Professional Documents
Culture Documents
AnaPhy Reviewer
Uploaded by
Ann Margarette Morales0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views5 pagesAnaPhy Reviewer
Uploaded by
Ann Margarette MoralesCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
1. Art of spreading the parts of an organism to attain their position, 30.
30. appears to be stratified but instead consists of a single layer of
relations, function, and structure anatomy irregularly shaped and differently sized columnar cells.
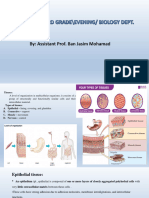
2. Cutting something to see what’s inside anatomy Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
3. Concerned with the effect of disease on cell, tissue, organ, and 31. Concerned with cells (specialty of Physio) Cell Physiology
system (specialty of physio) pathological physiology 32. side or direction toward the side of the body. lateral
4. the language of medicine. For those not familiar with this, they 33. thinness of the cell, is present where rapid passage of chemical
may seem difficult to pronounce and may appear to be rather compounds is observed simple squamous epithelium
complicated. However, just as when learning any language, once 34. Delivers air to alveoli (sites in lungs where gas exchange occurs)
the structure of the vocabulary is known, the words themselves respiratory system
become understandable. Medical terminology 35. Returns tissues fluids to the bloodstream lymphatic system
5. position closer to the surface of the body. Superficial 36. Bone and Cartilage (Provide structure and strength to the body and
6. Stores urine prior to voluntary elimination Urinary system protect soft tissues) supportive connective tissue
7. results when cell, organ or system adjusts its activity automatically 37. epithelium, refers to the sheets of cells that cover exterior surfaces
8. the study of the normal function of cell, tissue, organs, systems, of the body, lines internal cavities and passageways, and forms
and organisms physiology certain glands. Epithelial tissue
9. types of connective tissue fibers and ground substances 38. Subdivisions of the thoracic cavity left and right pleural cavities,
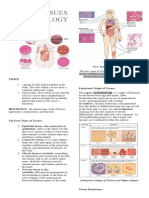
10. Face up orientation supine mediastinum, abdominopelvic, pelvic
11. It is a stratified squamous epithelial membrane resting on top of 39. Specific area (form of GA) Regional anatomy
connective tissue. 40. foundation of a medical term. It usually indicates the body organ or
12. Concerned with specific organ (specialty of physio) special anatomical part which is being described. Root word
physiology 41. Types of Tissues
13. Major organs of the cardiovascular system heart, blood, blood Ecang Connected My Nene
vessels Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nervous
14. front or direction toward the front of the body. anterior 42. Like blood cells, mast cells are derived from _____ ____ _____
15. Forms of Microscopic Anatomy cytology and histology and are part of the immune system. Hematopoietic stem cells
16. Produces female sex cells (oocytes) and hormones 43. occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or
17. Protects Against environmental hazards integumentary system mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the
18. Superficial marking (form of GA) surface anatomy fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input
19. Distributes heat and assists in control of body temperature or by other disturbances Negative feedback
cardiovascular system 44. _____, ___ ______, ________, _____ ____, and ________ ____
20. Clinical technology allows many different views of the body are found in connective tissue proper but are actually part of the
Xray, positron emission tomography scan, computerized immune system protecting the body
tomography scans, magnetic resonance imaging scans, ultrasound Mast cells, macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells, phagocytic
images, spiral CT scans, digital subtraction angiography images cells
21. Major Organs of the Nervous System Mary Marga Likes Pineapple Pizza
Boy Sailed Para Sayo 45. Generalized Functions of Epithelial Tissue
Brain, Spinal Cord, Peripheral nerves, Sense Organs 46. formed from the same protein subunits as collagen fibers; these
22. an organ or cell that responds to the command of control center fibers remain narrow and are arrayed in a branching network;
Effector found throughout the body, but are most abundant in the reticular
23. Concerned with cells (form of MA) Cytology tissue of soft organs, such as liver and spleen, where they anchor
24. allow organs to change in shape and size cavities and provide structural support to the parenchyma
25. Specialties of Anatomy Gross & Microscopic Anatomy 47. describes tissue with a single layer of irregularly shaped cells that
26. By using precise anatomical terminology, we eliminate ambiguity give the appearance of more than one layer. pseudostratified
27. position farther from the surface of the body. Deep 48. it is composed of epithelium attached to a layer of connective
28. secretion that involves the rupture and destruction of the entire tissue, for example, your skin epithelial membranes
gland cell Holocrine secretion 49. a plane that divides the body into unequal right and left sides
29. It modifies the meaning of a word. It usually consists of one or two parasagittal plane
syllables and is placed before the root word. Prefix 50. Provides protection and support for other tissues muscular system
51. It is responsible for keeping internal environment within certain
limits. Homeostatic regulation
52. Functions of connective tissues 74. The ending that follows a root word
Support and connect other tissues 75. contains the protein elastin along with lesser amounts of other
Protection proteins and glycoproteins; after being stretched or compressed, it
Transport of fluid, nutrients, waste, and chemical messengers will return to its original shape; prominent in elastic tissues found
Adipose cells store surplus energy in skin and the elastic ligaments of the vertebral column.
