Professional Documents
Culture Documents
General Zoology
Uploaded by
Johnren Godinez BoocCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
General Zoology
Uploaded by
Johnren Godinez BoocCopyright:
Available Formats
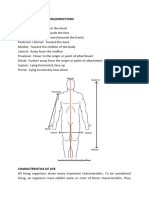
GENERAL ZOOLOGY (LAB)
connective tissue, epithelial tissue,
muscle, and nerve tissue. Tissues form
Properties of Life and the organs such as the heart and lungs, which
Characteristics of Animals provide functions for the organism
throughout its entirety.
Properties of Life
Biology is the study of living things.
Biology has been battling three
challenges since it was founded: What
are the similar characteristics that make
something "alive"? And how do we find
acceptable levels of organization in
something's structure after we know it's Metabolism
alive? In the end, given the astounding Thousands of connected chemical
variety of life, how do we classify the processes are needed for life to continue
various types of organisms so that we functioning. These responses let
can more effectively comprehend them? organisms carry out work, such as travel
Biologists strive to seek answers to these around or capture prey, and they also
and other problems as new organisms are grow, reproduce, and preserve the
found daily. physical makeup of their bodies. In order
Order, sensitivity or response to the to carry out the chemical reactions that
environment, reproduction, growth and maintain life, living things must produce
development, regulation, homeostasis, energy and absorb nutrients. The sum of
and energy processing are among the an organism's biological reactions is
characteristics associated with all living referred to as its metabolism. Organisms
species. These nine elements contribute consume energy to sustain their
to the essence of life when considered metabolic processes. It is the sum of all
together. chemical activity in the body. Some
In the discipline of biology, there are species effectively catch sunlight and
some characteristics that have been change it into chemical energy; others
broadly agreed upon to explain life. apply chemical energy to molecules they
Order, sensitivity or response to the consume as food.
environment, reproduction, adaptation, Metabolism has been split into two parts:
growth and development, regulation, anabolism and catabolism. In anabolism,
homeostasis, energy processing, and organisms construct more complicated
evolution are all characteristics of all substances from less complicated ones,
living species. These nine elements assist whereas catabolism does the opposite.
in defining life when regarded properly. Catabolic processes can render saved
energy available, whereas anabolic
Organization processes commonly burn energy.
Living things are very structured, which
means they are made up of specialized, Homeostasis
coordinated elements. All organisms are
composed of consisting of one or more
cells, which serve as the basic building
blocks of life.
Even unicellular organisms are
complicated! Atoms combine to form
molecules, which then combine to form
cell organelles and structures. Similar
cells form tissues in multicellular Multiple structures exist in organisms to
organisms. Tissues, in turn, work preserve an excellent interior
together to form organs (body structures environment. Even the tiniest organisms
that serve a specific purpose). Organs are complicated, needing the use of
collaborate to produce organ systems. many systems of regulation to manage
Humans and other multicellular internal activities, respond to stimuli, and
organisms are made up of numerous cope with environmental challenges.
cells. Multicellular creatures' cells can be Nutrient transfer and the flow of blood
differentiated to perform certain tasks are two physiological activities that are
and are arranged into tissues such as controlled in an organism. Organs
GENERAL ZOOLOGY (LAB)
(groups of tissues that operate together)
communicate oxygen around the body,
remove waste, give nutrition to every
cell, and regulate body temperature.
Cells require specific parameters for
them to operate properly, such as the
proper temperature, pH, and
concentration of various substances.
However, these factors may alter from
one moment to the next.
By homeostasis (literally, "steady state"),
a living thing's capacity to sustain
consistent internal environments,
organisms can maintain their internal
conditions within a certain limit,
constantly, despite external alterations.
Growth
DNA-encoded information regulates
how organisms evolve and develop as
they mature. All organisms execute
instructions written in their genes. The
genes supply instructions that control
cellular growth and development, which
guarantees the children receive their
parents' features. Living organisms grow
in a controlled manner. Individual cells
grow in size, and multicellular organisms
gather a vast number of cells during cell
division. You began as a single cell and
have grown to have tens of trillions of
cells in your body. Anabolic processes
are responsible for the formation of
large, complex molecules such as
proteins and DNA, the genetic material.
Reproduction
Living organisms are capable of
reproducing to generate new organisms.
Reproduction can be asexual (with a
single-parent organism) or sexual (with
two parents). Single-celled organisms,
such as the dividing bacteria illustrated
in the left panel of the image on the right,
can reproduce by essentially splitting in
two!
