Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Entrep and Bio Reviewer
Entrep and Bio Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jesyrae Nykollai HuligangaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Entrep and Bio Reviewer
Entrep and Bio Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jesyrae Nykollai HuligangaCopyright:
Available Formats
ENTREP
1. A potential market is a market you haven’t reached that covers people interested in the
product, but not yet buyers. If a brand expands its products, it can attract and attain new
demographics that aren’t customers now.
-Potential market is the part of the total population that has shown some level of interest in
buying a particular product or service. This includes individuals, firms and organizations.
Potential market is also called Total addressable market (TAM).
Based on the potential market, the manufacturers or marketers can plan for the budgets and
expenses for production and other activities e.g. marketing, promotions etc.
2. personality, class consciousness, attitudes, perceived risk, and purchase importance.
Identify what the customers want
Distribute feedback throughout your organization
Keep a Close Eye On/ Pay attention Your Competitors
Create product/service features based on customer feedback
Plan How to Implement Customer Needs into Your Operations
REVIEWER BIO
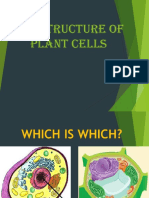
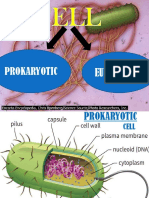
ORGANELLE= “little organ”, found only inside eukaryotic cells, all the stuff in between the
organelles is cytosol, everything in a cell except the nucleus is cytoplasm
CELL MEMBRANE- Boundary of the cell, made of a phospholipid bilayer
NUCLEUS- Control center of the cell, contains DNA, surrounded by a double membrane,
usually the easiest organelle to see under a microscope and one per cell
CYTOSKELETON- Acts as skeleton and muscle, provides shape and structure, helps move
organelles around the cell, made of three types of filaments
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM- A.k.a. “ER”, connected to nuclear membrane, highway of the
cell
@(Rough ER: studded with ribosomes; it makes proteins; Smooth ER: no ribosomes; it makes
lipids)
RIBOSOMES- Site of protein synthesis, found attached to rough ER or floating free in
cytosol, produced in a part of the nucleus called the nucleolus
GOLGI APPARATUS- Looks like a stack of plates, stores, modifies and packages proteins,
molecules transported to and from the Golgi by means of vesicles
LYSOSOMES- Garbage disposal of the cell, contain digestive enzymes that break down
wastes
MITOCHONDRIA- “Powerhouse of the cell”, cellular respiration occurs here to release
energy for the cell to use, bound by a double membrane, has its own strand of DNA
CHROLOPLAST- Found only in plant cells, contains the green pigment chlorophyll, site of
food (glucose) production, bound by a double membrane
CELL WALL- Found in plant and bacterial cells, rigid, protective barrier, located outside of
the cell membrane, made of cellulose (fiber)
VACOULES- Large central vacuole usually in plant cells, many smaller vacuoles in animal
cells, storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc.
CENTROILE- Aids in cell division, usually found only in animal cells, made of microtubules
CYTOPLASM- entire region of cell withing cell membrane
PEROXISOMES- are small, round organelles enclosed by single membrane which carry out
oxidation reactions that break down fatty acids and amino acids
LYSOSOME use their hydrolytic enzymes to destroy pathogens that might enter the cell
through phagocytosis.
CENTRAL VACUOLE plays a key role in regulating the cell’s concentration of water in
changing environmental conditions.
You might also like
- Organelles Cheat SheetDocument8 pagesOrganelles Cheat Sheetapi-55809756No ratings yet
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument8 pagesCell Organelles Worksheete50% (2)
- General Biology 1Document12 pagesGeneral Biology 1Samariah Nicole AbajeroNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Cell OrganisationDocument106 pagesCell Structure and Cell Organisationwienna1987No ratings yet
- Karlos Miguel CDocument3 pagesKarlos Miguel CKarlos Miguel NepalesNo ratings yet
- Activity No.1 - The CellDocument3 pagesActivity No.1 - The CellCelestine MambulaoNo ratings yet
- BIO ReviewerDocument14 pagesBIO ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Activity 2. Plant Cell Vs Animal CellDocument5 pagesActivity 2. Plant Cell Vs Animal CellMary Joyce BonayonNo ratings yet
- GenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2Document7 pagesGenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2The GreatNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGYDocument27 pagesBIOLOGYElijah AtudilloNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument3 pagesBiology ReviewerflowenceNo ratings yet
- Trixie OrganellesDocument2 pagesTrixie OrganellesMir SantillanNo ratings yet
- The Structure of Plant CellsDocument21 pagesThe Structure of Plant CellsEvelyn SevillaNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Part and FunctionsDocument1 pagePlant Cells Part and FunctionskeroycandoleNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions FunctionsDocument4 pagesLesson 3: Lesson 3: Cell Cell Structures Structures AND AND Functions Functionskruyll vlogsNo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Function: CellsDocument8 pagesCell Structures and Function: CellsChardean Gel BaclaanNo ratings yet
