Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Concrete Beam Analysis
Uploaded by
JagannathanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Concrete Beam Analysis
Uploaded by
JagannathanCopyright:
Available Formats
WESTERN UNIVERSITY
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
CEE 9628b Prestressed Concrete (Assignment # 4)
Dr. Maged A. Youssef, P.Eng. Page: 1
If you consider that there is missing information, you are urged to make a reasonable assumption and
submit a clear statement of this assumption.
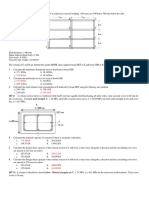
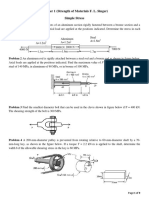
Problem 1:
The rectangular stress-block parameters that were derived in the lecture notes are based on a constant
section width and having a zero-strain point within the section height. However, with some modification,
they can be used in other situations. You are required to use the factors to determine the magnitude and
position of the resultant concrete force for the two sections shown in Fig. 1.
Given:
f c' = 40 MPa, ε o -0.002, 𝜀 0.0023, 𝜀 0.001
Hint: Add a fictitious area to the cross-section to obtain a constant width area and/or to reach the point
of zero strain; determine the resultant by subtracting the force on the fictitious area from the resultant
of the total area.
100 m
1500 mm
600 mm
600 mm
250 mm 250 mm
Fig. 1 Cross section of Concrete Beams
WESTERN UNIVERSITY
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
CEE 9628b Prestressed Concrete (Assignment # 4)
Dr. Maged A. Youssef, P.Eng. Page: 2
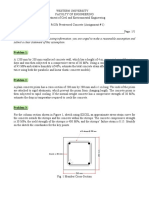
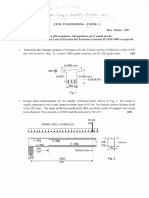
Problem 2:
Fig. 2 shows the cross-section of a precast pre-tensioned single-tee beam. The beam is simply supported
and has a span of 18 m. The low-relaxation prestressing strands were tensioned to a stress of 1250 MPa
in the pre-tensioning bed, before casting the concrete. The stress-strain curve of the strands is shown in
Fig. 3 (fpu = 1860 MPa, Ep= 200,000 MPa). The strands have constant eccentricity along the span of the
beam, and you can ignore prestress losses. Given that 𝑓 ′ 40 MPa, 𝜀 0.002 mm/mm, calculate
the moment and curvature at prestressing, cracking, and decompression.
60 mm
2200 mm
1000 mm
200 mm
CG of
Strands
14-15 mm seven-wire strand
250 mm
Fig. 2 Beam Section
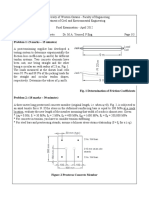
Stress
f
p pu
f
p py
E
p p
Strain
0.0415
Fig. 3 Strand Stress-Strain Curve
You might also like
- Manhole Design per AASHTO LRFD 2014Document23 pagesManhole Design per AASHTO LRFD 2014Rafique Munde100% (2)
- Lamborghini Diablo Engine Parts ManualDocument40 pagesLamborghini Diablo Engine Parts ManualAndrei Huţanu100% (1)
- Chapter 04 SealDocument25 pagesChapter 04 Sealdewidar1234100% (1)
- Box Culvert 5cells - 4m X 4mDocument40 pagesBox Culvert 5cells - 4m X 4mshashiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 DC MachinesDocument80 pagesChapter 4 DC MachinesKorsa KorsaNo ratings yet
- Jasper PDFDocument72 pagesJasper PDFLimuel Milo Lebios100% (1)
- Concrete DesignDocument19 pagesConcrete DesignXprts Review100% (4)
- ROLLS ROYCE Gasturbines - tcm92-4977Document20 pagesROLLS ROYCE Gasturbines - tcm92-4977Vipin Thathiriyat100% (3)
- TrussDocument14 pagesTrussD MNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Concrete Beam Deflection and Minimum ThicknessDocument7 pagesReinforced Concrete Beam Deflection and Minimum ThicknessLester John PrecillasNo ratings yet
