Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dokument Bez Tytułu
Uploaded by
Rozalia OttoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dokument Bez Tytułu
Uploaded by
Rozalia OttoCopyright:
Available Formats
Mitosis is a crucial process in the life cycle of eukaryotic organisms.
It is the process
of cell division in which a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. The
process of mitosis is important for growth, development, and repair of tissues in
multicellular organisms. In this article, we will explore the process of mitosis in
detail, including the different stages of mitosis, its significance in cell growth, and the
factors that influence mitosis.
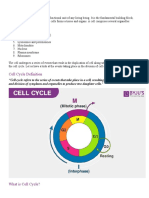
The process of mitosis can be divided into four main stages: prophase, metaphase,
anaphase, and telophase. During the prophase stage, the chromatin fibers in the
nucleus condense to form visible chromosomes. The nuclear membrane also
disintegrates, allowing the chromosomes to move freely in the cytoplasm. In the
metaphase stage, the chromosomes align at the equator of the cell, forming the
metaphase plate. The spindle fibers, which are formed by the centrioles, attach to the
kinetochores of the chromosomes and start to pull them apart in the anaphase
stage. In the final stage of mitosis, the telophase, the two sets of chromosomes
reach opposite poles of the cell, and a new nuclear membrane forms around each
set, forming two identical daughter cells.
Mitosis is crucial for the growth and development of multicellular organisms. During
the growth of an organism, cells divide through mitosis to form new cells, which can
differentiate into various types of cells that form different tissues and organs in the
body. Mitosis is also important for repairing damaged tissues, such as the skin or the
lining of the gut. When cells are damaged, they can divide through mitosis to replace
the damaged cells, ensuring the proper functioning of the organ or tissue.
There are several factors that can influence the process of mitosis. One important
factor is the availability of nutrients and growth factors. Cells require nutrients such
as glucose and amino acids to carry out the process of mitosis, and growth factors
such as insulin and IGF-1 can stimulate cell division. The availability of these factors
can influence the rate of cell division and the success of the process.
Another important factor that can influence mitosis is DNA damage. Cells have
mechanisms to detect DNA damage and prevent mitosis from occurring until the
damage is repaired. If the damage cannot be repaired, the cell may undergo
apoptosis, or programmed cell death, to prevent the propagation of damaged DNA.
In conclusion, mitosis is a critical process in the life cycle of eukaryotic organisms. It
is the process of cell division in which a single cell divides into two identical
daughter cells. The process of mitosis can be divided into four stages, including
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Mitosis is crucial for the growth and
development of multicellular organisms, as well as the repair of damaged tissues.
Factors such as nutrient availability and DNA damage can influence the process of
mitosis, highlighting the complex nature of this fundamental process.
You might also like
- Cell Cycle: Prepared By: Ms. Charis D. Juanico, General Biology 1 TeacherDocument59 pagesCell Cycle: Prepared By: Ms. Charis D. Juanico, General Biology 1 TeacherTrisha Loise VillacampaNo ratings yet
- Introduction to the Human Cell: The Unit of Life & DiseaseFrom EverandIntroduction to the Human Cell: The Unit of Life & DiseaseRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bio 1Document13 pagesBio 1Mary Ann FriasNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument4 pagesCell DivisionHajie RosarioNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument20 pagesCell DivisionSoumodip ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Overview of Cell Cycle by Javali.GDocument15 pagesOverview of Cell Cycle by Javali.GJavali.GNo ratings yet
- Mitosis DefinitionDocument19 pagesMitosis DefinitionMar Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesCell Divisionhm khanNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument12 pagesCell CycleVega, Charles Gabriel G.No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument1 pageUntitledsuckamaNo ratings yet
- Understanding MitosisDocument1 pageUnderstanding MitosismicelforuniNo ratings yet
- Pathology of CellDocument7 pagesPathology of CellamanuelNo ratings yet
- Bio SciDocument3 pagesBio ScilowdicakesNo ratings yet
