Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module 1M: Intro To Medical Microbiology and Cellular Biology Microbiology
Module 1M: Intro To Medical Microbiology and Cellular Biology Microbiology
Uploaded by
Rica Bacarro0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesIndigenous microbes normally reside within the human body and provide benefits such as inhibiting pathogenic growth. Opportunistic pathogens usually do not cause disease but can do so when the host is weakened. There are two categories of microbes - acellular, which lack cells and include viruses and prions, and cellular microbes which have cells like bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Microbiology allows recognition of pathogenic microbes and optimal patient care.
Original Description:
JGJDGFSX
Original Title
1m-MC3
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIndigenous microbes normally reside within the human body and provide benefits such as inhibiting pathogenic growth. Opportunistic pathogens usually do not cause disease but can do so when the host is weakened. There are two categories of microbes - acellular, which lack cells and include viruses and prions, and cellular microbes which have cells like bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Microbiology allows recognition of pathogenic microbes and optimal patient care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesModule 1M: Intro To Medical Microbiology and Cellular Biology Microbiology
Module 1M: Intro To Medical Microbiology and Cellular Biology Microbiology
Uploaded by
Rica BacarroIndigenous microbes normally reside within the human body and provide benefits such as inhibiting pathogenic growth. Opportunistic pathogens usually do not cause disease but can do so when the host is weakened. There are two categories of microbes - acellular, which lack cells and include viruses and prions, and cellular microbes which have cells like bacteria, archaea, and fungi. Microbiology allows recognition of pathogenic microbes and optimal patient care.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
MODULE 1M: INTRO TO MEDICAL MICROBIOLOGY Indigenous Microbiota
AND CELLULAR BIOLOGY > Resident Microbes
• Lives within the body
Microbiology • Are beneficial because:
> Study of microbes o Inhibits growth of pathogens in
areas they reside by occupying space
Microbes o Deplete the food supply
> very small living and nonliving entities o Secrete materials that may prevent
> need to use various types of microscopes to be or reduce pathogen growth
seen and studied (Not all but majority) • Ex. Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus)
> ex. of microbe that doesn’t need: fungi o Normally found in the skin
2 Categories of Microbes > Opportunistic Pathogens
• Usually don’t cause any problems
> Acellular Microbes • Causes disease when host is stressed
• Also called infectious particles (especially w/ surgery), weakened or
• Absence of cells immunosuppressed
• Include viruses and prions • Microbes waiting for opportunity to cause
disease
> Cellular Microbes • Potentially harmful if given access to areas
• Has cells they don’t belong
• Include all bacteria, archaea, protozoa, o Escherichia coli (E. coli)
algae, fungi - Synthesizes vit. K
- normal in colon
Prokaryotic - causes sepsis if reaches the
> unicellular blood stream
> going to be very small o Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus)
> bacteria - Normal in skin
- Causes infections when
Eukaryotic enters the blood stream
> multicellular 2 Categories of Diseases
> protists and fungi > Infectious Disease
• When a pathogen colonizes the body and
Pathogens subsequently causes disease
> disease-causing microbes • When inside, they can release toxins that
> only 3% of microbes will then cause harm
Non-pathogens > Microbial Intoxication
> do not cause diseases • When a person ingests a toxin that been
> beneficial or useless pre-formed by a microbe
> 97% of microbes o Vestibulum botulinum
1. Spore forming microorganism
Importance of Microbiology 2. Found in spoiled canned food
> Allows us to acknowledge which microbes we 3. Toxin is already formed within the
should look out for and which ones we should take can, you’re just ingesting it
care 4. Causes botulism
> knowing the difference allows optimum patient - Infection causing paralysis
care
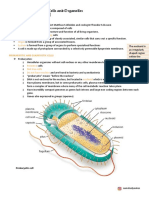
Microbial Cell Structure • Golgi Apparatus
> Eukaryotes o Packages the proteins formed in the
- Multicellular organism ER into small vesicles for storage and