- 1 Printed Mit Correl Design Term Sy 2014 2015 DraftDocument14 pages1 Printed Mit Correl Design Term Sy 2014 2015 DraftAllyza MabutolNo ratings yet
- LiquidRet IndianDocument13 pagesLiquidRet Indianchandra BandaraNo ratings yet
- 1 ACI - Builder With Hand Calculation PDFDocument29 pages1 ACI - Builder With Hand Calculation PDFEvilsNo ratings yet
- Vacuum Pump SOPDocument7 pagesVacuum Pump SOPSonratNo ratings yet
- EXXON IP-10-01-01 Centrifugal PumpsDocument9 pagesEXXON IP-10-01-01 Centrifugal PumpsyerkoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document2 pagesAssignment 3JagannathanNo ratings yet
- 2012 ExamDocument3 pages2012 ExamJagannathanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Wasim AbbassNo ratings yet
- Probset 2.2Document1 pageProbset 2.2Ken AndradeNo ratings yet
- Assignment 8Document3 pagesAssignment 8JagannathanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1JagannathanNo ratings yet
- Exam Paper-FinalDocument5 pagesExam Paper-FinalLebusa PosholiNo ratings yet
- Determine shear stress and shaft rotationDocument5 pagesDetermine shear stress and shaft rotationSchehzeb ManzarNo ratings yet
- Problem 6: Answer: 138.24kN, 157.93kN, 304kNDocument1 pageProblem 6: Answer: 138.24kN, 157.93kN, 304kNMarvin Carl GranadaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document3 pagesAssignment 2Pranaw PariharNo ratings yet
- Civn 2009: Materials and Structures Ii Tutorial No. IiDocument2 pagesCivn 2009: Materials and Structures Ii Tutorial No. Iimotsepe thompsonNo ratings yet
- Prestressed Concrete Column Design Interaction DiagramDocument1 pagePrestressed Concrete Column Design Interaction DiagramJagannathanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - New PDFDocument2 pagesAssignment 2 - New PDFprasadNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 2Document3 pagesTutorial 2rafidah mazlanNo ratings yet
- Effects of prestress on shear capacityDocument13 pagesEffects of prestress on shear capacityRagheb IbrahimNo ratings yet
- MERGE-QUIZ MechnicsDocument32 pagesMERGE-QUIZ MechnicsAngel NaldoNo ratings yet
- CEPC25 Nov 2021Document2 pagesCEPC25 Nov 2021Lokesh Kumar MeenaNo ratings yet
- Detecting Corrosion in Reinforced Concrete with Nondestructive Evaluation MethodsDocument9 pagesDetecting Corrosion in Reinforced Concrete with Nondestructive Evaluation Methodszaman ahmadNo ratings yet
- Nanyang Technological University: Manufacturing Lab ReportDocument5 pagesNanyang Technological University: Manufacturing Lab ReportPrayogo TioNo ratings yet
- Review ProblemsDocument3 pagesReview ProblemsJihan PacerNo ratings yet
- MD1 Plate 1 Review of Kine and MDB Feb2024Document2 pagesMD1 Plate 1 Review of Kine and MDB Feb2024Lledniw GamesNo ratings yet
- PRESTRESSED CONCRETE DESIGN ASSIGNMENT 3Document2 pagesPRESTRESSED CONCRETE DESIGN ASSIGNMENT 3YELLAMANDA SANKATI100% (1)
- UNI - Z241 - 17 - 5 - 600x300 ModifiedDocument23 pagesUNI - Z241 - 17 - 5 - 600x300 ModifiedpaulaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 8 Prestress Concrete and LossesDocument2 pagesTutorial 8 Prestress Concrete and Lossesvat007No ratings yet
- Elective-II: Finite Element Method: B.E. (Mechanical Engineering) Eighth Semester (C.B.S.)Document4 pagesElective-II: Finite Element Method: B.E. (Mechanical Engineering) Eighth Semester (C.B.S.)Sufiyan RehmanNo ratings yet
