Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Learn Engineering Drawing Fundamentals
Uploaded by
Yonael MezmureOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Learn Engineering Drawing Fundamentals
Uploaded by
Yonael MezmureCopyright:
Available Formats
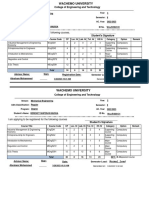
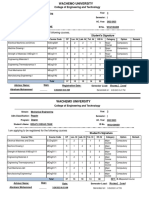
Course Number MEng 2061
Course Title Engineering Drawing
Degree Program BSc in civil Engineering
Module Basic Engineering Skill
Module Coordinator -NN-
Lecturer Mr. Yonael m. (MSc.)
ECTS Credits 5
Contact Hours (per week) 2+0+3+5
Course Objectives & Course Objectives
Competences to be Will enable students:
Acquired
To develop the understanding of drawings,
To improve the concept of orthographic projects etc., at the
end of the course they should be in a position to understand
the language of Engineers, i.e., drawing.
To develop idea of preparation of various types of drawing
industrial sectors,
To expose students to actual technical drawing techniques for
variety of components, so that they understand any type of
technical drawing in practice.
Competences (Learning Outcomes)
Improved sketching skills
Easily understanding of geometrical drawing
Prepare various types of drawings industrial sectors
Understand the language of drawing and use drawing as a means of
communication ideas
Prepare different drawings
Easily understand technical drawings
Will have one big Engineering concept
Course 1. Introduction
Description/Course Importance of Engineering Drawing
Contents Standard Paper layout
Drawing instruments and their uses
Alphabets of lines
Technical Lettering
2. Geometrical Constructions**
2.1 Lines and angles
2.2 Construction of Regular polygons
2.3 Construction of curves used in engineering practices
2.3.1. Simple curves and arcs
2.3.2. Conic Sections: Ellipse, parabola, hyperbola
2.3.3. Cycloid curves: cycloid, epicycloids, and hypocycloid
2.3.4. Involutes: Archimedean spiral
3. Orthographic projection
3.1. Introduction
3.2. Principles of Orthographic projection
3.3. Projection of points and lines
3.4. Projection of planes
3.4.1 Point projections on a plane
3.4.2 Edge view, True shape and True slope of a plane
3.4.3 Finding shortest distances
3.4.4 Piercing points
3.5. Projection of solids
4. Multi-view Representation
4.1. Introduction
4.2. First angle method of projection
4.2 Third angle method of projection
5. Auxiliary and Revolved views
5.1 Primary auxiliary views
5.2 Secondary auxiliary views
5.3 Revolved views
6. Pictorial Drawings
6.1 Introduction
6.2 axonometric projections
6.3 Isometric drawing
6.3 Oblique drawing
7. Sectioning
7.1 Introduction
7.2 Types of sectional views
7.2.1 Full Section
7.2.2 Offset Section
7.2.3 Half Section
7.2.4 Broken out section
7.2.5 Revolved Section
7.2.6 Removed Section
7.2.7 Phantom Section
7.2.8 Auxiliary section
7.3 Techniques in Sectioning
8. Basic Dimensioning
8.1 General concepts on size and location dimensioning
8.2 Basic dimensioning practice
8.2.1 Dimension line
8.2.2 Extension line
8.2.3 Arrow heads
8.2.4 Leaders and pointers
8.2.5 Finish marks
8.3 Method of dimensioning
8.3.1 Aligned method
8.3.2 Unidirectional method
9 Intersections and Developments
9.1 Introduction
9.2 Methods for finding the line of intersection
9.2.1 Element method
9.2.2 cutting plane method
9.2.3 Common sphere method
9.3 Common intersections
9.3.1 Cone and cylinder intersection
9.3.2 Right cone – vertical cylinder intersection
9.4 Development of cylinders
9.5 Development of T-pieces
9.5 Development of Pyramids
9.6 Development of cones
**-Since this chapter is giving steps for construction are given, better
given as a reading assignment with handouts and work more in the
tutorial time
Pre-requisites None
Semester Year II, Semester I
Status of Course Compulsory
Teaching & Learning Lecture on each topic
Methods Tutorials in the class: representative exercises will be given for
students and each student will discuss with his instructor and/or
technical assistant to increase the depth of understanding
Home exercises will be given for each student: these exercises are
aimed to be done by individual student as home assignment.