- Cell and TissueDocument10 pagesCell and TissueCarl SantosNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument22 pagesCell StructureHab DogNo ratings yet
- Biology Group 1Document17 pagesBiology Group 1Renan PunayNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life 1Document22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life 1Matt Andrei AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Edible Plant CellDocument4 pagesEdible Plant CellgeorgiaNo ratings yet
- LEC 0 General Biology 1 NotesDocument53 pagesLEC 0 General Biology 1 NotesAnna Liza Evangelista MartinitoNo ratings yet
- Unit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument10 pagesUnit II: Cell, Tissues, Glands, and MembranesEds BernardoNo ratings yet
- Cell Theory ModuleDocument14 pagesCell Theory ModuleEunice Moureen Maravilla100% (2)
- Earth and ScieDocument3 pagesEarth and SciesideyysNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument35 pagesChapter IOltagon Nicole DupingayNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell Their Functions: Cell Membrane-: CytoplasmDocument2 pagesAnimal Cell Their Functions: Cell Membrane-: CytoplasmMarielle YsabelNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 REVIEWDocument16 pagesUnit 4 REVIEWJuliana RiveraNo ratings yet
- 1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellDocument5 pages1C-Tabugoc - LA2 Plant CellClint Jhun TabugocNo ratings yet
- MCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLDocument9 pagesMCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLGabi taofeekatNo ratings yet
- Immunology: Section 4-2, Parts of The Eukaryotic CellDocument20 pagesImmunology: Section 4-2, Parts of The Eukaryotic CellJoia De LeonNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure & Free RadicalsDocument37 pagesCell Structure & Free RadicalsSAMANTHA WHITTAKERNo ratings yet
- CellDocument7 pagesCellnik29569No ratings yet
- Module 2 Cell AnatomyDocument5 pagesModule 2 Cell Anatomy10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Human Histology - IntroductionDocument11 pagesChapter 1 Human Histology - IntroductionDessirie EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Definitions For The ProjectDocument2 pagesDefinitions For The Projectzoe.pizarrofNo ratings yet
- Science PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICDocument8 pagesScience PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICsecurity securedNo ratings yet
- Parts of The CellDocument3 pagesParts of The CellMa Claire TumboconNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells: by Fortunate Refil Bsed Sci 2Document20 pagesPlant Cells: by Fortunate Refil Bsed Sci 2Marifer DapatNo ratings yet
- Cell OrganellesDocument3 pagesCell OrganellesMotie KassabNo ratings yet
- Cell Biology PresentationDocument14 pagesCell Biology Presentationahmadihamed1459No ratings yet
- Animal Cell and Plant Cell: John Anderson V. Hernandez 11-JOBS Assignment #1Document5 pagesAnimal Cell and Plant Cell: John Anderson V. Hernandez 11-JOBS Assignment #1Anderson HernandezNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and Functions PDFDocument43 pagesCell Structure and Functions PDFFíre B DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm and OrganellesDocument15 pagesCytoplasm and OrganellesAndrew MahilumNo ratings yet
- Cell 2 Grading in Science ViiDocument6 pagesCell 2 Grading in Science ViiJerez De PaduaNo ratings yet
- Biology 1st DiscussionDocument52 pagesBiology 1st DiscussionBea BulasaNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure VocabDocument1 pageCell Structure VocabFatima ZaidiNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Cell BIOLOGYDocument43 pagesParts of A Cell BIOLOGYSam Ferbyn LomotanNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatDocument7 pagesCell Organelles - Notes Cell Theory Cells Are The Basic Unit of Life. The Cell Theory States ThatSpongie BobNo ratings yet
- Cell Organelles WorksheetDocument7 pagesCell Organelles WorksheetKenneth ParungaoNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDocument45 pagesTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- MLG 2 (Part 1) The Cell Theory and Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument5 pagesMLG 2 (Part 1) The Cell Theory and Cell Structure and FunctionsJohn Tolentino LaronaNo ratings yet
- Activity-Week 4-Cell Organelles-Group A3Document5 pagesActivity-Week 4-Cell Organelles-Group A3Christian Aldwyn DizonNo ratings yet
- Week 4 - Plant Structure and FunctionsDocument50 pagesWeek 4 - Plant Structure and FunctionsPrincess De LeonNo ratings yet
- Why Is It Important To Learn About CellsDocument1 pageWhy Is It Important To Learn About Cellsrambo0% (1)
- Cells and Organelles - 1Document6 pagesCells and Organelles - 1Izabayo philippeNo ratings yet
- NANOTECHNOLOGY REVIEW: LIPOSOMES, NANOTUBES & PLGA NANOPARTICLESFrom EverandNANOTECHNOLOGY REVIEW: LIPOSOMES, NANOTUBES & PLGA NANOPARTICLESNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- MedtermDocument1 pageMedtermJesyrae Nykollai HuligangaNo ratings yet
- Cpar ReviewerDocument1 pageCpar ReviewerJesyrae Nykollai HuligangaNo ratings yet
- Gathering of MaterialsDocument1 pageGathering of MaterialsJesyrae Nykollai HuligangaNo ratings yet
- Cpar Act 1Document2 pagesCpar Act 1Jesyrae Nykollai HuligangaNo ratings yet
- P6 ExpiDocument2 pagesP6 ExpiJesyrae Nykollai HuligangaNo ratings yet
- Bioa CT 1Document1 pageBioa CT 1Jesyrae Nykollai HuligangaNo ratings yet