Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mech
Mech
Uploaded by
AGH BIOMEDOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mech
Mech
Uploaded by
AGH BIOMEDCopyright:
Available Formats
SECTION 2 HYDRAULICS AND MECHANICS
2.1 DETECTOR UNIT ........................................................................... 1
2.1.1 Outline .................................................................................. 1
2.1.2 Functions .............................................................................. 1
2.1.2.1 Mixing Chamber....................................................... 1
2.1.2.2 Transducer Chamber (Detector Block No.40 Assy) . 1
2.1.2.3 Thermistor ............................................................... 1
2.1.3 Signal Input/Output ............................................................... 1
2.2 CP UNIT ......................................................................................... 2
2.2.1 Outline .................................................................................. 2
2.2.2 Functions .............................................................................. 2
2.2.2.1 Applicable Collection Tube and Adaptors ................ 2
2.2.3 Signal Input/Output ............................................................... 3
2.3 SYRINGE UNIT .............................................................................. 4
2.3.1 Outline .................................................................................. 4
2.3.2 Features................................................................................ 4
2.3.3 Signal Input/Output ............................................................... 4
2.4 MOTOR .......................................................................................... 5
pocH-100i S/M December 13, 2007
SECTION 2 HYDRAULICS AND MECHANICS 2.1.2.3 Thermistor
2.1 DETECTOR UNIT A thermistor for temperature compensation is located in the detector
unit.
2.1.1 Outline
Transducer Chamber
The Detector Unit consists of the Mixing Chamber for whole blood Mixing Chamber
dilutions, the open type Transducer Chamber and the Hgb Flow Cell.
2.1.2 Functions Thermistor
2.1.2.1 Mixing Chamber
(1) The first dilution sample is prepared with 15 uL of whole blood
sample (1:130), and the second dilution sample is prepared with 200
uL of the first dilution sample (1:1360).
(2) Sample is mixed by spouting the diluent into the chamber.
(3) Sample is discharged by applying vacuum.
(4) Diluent is discharged by syringe operation.
(5) Overflow is drained outside the Main Unit.
2.1.2.2 Transducer Chamber (Detector Block No.40 Assy) Hgb Flow Cell
(1) Sheath flow transducer with a ceramic jet nozzle of 0.2 mm inner Figure 2-1: Detector Unit
diameter (front sheath only).
(2) One aperture of 75 um diameter is commonly used for WBC and
RBC detection. 2.1.3 Signal Input/Output
(3) Two nozzles dispense the diluent and lyse from over the transducer
chamber. The volumes of these reagents are determined to 500 uL With PCB No.3057T1 (Analog, Logger, Driver board)
by syringe. - Thermistor analog signals
(4) Lowered detection voltage level (to 58V). - Hgb detection signals
(5) The Hgb Flow Cell (Hgb Unit No.16) is combined with the - Cell detection resistance pulses
transducer.
pocH-100i S/M 2-1 December 13, 2007
2.2 CP UNIT 2.2.2 Functions
2.2.1 Outline 2.2.2.1 Applicable Collection Tube and Adaptors
One sample tube is set in the open-door type holder with a tube Refer to Section 1.7.9 for the collection tubes.
adapter. Refer to Section 1.7.10 for the adaptors for each sample tube.
The piercer is held by the arm located in the top, and the stepping motor Jump to Section 1.7.9 �]
drives it down to pierce the sample cap. Open tube is also applicable. Jump to Section 1.7.10 �]
The control tube or micro tube requires special adaptors. 2.2.2.2 Door Lock
Reference: The CP Unit is shown below. The Cap Piercing Unit of When the piercer is moving down and “Aspirating” is displayed on the
pocH-100i is named as “Aspiration Unit No. 11”. LCD, the sample door is locked by solenoid for security.
