Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Plant Cells Part and Functions
Uploaded by
keroycandoleOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Plant Cells Part and Functions
Uploaded by
keroycandoleCopyright:
Available Formats
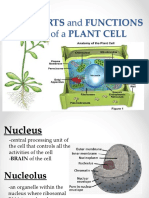
PLANT CELLS PART AND FUNCTIONS.
CELL WALL -It is a rigid layer which is composed of polysaccharides cellulose, pectin and
hemicellulose. It is located outside the cell membrane. It also comprises glycoproteins
CYTOPLASM-A gelatinous liquid that fills the inside of cell.
MITOCHONDRION -They are the double-membraned organelles found in the cytoplasm of all
eukaryotic cells.
CELL MEMBRANE-It is the semi-permeable membrane that is present within the cell wall. It is
composed of a thin layer of protein and fat.
CHLOROPLAST-It is an elongated organelle enclosed by phospholipid membrane.
PEROXISOME- organelles that sequester diverse oxidative reactions and play important roles in
metabolism, reactive oxygen species detoxification, and signaling.
CENTRAL VOCUOLE-It occupies around 30% of the cell’s volume in a mature plant cell. Tonoplast
is a membrane that surrounds the central vacuole.
RIBOSOMES-They are the smallest membrane-bound organelles which comprise RNA and
protein. They are the sites for protein synthesis, hence, also referred to as the protein factories
of the cell.
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM-A large, dynamic structure that serves many roles in the cell
including calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism.
NUCLEUS-The nucleus is a membrane-bound structure that is present only in eukaryotic cells.
The vital function of a nucleus is to store DNA or hereditary information required for cell
division, metabolism and growth.
GOLGI VESICLES- it packages proteins into membrane-bound vesicles inside the cell before the
vesicles are sent to their destination.
GOLGI APPARATUS-They are found in all eukaryotic cells, which are involved in distributing
synthesised macromolecules to various parts of the cell.
You might also like
- Parts and Functions: of A Plant CellDocument15 pagesParts and Functions: of A Plant CellAlleen Joy SolivioNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell FunctionsDocument3 pagesPlant Cell FunctionsRoxanne Anelly TulodNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument22 pagesCell StructureHab DogNo ratings yet
- Morphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDocument52 pagesMorphological Function of The Cell Presentation PHDoc HamsNo ratings yet
- Science PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICDocument8 pagesScience PROKARYOTICEUKARYOTICsecurity securedNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: The CellDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: The Celllourd nabNo ratings yet
- Topic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDocument45 pagesTopic 2-Parts and Functions of The CellDe Guia, Yuan Loriene Nina100% (1)
- Cell OrganellesDocument2 pagesCell OrganellesSurminie Muksin100% (1)
- General Biology 1Document12 pagesGeneral Biology 1Samariah Nicole AbajeroNo ratings yet
- Cell 2 Grading in Science ViiDocument6 pagesCell 2 Grading in Science ViiJerez De PaduaNo ratings yet
- Plantcell: Plant Cell StructureDocument2 pagesPlantcell: Plant Cell StructureMara NathaNo ratings yet
- LESSONS in BIOCHEMDocument39 pagesLESSONS in BIOCHEMMikhael Jay IglesiasNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesDocument6 pagesCytoplasm 2.: Cell OrganellesSai Deekshita VijayakumarNo ratings yet
- General Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology ReviewerBaby AleiraNo ratings yet
- Morphology of Prokaryotes & EukaryotesDocument21 pagesMorphology of Prokaryotes & EukaryotesDhanush VNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells: by Fortunate Refil Bsed Sci 2Document20 pagesPlant Cells: by Fortunate Refil Bsed Sci 2Marifer DapatNo ratings yet
- Definitions For The ProjectDocument2 pagesDefinitions For The Projectzoe.pizarrofNo ratings yet
- Eukaryotic Cell Structure SeranDocument4 pagesEukaryotic Cell Structure SeranLeah Jane MalinaoNo ratings yet
- ELS AC&PC (PartDefinitions)Document4 pagesELS AC&PC (PartDefinitions)jasminjajarefeNo ratings yet
