Professional Documents
Culture Documents
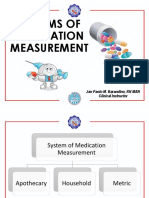
Systems of Measurements: Weight
Uploaded by
Keizelle EstoresOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Systems of Measurements: Weight
Uploaded by
Keizelle EstoresCopyright:
Available Formats
MODULE 1:
SYSTEMS OF WEIGHTS AND MEASURES
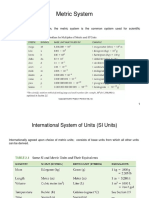
SYSTEMS OF MEASUREMENTS
STEMS / BASIC UNITS RULES OF THE METRIC SYSTEM
m 1. Arabic Numerals are used to express quantities in this system.
Length
• 10 mcg instead of X mcg
2. Parts of a unit or a fraction of a unit are expressed as decimals.
Weight • 1.5 mL instead of 1 1⁄2 mL
L g
3. The quantity whether in whole numbers or decimals is always written
before the abbreviation or symbol for a unit of measure.
Volume
PREFIXES AND RELATIVE VALUES • 5 g instead of g 5
4. Zeros should always be placed in front of the decimal
when the quantity is not a whole number.
• 0.3 cm instead of .3 cm
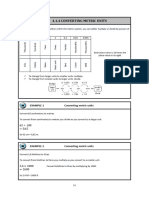
I. SAMPLE EXERCISES (CONVERSION)
Convert the following :
1. 4000g→kg
2. 0.037 cm → μm
3. 6,000,000 μL → L
4. 100cg→kg
5. 32daL→dL
SI UNITS / BASE UNITS
COMMONLY USED EQUIVALENTS
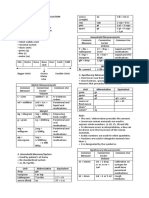
AVOIRDUPOIS SYSTEM • Derived from French, and was adopted by the English as a standard of weight in commerce.
• In this system, pound is the standard unit for weighing (1 pound = 16 ounces)
• All measures are derived from pounds. APOTHECARY SYSTEM
• Oldest system of measurement
• Base units in apothecary system are grain
(weight), minim (volume), and inch (length).
You might also like
- PCT Unit II - Units and MeasurementsDocument32 pagesPCT Unit II - Units and MeasurementsEuna De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- GCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandGCSE Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Metric System: Based On The Decimal System, The Metric System Is The Common System Used For Scientific MeasurementsDocument16 pagesMetric System: Based On The Decimal System, The Metric System Is The Common System Used For Scientific MeasurementsGehNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1 LessonDocument170 pagesGeneral Physics 1 LessonEunice AquinoNo ratings yet
- Chem1 Chapter3Document34 pagesChem1 Chapter3Xibes LinoNo ratings yet
- Gen Chem 1Document9 pagesGen Chem 1Chennille Ann Bleu GundayaoNo ratings yet
- Week 1 - Introduction To Chemistry, Measurement and MatterDocument44 pagesWeek 1 - Introduction To Chemistry, Measurement and MatterSport ManNo ratings yet
- Metrics and ConversionDocument16 pagesMetrics and ConversionNamrata MangalNo ratings yet
- Chemlec ReviewerDocument4 pagesChemlec ReviewerJay Mark CapanangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document65 pagesChapter 5Pirate CaribbeanNo ratings yet
- Chem Reviewer MidtermsDocument4 pagesChem Reviewer MidtermsJayrick James AriscoNo ratings yet
- Grade 7 Math Week 2Document4 pagesGrade 7 Math Week 2Tina SayconNo ratings yet
- Week2 NotetakingtemplateDocument10 pagesWeek2 Notetakingtemplateapi-534935628No ratings yet
- MeasurementDocument63 pagesMeasurementRochelle NuguidNo ratings yet
- 002 - Converting Metric UnitsDocument4 pages002 - Converting Metric Unitspx8gm8r52sNo ratings yet
- Chem 11 Test 1 Study GuideDocument61 pagesChem 11 Test 1 Study GuidewilNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Lecture 2Document34 pagesGeneral Chemistry Lecture 2Michaela BorjaNo ratings yet
- The Metric System and Scientific Method AnsweredDocument11 pagesThe Metric System and Scientific Method AnsweredKenn CollinsNo ratings yet
- Conversions Between Imperial Metric PDFDocument4 pagesConversions Between Imperial Metric PDFJoselyn MessinaNo ratings yet
- pctb3 Common MeasurementsDocument3 pagespctb3 Common MeasurementsElectraKizzNo ratings yet
- Week 4a Units of Measurement StudentsDocument14 pagesWeek 4a Units of Measurement StudentsRhe YaNo ratings yet