Assessment/Evaluation & Class Activity: 10%
Grading System Individual Assignment: 20%
Mid-term examination: 20%
Final examination: 50%
Attendance Requirements At least
75% of the lecture class and
90% of the tutorial class should be attended
Literature Frederick E. Gieseck, Technical Drawing, Jul 18, 2005
Warren J. Luzzader and Jon M. Duff, Fundamentals of Engineering
Drawing, Prentice Hall, New Jersy, 11th ed, 1983
Cecil Jensen and Jay D. Helsel, Engineering Drawing and Design,
Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, New York, 5th ed, 1996
R.R Nair and TVG Setty, Descriptive Geometry, AAU, 1981
Engineering Drawing and Graphic Technology - Thomas French,
Charles Vierck, and Robert Foster, Jan, 1993. (better text Not
Available)
Modern Engineering Graphics and Design - Voland G.S., Dec 1999
You might also like
- Engineering Drawing 1032 For StudentsDocument2 pagesEngineering Drawing 1032 For StudentsBerihu GirmayNo ratings yet
- DDDDDocument5 pagesDDDDOne ScorpionNo ratings yet
- BTech (M.E.) Syllabus-Revised - Marine Engineering Graphics (UG11P4103)Document3 pagesBTech (M.E.) Syllabus-Revised - Marine Engineering Graphics (UG11P4103)Aaditya KewlaniNo ratings yet
- 2005-Engineering GraphicsDocument18 pages2005-Engineering Graphicssanjithr619No ratings yet
- BTech FY EG SyllabusDocument4 pagesBTech FY EG SyllabuskhushbooNo ratings yet
- Wolkite University Mechanical Engineering Engineering Drawing CourseDocument1 pageWolkite University Mechanical Engineering Engineering Drawing CoursebiniyamNo ratings yet
- 3315002architectural Drawing-IDocument5 pages3315002architectural Drawing-IDarshit KotadiyaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing & CAD - Module DescriptionDocument5 pagesEngineering Drawing & CAD - Module DescriptionCynthia UmubyeyiNo ratings yet
- CE204IU - Computer Aided Design and Drafting - SyllabusDocument4 pagesCE204IU - Computer Aided Design and Drafting - SyllabusVu Xuan BachNo ratings yet
- Course ObjectivesDocument6 pagesCourse ObjectivesJis AntoNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual EGLDocument100 pagesLab Manual EGLKartik SharmaNo ratings yet
- IMEED NMU SyllabusDocument3 pagesIMEED NMU Syllabusnavneet patilNo ratings yet
- Me101 Course Outline 2014Document3 pagesMe101 Course Outline 2014LeoMessi YdeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Course OverviewDocument5 pagesEngineering Graphics Course OverviewArif WaitsNo ratings yet
- Course Title: Engineering Graphics Course Code: 2005 Course Category: F Periods/ Week: 5 Periods/ Semester: 75 Credit: 0Document5 pagesCourse Title: Engineering Graphics Course Code: 2005 Course Category: F Periods/ Week: 5 Periods/ Semester: 75 Credit: 0vaisakmctNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Engineering Drawing by Quamrul IslamDocument464 pagesMechanical Engineering Drawing by Quamrul IslamTahmima HoqueNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Manual FinalDocument99 pagesEngineering Graphics Manual Finalgpt krtlNo ratings yet
- EGD - 3110013 - Lab - Manual - EVEN - 2023 - 24Document57 pagesEGD - 3110013 - Lab - Manual - EVEN - 2023 - 24s48068541No ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing II (For Diploma in Engineering) : December 2019Document9 pagesEngineering Drawing II (For Diploma in Engineering) : December 2019Kamalnath GNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing-II Book for Diploma StudentsDocument9 pagesEngineering Drawing-II Book for Diploma StudentsJithesh.k.sNo ratings yet
- 20ME3102Document1 page20ME3102budireddipradeep34No ratings yet
- CE210-CED - Course Spec FormDocument3 pagesCE210-CED - Course Spec FormSami ullah khan BabarNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductionDocument24 pages1 Introductiongrvmaurya999No ratings yet
- Computer OrganizationDocument4 pagesComputer OrganizationAluNo ratings yet
- Course Code: 3300007Document8 pagesCourse Code: 3300007k k suraniNo ratings yet
- Drawing ManualDocument112 pagesDrawing ManualamarparimiNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics Manual Final PDFDocument98 pagesEngineering Graphics Manual Final PDFPradeep AppuNo ratings yet