- Reproduction of CellsDocument1 pageReproduction of CellsruivaacobreadaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesModule 2 Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionBalolot RalphNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Process ProjectDocument2 pagesMitosis Process Projectapi-242679288No ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentAngelo Gomez BadatoNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument19 pagesCell CycleAnahita SuriNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle (Rubina)Document35 pagesCell Cycle (Rubina)RubinaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1Abigail AbiadaNo ratings yet
- General Biology I Long Test ReviewerDocument18 pagesGeneral Biology I Long Test ReviewerJillian GarcilanNo ratings yet
- B.SC., 2 Year, 3 Semester Paper-III: Cell Biology, Genetics and Immunology Cell DivisionDocument24 pagesB.SC., 2 Year, 3 Semester Paper-III: Cell Biology, Genetics and Immunology Cell DivisionLAZY I LEoPARDNo ratings yet
- Gr11 GENETICS - THE CELL CYCLEDocument10 pagesGr11 GENETICS - THE CELL CYCLECHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- BioChem Study QuestionsDocument9 pagesBioChem Study QuestionsLaya ShrbagiNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument12 pagesMITOSISLarissa PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Assignment in Science: Jeamnard Balitaan II-ShakespeareDocument7 pagesAssignment in Science: Jeamnard Balitaan II-ShakespeareCatherine PagdonsolanNo ratings yet
- Ultrastructre of Cells Lect 5Document23 pagesUltrastructre of Cells Lect 5shahdzewailNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Write UpDocument4 pagesMitosis Write UpPrincessTNo ratings yet
- Module 2. Content Module Topic: Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesModule 2. Content Module Topic: Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionErolin PobleteNo ratings yet
- Technical Definition and Description Final DraftDocument5 pagesTechnical Definition and Description Final Draftapi-252711494No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument27 pagesCell DivisionLavinia DonaldNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Cell DivisionDocument30 pagesWeek 2 Cell Divisionlau dashNo ratings yet
- mitosis-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesmitosis-WPS OfficeSheila Mae AramanNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Cell Division, Diversity and OrganisationDocument12 pages1.3 Cell Division, Diversity and OrganisationMo_Bash1No ratings yet
- Tissue Renewal and Repair RegenerationDocument13 pagesTissue Renewal and Repair Regenerationمحسن حدوان عليخانNo ratings yet
- GENBIO1MOD3Document11 pagesGENBIO1MOD3Renzsoc JalmascoNo ratings yet
- Cell CycleDocument2 pagesCell CycleJam TabucalNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument23 pagesCell DivisionInsatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- MITOSISDocument28 pagesMITOSIShariz mikhaelNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument17 pagesCell DivisionGenevieve GanubNo ratings yet
- Subhashree Parida 2101020204-AssignmentDocument8 pagesSubhashree Parida 2101020204-AssignmentHero PratikNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell Division.Document1 pageCell Cycle and Cell Division.ag8211729No ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument20 pagesCell DivisionABHINABA GUPTANo ratings yet
- Mitosis and Meiosis ReviewDocument1 pageMitosis and Meiosis Reviewwilz.zliw773No ratings yet
- Week 3 Modules Grade 12Document13 pagesWeek 3 Modules Grade 12Joe NasalitaNo ratings yet
- Mitosis Gcse BiologyDocument1 pageMitosis Gcse BiologycrainerNo ratings yet
- What Is MitosisDocument3 pagesWhat Is MitosisJemuel Bucud LagartoNo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument2 pagesMitosishelenarivascNo ratings yet
- 2A-Delion, Asida M. Activity 2-Mitosis and MeiosisDocument4 pages2A-Delion, Asida M. Activity 2-Mitosis and MeiosisAsida Maronsing DelionNo ratings yet
- GENERAL BI0LOGY 1 Cell Cycle Mitosis & MeiosisDocument12 pagesGENERAL BI0LOGY 1 Cell Cycle Mitosis & MeiosisPercival RiegoNo ratings yet
- Biology Mitosis and Meiosis EssayDocument2 pagesBiology Mitosis and Meiosis Essayhammad133No ratings yet
- Cell CicleDocument1 pageCell CiclediogoNo ratings yet
- Underwood: Chapter 3: Disorders of Growth, Differentiation and MorphogenesisDocument27 pagesUnderwood: Chapter 3: Disorders of Growth, Differentiation and MorphogenesisSANo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument16 pagesCell Divisionh6wcr2wgdfNo ratings yet
- Cell DivisionDocument6 pagesCell DivisionAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Week 5 Mitosis and MiosisDocument11 pagesWeek 5 Mitosis and MiosisEarl RénzNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document8 pagesWeek 2lilyrosemary.masilangNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell Biology #2Document34 pagesPlant Cell Biology #2Anirudh Moza 16009No ratings yet
- MitosisDocument24 pagesMitosisbrieNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle PDFDocument12 pagesCell Cycle PDFAtiya FalakNo ratings yet