- Week 1 Unit of MeasurementDocument22 pagesWeek 1 Unit of Measurementkobep4894No ratings yet
- KS4 Mathematics: S8 MeasuresDocument51 pagesKS4 Mathematics: S8 MeasuressalmaNo ratings yet
- CHPT 1Document51 pagesCHPT 1Hayley Van SchoorNo ratings yet
- Wagas Report (Significant Fig) - 054836Document76 pagesWagas Report (Significant Fig) - 054836Wilma WagasNo ratings yet
- Romasanta - GeneralChemistry - Two System of MeasurementDocument10 pagesRomasanta - GeneralChemistry - Two System of MeasurementJohn RomasantaNo ratings yet
- Chemical FoundationsDocument14 pagesChemical Foundationsvrejie46No ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument5 pagesLab ReportyesimznakipogluNo ratings yet
- 109 - Win19 - Chapter 1Document32 pages109 - Win19 - Chapter 1sydney shepardNo ratings yet
- Conversion of Units) Temp, Mass, Volume, Length, Density) G7Document65 pagesConversion of Units) Temp, Mass, Volume, Length, Density) G7Melanie Niña Cullar100% (1)
- Gen Chem 1 PDFDocument18 pagesGen Chem 1 PDFDennisBrionesNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.1 (PPT) Units - Measurements Grade 10 PhysicsDocument93 pagesTopic 1.1 (PPT) Units - Measurements Grade 10 PhysicsLaw PeterNo ratings yet
- Units, Physical Quantities, and MeasurementDocument46 pagesUnits, Physical Quantities, and MeasurementChristian CincoNo ratings yet
- Metric System Common Measure Conversion Factor Common UseDocument4 pagesMetric System Common Measure Conversion Factor Common UseMarielle ChuaNo ratings yet
- Weight and Measure: Type of SystemsDocument11 pagesWeight and Measure: Type of SystemsGRACIE COSSETTE PAUTNo ratings yet
- Measurements and Si UnitsDocument2 pagesMeasurements and Si UnitsNick MillerNo ratings yet
- NGEC-9 Topic 1 PPTDocument25 pagesNGEC-9 Topic 1 PPTAaron Joshua SantoyoNo ratings yet
- Units, Physical Quantities and Measurements in PhysicsDocument23 pagesUnits, Physical Quantities and Measurements in PhysicsDavid Lancelot PiadNo ratings yet
- Meas Change Metric Mac2Document6 pagesMeas Change Metric Mac2scribd.thctNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan For Demo TeachingDocument6 pagesLesson Plan For Demo TeachingPaño Burce MilletNo ratings yet
- W1 Module 1 - Introduction, Matter and ItsDocument18 pagesW1 Module 1 - Introduction, Matter and ItsMeira LacumboNo ratings yet
- Scramble D: WordsDocument39 pagesScramble D: WordsSheanneNo ratings yet
- Measurement in ChemistryDocument48 pagesMeasurement in ChemistryHoney Marie BarnuevoNo ratings yet
- 0 Reviewer MeasurementsDocument17 pages0 Reviewer MeasurementsCylle Jerone BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Drilling Calculations CD Complete CourseDocument177 pagesDrilling Calculations CD Complete CoursecarmenNo ratings yet
- Sig FigDocument20 pagesSig Figjohnpatrick.creusNo ratings yet
- GCSE Biology: Re-Think & Revise OsmosisDocument6 pagesGCSE Biology: Re-Think & Revise OsmosisSamuelNo ratings yet
- Co2 2023-2024Document45 pagesCo2 2023-2024RICHELLE L. HERNANDEZNo ratings yet
- 4.4 Measurement StandardDocument25 pages4.4 Measurement StandardMiles Paculba100% (1)
- Math 6 DLP 63 - Converting From One Unit of Measure To Another PDFDocument11 pagesMath 6 DLP 63 - Converting From One Unit of Measure To Another PDFMelinda Rafael100% (1)
- Analysis of Measurement 2Document32 pagesAnalysis of Measurement 2GILBERT KWAKU ASIAMAHNo ratings yet
- AdadDocument31 pagesAdadRoge DianNo ratings yet
- Converting From One System of Measurement To AnotherDocument23 pagesConverting From One System of Measurement To AnotherAshaNo ratings yet
- Grade 12 LM General Physics 1 Module1Document15 pagesGrade 12 LM General Physics 1 Module1Josue NaldaNo ratings yet
- Systems of MeasurementDocument36 pagesSystems of Measurementhey aadarshaNo ratings yet
- CHM 101 MergedDocument444 pagesCHM 101 Mergedomoniyioluwajoba34No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 GC Phy110Document30 pagesChapter 1 GC Phy110RikachuNo ratings yet