53. In bone, the matrix is rigid and described as ______ because of the 76. Specific system (form of GA)
deposited calcium salts. calcified 77. a position below or lower than another part of the body prope
54. apical surface of this membrane is exposed to the external 78. Concerned with system (specialty of physio)
environment and is covered with dead, keratinized cells that help 79. Body cavity that includes the thoracic cavity and the
protect the body from desiccation and pathogens. abdominopelvic cavity
Cutaneous membrane 80. first connective tissue to develop in the embryo, stem cell line from
55. Processes and digests food and absorbs and conserves water which all connective tissues are later derived.
Digestive system 81. Generates heat that maintains body temperature
56. Provides support and protection for other tissues skeletal system 82. Major organs of the integumentary system
57. Major Organs of the Lymphatic System 83. All vertebrates share a basic pattern of organization, most
Sobra Talagang Love ni Liza si Tiza noticeable during embryology
Spleen, Thymus, Lymphatic vessels, Lymph nodes, tonsils 84. Major Organs of the Endocrine Glands
58. thin layer or sheet of cells that covers the outside of the body (for 85. - a large cell derived from a monocyte
example, skin), the organs (for example, pericardium), internal
86. two-dimensional surface of a three-dimensional structure that has
passageways that lead to the exterior of the body (for example,
abdominal mesenteries), and the lining of the moveable joint been cut
cavities.
87. _________ and ______ secreted by fibroblasts combine with extra-
Tissue membrane
59. Stores energy reserves Digestive system cellular fluids to produce a viscous ground substance that, with
60. This cavity is bordered by the pelvis, with a floor of muscle embedded fibrous proteins, forms the extra-cellular matrix.
Pelvic cavity 88. divides the body or organ horizontally into upper and lower
61. Concerned with tissues (form of MA) Histology portions.
62. Homeostatic regulation involves _ _ _ 89. Recite the 10 directional terms
Rica Cares for Eda 90. Levels of Organization
Receptor, control center, effector 91. back or direction toward the back of the body. The popliteus is
63. New gland cells differentiate from cells in the surrounding tissue to posterior to the patella.
replace those lost by secretion Holocrine secretion 92. most common type of stratified epithelium in the human body.
64. Coordinates or moderates activities of other organ systems 93. Changes from conception to physical maturity conception to
Nervous system physical maturity
65. A subdivision of the thoracic cavity that is lined by the peritoneum 94. Recite the standard anatomical position
and extends from the diaphragm to the superior margins of the 95. Provides movement
pelvis 96. Serous fluid that Covers abdominal organs and forms double sheets
Abdominopelvic Cavity of mesenteries that suspend many of the digestive organs.