- CE-112 Course Outlines S2015Document1 pageCE-112 Course Outlines S2015Shakeeb KhanNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing IDocument3 pagesEngineering Drawing IAnil MarsaniNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Engineering Drawings and Plans, Lab. MidtermDocument16 pagesModule 5 - Engineering Drawings and Plans, Lab. MidtermJahara N. CuerdoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing IIfor Diplomain EngineeringDocument9 pagesEngineering Drawing IIfor Diplomain EngineeringMovie ClipsNo ratings yet
- Engineering Graphics I PDFDocument10 pagesEngineering Graphics I PDFRahul JaiswalNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing 1.1 SyllabusDocument3 pagesEngineering Drawing 1.1 SyllabusReynald ApostolNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Course Outline 2020 - 21Document3 pagesEngineering Drawing Course Outline 2020 - 21yohannes lemiNo ratings yet
- Modul 1 Eng-Drawing - IntroductionDocument34 pagesModul 1 Eng-Drawing - IntroductionnanangasNo ratings yet
- ARC 204-Graphics CoDocument4 pagesARC 204-Graphics CoMegha PanchariyaNo ratings yet
- Eg With Auto CadDocument23 pagesEg With Auto CadDeepak DahiyaNo ratings yet
- Engineering-Graphics PDFDocument2 pagesEngineering-Graphics PDFbhargaviNo ratings yet
- GE8152 Engineering Graphics - Course Materials PDFDocument110 pagesGE8152 Engineering Graphics - Course Materials PDFkabilanNo ratings yet
- Mec 103 1. Zero LectureDocument20 pagesMec 103 1. Zero LectureDhruva is liveNo ratings yet
- Engeering Graphic 1st YearDocument64 pagesEngeering Graphic 1st YearRajpurohit Samundra0% (1)
- B.Arch Syllabus 3rd Sem.Document9 pagesB.Arch Syllabus 3rd Sem.dasapathri jahnaviNo ratings yet
- Zero LectureDocument18 pagesZero LectureOcean GillNo ratings yet
- Teaching Plan Engg GraphicsDocument3 pagesTeaching Plan Engg GraphicssatishNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing Course OutlineDocument2 pagesEngineering Drawing Course OutlineAbiyu Alemayehu100% (1)
- Engineering Drawing Content and TypesDocument13 pagesEngineering Drawing Content and TypesJahara N. CuerdoNo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing 1 SyllabusDocument3 pagesEngineering Drawing 1 SyllabusReynald ApostolNo ratings yet
- Engineering CAD CAM Graphics Course Curriculum and OutcomesDocument41 pagesEngineering CAD CAM Graphics Course Curriculum and OutcomesSACHET GAJBHIYENo ratings yet
- Engineering Drawing IIfor Diplomain EngineeringDocument9 pagesEngineering Drawing IIfor Diplomain Engineeringeunicedolphine2022No ratings yet
- Computer Aided Engineering Drawing: Lab ManualDocument15 pagesComputer Aided Engineering Drawing: Lab ManualJosh Marshal Blessing MuchenjekwaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Booklet July 2021Document22 pagesAssignment Booklet July 2021Saksham TiwariNo ratings yet
- Oswego Update Project: "Technical Drawing"Document52 pagesOswego Update Project: "Technical Drawing"edward_sheed28No ratings yet
- RS10510 - Curriculum - Civil Engineering 9-12Document362 pagesRS10510 - Curriculum - Civil Engineering 9-12David ParajuliNo ratings yet
- 18 - 1ES114 - Engineering Drawing PDFDocument2 pages18 - 1ES114 - Engineering Drawing PDFAbhay SoniNo ratings yet
- Ted 123-04 Tangency and Circles Given ConditionsDocument5 pagesTed 123-04 Tangency and Circles Given Conditionskitesho.kibetNo ratings yet
- Town Planning PDFDocument86 pagesTown Planning PDFjammy_titans100% (1)