- Eu = true export
- Karyo = nut or nucleus • Lysosomes
- TRUE nucleus o Type of vesicle
- DNA is enclosed by nuclear membrane o Contains lysozyme and other
- 10x larger than most prokaryotes digestive enzymes
o In charge of phagocytosis
Parts of the Eukaryote - Digesting pathogens and
• Nucleus worn-out cells
o Command center of the cell • Peroxisomes
o Most products manufactured within o Type of vesicle
nucleus and then transported out to o Breaks down H2O2 (hydrogen
be finalized peroxide) into H and H2O
o Pink center o Uses catalase enzyme
o Chromatin / chromosomes • Mitochondria
- Contain genetic material o Powerhouse of the cell
o Nucleoplasm o ATP production
- Works like the cytoplasm
o Nuclear envelope Not Present in all Eukaryotes
- Works like cell membrane of • Cell wall
nucleus o In plant cells
• Cell Membrane o Provides rigidity, shape & protection
o Separates cell from external o Much simpler in prokaryotes
environment • Flagella
o Regulates passage of different o Long thin filament
materials in and out of the cell o Motility
o Selectively permeable o Whip-like structure
o Blue outer layer • Cilia
• Cytoplasm o Shorter, thinner
o Semifluid gelatinous matrix where o For locomotion
organelles are immersed o Not whiplike, moves like wiggling to
• Endoplasmic reticulum and fro
o Convoluted membranes
o Transport network
o Right beside the nucleus
o Rough ER
- Formation of proteins
because of ribosomes
o Smooth ER
- No ribosomes
- Transports lipids and carbs
• Ribosomes
o Assist in protein formation
o Forms peptide bonds between
amino acids
o Translation occurs
> Prokaryotes • Flagella
- Unicellular organisms o For locomotion
- Pro = Before o Flagellin: 3 or more protein threads
- Karyo = Nut or nucleus - Twisted like a rope
- NO TRUE nucleus o 4 Types of Flagella → picture
- DNA not enclosed by nuclear membrane - Based on location & number
- DNA is squiggly & scattered all around cell
- Smaller in size
Parts of the Prokaryote
• Cytoplasm
• Cell membrane
• Chromosome
o Only single, long, supercoiled
circular DNA
o Control center of bacterial cell
• Ribosomes
• Plasmid
o Small, circular molecule of double- • Pili / Fimbriae
stranded DNA o Hair-like structures
o AKA Extrachromosomal DNA o Arise from cytoplasm
because it’s found outside the main o Made up of pilin
chromosome / like an extra - Proteins
chromosome - Shorter and thinner than
• Cell wall flagella
o Defines shape of cell, provide - Not for motility
rigidity, strength, and protection - Function: attachment
o Main component: Peptidoglycan • Pili (fimbriae) Vs Flagella
o Polysaccharide
• Glycocalyx layer Pili (fimbriae) Flagella
o Present in some bacteria hair-like rope like
o Layer found outside cell wall (The Structure
capsule / orange in the picture) shorter, thinner longer, thicker
o Slimy, gelatinous material produced
by cell membrane & secreted Component Pilin flagellin
outside cell wall
o Prokaryotes have a more complex
outer layering → Allows them to Function Attachment locomotion
survive most of the immune
mechanisms of the body
You might also like
- SketchyMicro ChartDocument14 pagesSketchyMicro ChartSonia100% (8)
- Micro Not in SketchyDocument4 pagesMicro Not in Sketchyrpascua123No ratings yet
- Microbiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideFrom EverandMicrobiology: a QuickStudy Laminated 6-Page Reference GuideNo ratings yet
- Basics of MicrobiologyDocument83 pagesBasics of Microbiologyaakash100% (1)
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesSahar Bakrey91% (47)
- MIC159 Microbial World: Siti Sarah Jumali Room 3/14Document36 pagesMIC159 Microbial World: Siti Sarah Jumali Room 3/14Muhamad Fariz NugrahaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MycologyDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Mycologysarguss14100% (2)
- Fundamentals in Nursing Practice: NCM 103 / RLE / Second Semester Midterms Cdu - CNDocument35 pagesFundamentals in Nursing Practice: NCM 103 / RLE / Second Semester Midterms Cdu - CNRica BacarroNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Microbiology: Dr. Thaigar Parumasivam Email: Thaigarp@usm - MyDocument26 pagesAn Overview of Microbiology: Dr. Thaigar Parumasivam Email: Thaigarp@usm - MyHuii Jiing WongNo ratings yet
- Sciences: Grade 11 TextbookDocument376 pagesSciences: Grade 11 TextbookPriyanka KanaNo ratings yet
- HURST 2016 - Their World, A Diversity of MISS Environments LB 5384 PDFDocument391 pagesHURST 2016 - Their World, A Diversity of MISS Environments LB 5384 PDFEduardo100% (1)