66. Deals with the functions and activities of life or of living matter 97. refers to the sheets of cells
Physiology 98. 2 types of glandular epithelium
67. Ventral cavity that contains the heart and lungs Thoracic Cavity 99. A plane that divides the body or an organ into an anterior (front)
68. made from fibrous protein subunits linked together to form a long portion and a posterior (rear) portion.
and straight fiber Collagen Fiber 100. number of cell layers in the tissue can be one— where every cell
69. while flexible, have great tensile strength, resist stretching, and rests on the basal lamina
give ligaments and tendons their characteristic resilience and 101. Major Organs of the Respiratory System
strength. 102. Specialties of Physiology
70. These fibers hold connective tissues together, even during the 103. Includes the loose connective tissues and dense connective tissue
movement of the body (Both tissues have a variety of cell types and protein fibers
71. Provides sounds for communication suspended in a viscous ground substance)
72. Provides milk to nourish newborn infant 104. The purpose of this language is not to confuse, but rather to
73. Faced-down orientation increase precision and reduce medicalerrors.
105. Provides and interprets sensory information about external 137. (each pleural cavity contains one lung) lined by the visceral and
conditions parietal pleura
106. accumulates near the apical portion of the cell. That portion of the 138. Defends against infection and disease
cell and its secretory contents pinch off from the cell and are 139. Directs long-term changes in the activities of other organ systems
released. 140. Helps regulate body temperature
107. More than one layer, only the basal layer of cells rests on the basal 141. Major Organs of the Skeletal System
lamina cell shape of epithelial tissue 142. Cavity that contains the liver, stomach, spleen and most of the
108. internal chambers holding vital organs large intestine
109. How does a cell/organ work? 143. Cells that Store lipids as many drops,High Metabolic activity
110. excitable, responding to stimulation and contracting to provide 144. arrangement gives the appearance of stratification; but in fact all
movement, and occurs as three major types the cells are in contact with the basal lamina, although some do not
111. Supports developing embryo from conception to delivery reach the apical surface
112. Provides oxygen on the bloodstream and Removes carbon dioxide 145. Major Organs of the Muscular System
to the bloodstream 146. Flattened and thin cell shape of epithelial tissue
113. processes information supplied by receptor and generates a 147. Excretions from exocrine gland
response (command) 148. Excretes waste products from the blood
114. examples of endocrine gland 149. results from activity of nervous system or endocrine system
115. rectangular, taller than it wide cell shape of epithelial tissue 150. Directs immediate responses to stimuli
116. Forms of Microscopic Anatomy 151. Standard body “map”.
117. protect vital organs 152. fibers are loosely organized, leaving large spaces in between
118. 2 types of tissue membrane 153.
119. this vertical plane runs directly down the middle of the body 154. Controls many structural and functional changes during
120. a natural lubricant that enables the bones of a joint to move freely development
against one another without much friction. 155. These line the coelomic cavities of the body, that is, those cavities
121. the middle or direction toward the middle of the body. The hallux that do not open to the outside, and they cover the organs located
is the medial toe. within those cavities.
122. 3 classifications of the Connective Tissues 156. contains the pericardium (pericardial cavity), another serous
123. Adjusts metabolic activity and energy use by the body membrane that surrounds the heart
124. An example of negative feedback 157. found in connective tissue proper, has many cytoplasmic granules
125. store lipids as a single large drop and are metabolically less active. (These granules contain the chemical signals _____ and ______)
Their effectiveness at storing large amounts of fat is witnessed in 158. structure made up of one or more cells modified to synthesize and
obese individuals. secrete chemical substances
126. 4 Planes referred to in anatomy and medicine 159. Produced by by the epithelial exocrine glands, covers the epithelial
layer
127. composite of connective and epithelial tissues. Sometimes called
160. ductless gland that releases secretions directly into surrounding
mucosae, these line the body cavities and hollow passageways that tissues and fluids
161. Absorbs nutrients (ions, water, and the breakdown products of
open to the external environment, and include the digestive,
dietary sugars, proteins, and fats)
respiratory, excretory, and reproductive tracts.