- ME-1203 Solid Mechanics-EEE (Solved Problem Slide)Document9 pagesME-1203 Solid Mechanics-EEE (Solved Problem Slide)sadfNo ratings yet
- Steel Structures - I: B.E. (Civil Engineering) Sixth Semester (C.B.S.)Document16 pagesSteel Structures - I: B.E. (Civil Engineering) Sixth Semester (C.B.S.)Pratik GhimireNo ratings yet
- Sheet No.2 (Simple Stress)Document3 pagesSheet No.2 (Simple Stress)elhalawanyh46No ratings yet
- Crack Width For Oht TankDocument1 pageCrack Width For Oht Tankselvakumar sNo ratings yet
- ES 13 1920A Problem Set 2Document5 pagesES 13 1920A Problem Set 2Charmaine ColetaNo ratings yet
- Design prestressed concrete beams and sectionsDocument13 pagesDesign prestressed concrete beams and sectionsSuryakant MangajNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Simulation of Low Concrete Strength Beam Beam-Column Joint Strengthened With CFRPDocument10 pagesFinite Element Simulation of Low Concrete Strength Beam Beam-Column Joint Strengthened With CFRPlalitha kandikaNo ratings yet
- 3862 15A01308 Mechanics of SolidsDocument2 pages3862 15A01308 Mechanics of SolidsAnonymous ML4hh4MOyBNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2Dechas Mohammed100% (2)
- SOM - Unit Test 1Document1 pageSOM - Unit Test 1narayan1982No ratings yet
- RC2 Take Home Exam 3Document2 pagesRC2 Take Home Exam 3عبد الله خالدNo ratings yet
- Solution To Assignment-3-T2-2019Document8 pagesSolution To Assignment-3-T2-2019Adrian VuNo ratings yet
- CE668 - End Sem Exam-Jul 2021Document3 pagesCE668 - End Sem Exam-Jul 2021santoshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document5 pagesChapter 5Tan Mei QianNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - Concrete Beam ReinforcementDocument21 pagesLecture 9 - Concrete Beam ReinforcementKhaled AlregebNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument4 pagesAssignmentSolly Fils De MarierNo ratings yet
- TPB Fracture Test ManualDocument14 pagesTPB Fracture Test ManualMichael Asmith UniqueNo ratings yet
- 1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 1Document5 pages1st Sem Es 13 Prob Set 1onenoteforlocadNo ratings yet
- f6cb57702022 Endsem MOSDocument2 pagesf6cb57702022 Endsem MOSshreyas shahNo ratings yet
- Presstres MidDocument2 pagesPresstres MidTarun KumarNo ratings yet
- Experimental Research of Beams With Corrugated Web: Vladimir Zubkov, Alexey LukinDocument6 pagesExperimental Research of Beams With Corrugated Web: Vladimir Zubkov, Alexey LukinTamir EnkhNo ratings yet
- AE Civil Paper IDocument3 pagesAE Civil Paper INaveen KaleraNo ratings yet
- 02 Unit II 2017-18 Classroom Problems ONLY PDFDocument8 pages02 Unit II 2017-18 Classroom Problems ONLY PDFIssac PaulNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials QP BANKDocument15 pagesStrength of Materials QP BANKmechfameNo ratings yet
- Production GATE/ESE METAL FORMING & SHEET METAL OPERATIONDocument60 pagesProduction GATE/ESE METAL FORMING & SHEET METAL OPERATIONDeepak KumarNo ratings yet
- Hwre 3rd Year 2022, Rc-II Assigment 1Document2 pagesHwre 3rd Year 2022, Rc-II Assigment 1Tesfa HunderaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Solids GTU PapersDocument17 pagesMechanics of Solids GTU Papersvaibhav shahNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 1 RC - IIDocument3 pagesAssignment - 1 RC - IIdawitdeginet096No ratings yet