- Chapter 1 ReviewDocument6 pagesChapter 1 ReviewDung NguyenNo ratings yet
- Chap 14 Micropara ReviewerDocument25 pagesChap 14 Micropara RevieweryanNo ratings yet
- 3-17 Microbes Major GroupsDocument11 pages3-17 Microbes Major GroupsTanay PanjaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsDocument62 pagesChapter 2: Prokaryotic & Eukaryotic CellsIsabelle Hazel BenemileNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document14 pagesUnit 1Pratik PawarNo ratings yet
- Micro Chapter 2Document34 pagesMicro Chapter 2Farrah GwynethNo ratings yet
- L1.3 - Cell Structures Note PackageDocument4 pagesL1.3 - Cell Structures Note Package中华雅思王No ratings yet
- Micro Part 1Document109 pagesMicro Part 1amena wajeehNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microbiology: Dr. Venkata Krishna B. (M.SC., NET., PH.D.)Document27 pagesIntroduction To Microbiology: Dr. Venkata Krishna B. (M.SC., NET., PH.D.)Peak LevelNo ratings yet
- Prokaryotes Vs EukaryotesDocument8 pagesProkaryotes Vs EukaryotesJeanelle VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Microbiology: Dr. Nada Abdallah Basheer Clinical MicrobiologistDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Microbiology: Dr. Nada Abdallah Basheer Clinical MicrobiologistAva EbsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Microbial World AND YOUDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Microbial World AND YOUChristian AbordoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Structure and Taxonomy HandoutDocument11 pagesCellular Structure and Taxonomy Handoutkjdobdin23No ratings yet
- Lesson II: The Living Cells: Jonald P. Regio, RN, RMTDocument30 pagesLesson II: The Living Cells: Jonald P. Regio, RN, RMTDana TabingNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesDocument5 pages1.2 Prokaryotes and EukaryotesJosh Miguel BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Micr Lec - MidtermsDocument20 pagesMicr Lec - Midtermsyvette montesNo ratings yet
- Chem113lec Week 3.2Document5 pagesChem113lec Week 3.2Darryl orcaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To BiologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To BiologyFransiel B. AkistoyNo ratings yet
- Basic Microbiology Aid NursesDocument71 pagesBasic Microbiology Aid NursesRubina AkbarNo ratings yet
- Medical Microbiology Anesthesia Lecture 2Document39 pagesMedical Microbiology Anesthesia Lecture 2Ubaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Medical Microbiology Anesthesia Lecture 2Document39 pagesMedical Microbiology Anesthesia Lecture 2Ubaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrobesDocument10 pagesIntroduction To MicrobesAngela WeaslyNo ratings yet
- Scientists That Contribute To The Discovery of The CellDocument6 pagesScientists That Contribute To The Discovery of The Celljerikbenito46No ratings yet
- Cell ReviewerDocument6 pagesCell ReviewerEva Marie GaaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Chapter 2 NotesDocument39 pagesUnit 1-Chapter 2 NotesssNo ratings yet
- SBT 2173: Introduction To Microbiology: Dr. Elizabeth Mitaki Lesson 1Document30 pagesSBT 2173: Introduction To Microbiology: Dr. Elizabeth Mitaki Lesson 1Derrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & FunctionDocument76 pagesCell Structure & Functionuday xeroxNo ratings yet
- (M1) The CellDocument14 pages(M1) The CellBSN 1-1No ratings yet
- Igcse Biology Notes: Unit 1: Characteristics of LivingDocument50 pagesIgcse Biology Notes: Unit 1: Characteristics of LivingMa XóNo ratings yet
- Business Foundation: SAMI Academy of Excellence SAMI Academy of ExcellenceDocument31 pagesBusiness Foundation: SAMI Academy of Excellence SAMI Academy of ExcellenceTabish KhanNo ratings yet
- BNC MicroorganismsDocument11 pagesBNC Microorganismsashenafihailemariam43No ratings yet
- 1.Cell-The Unit of LifeDocument30 pages1.Cell-The Unit of LifeHridyanshu Singh RoyNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument8 pagesCellsAnchal ChadhaNo ratings yet
- Microbiology Notes Final-2Document58 pagesMicrobiology Notes Final-2arvindk962706No ratings yet
- Bacterial Structure 1Document30 pagesBacterial Structure 1محمد ناصرNo ratings yet
- Micropara NotesDocument4 pagesMicropara Notesorangechicken473No ratings yet
- MICROPARA - SEM 2Document11 pagesMICROPARA - SEM 2Ariel Marie PononNo ratings yet
- Final Midterm 1Document22 pagesFinal Midterm 1KristyNo ratings yet