In sexual reproduction, two parent
organisms construct sperm and egg cells
having fifty percent of their genetic
information, which blend to create a new
individual with a complete genetic set.
The illustration on the far right depicts
this process, known as fertilization.
Response
You might also like
- Mahavastu HandbookDocument43 pagesMahavastu Handbookstvcda58% (93)
- Grof, Stanislav - Cosmic Game, The Explorations of The Frontiers of Human ConsciousnessDocument216 pagesGrof, Stanislav - Cosmic Game, The Explorations of The Frontiers of Human ConsciousnessMahmoud Fawzy Khalil93% (14)
- Code To The MatrixDocument254 pagesCode To The MatrixKyle Jodoin100% (14)
- Notes in Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesNotes in Human Anatomy and PhysiologyRikki Mae Bueno100% (3)
- Grade 12 - Biology Resource BookDocument245 pagesGrade 12 - Biology Resource BookMali100% (6)
- Plant Life - A Brief History - 1st Edition (2015)Document281 pagesPlant Life - A Brief History - 1st Edition (2015)srinivaas kalyaan100% (5)
- DLL SampleDocument8 pagesDLL SampleMarc Angelo L. Sebastian100% (1)
- General BiologyDocument4 pagesGeneral BiologyKasai KristineNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument14 pagesGeneral BiologyLara Loraine Norbe VicenteNo ratings yet
- Bot 101 Lecture 1Document4 pagesBot 101 Lecture 1tdirk342No ratings yet
- Biology Characteristics of LifeDocument11 pagesBiology Characteristics of LifeANDREA LOUISE ELCANONo ratings yet
- Lecture BZE Life-HomeostasisDocument10 pagesLecture BZE Life-Homeostasiscarolinebrongelcopti24No ratings yet
- Attributes of LifeDocument3 pagesAttributes of LifeZoeNo ratings yet
- Unifying Themes in The Study of Life ScienceDocument41 pagesUnifying Themes in The Study of Life ScienceKath Tan AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- 7 Characteristic Features of LifeDocument1 page7 Characteristic Features of Lifemarjureeq4298No ratings yet
- Biology Reviewer Properties of LifeDocument5 pagesBiology Reviewer Properties of LifeJenie Rose C. PeningNo ratings yet
- Properties of Life: Biology Is The Science That Studies Life. What Exactly Is Life? This May Sound Like A SillyDocument27 pagesProperties of Life: Biology Is The Science That Studies Life. What Exactly Is Life? This May Sound Like A SillySandra Nicole RiveraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Lessons 1 To 2-BIODocument59 pagesChapter 2 Lessons 1 To 2-BIOAndy PresendorNo ratings yet
- Define BiologyDocument11 pagesDefine BiologyPatricia PaezNo ratings yet
- THE-NATURE-OF-LIFE scienceDocument37 pagesTHE-NATURE-OF-LIFE sciencekylamae JinonNo ratings yet
- Properties of LifeDocument4 pagesProperties of LifeAndy Bautista De LeonNo ratings yet
- Study of Life and Living OrganismsDocument5 pagesStudy of Life and Living OrganismsVidGe MasaquelNo ratings yet
- Human Biology 1Document14 pagesHuman Biology 1Arwa AhmedNo ratings yet
- Cells, Homeostasis & Response: Intro to BiologyDocument7 pagesCells, Homeostasis & Response: Intro to BiologyYsabela Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope of Biology: (GK., Bios, Life Logous, Study) Is The Study of Living BeingsDocument25 pagesNature and Scope of Biology: (GK., Bios, Life Logous, Study) Is The Study of Living BeingsFarhan ChNo ratings yet
- God's Gift of Life ScienceDocument96 pagesGod's Gift of Life Sciencemicx ramos100% (2)
- Characteristics of LifeDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of LifeVan Denver E. BautistaNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of LifeDocument5 pagesCharacteristics of LifeVan Denver Evangelista BautistaNo ratings yet
- AnatomyDocument6 pagesAnatomygreatkill07No ratings yet
- Cells and Organization: What Is Life?: The Seven Characteristics of LifeDocument9 pagesCells and Organization: What Is Life?: The Seven Characteristics of LifeClarisse MendozaNo ratings yet
- L1 - Introduction To Biology Part 1Document38 pagesL1 - Introduction To Biology Part 1Noriko MatsumotoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology 1Document6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology 1Dianne LarozaNo ratings yet
- 1.homeostasis and Homeodynamism (Life and Hemostasis)Document23 pages1.homeostasis and Homeodynamism (Life and Hemostasis)HarshilPatelNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Living ThingsDocument14 pagesCharacteristics of Living Thingscourse heroNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiochemistryDocument11 pagesIntroduction To BiochemistrySamson Roberto SaballegueNo ratings yet