2.2.2.3 Sensors
Door open/close: Photo interrupter
Adaptor detection: Micro switch
Piercer home position (upper end): Photo interrupter
Door Sensor
Adaptor Sensor
Figure 2-2-1: CP Unit
Figure 2-2-2: Door and Adaptor Sensors
pocH-100i S/M 2-2 December 13, 2007
2.2.3 Signal Input/Output
With PCB No.3057T1 (Analog, Logger, Driver board)
- Piercer home position sensor signal (photo interrupter)
- Door sensor signal (photo interrupter)
- Adaptor sensor (Micro switch)
- Piercer up/down driving motor (STM2) signal
- Door lock solenoid driving signal
Piercer Home
Position
(Upper End)
Figure 2-2-3: Piercer Home Position Sensors
pocH-100i S/M 2-3 December 13, 2007
2.3 SYRINGE UNIT
Syringe Unit No.21
2.3.1 Outline (diluent)
The stepping motor driving stroke is transferred to the volumetric piston
Syringe Unit No.22
by the timing belt. (sample and sheath)
2.3.2 Features
(1) Syringe Unit No. 21
- 1 each of Ceramic piston of 12 mm diameter
- For diluent dispense and lyse quantity measurement
(2) Syringe Unit No. 22
- 2 each of SUS piston of 2 mm diameter
- For sample aspiration and sheath flow
- The entire unit should be replaced when needed. Seal and o-ring
replacement is not allowed for data assurance.
2.3.3 Signal Input/Output
With PCB No.3057T1 (Analog, Logger, Driver board)
- Syringe home position sensor signals
Photo Interrupter1: Syringe Unit No.21 (large)
Photo Interrupter2: Syringe Unit No.22 (small)
- Syringe up/down driving motor signal
STM1: Syringe Unit No.21 (large)
STM3: Syringe Unit No.22 (small)
Figure 2-3: Syringe Unit
pocH-100i S/M 2-4 December 13, 2007
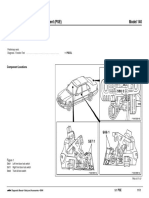
2.4 MOTOR
STM Driving Unit Operation (CW direction)
STM1 Syringe Unit No. 21 (for diluent: large) Up
STM2 Piercer up/down Up
STM3 Syringe Unit No. 22 (for sample: small) Down
STM4 Piercer back/forth Back
STM5 Pinch Valve No. 4 (double) Close
STM6 Pinch Valve No. 3 Close
STM1 STM3
Diluent Syringe Sample Syringe STM2
Piercer Up/down
STM4
Piercer Back/Forth
STM6
Pinch Valve
STM5
W-Pinch Valve
(Left Side Interior) (Front Interior) (Right Side Interior)
pocH-100i S/M 2-5 January 2003
You might also like
- Starrett 3812Document18 pagesStarrett 3812cdokepNo ratings yet
- Manual S22Document19 pagesManual S22Anonymous HKuYF6kNo ratings yet
- To All Holders of Hamilton Sundstrand'S Component Maintenance Manual 21-32-20 Applicability: Emb135, Emb145 This Sheet Transmits Revision No. 4 Date Aug 29/07 HighlightsDocument138 pagesTo All Holders of Hamilton Sundstrand'S Component Maintenance Manual 21-32-20 Applicability: Emb135, Emb145 This Sheet Transmits Revision No. 4 Date Aug 29/07 HighlightsTAR AEROLINEASNo ratings yet
- Short-Circuit Analysis IEC StandardDocument454 pagesShort-Circuit Analysis IEC Standardelectrica383% (6)
- Scania Truck Sms Fault Codes DTCDocument11 pagesScania Truck Sms Fault Codes DTCSurafel Abebe100% (1)
- LG w1943sb Lgd-tlc1 SMDocument42 pagesLG w1943sb Lgd-tlc1 SMmirkovsNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation NotesDocument61 pagesInstrumentation NotesVidya Muthukrishnan100% (1)
- Slickline Services Schlumberger Pressure Control EquipmentDocument62 pagesSlickline Services Schlumberger Pressure Control EquipmentHusseen HusseenNo ratings yet
- Model User Guide For Generic Renewable Energy System ModelsDocument74 pagesModel User Guide For Generic Renewable Energy System ModelsRitesh StanleyNo ratings yet