- Video and Camcorder Servicing and TechnologyFrom EverandVideo and Camcorder Servicing and TechnologyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Prestressed Concrete Column Design Interaction DiagramDocument1 pagePrestressed Concrete Column Design Interaction DiagramJagannathanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5Document1 pageAssignment 5JagannathanNo ratings yet
- CEE 9628b Prestressed Concrete ProblemsDocument2 pagesCEE 9628b Prestressed Concrete ProblemsJagannathanNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document1 pageAssignment 1JagannathanNo ratings yet
- Ladder PDFDocument144 pagesLadder PDFAung MinsoeNo ratings yet
- Partial Vapour Pressure of SO2 Over H2ODocument1 pagePartial Vapour Pressure of SO2 Over H2OJia Yuan ChngNo ratings yet
- Automobile Design (5051)Document4 pagesAutomobile Design (5051)Ziyad KprNo ratings yet
- CFD Simulation of Steady Flow past a CylinderDocument17 pagesCFD Simulation of Steady Flow past a CylinderCarl AriffNo ratings yet
- IPM ModelDocument66 pagesIPM Modelbobo249No ratings yet
- Calculating Two-Phase Pressure DropDocument8 pagesCalculating Two-Phase Pressure DroprondonjjNo ratings yet
- BATCH SETTLING OF SOLID SLURRIES: MOTIVATION, OBJECTIVES, THEORY, EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE AND CALCULATIONDocument25 pagesBATCH SETTLING OF SOLID SLURRIES: MOTIVATION, OBJECTIVES, THEORY, EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE AND CALCULATIONSUYASH SUNIL ABNAVE PGP 2020 BatchNo ratings yet
- Amendment No. 1 November 2019 TO Is 16700: 2017 Criteria For Structural Safety of Tall Concrete BuildingsDocument3 pagesAmendment No. 1 November 2019 TO Is 16700: 2017 Criteria For Structural Safety of Tall Concrete BuildingsSafora ShaikNo ratings yet
- Moments & Centre of Mass QPDocument14 pagesMoments & Centre of Mass QPs.beshimova2026No ratings yet
- DancomechDocument2 pagesDancomechTakrimi IsmailNo ratings yet
- BullEx ITS User Manual XtremeDocument44 pagesBullEx ITS User Manual XtremeJonasDispersyn100% (1)
- PHY4 June 2005Document2 pagesPHY4 June 2005api-3726022No ratings yet
- AVMM Ch08Document13 pagesAVMM Ch08Alex BrandãoNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Engineering Document TitleDocument4 pagesThermodynamics Engineering Document TitleZaky MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- Dishwasher Parts5995491072Document12 pagesDishwasher Parts5995491072Magnifico SuperiorNo ratings yet
- Military Engine: 745-1119 KW / 1000-1500 HP UnregulatedDocument2 pagesMilitary Engine: 745-1119 KW / 1000-1500 HP Unregulatedmuhammet fidanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial CH 6Document4 pagesTutorial CH 6WinxTynix 8000No ratings yet
- Shell Turbo Oil T32: Performance, Features & BenefitsDocument2 pagesShell Turbo Oil T32: Performance, Features & BenefitsElias GabrielNo ratings yet
- Liebherr Over Height FrameDocument4 pagesLiebherr Over Height FrameLiebherrNo ratings yet
- Flow Past Immersed ObjectivesDocument45 pagesFlow Past Immersed ObjectivesjassimNo ratings yet
- Supporting and Design Consideration of Small-Bore PipingDocument4 pagesSupporting and Design Consideration of Small-Bore PipingTUSHAR BANGERANo ratings yet