- Anatomy NoteDocument8 pagesAnatomy Notechiamaka anthonyNo ratings yet
- Biology, The Scientific Method & The Metric SystemDocument10 pagesBiology, The Scientific Method & The Metric Systemrakhmatov UlanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Life ScienceDocument19 pagesIntroduction To Life ScienceMarchee AlolodNo ratings yet
- Life Science Module 4 Lesson 3 and 4Document76 pagesLife Science Module 4 Lesson 3 and 4Mae AlfaroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To BiologyDocument22 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To BiologyvincraigNo ratings yet
- 1 - Introduction To BiologyDocument3 pages1 - Introduction To BiologyCOULINE ANN LLORENTENo ratings yet
- Biology Final ExamDocument17 pagesBiology Final ExamAliya BayramovaNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument86 pagesBiologyhoxojew752No ratings yet
- Campbell Biology - Chapters 1 Ans 2 SummaryDocument17 pagesCampbell Biology - Chapters 1 Ans 2 SummaryYana JohansonNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of LifeDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of LifeJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology (1-Ya)Document108 pagesAnatomy and Physiology (1-Ya)Rhelina MinNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Biology Chapter 1Document40 pagesConcepts of Biology Chapter 1hazharomar958No ratings yet
- LIFE SCIENCE - Lesson 1 NotesDocument2 pagesLIFE SCIENCE - Lesson 1 NotesRivaille JaegerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Exploring Life ADocument7 pagesChapter 1: Exploring Life Akhoapham2009No ratings yet
- Biology—The Study of LifeDocument8 pagesBiology—The Study of LifeNathaniel Victor BalerNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 BIO101Document9 pagesLecture 1 BIO101Ahamadul Islam OnonnoNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Biochemistry ClassDocument14 pagesWelcome To Biochemistry Classleexie2821No ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To BiologyPamela MorcillaNo ratings yet
- Shs Reviewer BiologyDocument43 pagesShs Reviewer BiologyWildred LamintaoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Introduction To BiologyDocument74 pagesLesson 1 - Introduction To BiologyMichael PapioNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument33 pagesIntroduction To BiologyAghoweh Clintin TonifarNo ratings yet
- MC100 Human Anatomy and Physiology: The Human Body: Anatomy - Is The Study of The Body's Development AnatomyDocument17 pagesMC100 Human Anatomy and Physiology: The Human Body: Anatomy - Is The Study of The Body's Development AnatomyRikki Mae BuenoNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY REVIEWER (MDL+QSTNS)Document170 pagesANAPHY REVIEWER (MDL+QSTNS)Jewell Nivera CarpioNo ratings yet
- Local Media2210703659562817356Document41 pagesLocal Media2210703659562817356Regie MorialNo ratings yet
- Biology Keywords Under 40 CharactersDocument1 pageBiology Keywords Under 40 CharactersJun QiangNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of LifeDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of LifeShahrat Farsim ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- ReviewerDocument7 pagesReviewerDapflean Centeno MusniNo ratings yet
- INTRO BIO and LIFEDocument33 pagesINTRO BIO and LIFEzkkpxh4dnrNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1Document18 pagesLesson 1Ace De Jesus RascoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Course PacksDocument51 pagesLesson 2 Course PacksJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- Booc, Johnren G. (Theory of Darwin & Lamarck)Document1 pageBooc, Johnren G. (Theory of Darwin & Lamarck)Johnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- Booc, Johnren G. (Timeline of Human Evolution)Document1 pageBooc, Johnren G. (Timeline of Human Evolution)Johnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- Booc, Johnren G. (Charles Darwin & Evolution)Document1 pageBooc, Johnren G. (Charles Darwin & Evolution)Johnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- Industrial Revolution in The 17th CenturyDocument2 pagesIndustrial Revolution in The 17th CenturyJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- Communication Ethics NotesDocument18 pagesCommunication Ethics NotesJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- Nat Reviewer For Life Science 2022-2023Document6 pagesNat Reviewer For Life Science 2022-2023Johnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- BsPsych 1B Booc Activity3Document1 pageBsPsych 1B Booc Activity3Johnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- BsPsych 1B Booc