162. A plane that divides the body or an organ vertically into right and
128. Mammalian skin is an example of this dry, keratinized, stratified
left sides
squamous epithelium
163. Anatomical terminology is derived from _____ and _____ because
129. Major Organs of the Digestive System
these languages are no longer used in everyday conversation, the
130. group of cells found together in the body. The cells within a tissue
meaning of their words does not change.
share a common embryonic origin.
164. A gland in which its secretions leave through a duct that opens
131. Serous fluid that covers the heart
directly, or indirectly, to the external environment
132. Types of Epithelial Membranes
165. a position in a limb that is nearer to the point of attachment or the
133. AKA Wharton’s Jelly
trunk of the body. The brachium Is proximal to the antebrachium
134. a position in a limb that is farther from the point of attachment or
166. In ____ ______ an initial stimulus produces a response that
the trunk of the body. The crus is distal to the femur.
enhances the change in the original condition.
135. Major Organs of the female reproductive system
136. Stores calcium and other minerals
167. a mixture of glycoproteins and collagen, and provides an 200. reinforced by bundles of fibers that provide tensile strength,
attachment site for the epithelium, separating it from underlying elasticity, and protection.
connective tissue. 201. a multipotent adult stem cell - can differentiate into any type of
168. the most abundant cell in connective tissue proper. connective tissue cells needed for repair and healing of damaged
169. is formed solely from connective tissue. These membranes tissue.
encapsulate organs, such as the kidneys, and line our movable 202. the nucleus of the box like cells appears round and is generally
joints. located near the center of the cell.
170. Distributes blood cells, water, and dissolved materials including 203. Body cavity that includes the cranial cavity and the spinal cavity
nutrients, waste products, oxygen, carbon dioxide 204. imaginary two-dimensional surface that passes through the body.
171. When irritated or damaged, mast cells release ________, an 205. the inner layer of the synovial membrane release hyaluronan into
inflammatory mediator, which causes vasodilation and increased the joint cavity.
blood flow at a site of injury or infection, along with itching, 206. Cell shapes of epithelial tissues
swelling, and redness recognized as an allergic response 207. Found between many organs where it acts both to absorb shock
172. Produces male sex cells (sperms) and hormones and bind tissues together. It allows water, salts, and various
173. Major Organs of the Urinary System nutrients to diffuse through to adjacent or imbedded cells and
174. 3 major types of Muscle Tissue tissues.
175. Serous fluid that covers the lungs 208. Transverse planes produce images referred to as ___ _______.
176. Lymph and Blood (Various Specialized cells circulate in a watery 209. also excitable, allowing the propagation of electrochemical signals
fluid containing salts, nutrients, and dissolved proteins.) in the form of nerve impulses that communicate between different
177. 2 body cavities regions of the body
178. recruit other cells of the immune system to infected sites and 210. When stimulated, macrophages release ______, small proteins that
stimulate their activities act as chemical messengers.
179. Most common type of secretion 211. Cells that store lipids that fill most of the cytoplasm
180. Every organism must maintain _______for survival 212. connective tissue membrane that lines the cavity of a freely
181. a position above or higher than another part of the body proper. movable joint.
The orbits are superior to the oris. 213. Other cells move in and out of the connective tissue in response to
182. Found in the glands and ducts and is uncommon ______ _____.
183. 3 classifications of serous fluids 214. secretions are enclosed in vesicles that move to the apical surface
184. binds the cells and organs of the body together and functions in the of the cell where the contents are released by exocytosis
protection, support, and integration of all parts of the body. 215. It means “own layer” and help support the fragile epithelial layer
185. Regulates blood ion concentration and Ph 216. Fluid secreted by the cells of the thin squamous mesothelium,
186. composed of mesodermally derived epithelium (mesothelium) that lubricates the membrane, and reduces abrasion and friction
is supported by the connected tissue between organs
187. Controls water balance by regulating the volume of urine produced 217. Its Cell Junction is a specialized intercellular connection between
188. senses an environmental change or stimuli their cell membranes formed by adjoining cells
189. cavity that contains the reproductive organs, urinary bladder and 218. nucleus of the tall column-like cells tends to be elongated and
the final portion of the large intestine located in the basal end of the cells. Like the cuboidal epithelia,
190. Major organs of the Male Reproductive System this epithelium is active in the absorption and secretion of
191. 2 general points with homeostasis molecules.