- Measurements: Pharmaceutical Chemistry 1 Lecture Alexandra D. Atienza, RPH, Ms Pharm (Cand)Document33 pagesMeasurements: Pharmaceutical Chemistry 1 Lecture Alexandra D. Atienza, RPH, Ms Pharm (Cand)esmrphNo ratings yet
- 01 Chemistry and MeasurementsDocument36 pages01 Chemistry and MeasurementsvincentNo ratings yet
- Name and Logo Design Contest For Public Wi-Fi Network Services Terms & ConditionsDocument2 pagesName and Logo Design Contest For Public Wi-Fi Network Services Terms & ConditionsAc RaviNo ratings yet
- Aims and Principles of Foreign Language TeachingDocument3 pagesAims and Principles of Foreign Language TeachingresearchparksNo ratings yet
- CH 121: Organic Chemistry IDocument13 pagesCH 121: Organic Chemistry IJohn HeriniNo ratings yet
- Kompilasi Soal Paket BDocument10 pagesKompilasi Soal Paket Babdul wahidNo ratings yet
- LP ScienceDocument8 pagesLP ScienceMarla Jean FabroNo ratings yet
- Adding Rows Dynamically in A Table Using Interactive Adobe FormsDocument5 pagesAdding Rows Dynamically in A Table Using Interactive Adobe Formsbharath_sajjaNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: This Activity Contains 15 QuestionsDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: This Activity Contains 15 QuestionsRaman Kulkarni100% (1)
- TDBFP - Gear Pump API 676 PDFDocument42 pagesTDBFP - Gear Pump API 676 PDFRamon A. Ruiz O.No ratings yet
- Spark RPG Colour PDFDocument209 pagesSpark RPG Colour PDFMatthew Jackson100% (1)
- Pseudomonas AeruginosaDocument26 pagesPseudomonas AeruginosaNur AzizahNo ratings yet
- WINTER 2023 Course Outline: ENME 479 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies IIDocument8 pagesWINTER 2023 Course Outline: ENME 479 Mechanics of Deformable Bodies IIKai McDermottNo ratings yet
- Giki Students Hand Book 08Document75 pagesGiki Students Hand Book 08Jawad Rasheed Sheikh100% (1)
- Model Teaching CompetenciesDocument12 pagesModel Teaching CompetenciesTeachers Without BordersNo ratings yet
- Three Steps For Reducing Total Cost of Ownership in Pumping SystemsDocument13 pagesThree Steps For Reducing Total Cost of Ownership in Pumping SystemsJuan AriguelNo ratings yet
- 14.victorian Era Inventions and Changes Pupils PDFDocument1 page14.victorian Era Inventions and Changes Pupils PDFSam FairireNo ratings yet
- Voting BehaviorDocument23 pagesVoting BehaviorWela Paing FallitangNo ratings yet
- Literatur Riview Tentang Faktor Penyebab Klaim Tidak Layak Bayar BPJS Kesehatan Di Rumah Sakit Tahun 2020Document8 pagesLiteratur Riview Tentang Faktor Penyebab Klaim Tidak Layak Bayar BPJS Kesehatan Di Rumah Sakit Tahun 2020Maulida LutfiaNo ratings yet
- Forward Planning DocumentDocument24 pagesForward Planning Documentapi-396981495No ratings yet
- Well Control - Pore PressureDocument31 pagesWell Control - Pore PressureMiguel Pinto PonceNo ratings yet
- RAB PLTS Hybrid 1kWp-ScheneiderDocument4 pagesRAB PLTS Hybrid 1kWp-ScheneiderilhamNo ratings yet
- z01 PDFDocument12 pagesz01 PDFZdravko RusevNo ratings yet
- A Woman Who Is at 36 Weeks of Gestation Is Having A Nonstress TestDocument25 pagesA Woman Who Is at 36 Weeks of Gestation Is Having A Nonstress Testvienny kayeNo ratings yet
- Somatic TherapiesDocument170 pagesSomatic TherapiesDelyn Gamutan Millan100% (2)
- 05 N141 31673Document21 pages05 N141 31673priya thakurNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 - HEALTH - Q4 Module 1 - W1Document12 pagesGrade 6 - HEALTH - Q4 Module 1 - W1Love Lei67% (3)
- ToRs ESIA Maputo Sewerage System FinalDocument36 pagesToRs ESIA Maputo Sewerage System FinalVirgilio MuandoNo ratings yet
- Training SCLDocument60 pagesTraining SCLAlu menzikenNo ratings yet
- Momo Nation Cafe ProfileDocument28 pagesMomo Nation Cafe ProfileMain AparchitNo ratings yet
- DX-790-960-65-17.5i-M: Electrical PropertiesDocument2 pagesDX-790-960-65-17.5i-M: Electrical PropertiesАлександрNo ratings yet
- Cross Cultural Management: Hana MaumetDocument32 pagesCross Cultural Management: Hana MaumetGiovanni Francesco PalmaNo ratings yet