- MicroPara 03 - Prokaryotic CellsDocument23 pagesMicroPara 03 - Prokaryotic CellsJianne CaloNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MicrobiologyDocument6 pagesIntroduction To MicrobiologySeon u 'No ratings yet
- Eukariot Dan ProkariotDocument37 pagesEukariot Dan ProkariottidaniadevNo ratings yet
- Bacteria and Viruses Study GuideDocument2 pagesBacteria and Viruses Study GuideEmily GillisNo ratings yet
- PPT1.2 Cell Doctrine PDFDocument44 pagesPPT1.2 Cell Doctrine PDFBharath KumarNo ratings yet
- Bio Chapter 2Document57 pagesBio Chapter 2Xue Yi LamNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Microorganims - Lecture Notes - CompleteDocument90 pagesUnit 1 - Microorganims - Lecture Notes - CompleteNkosenhle N DubeNo ratings yet
- Self-Study Guide Questions #1: Prokaryotes EukaryotesDocument4 pagesSelf-Study Guide Questions #1: Prokaryotes EukaryotesDaniel EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Medical Microbiology: DM Sukrama Dept - Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Udayana UniversityDocument67 pagesIntroduction To Medical Microbiology: DM Sukrama Dept - Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Udayana Universityigus6960% (1)
- UntitledDocument44 pagesUntitledRica BacarroNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument37 pagesUntitledRica BacarroNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument42 pagesUntitledRica BacarroNo ratings yet
- Catchup Schedule PR PDFDocument2 pagesCatchup Schedule PR PDFGama Adi SafutraNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Poultry DiseasesDocument22 pagesHandbook of Poultry DiseasesSoufian CherkiNo ratings yet
- Microbiological ResearchDocument11 pagesMicrobiological ResearchUsoa PeralNo ratings yet
- DAFTAR PUSTAKA Case BronkiolitisDocument2 pagesDAFTAR PUSTAKA Case BronkiolitisAnilNo ratings yet
- By Harshitha PR 1 M.Sc. Biotechnology: General Structure and Reproduction in Protozoa PlasmodiumDocument12 pagesBy Harshitha PR 1 M.Sc. Biotechnology: General Structure and Reproduction in Protozoa PlasmodiumKavisa GhoshNo ratings yet
- ORTIZ - AMAZING - BSMT1-A (Module 4 - Post-Task)Document1 pageORTIZ - AMAZING - BSMT1-A (Module 4 - Post-Task)ace starNo ratings yet
- Explanation Text 2ndDocument2 pagesExplanation Text 2ndMalaa Sari04No ratings yet
- Infeksi Dengue 29052021Document43 pagesInfeksi Dengue 29052021Feby JuwitaNo ratings yet
- 1.5 ProkaryotesDocument17 pages1.5 ProkaryotesKate Rashell SevillaNo ratings yet
- List N Disinfectant Results Table - ExploreDocument113 pagesList N Disinfectant Results Table - ExplorehmareidNo ratings yet
- Pre-Placement Immunization Form (June 2017) BrockDocument2 pagesPre-Placement Immunization Form (June 2017) BrockroldinpgNo ratings yet
- Epi#3Document19 pagesEpi#3JNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Activities of Spices and HerbsDocument7 pagesAntimicrobial Activities of Spices and HerbsLucía MercedesNo ratings yet
- ActinobacillosisDocument17 pagesActinobacillosisKhalid Gul100% (1)
- HMDocument21 pagesHMshyamchepurNo ratings yet
- Avika ReportDocument2 pagesAvika ReportChinish KalraNo ratings yet
- Bacillus Genetic Stock Center Catalog of Strains, Seventh EditionDocument58 pagesBacillus Genetic Stock Center Catalog of Strains, Seventh EditionOorrmm JubujubuNo ratings yet
- Lecture I Micro para ReviewerDocument3 pagesLecture I Micro para ReviewerJo Marchianne PigarNo ratings yet
- OJMM Pattern of Acute Parasitic Diarrhoea in ChildrenDocument6 pagesOJMM Pattern of Acute Parasitic Diarrhoea in ChildrenriskaNo ratings yet
- Ancy Lost OmaDocument41 pagesAncy Lost OmaMuhmmad TahaNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis of Bacterial Infections in Animals 5Th Edition John F Prescott Full Chapter PDF ScribdDocument67 pagesPathogenesis of Bacterial Infections in Animals 5Th Edition John F Prescott Full Chapter PDF Scribdtodd.feuer645100% (7)
- Staphylococcus Aureus: Antiseptic Resistance Gene Distribution Antimicrobial Agent of Susceptibilities andDocument8 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus: Antiseptic Resistance Gene Distribution Antimicrobial Agent of Susceptibilities andRisna IrvianiNo ratings yet
- Host Pathogen InteractionDocument20 pagesHost Pathogen InteractionShaker HusienNo ratings yet
- Acute Pharyngitis in Adolescents and AdultsDocument45 pagesAcute Pharyngitis in Adolescents and AdultsAlanGonzalezNo ratings yet
- Parasit ProtozoaDocument19 pagesParasit ProtozoaVani VrenikaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Effect of Rosemary ExtractsDocument10 pagesAntimicrobial Effect of Rosemary ExtractsNgân KimNo ratings yet