192. effectively traps available water to form the synovial fluid 219. gradual changes in the shapes of the apical cells as the bladder fills
193. cells in a tissue share morphological features and are arranged in an with urine. It is found only in the urinary system
orderly pattern that achieves the tissue’s functions. 220. 3 methods of secretion
194. Boxy, as wide as it is all cell shape of epithelial tissue 221. tissue forms in the umbilical cord and is no longer present after
195. Provides sensory information birth, leaving only scattered mesenchymal cells throughout the
196. Types of adipocytes body.
197. The basal lamina attaches to a ____ ____, which is secreted by the 222. Fibroblast are present in all connective tissue proper. Fibrocytes,
underlying connective tissue, forming a ______ _______ that helps adipocytes, and mesenchymal cells are fixed cells, which means
hold it all together they remain within the connective tissue.
198. Forms blood cells 223. less active form of fibroblast, is the second most common cell type
199. Cell types of connective tissues in connective tissue proper.
224. a type of blood cell, which enters the connective tissue matrix from
the blood vessels.
225. secreted by fibroblasts, it is made of polysaccharides, specifically
hyaluronic acid, and proteins.
226. These combine to form a ________ with a protein core and
polysaccharide branches.
227. The proteoglycan attracts and traps available moisture forming the
clear, viscous, colorless matrix known as ______ _________.
228. Cells that store lipids that fill most of the cytoplasm
229. _____ adipose tissue is most abundant. It can appear yellow and
owes its color to carotene and related pigments from plant food.
White fat contributes mostly to lipid storage and can serve as
insulation from cold temperatures and mechanical injuries. White
adipose tissue can be found protecting the kidneys and cushioning
the back of the eye.
230. _____ adipose tissue is more common in infants, hence the term
“baby fat.”
231. The many _________ in the cytoplasm of brown adipose tissue
help explain its efficiency at metabolizing stored fat.
232. Brown adipose tissue is _________, meaning that as it breaks
down fats, it releases metabolic heat, rather than producing
adenosine triphosphate (ATP), a key molecule used in metabolism.
233. shows little specialization.
234. contains all the cell types and fibers previously described and is
distributed in a random, web-like fashion.
235. fills the spaces between muscle fibers, surrounds blood and lymph
vessels, and supports organs in the abdominal cavity. It underlies
most epithelia and represents the connective tissue component of
epithelial membranes, which are described further in a later
section.
236. mesh-like, supportive framework for soft organs such as lymphatic
tissue, the spleen, and the liver.
237. Reticular cells produce the __________ _____ that form the
network onto which other cells attach. It derives its name from the
Latin reticulus, which means _____ ____.
238. Dense regular connective tissue consists of _________ _____
packed into parallel bundles. Dense irregular connective tissue
consists of collagenous fibers interwoven into a mesh-like
network.
239. The distinctive appearance of the cartilage is due to
polysaccharides called ________ ______, which bind with ground
substance proteins to form proteoglycans. Embedded within the
cartilage matrix are __________, or cartilage cells, and the space
they occupy are called _______ (singular = lacuna).
240. layer of dense irregular connective tissue that encapsulates the
cartilage.
241. Cartilaginous tissue is _________, thus all nutrients need to
diffuse through the matrix to reach the chondrocytes. This is a
factor contributing to the very slow healing of cartilaginous tissues.
