWW - Crackjee.xyzRashmi Ranjan DasNo ratings yet
- Homework Packet / Unit 2: HW #2.1: Contained in Separate Handout HW #2.2Document7 pagesHomework Packet / Unit 2: HW #2.1: Contained in Separate Handout HW #2.2api-368121935No ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 37 Science (086) Class-X, Session: 2021-22Document6 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 37 Science (086) Class-X, Session: 2021-22E. Poorna AshikNo ratings yet
- Electrochemsitry Grade 12Document1 pageElectrochemsitry Grade 12random alwaysNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - ElectrochemistryDocument8 pagesChapter 3 - ElectrochemistryMADHAVNo ratings yet
- Question 801367Document4 pagesQuestion 801367niveditasingh2472No ratings yet
- The Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry: ElectrochemistryDocument21 pagesThe Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry: ElectrochemistrySreeyaNo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesFrom EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electrocatalyst Materials and Interfacial Characterization: Energy Producing Devices and Environmental ProtectionFrom EverandFundamentals of Electrocatalyst Materials and Interfacial Characterization: Energy Producing Devices and Environmental ProtectionNo ratings yet
- Thermochemistry Hess - S LawDocument8 pagesThermochemistry Hess - S LawsumathiNo ratings yet
- 7.4 The Solubility of Solids in LiquidsDocument2 pages7.4 The Solubility of Solids in LiquidssumathiNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 7 (7.1) and CalorimeterDocument5 pagesTOPIC 7 (7.1) and CalorimetersumathiNo ratings yet
- Electrochemistry Nerst EquationDocument7 pagesElectrochemistry Nerst EquationsumathiNo ratings yet
- Ethanoyl Chloride Propanoyl Chloride: Chapter 19: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 19.5 Acyl Chloride 1. Iupac NamingDocument7 pagesEthanoyl Chloride Propanoyl Chloride: Chapter 19: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 19.5 Acyl Chloride 1. Iupac NamingsumathiNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction of Carboxylic Aci1Document4 pagesChemical Reaction of Carboxylic Aci1sumathiNo ratings yet
- CARBOXYLIC ACID PreparationDocument3 pagesCARBOXYLIC ACID PreparationsumathiNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid Physical PropertiesDocument5 pagesCarboxylic Acid Physical PropertiessumathiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Transition ElementsDocument5 pagesChapter 13 Transition ElementssumathiNo ratings yet
- Experiences With Online LearningDocument1 pageExperiences With Online LearningsumathiNo ratings yet
- 8.5 Electrolysis 1. Electrolytic Cell: Etopic 8 ElectrochemistryDocument7 pages8.5 Electrolysis 1. Electrolytic Cell: Etopic 8 ElectrochemistrysumathiNo ratings yet
- Nomenclature IIDocument1 pageNomenclature IIsumathiNo ratings yet
- Pergerakan Bahan Merentas Membran Plasma: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembraneDocument2 pagesPergerakan Bahan Merentas Membran Plasma: Movement of Substances Across The Plasma MembranesumathiNo ratings yet
- Jarak Dan Sesaran: Menganalisis Gerakan LinearDocument5 pagesJarak Dan Sesaran: Menganalisis Gerakan LinearsumathiNo ratings yet
- Praktis SPM 2Document2 pagesPraktis SPM 2sumathiNo ratings yet