- Electro-Pneumatics: Module EP-5: Sensors in Electro-Pneumatics (Proximity Switches and Pressure Switches)Document36 pagesElectro-Pneumatics: Module EP-5: Sensors in Electro-Pneumatics (Proximity Switches and Pressure Switches)Joesun Lizardo100% (1)
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Document33 pagesRefrigeration and Air Conditioning 2Christina OhNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSICS 2 - Q4 - Week 1 1Document24 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS 2 - Q4 - Week 1 1Recan Alfeche100% (1)
- LECTURE 8 Induction Machines 02Document132 pagesLECTURE 8 Induction Machines 02MINH Nguyễn TuấnNo ratings yet
- ARSC 443 - 1.4 Loads On Structures - ARSC 443-ARCH42S2 - Architectural StructuresDocument4 pagesARSC 443 - 1.4 Loads On Structures - ARSC 443-ARCH42S2 - Architectural StructuresJUDY ANN MALANANo ratings yet
- BFK InstructionsDocument98 pagesBFK InstructionsArturo100% (2)
- LOPA PresentationDocument64 pagesLOPA Presentationsurya chandraNo ratings yet
- 7080 HandbookDocument139 pages7080 Handbookdony prabuNo ratings yet
- AFR-200 NovaTrend CE en User ManualDocument32 pagesAFR-200 NovaTrend CE en User ManualFarinel InfanteNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Presentation: Kaustubh G Setloor Gurukiran Udupa Jatin Karthik N Keshav JhaDocument10 pagesGroup 2 Presentation: Kaustubh G Setloor Gurukiran Udupa Jatin Karthik N Keshav Jhakarthik nNo ratings yet
- CE2 Operation ManualDocument28 pagesCE2 Operation Manualhayder ahmedNo ratings yet
- TMP DSM501A Dust Sensor630081629 PDFDocument8 pagesTMP DSM501A Dust Sensor630081629 PDFAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Manual PCV2 2 EnglishDocument9 pagesManual PCV2 2 EnglishTesla Ec100% (1)
- BX 3010 (Dec13)Document544 pagesBX 3010 (Dec13)Lâm Hồ Ngọc HãnNo ratings yet
- Innova Pressure Control BD InstallationDocument10 pagesInnova Pressure Control BD Installationbruce huNo ratings yet
- 05-680 Gasenz User Manual Ntron Standard EC V233P Issue 1.2Document28 pages05-680 Gasenz User Manual Ntron Standard EC V233P Issue 1.2Aarsol AdvanceNo ratings yet
- Potentiometric Error DectectorDocument20 pagesPotentiometric Error DectectorBalraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Design Experiment 3: Programmable Logic ControllerDocument5 pagesDesign Experiment 3: Programmable Logic ControllerKim Angelo GonzalesNo ratings yet
- LabPlanningManual 02 enDocument12 pagesLabPlanningManual 02 enJulio AlceramNo ratings yet
- DSM 501Document10 pagesDSM 501محمد عقيل عبد الامير ستارNo ratings yet
- Model No. UTG-2800: 283 Veterans BLVD Carlstadt, NJ. 07072 (201) 933-6300Document19 pagesModel No. UTG-2800: 283 Veterans BLVD Carlstadt, NJ. 07072 (201) 933-6300enticoNo ratings yet
- Switches N Discrete OpsDocument11 pagesSwitches N Discrete OpsGaurav R AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Laporan Tugas Talkback Babysitting Sistem TelekomunikasiDocument18 pagesLaporan Tugas Talkback Babysitting Sistem TelekomunikasiYusrahimah HelmiNo ratings yet
- Air PianoDocument18 pagesAir Pianosnehax2No ratings yet
- Particle / Dust Sensor Module: DSM 501 SeriesDocument7 pagesParticle / Dust Sensor Module: DSM 501 SeriesAnkit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Electrum Av: Transistor Igbt and Mosfet Driver Dr2180P-B1 Analogue of 2Sd315Ai User'S ManualDocument11 pagesElectrum Av: Transistor Igbt and Mosfet Driver Dr2180P-B1 Analogue of 2Sd315Ai User'S Manualfenix1233No ratings yet
- CE1 Operation ManualDocument27 pagesCE1 Operation Manualhayder ahmedNo ratings yet