You might also like
- BM1 Sel-Organisme, HomeostasisDocument34 pagesBM1 Sel-Organisme, HomeostasisHalimahNurulIstiqomahAzzahraNo ratings yet
- Tissues Chapter NotesDocument19 pagesTissues Chapter NotesGagan Deep100% (2)
- Test Bank For Principles of Human Physiology 4th Edition by StanfieldDocument24 pagesTest Bank For Principles of Human Physiology 4th Edition by Stanfieldjohnlipceqgkjnbt100% (41)
- 2.2 Cell Organisation 20.1.2016Document19 pages2.2 Cell Organisation 20.1.2016sylent gohNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE3Document4 pagesSCIENCE3Mylene EsicNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Anatomy and PhysiologyCHESKA LYKA ASILONo ratings yet
- Deptals ReviewerDocument8 pagesDeptals ReviewerAnsel Francis RapsingNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Document15 pagesAnatomy Physiology Study Guide Test 1Jennifer BrownNo ratings yet
- Pengantar Fisiologi: Dr. Eka Bebasari, M.SC Bagian Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas RiauDocument41 pagesPengantar Fisiologi: Dr. Eka Bebasari, M.SC Bagian Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas RiauNurul Ulya RahimNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 4Document4 pagesAnaphy Chapter 4Riy KimNo ratings yet
- AnaphyDocument2 pagesAnaphyFlorence Nichole RoganNo ratings yet
- Simple Epithelium Stratified EpitheliumDocument2 pagesSimple Epithelium Stratified EpitheliumFlorence Nichole RoganNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReportingDocument8 pagesAnaphy ReportingRushyl Angela FaeldanNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Document10 pages11 Biology Revision Study Material Chapter 7Saurav Soni100% (1)
- 2nd Semester MidtermsDocument45 pages2nd Semester Midtermsguillesjhobel0701No ratings yet
- By Muhammad Shahid MSN, BSN, DPBCN, RN, BSCDocument37 pagesBy Muhammad Shahid MSN, BSN, DPBCN, RN, BSCMuhammad ShahidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Points To RememberDocument7 pagesChapter 7 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4100% (1)
- 1 TISSUES Online Teaching - REVISED 2021 AnaphyDocument38 pages1 TISSUES Online Teaching - REVISED 2021 AnaphySerendipity ParkNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Animal's Specialized StructuresDocument58 pages1.1 Animal's Specialized StructuresNathaliabee100% (1)
- LECTURE 3 - Body Cells and TissuesDocument11 pagesLECTURE 3 - Body Cells and TissuesGGonzales KarlaNo ratings yet
- Present 1 - HistologyDocument59 pagesPresent 1 - HistologySultanNo ratings yet
- Histology LecDocument258 pagesHistology LecBan JMNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument44 pagesAnimal TissuesMary Sutingco100% (1)
- General Biology 2 Quarter 4 (Week 1-4) : Animals Specialized StructuresDocument18 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Quarter 4 (Week 1-4) : Animals Specialized StructuresHannah CastroNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About Biological Tissue. For Other Uses, SeeDocument5 pagesThis Article Is About Biological Tissue. For Other Uses, Seerjohn 7No ratings yet
- Human Body OrganizationDocument11 pagesHuman Body OrganizationCay C. CordovaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Proper For Week 7Document5 pagesLesson Proper For Week 7Merlyn NavarroNo ratings yet
- Tissues 1.Document2 pagesTissues 1.Adeaga ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Q1 GenBio1 SLKWeek2 EditDocument21 pagesQ1 GenBio1 SLKWeek2 EditInele Ellia AgRe100% (1)
- Animal Tissues 2023Document70 pagesAnimal Tissues 2023yxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer Grade 12 STEM First SemesterDocument8 pagesBiology Reviewer Grade 12 STEM First SemesterEfren Lucero100% (2)
- Lesson 4Document11 pagesLesson 4Semper Ann LawagueyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2Deolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- 4 - TissueDocument13 pages4 - TissueGel Austin PascuaNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument11 pagesHistologyKeith OmwoyoNo ratings yet
