Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Definitions Momentum
Definitions Momentum
Uploaded by
ZUHAYER RASIN0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesConservation of momentum states that the total momentum of interacting objects remains constant if no external forces act. Newton's second law defines force as directly proportional to the rate of change of momentum. Momentum is defined as the product of an object's mass and velocity.
Energy is defined as the ability to do work, with units of joules. Work is done when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force. Power is defined as the rate at which work is done. Efficiency refers to the ratio of useful output energy or power to the total input energy or power.
Original Description:
Original Title
Untitled
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentConservation of momentum states that the total momentum of interacting objects remains constant if no external forces act. Newton's second law defines force as directly proportional to the rate of change of momentum. Momentum is defined as the product of an object's mass and velocity.
Energy is defined as the ability to do work, with units of joules. Work is done when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force. Power is defined as the rate at which work is done. Efficiency refers to the ratio of useful output energy or power to the total input energy or power.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesDefinitions Momentum
Definitions Momentum
Uploaded by
ZUHAYER RASINConservation of momentum states that the total momentum of interacting objects remains constant if no external forces act. Newton's second law defines force as directly proportional to the rate of change of momentum. Momentum is defined as the product of an object's mass and velocity.
Energy is defined as the ability to do work, with units of joules. Work is done when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force. Power is defined as the rate at which work is done. Efficiency refers to the ratio of useful output energy or power to the total input energy or power.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
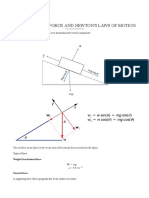
Definitions
momentum
Conservation of momentum: When two or more bodies act on
one another, the total momentum of bodies remains constant,
provided no external forces act.
When two bodies collide then, total momentum before
collision = total momentum after collision if no external force
acts.
Newtons second law: Force is directly proportional to the rate
of change of momentum.
Momentum: The product of mass and velocity is called
momentum.
Energy, work and power
Energy: Energy is the ability to do work. Unit – Joule(J).
Work: A work is done when a force moves an object in the
direction of the force.
Power: Power is the rate of work done.
Efficiency: Efficiency is the rate of useful energy/power output
by total energy/ power input.
Nuclear fission: Unstable large nucleus broken own into
smaller nucleus.
Nuclear fusion: small unstable nucleus joins up to form large
nucleus.
You might also like
- Unit 4: Newton's Laws of MotionDocument70 pagesUnit 4: Newton's Laws of MotionA.?? MkhabelaNo ratings yet
- General Physics: Newton Law of MotionDocument4 pagesGeneral Physics: Newton Law of MotionJewel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Review Review Im CryingggDocument11 pagesReview Review Im CryingggMaryann San JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Newton English1Document30 pagesNewton English1Puspa LestariNo ratings yet
- NoteDocument2 pagesNoteSudhanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: Newton's Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesDynamics: Newton's Laws of Motionsayma_akhter5074No ratings yet
- Physics Kinetmatics NoteDocument2 pagesPhysics Kinetmatics Noteb52352986No ratings yet
- The Laws of Motion: - Sir Isaac NewtonDocument51 pagesThe Laws of Motion: - Sir Isaac NewtonBrian NkhomaNo ratings yet
- G8 Science ReviewerDocument9 pagesG8 Science ReviewerIntroverted RNo ratings yet
- Newton's Law of MotionDocument28 pagesNewton's Law of MotionJosh JavierNo ratings yet
- Physics Lesson ReviewDocument4 pagesPhysics Lesson ReviewШунаси ХалиловNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two - Newtons Law-FDocument67 pagesChapter Two - Newtons Law-Fnajjar119No ratings yet
- Fisika Dasar - Buk Fitriyanti - Kuliah 03 - GayaDocument20 pagesFisika Dasar - Buk Fitriyanti - Kuliah 03 - GayaMUHAMMAD SALAFYNo ratings yet
- DefinitionsDocument4 pagesDefinitionsmrshiviannaidooNo ratings yet