- Shipbuilding 1st & 2nd Semester SyllabusDocument54 pagesShipbuilding 1st & 2nd Semester SyllabusDiploma in Engineering Shipbuilding TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Basics of Engineering DrawingDocument151 pagesBasics of Engineering DrawingAhmad ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Amanuel Temesgen Simulation and Modeling 2Document33 pagesAmanuel Temesgen Simulation and Modeling 2Yonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 TunnelDocument13 pagesChapter 5 TunnelYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Improvement of Glass Solar Still PerformanceDocument8 pagesImprovement of Glass Solar Still PerformanceYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Wachemo University Course RegistrationDocument10 pagesWachemo University Course RegistrationYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- ANSYS Laminar Pipe Flow Simulation SetupDocument29 pagesANSYS Laminar Pipe Flow Simulation SetupYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Revised Modularized Undergraduate CurriculumDocument276 pagesRevised Modularized Undergraduate CurriculumYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- I Am Applying To Be Registered For The Following Courses.Document26 pagesI Am Applying To Be Registered For The Following Courses.Yonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Pipe Flow Ass 2 Adv Fluid Mech 1Document18 pagesModeling and Simulation of Pipe Flow Ass 2 Adv Fluid Mech 1Yonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- ME Harmonization Curricilum Final PDFDocument307 pagesME Harmonization Curricilum Final PDFKandasamy Venkatachalam100% (1)
- 4TH Year Intern-30-2015Document3 pages4TH Year Intern-30-2015Yonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Wachamo Universty College of Engineering and Technology: MarchDocument26 pagesWachamo Universty College of Engineering and Technology: MarchYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Your Business Plan Is Divided Into The Following Sections: Business OverviewDocument12 pagesYour Business Plan Is Divided Into The Following Sections: Business OverviewYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Wachemo University Course RegistrationDocument10 pagesWachemo University Course RegistrationYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- MEng3181-Manufacturing Engineering I-Course Outline - 103309Document2 pagesMEng3181-Manufacturing Engineering I-Course Outline - 103309Yonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Department - of - Mechanical - Engineering - Teaching - Load - For - 2015 E. C 2ndDocument2 pagesDepartment - of - Mechanical - Engineering - Teaching - Load - For - 2015 E. C 2ndYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Teaching Load For 2015 E.C 1st Semester (Tentative)Document2 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Teaching Load For 2015 E.C 1st Semester (Tentative)Yonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Teaching LoadDocument2 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Teaching LoadYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Please Attach Student's Registration SlipDocument1 pagePlease Attach Student's Registration SlipYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument1 pageProposalYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Water Supply Assignment 1Document2 pagesWater Supply Assignment 1Yonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Proposal On Soap Research ProjectDocument16 pagesChapter One: Proposal On Soap Research ProjectYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae Replace With First Name(s) Surname(s)Document2 pagesCurriculum Vitae Replace With First Name(s) Surname(s)Valentina100% (1)
- Edited Dene Internship RiportDocument45 pagesEdited Dene Internship RiportYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Wachemo University Mechanical Engineering Industrial Management CourseDocument2 pagesWachemo University Mechanical Engineering Industrial Management CourseYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Wachemo University Research Payment Sheet SummaryDocument1 pageWachemo University Research Payment Sheet SummaryYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Thermal Engineering MSC. Vacancy ExamDocument3 pagesThermal Engineering MSC. Vacancy ExamYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- The Cooling Techniques of The Solar StilDocument19 pagesThe Cooling Techniques of The Solar StilYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- (Copy) Tentative Class Schedule 2010 (2nd Semster)Document5 pages(Copy) Tentative Class Schedule 2010 (2nd Semster)Yonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Fabrication of Composite From Natural Rubber Reinforced Local Wood (Korcha) False Banana (Enset) FiberDocument1 pageFabrication of Composite From Natural Rubber Reinforced Local Wood (Korcha) False Banana (Enset) FiberYonael MezmureNo ratings yet