- Tissue, Glands, and Membranes Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesTissue, Glands, and Membranes Epithelial TissueMoises MontalboNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument6 pagesBIOLOGYKiana BNo ratings yet
- Tissue Level of Organisation: Unit IiDocument15 pagesTissue Level of Organisation: Unit IiIyappan SubramaniNo ratings yet
- Quizzes ReviewerDocument8 pagesQuizzes ReviewerAis WallensteinNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument40 pagesTissuesInsatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- Histology Presentation PDFDocument67 pagesHistology Presentation PDFAbd ElNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument17 pagesAnimal TissuesMuskan Shree100% (1)
- Animal CellDocument5 pagesAnimal CellNan Fen Jin Sabolarce100% (1)
- محاضرات أنسجة 2017Document20 pagesمحاضرات أنسجة 2017Salam H Alhelali100% (2)
- 2 Cell and TissueDocument45 pages2 Cell and Tissuemandefro2No ratings yet
- Family: Other Images Provided by Science: A Closer Look (Maryland), Pages 28 and 30 (Macmillan/Mcgraw-Hill, 2008)Document49 pagesFamily: Other Images Provided by Science: A Closer Look (Maryland), Pages 28 and 30 (Macmillan/Mcgraw-Hill, 2008)Zay SalazarNo ratings yet
- 3 Tissue of Human Body NotesDocument11 pages3 Tissue of Human Body Notesghanshyam agnihotryNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Anaphy - Fernandez, Rr12Document5 pagesModule 4-Anaphy - Fernandez, Rr12Veronica ShaneNo ratings yet
- ANPH-M1-CU3. The Tissues and Integumentary SystemDocument33 pagesANPH-M1-CU3. The Tissues and Integumentary Systemajd100% (1)
- Tissue Gen Bio ReviewerDocument9 pagesTissue Gen Bio ReviewerAlfred CariñoNo ratings yet
- TISSUEDocument4 pagesTISSUEzairazapanta001No ratings yet
- Tissues and Cells Part 1 - Grade 7 - BiologyDocument4 pagesTissues and Cells Part 1 - Grade 7 - BiologyYasmina Jamal GholoumNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4Document4 pagesZoology Notes: 007 Chapter 4humanupgradeNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerAnn Fenelope AniscoNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument22 pagesTissueRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Zikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsDocument37 pagesZikri Aiman-Cell Organization in AnimalsZikriAimanNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study Guide (1123)Document5 pagesExam 1 Study Guide (1123)S. MartinezNo ratings yet
- Stem 11 Genbio 1 NotesDocument1 pageStem 11 Genbio 1 NotesKalila MckenzieNo ratings yet
- College Level Anatomy and Physiology: Essential Knowledge for Healthcare Students, Professionals, and Caregivers Preparing for Nursing Exams, Board Certifications, and BeyondFrom EverandCollege Level Anatomy and Physiology: Essential Knowledge for Healthcare Students, Professionals, and Caregivers Preparing for Nursing Exams, Board Certifications, and BeyondNo ratings yet
- I. Human Body OrientationDocument10 pagesI. Human Body OrientationAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Nature and Background of Social DancesDocument2 pagesNature and Background of Social DancesAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Folk DanceDocument5 pagesFolk DanceAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- CalorimetryDocument2 pagesCalorimetryAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsDocument3 pagesRotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid MechanicsAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Center of MassDocument2 pagesCenter of MassAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Capacitance and DielectricsDocument2 pagesCapacitance and DielectricsAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Center of Mass (Momentum, Impulse, and Collision)Document2 pagesCenter of Mass (Momentum, Impulse, and Collision)Ann Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Current, Resistance, and Electromotive ForceDocument3 pagesCurrent, Resistance, and Electromotive ForceAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Electrical PotentialDocument2 pagesElectrical PotentialAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Electric ChargeDocument3 pagesElectric ChargeAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- For PrintingDocument5 pagesFor PrintingRina RomanoNo ratings yet