- Interactions and ForceDocument2 pagesInteractions and Forcezhungjian586No ratings yet
- 04 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovDocument17 pages04 - Fundamentals of Physics - Naghi GasimovKVP LyricsNo ratings yet
- Unit-2 Force and NLMDocument6 pagesUnit-2 Force and NLMMohit ChokniwalNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument6 pagesNewton's Laws of Motionrizki siwiNo ratings yet
- Class IX: Science Chapter 2: Force and Laws of Motion Chapter NotesDocument2 pagesClass IX: Science Chapter 2: Force and Laws of Motion Chapter NotesGKJK2530No ratings yet
- Module 3 PhysciDocument124 pagesModule 3 Physciburner accNo ratings yet
- LM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1Document53 pagesLM5 - Newton's Laws of Motion and Applications - GPHYS1burner accNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument11 pagesForceAnastasia LarasatiNo ratings yet
- ForceDocument2 pagesForceFatima SrutyNo ratings yet
- ForcesDocument23 pagesForcesNancy Kawilarang100% (1)
- Presentation - of MotionDocument16 pagesPresentation - of Motionharshdipraj123No ratings yet
- General Physics Ch2.2Document6 pagesGeneral Physics Ch2.2nahomNo ratings yet
- 10physics2 2 PDFDocument6 pages10physics2 2 PDFSami NeriNo ratings yet
- Netwon's Laws NotesDocument14 pagesNetwon's Laws NotesRona Patricia MacabugaoNo ratings yet
- Physics-Notes 02Document7 pagesPhysics-Notes 02JanusNo ratings yet
- Forces and Friction: Nahdir Austin Honors Physics Period 2Document6 pagesForces and Friction: Nahdir Austin Honors Physics Period 2Asheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- 09 - Newton's Laws - BDocument11 pages09 - Newton's Laws - Boutubefory49No ratings yet
- Week 8 ForcesDocument38 pagesWeek 8 ForcesSALMA AREKATNo ratings yet
- Affiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New DelhiDocument4 pagesAffiliated To Central Board of Secondary Education - New Delhideetchu10No ratings yet
- Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture 4: Dale GaryDocument28 pagesPhysics 111: Mechanics Lecture 4: Dale GaryLahariNo ratings yet
- Physics - Force and MotionDocument10 pagesPhysics - Force and MotionÅBanDonNo ratings yet
- Wk6 GenPhys1 - 0926 30Document8 pagesWk6 GenPhys1 - 0926 30JenRose Gadon SoliguenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 PhysicDocument5 pagesChapter 4 PhysicWaleska MendezNo ratings yet
- GS104 - Exam I - ReviewDocument1 pageGS104 - Exam I - ReviewlonglistNo ratings yet
- Eastern Cape Revision P1 Combine 2017 2019 - 240122 - 174513Document225 pagesEastern Cape Revision P1 Combine 2017 2019 - 240122 - 174513owaratoamalingaNo ratings yet
- The Laws of MotionDocument15 pagesThe Laws of MotionAmar Poñado BagacinaNo ratings yet
- The Laws of MotionDocument44 pagesThe Laws of Motionmahsan abbasNo ratings yet
- Chap3 Newton LawsDocument65 pagesChap3 Newton LawsAnwar Ul HaqNo ratings yet
- 4 - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument20 pages4 - Newton's Laws of MotionSaloni PatelNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Kinematics and Dynamics of ParticlesDocument129 pagesChapter Two: Kinematics and Dynamics of ParticlesEphrem ChernetNo ratings yet
- Document 3Document2 pagesDocument 3Justin TallaferNo ratings yet
- Newton's Third Law of Motion: Sunil Kumar SinghDocument5 pagesNewton's Third Law of Motion: Sunil Kumar SinghIekram RamiekNo ratings yet
- Unit: 03 Dynamics: Miss Saniya Physics Merit Boarding & Day SchoolDocument15 pagesUnit: 03 Dynamics: Miss Saniya Physics Merit Boarding & Day SchoolUmer FarooqNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of MotionDocument13 pagesNewton's Laws of MotionChinmay SharmaNo ratings yet
- Newtons LawsDocument6 pagesNewtons Lawsapi-239131622No ratings yet
- Newtons Laws MrymDocument3 pagesNewtons Laws Mrymapi-345837027No ratings yet
- Dynamics: What Is A Force?Document13 pagesDynamics: What Is A Force?TorettoNo ratings yet
- 04 Newton's Laws of MotionDocument17 pages04 Newton's Laws of MotionZohaib IkramNo ratings yet
- Work and Energy Cbse IxDocument27 pagesWork and Energy Cbse IxDayal singh shekhawatNo ratings yet
- AP B Chapter 4 Newtons Laws PDFDocument19 pagesAP B Chapter 4 Newtons Laws PDFAbcNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document23 pagesLecture 2nnurman347No ratings yet
- Force & NLM: PhysicsDocument14 pagesForce & NLM: PhysicsAnant DwivediNo ratings yet
- Force and Newton's Laws: Concise 2-Page Class 10 CBSE NotesDocument2 pagesForce and Newton's Laws: Concise 2-Page Class 10 CBSE Notesamaan 10 BNo ratings yet
- Laws of MotionDocument74 pagesLaws of MotionRaichal P BijuNo ratings yet
- Ap 1 DynamicsDocument10 pagesAp 1 DynamicsCai MingleiNo ratings yet