- Reflection PaperDocument12 pagesReflection PaperMarfe MontelibanoNo ratings yet
- k-350 k-355 Teknik DataDocument7 pagesk-350 k-355 Teknik DataRafael PerezNo ratings yet
- Final - Hafl Yearly Exam 2022 (Scheme)Document1 pageFinal - Hafl Yearly Exam 2022 (Scheme)Vineet YadavNo ratings yet
- Instructions: Ashoka University Ma Economics Entrance ExaminationDocument10 pagesInstructions: Ashoka University Ma Economics Entrance ExaminationJayesh RaghuwanshiNo ratings yet
- Melanie Donato Loyola Seeks Agricultural Technologist RoleDocument5 pagesMelanie Donato Loyola Seeks Agricultural Technologist RoleIan Dante ArcangelesNo ratings yet
- Photovoltaic Powered DC-DC Boost Converter Based oDocument12 pagesPhotovoltaic Powered DC-DC Boost Converter Based oMeryouma LarbNo ratings yet
- Flat Ends With A Relief GrooveDocument11 pagesFlat Ends With A Relief GrooveEng-CalculationsNo ratings yet
- Minimet 1000Document30 pagesMinimet 1000Javier MartínezNo ratings yet
- Course Number Course Title Term Academic Year MECH 375 Mechanical Vibrations Fall 2021-2022 Course Instructor Office Email Office HoursDocument9 pagesCourse Number Course Title Term Academic Year MECH 375 Mechanical Vibrations Fall 2021-2022 Course Instructor Office Email Office HoursKyron CallisteNo ratings yet
- Luciana Session 3 - Mindvana Session NotesDocument5 pagesLuciana Session 3 - Mindvana Session NotesNehaNo ratings yet
- University of Zambia PHY1015 Tutorial Sheet 4 2021/2022 Newton’s Laws of MotionDocument2 pagesUniversity of Zambia PHY1015 Tutorial Sheet 4 2021/2022 Newton’s Laws of MotionAngel JereNo ratings yet
- CONTINGENCY PLAN FOR COVID 19 - A$ SizeDocument15 pagesCONTINGENCY PLAN FOR COVID 19 - A$ Sizemaribel bathanNo ratings yet
- QualitativeDocument306 pagesQualitativeParintins Parintins100% (1)
- Bhopal Engg CollegesDocument7 pagesBhopal Engg CollegesManasvi MehtaNo ratings yet
- 1MA178 4e NoiseFigureDocument31 pages1MA178 4e NoiseFigureBisuNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Lesson 2Document4 pagesModule 1 Lesson 2SOMERA Princess Nicole V.No ratings yet
- Finding The Area Between CurvesDocument6 pagesFinding The Area Between CurvesZaheer Ahmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Genetic Engineering and GMOs: Benefits, Risks, and InsightsDocument2 pagesGenetic Engineering and GMOs: Benefits, Risks, and InsightsJerald De La CruzNo ratings yet
- IJLL - SanskritDocument6 pagesIJLL - SanskritSudarshan RaghununanNo ratings yet
- Oop Lab Assignment PDFDocument2 pagesOop Lab Assignment PDFHurara KhanNo ratings yet
- MGTI619 - Internship Report-Management Organization Analysis Report (DGKCC)Document27 pagesMGTI619 - Internship Report-Management Organization Analysis Report (DGKCC)zrdNo ratings yet
- Centre of MassDocument32 pagesCentre of MassR.Yashwanth Raj XBNo ratings yet
- Pulping of Pineapple Leaves VillaberDocument5 pagesPulping of Pineapple Leaves VillaberJonaisa FandiyaNo ratings yet
- Unit Plan Lesson 4-3Document13 pagesUnit Plan Lesson 4-3api-547362187No ratings yet
- Pakistan Lecture Natural Resources CultureDocument3 pagesPakistan Lecture Natural Resources CultureMalik50% (2)
- DS3400 User's GuideDocument174 pagesDS3400 User's Guidecesco_78No ratings yet
- The Essence of Architecture as a Territorial EntityDocument11 pagesThe Essence of Architecture as a Territorial Entitymercyella prasetyaNo ratings yet
- Udyog Aadhaar Registration Certificate PDFDocument1 pageUdyog Aadhaar Registration Certificate PDFnishant kumarNo ratings yet
- Prasetyawan 2020Document9 pagesPrasetyawan 2020Tania CanchanyaNo ratings yet
- Amos Rapoport - Symbolism and Environmental DesignDocument7 pagesAmos Rapoport - Symbolism and Environmental DesignJonathan CainoNo ratings yet