- Organ Systems OverviewDocument4 pagesOrgan Systems OverviewdivineNo ratings yet
- Health System Building Blocks and Organ.2Document4 pagesHealth System Building Blocks and Organ.2Advait RajagopalNo ratings yet
- Anatomical Descriptive Source - Integumentary Skin, Tissue, and CellsDocument6 pagesAnatomical Descriptive Source - Integumentary Skin, Tissue, and CellsGURPARABJOT KAURNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HUman Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument16 pagesIntroduction To HUman Anatomy and PhysiologyBeah Marie AlisosoNo ratings yet
- A Review Article of Sharir Rachanaw.s.r. AnatomyDocument4 pagesA Review Article of Sharir Rachanaw.s.r. AnatomyIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System British English TeacherDocument14 pagesThe Cardiovascular System British English TeacherКатя ЗоркоNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 3rd Edition Donald C RizzoDocument35 pagesTest Bank For Fundamentals of Anatomy and Physiology 3rd Edition Donald C Rizzotithly.decamplh56c7100% (44)
- Human Body EssayDocument1 pageHuman Body EssayAtlas CruxNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Accompany Saladin Human Anatomy 6th Edition Eric WiseDocument37 pagesTest Bank For Accompany Saladin Human Anatomy 6th Edition Eric Wisekillyoukkalm100% (14)
- Comic StripDocument2 pagesComic StripSatori TendōNo ratings yet
- Nociception: Vidosavljević Tamara Perović KsenijaDocument47 pagesNociception: Vidosavljević Tamara Perović KsenijaKsenija PerovicNo ratings yet
- Q2 1st ST MATH SCIENCE FILIPINO MAPEHDocument10 pagesQ2 1st ST MATH SCIENCE FILIPINO MAPEHJemiel BraveNo ratings yet
- Full Download Test Bank For Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition Kevin T Patton PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Test Bank For Anatomy and Physiology 10th Edition Kevin T Patton PDF Full Chapterstudioustapa4839100% (14)
- Human Biology 12th Edition Test Bank Sylvia MaderDocument41 pagesHuman Biology 12th Edition Test Bank Sylvia Maderdorislanhpr028No ratings yet
- General ZoologyDocument2 pagesGeneral ZoologyJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- DLab Activity 1 - Understanding Human BodyDocument9 pagesDLab Activity 1 - Understanding Human BodySYDNEY JILL ACHAINo ratings yet
- Learnhive - CBSE Grade 5 Science Human Body - Lessons, Exercises, and Practice TestsDocument9 pagesLearnhive - CBSE Grade 5 Science Human Body - Lessons, Exercises, and Practice TestsBadri Narayan MishraNo ratings yet
- Dissection of RatDocument12 pagesDissection of RatFathiah NhNo ratings yet
- Exercises (Basic Human Anatomy and Medical Terminologies)Document7 pagesExercises (Basic Human Anatomy and Medical Terminologies)tomaNo ratings yet
- Bio-1-Peta - 3rd-Quarter-S1s2 2Document3 pagesBio-1-Peta - 3rd-Quarter-S1s2 2Anne MarielNo ratings yet
- Annual Padagogical Plan Session 2022-23 Class 9th To 12thDocument10 pagesAnnual Padagogical Plan Session 2022-23 Class 9th To 12thpriyanka tripathiNo ratings yet
- Practicalities of Iyengar Yoga Therapy For Serious ConditionsDocument7 pagesPracticalities of Iyengar Yoga Therapy For Serious Conditionsyog100% (1)
- DLP Science Q2 W3Document6 pagesDLP Science Q2 W3Julieann MarceloNo ratings yet
- Budget of Work Quarter 2Document3 pagesBudget of Work Quarter 2Grace GaraldeNo ratings yet
- Knowledge, Awareness and Attitude Towards Organ Donation Among Undergraduate Medical Students of HaryanaDocument5 pagesKnowledge, Awareness and Attitude Towards Organ Donation Among Undergraduate Medical Students of HaryanaVinissha JeyarajNo ratings yet
- Interpol Report 2021Document38 pagesInterpol Report 2021Local12wkrcNo ratings yet
- Lesson 22Document3 pagesLesson 22Huong Nguyen ThuyNo ratings yet
- Holden Ubd Stage 3Document21 pagesHolden Ubd Stage 3api-644093010No ratings yet