- Freescale Semiconductor Application Note PDFDocument8 pagesFreescale Semiconductor Application Note PDFAfaque shaikhNo ratings yet
- GC-1502 2-ch High Speed Counter Module User ManualDocument13 pagesGC-1502 2-ch High Speed Counter Module User Manualgilson lopesNo ratings yet
- Specn For LHB TYPE RMPUDocument43 pagesSpecn For LHB TYPE RMPUpraveen_01236No ratings yet
- Chap. II. Input Output Devices: CapteursDocument4 pagesChap. II. Input Output Devices: CapteursReda keNo ratings yet
- CA-01, 02 Coagulometer (New)Document40 pagesCA-01, 02 Coagulometer (New)leopa78No ratings yet
- Apple Technician Guide For LED Cinema Display 24 Inch PDFDocument92 pagesApple Technician Guide For LED Cinema Display 24 Inch PDFDeadmanNo ratings yet
- KT6200 Service ManualDocument21 pagesKT6200 Service ManualAmarildo JuniorNo ratings yet
- E2em003 ReportDocument174 pagesE2em003 ReportLumisense TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Novo GPMDocument21 pagesNovo GPMjuliano diasNo ratings yet
- SP0793-E951.00-G25-0014 - Rev B - DC DC Power Supply System - Technical Specifications - ABB - 2021-02-03Document8 pagesSP0793-E951.00-G25-0014 - Rev B - DC DC Power Supply System - Technical Specifications - ABB - 2021-02-0318-01-0096No ratings yet
- Bai TN So 3 Dieu Khien Trinh Tu Voi Relay Su Dung Thiet Bi SMC - ENDocument9 pagesBai TN So 3 Dieu Khien Trinh Tu Voi Relay Su Dung Thiet Bi SMC - ENTÀI NGUYỄN THÀNHNo ratings yet
- Experiment No.: 1: Title: SwitchesDocument19 pagesExperiment No.: 1: Title: SwitchesAnil NavaleNo ratings yet
- 34uc97 Lm43a LGDocument31 pages34uc97 Lm43a LGdouglasleitedelima1203No ratings yet
- Instruction Manual: Bon CP-33 ID Chart ProjectorDocument20 pagesInstruction Manual: Bon CP-33 ID Chart Projectorandres2013bioNo ratings yet
- PC160 Merik Home Access Home DepotDocument8 pagesPC160 Merik Home Access Home DepotIsaac SantoyNo ratings yet
- Mercedes w140 Kasa Arıza Kodları PSE Control Module Model 140Document28 pagesMercedes w140 Kasa Arıza Kodları PSE Control Module Model 140Emrah UÇKUNNo ratings yet
- L1710S (L1710sm-Al - R, Au - R, Ad - R, Ag - R) CL-61Document18 pagesL1710S (L1710sm-Al - R, Au - R, Ad - R, Ag - R) CL-61Deki PericNo ratings yet
- En DM00026181Document15 pagesEn DM00026181Michael GuiuanNo ratings yet
- BESCHREIBUNG KD01 VTS01 EngDocument12 pagesBESCHREIBUNG KD01 VTS01 EngIainNo ratings yet
- Industrial Protection System Using Arduino and Bluetooth ModuleDocument32 pagesIndustrial Protection System Using Arduino and Bluetooth Modulehamed razaNo ratings yet
- Valvula Seguridad Herion Scsq10Document2 pagesValvula Seguridad Herion Scsq10Base SistemasNo ratings yet
- Valvula Seguridad Herion Scsq10Document2 pagesValvula Seguridad Herion Scsq10Base SistemasNo ratings yet
- M185XW01 V6Document27 pagesM185XW01 V6Khan SahibNo ratings yet
- 1.1 Overview: Ankaj Mohindroo (C07504)Document34 pages1.1 Overview: Ankaj Mohindroo (C07504)harshal_lowerfeesNo ratings yet
- 09 Counter CellDocument3 pages09 Counter CellTana AzeezNo ratings yet
- TESTO-6651-6600 VOL2-1-20.en - EsDocument20 pagesTESTO-6651-6600 VOL2-1-20.en - EsEliana Guzman PachecoNo ratings yet
- Csv1-2837-2021-Id-Ele-Li-314-0 Listado de Materiales Celda de MTDocument35 pagesCsv1-2837-2021-Id-Ele-Li-314-0 Listado de Materiales Celda de MTMiguel Enrique Diaz EstupiñanNo ratings yet
- Ams4a051 Winch Operators Display Panel RevlDocument48 pagesAms4a051 Winch Operators Display Panel Revlbaggo81No ratings yet
- Cocbdir Direct Open For Cbs Via Mmi: 1Mrs752349-MumDocument6 pagesCocbdir Direct Open For Cbs Via Mmi: 1Mrs752349-Mumhaichau199No ratings yet