- Cell The Basic Unit of Life 1Document22 pagesCell The Basic Unit of Life 1Matt Andrei AmorosoNo ratings yet
- Ans 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument33 pagesAns 201 Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsAdewaleNo ratings yet
- Kingdom: Animal CellDocument8 pagesKingdom: Animal CellShaila IvoryNo ratings yet
- Activity No.1 Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument4 pagesActivity No.1 Cell and Molecular Biologyjocelynmillano115100% (1)
- Plant Cell - LayoutDocument3 pagesPlant Cell - LayoutMahiNo ratings yet
- Cytoplasm and OrganellesDocument15 pagesCytoplasm and OrganellesAndrew MahilumNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The CellDocument2 pagesChapter 2 The CellGela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Trixie OrganellesDocument2 pagesTrixie OrganellesMir SantillanNo ratings yet
- Cells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesDocument34 pagesCells, Organelles, Microscopy TechniquesJeffrey100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Parts and Functions of The CellDocument26 pagesLesson 2 Parts and Functions of The CellDavid BayaniNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell PROJECTDocument6 pagesPlant Cell PROJECTYoussef AmrNo ratings yet
- GenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2Document7 pagesGenBio Notes Lesson 1 and 2The GreatNo ratings yet
- Biology ProjectDocument6 pagesBiology ProjectBemnet TayeNo ratings yet
- Module For Anaphy CellDocument11 pagesModule For Anaphy CellBJ Bernardo IlNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument54 pagesCELLSJoie MonrealNo ratings yet
- Ploginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal CellsDocument2 pagesPloginpartpppppp: Parts of Animal CellsNelson De LimaNo ratings yet
- Informe The CellDocument6 pagesInforme The CelljohannaNo ratings yet
- NucleusDocument10 pagesNucleusjhariesargente05No ratings yet
- Animal Cell 3Document9 pagesAnimal Cell 3api-320844972No ratings yet
- Pro and EuDocument15 pagesPro and EuCy BathanNo ratings yet
- Cell Week 2Document22 pagesCell Week 2maureganitNo ratings yet
- Animal Cell: Cell Is The Structural and Functional Unit of OrganismsDocument12 pagesAnimal Cell: Cell Is The Structural and Functional Unit of OrganismsHEMA VATHINo ratings yet
- Function of Animal CellDocument2 pagesFunction of Animal CellLyn UmpadNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and OrganizationDocument46 pagesCell Structure and OrganizationLara Lyn PabloNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell: Parts Functions Cell MembraneDocument2 pagesPlant Cell: Parts Functions Cell MembraneMaxenia FaboresNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument4 pagesBiochemistryAaliyah Ashley CerboNo ratings yet
- Small: A Region Near The Nucleus in The Cell Cytoplasm, Containing ThecentriolesDocument2 pagesSmall: A Region Near The Nucleus in The Cell Cytoplasm, Containing ThecentriolesAnjo JimenezNo ratings yet
- Animal and Plant CellDocument3 pagesAnimal and Plant CellElmer Tunggolh, Jr.No ratings yet
- Forest Botany For Forestry StudentsDocument39 pagesForest Botany For Forestry StudentsMadan ThapaNo ratings yet
- Histonotes 1Document3 pagesHistonotes 1mayumi takagiNo ratings yet
- ENMANUEL MC 3 BSN1 Assignment No. 2 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic First TrinalDocument6 pagesENMANUEL MC 3 BSN1 Assignment No. 2 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic First TrinalJason Carbon EnmanuelNo ratings yet
- Cell 3Document25 pagesCell 3Rashul ChutaniNo ratings yet
- Marquez 3d CellDocument5 pagesMarquez 3d CellSatori TendōNo ratings yet
- Group 5-4Document84 pagesGroup 5-4googlegirl18No ratings yet
- CellDocument7 pagesCellnik29569No ratings yet
- Biology Study Material - Xi - 22-23-Compressed - 0Document14 pagesBiology Study Material - Xi - 22-23-Compressed - 0gana63693No ratings yet
- MCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLDocument9 pagesMCB 203 EUKARYOTIC CELLGabi taofeekatNo ratings yet
- بايو م 2Document7 pagesبايو م 2alidoctor678No ratings yet
- Intro, Cell, TissueDocument29 pagesIntro, Cell, Tissueanisa930804No ratings yet
- Cell & Intercellular JunctionsDocument35 pagesCell & Intercellular JunctionsDikpal BikramNo ratings yet