DRRMAWARENESSDocument2 pagesBsPsych 1B Booc DRRMAWARENESSJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- Panuto: Panoorin Ang Short Video Na "Document1 pagePanuto: Panoorin Ang Short Video Na "Johnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- Purpose - The Title Explains How Schools Utilize Information Technology in The Classroom To Its Fullest PotentialDocument3 pagesPurpose - The Title Explains How Schools Utilize Information Technology in The Classroom To Its Fullest PotentialJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER ENGLISH 3 Google DocsDocument6 pagesREVIEWER ENGLISH 3 Google DocsJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument21 pagesMITOSISJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- PLANT CELL Experiment No. 3Document4 pagesPLANT CELL Experiment No. 3Johnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Social Media On StudentsDocument5 pagesThe Effects of Social Media On StudentsJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- Activity-2.1 DilutionDocument1 pageActivity-2.1 DilutionJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- MeiosisDocument47 pagesMeiosisElah TapangNo ratings yet
- MutationsgeneticdisordersDocument38 pagesMutationsgeneticdisordersJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- Regulation of Cell Division: AP BiologyDocument26 pagesRegulation of Cell Division: AP BiologyNurul Rizqan SeptimaNo ratings yet
- Summarizing, Paraphrasing, and Direct QuotingDocument55 pagesSummarizing, Paraphrasing, and Direct QuotingJohnren Godinez BoocNo ratings yet
- CG in Science 5Document19 pagesCG in Science 5Jhoy Angeles PinlacNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 ResourcesDocument69 pagesChapter 1 ResourcesGovindNo ratings yet
- Phylogenrtictree Mode 2Document27 pagesPhylogenrtictree Mode 2ASUTOSH MISHRANo ratings yet
- WFDDocument97 pagesWFDajay WaliaNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan in Earth and Life Science: School: Quarter: Teacher: Week: Subject: DateDocument3 pagesLearning Plan in Earth and Life Science: School: Quarter: Teacher: Week: Subject: DateJobelle TabinasNo ratings yet
- Biology 1Document228 pagesBiology 1Ghanshyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- 8 Basic Principles of EthicsDocument3 pages8 Basic Principles of EthicsMutevu SteveNo ratings yet
- Biology 12th Edition Mader Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesBiology 12th Edition Mader Solutions Manualcatmammotham9t4100% (14)
- The Importance ofDocument2 pagesThe Importance ofMd Shohag Ali100% (1)
- 12 Strand Dna - Masterteacher 33Document5 pages12 Strand Dna - Masterteacher 33gs810694No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Biology in The 21st CenturyDocument14 pagesChapter 1 - Biology in The 21st CenturygermaniumgalliumNo ratings yet
- Thesis Report On Greening The Quays by Anne Erven PDFDocument42 pagesThesis Report On Greening The Quays by Anne Erven PDFAnne ErvenNo ratings yet
- Ph. D. ProposalDocument22 pagesPh. D. Proposalbhupesh joshiNo ratings yet
- Gaia Hypothesis AbawanDocument4 pagesGaia Hypothesis AbawanGlen Paul AbawanNo ratings yet
- G12 Q3 W5 M5 General-Biology-2 Pilario PDFDocument27 pagesG12 Q3 W5 M5 General-Biology-2 Pilario PDFJohn Michael Romarez100% (1)
- Evolution Theory's Impact on Living Things ClassificationDocument10 pagesEvolution Theory's Impact on Living Things ClassificationTikaNo ratings yet
- Bob's Legacy 2Document414 pagesBob's Legacy 2fredekzgredekNo ratings yet
- Developmental Biology - From A Cell To An Organism (Genetics Evolution)Document225 pagesDevelopmental Biology - From A Cell To An Organism (Genetics Evolution)ekamutiaraNo ratings yet
- EARTH SCIENCE-WPS OfficeDocument10 pagesEARTH SCIENCE-WPS OfficeJasmin AquinoNo ratings yet
- SBS Undergraduate Programmes Handbook-2019-Updated (31 July)Document224 pagesSBS Undergraduate Programmes Handbook-2019-Updated (31 July)eunice osei owusuNo ratings yet
- Communicating Environment: History of Bangla Environmental Magazines of Kolkata BY DR - Sabyasachi Chatterjee and Malyaban ChattopadhyayDocument21 pagesCommunicating Environment: History of Bangla Environmental Magazines of Kolkata BY DR - Sabyasachi Chatterjee and Malyaban ChattopadhyaymlybncNo ratings yet
- Nckebych 01Document13 pagesNckebych 01N. SaravananNo ratings yet
- Viruses: A Concise GuideDocument9 pagesViruses: A Concise GuideDenice Kate Rabon ArnocoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 2: Module 1-4Document32 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 2: Module 1-4Elaiza GaytaNo ratings yet