- Digsilent Powerfactory: Relay Model DescriptionDocument12 pagesDigsilent Powerfactory: Relay Model DescriptionBra BicabaNo ratings yet
- Detailed Manual: Toho Electronics Inc. Multi-Channel Board ControllerDocument35 pagesDetailed Manual: Toho Electronics Inc. Multi-Channel Board ControllerArchie MaguillanoNo ratings yet
- PCM DownloadDocument16 pagesPCM Downloadsan droidNo ratings yet
- Transistor Electronics: Use of Semiconductor Components in Switching OperationsFrom EverandTransistor Electronics: Use of Semiconductor Components in Switching OperationsRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Past Update RecordDocument3 pagesPast Update RecordAGH BIOMEDNo ratings yet
- Error MessageDocument28 pagesError MessageAGH BIOMEDNo ratings yet
- SchematicsDocument8 pagesSchematicsAGH BIOMEDNo ratings yet
- Professional Medical ProductsDocument6 pagesProfessional Medical ProductsAGH BIOMEDNo ratings yet
- User Manual: o - Two E700Document60 pagesUser Manual: o - Two E700AGH BIOMEDNo ratings yet
- Jitendra Hirwani: Inorganic ChemistryDocument8 pagesJitendra Hirwani: Inorganic ChemistryabhishekNo ratings yet
- Building Lighting Design NotesDocument10 pagesBuilding Lighting Design NotesMwaniki WilNo ratings yet
- Electric Counterbalance TruckDocument9 pagesElectric Counterbalance TruckNadeem AhmedNo ratings yet
- Air Compressor Attachment PartsDocument5 pagesAir Compressor Attachment PartsKarthii AjuNo ratings yet
- Test 3Document12 pagesTest 3Hiền Cao MinhNo ratings yet
- Rethink The Business Model For Sustainable DevelopmentDocument26 pagesRethink The Business Model For Sustainable DevelopmentLudor EngineeringNo ratings yet
- Control No. Output Voltage Discharge - Discontinued INDocument8 pagesControl No. Output Voltage Discharge - Discontinued INNicolas ArevaloNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Transformer SelectionDocument2 pagesThree Phase Transformer SelectionsaravananNo ratings yet
- Ceramic Chip CapacitorsDocument21 pagesCeramic Chip CapacitorsEnkhbayar BadarchNo ratings yet
- DP Unit 9 & 19. Redox ProcessesDocument12 pagesDP Unit 9 & 19. Redox ProcessesdeaNo ratings yet
- DC MotorDocument26 pagesDC MotorGerard AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Domekt CF 400 V C6M ENDocument1 pageDomekt CF 400 V C6M ENnpnickNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Chemistry As Notes PDF FreeDocument101 pagesEdexcel Chemistry As Notes PDF FreeThoon Nadi NaiNo ratings yet
- Manuel Entretien F50A F60A Yamaha en FrançaisDocument225 pagesManuel Entretien F50A F60A Yamaha en FrançaishenriandreaniNo ratings yet
- BSL Presentation On BasicsDocument41 pagesBSL Presentation On BasicsSathishNo ratings yet
- Bent Axis Fixed Displacement Heavy Duty Motors and Pumps: Motor/PumpDocument28 pagesBent Axis Fixed Displacement Heavy Duty Motors and Pumps: Motor/PumpDecio SchuckNo ratings yet
- CALCULUS (AutoRecovered)Document7 pagesCALCULUS (AutoRecovered)Carl Eugene de LemosNo ratings yet
- Ultra IR800Document2 pagesUltra IR800Vincent GabrielNo ratings yet
- 2015-03 Compressors-For-Industry en N39771 SCDocument40 pages2015-03 Compressors-For-Industry en N39771 SCMohamed MusaNo ratings yet
- Maharashtra State Board of Technical Education, Mumbai: Sant Gajanan Maharaj Rural Polytechnic, MahagaonDocument12 pagesMaharashtra State Board of Technical Education, Mumbai: Sant Gajanan Maharaj Rural Polytechnic, Mahagaonomkar sutarNo ratings yet