Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.2 Properties of Organic Families - Answer Key
Uploaded by
taya guy0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pagesThe document summarizes the key properties of various organic functional groups including alcohols, ethers, amines, aldehydes and ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, and amides. It describes their polarity, ability to form hydrogen bonds, solubility in water, typical melting and boiling points, and additional characteristics such as flammability, odor, and medicinal uses. The table allows comparison of these properties across different organic families.
Original Description:
Original Title
2.2 Properties of organic families - answer key
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the key properties of various organic functional groups including alcohols, ethers, amines, aldehydes and ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, and amides. It describes their polarity, ability to form hydrogen bonds, solubility in water, typical melting and boiling points, and additional characteristics such as flammability, odor, and medicinal uses. The table allows comparison of these properties across different organic families.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
6 views3 pages2.2 Properties of Organic Families - Answer Key
Uploaded by
taya guyThe document summarizes the key properties of various organic functional groups including alcohols, ethers, amines, aldehydes and ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, and amides. It describes their polarity, ability to form hydrogen bonds, solubility in water, typical melting and boiling points, and additional characteristics such as flammability, odor, and medicinal uses. The table allows comparison of these properties across different organic families.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
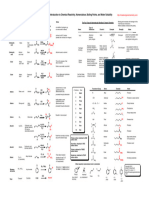
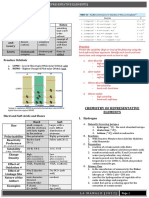
PROPERTIES OF ORGANIC FAMILIES
Family 1 Polarity Hydrogen bonding Solubility in Melting and boiling Additional
water points characteristics
Alcohols O-H bond is very polar; Alcohols experience H- Extremely soluble in Due to H-bonding, Extremely flammable
small alcohols are more bonding with other water due to H- most have higher
polar than large alcohols alcohols and water bonding. Solubility melting and boiling Most are poisonous
decreases with points than alkanes
increasing number with same number of
of carbon atoms. carbon atoms. Most are
liquid at room
temperature.
Ethers Bent shape around oxygen No H-bonding due to Usually soluble, Boiling points much Extremely flammable
means two C-O dipoles do no O-H bond. Can solubility decreases lower than alcohols.
not counteract each other. accept H-bonding from with increasing size
C-O bond is less polar than water. of carbon chains.
O-H, so an ether is less
polar than an alcohol.
Amines C-N and N-H bonds are N-H bonds allow H- Amines with four or Primary and secondary -Widely found in
polar. Amines are usually bonding. less carbons are boiling points are nature. Often toxic.
polar. miscible with water higher than tertiary Many have medicinal
(due to H-bonding). (which do not contain properties.
N-H bond). -Low molecular mass
Solubility decreases amines have
as # C increases. fishy/revolting/necrot
ic
smell.
-Act as weak acids.
Aldehydes C=O bond is polar, so both H-bonding cannot Those with low BP are lower than -Aldehydes have
and Ketones usually polar occur between molecular mass are corresponding alcohols, strong pleasant
molecules since no O-H very soluble in and higher than smell, while ketones
bond. H-bonds can water. Those with corresponding alkanes. smell musky
form with water. large molecular Aldehydes with large
mass are less molecular mass smell
soluble. fruity. Both used to
make perfumes.
-Can act as polar
solvents, but also as
solvents for non-
polar compounds.
Carboxylic Due to polar O-H and C=O H-bonding is strong, Those with low Melting and boiling are -Often have
Acids bonds, are polar and also occurs with molecular mass are very high. unpleasant odours.
compounds. water. very soluble. -OH group does not
Solubility decreases behave like basic
with increasing #C hydroxide ion (OH-).
atoms. -Melting and boiling
points are very high
due to exceptionally
strong H-bonding.
Esters Like carboxylic acids, usually Do not have O-H bonds Can accept H-bonds Low boiling points due -Pleasant odour and
polar. therefore cannot form from water, so to no H-bonds. Usually taste, used to
H-bonds. those with low volatile liquids at room produce perfumes
molecular mass are temperature. and artificial
soluble. Esters with flavours.
C chains longer -Taste of many fruits
than 3 are not come from esters.
soluble.
Amides C-N and N-H bonds are Primary amides have Soluble in water. Primary amides have -Amide called
polar and amides are similar stronger H-bonds than Solubility decreases higher melting and acetaminophen is
to carboxylic acids. carboxylic acids due to with increasing boiling than carboxylic painkiller
two N-H bonds. non-polar HC part. acids. Many are solid at -Urea (an amide),
Secondary also form H- room temperature. made from carbon
bonds. dioxide and
ammonia, first
organic compound
synthesized.
You might also like
- CAE ATPL 2 Airframes and SystemsDocument352 pagesCAE ATPL 2 Airframes and SystemsAŞKIN FIRAT100% (5)
- Water Pumps and Pumping SystemsDocument46 pagesWater Pumps and Pumping SystemsMohamed100% (1)
- ACI 318-08 Development and Splices of ReinforcementDocument6 pagesACI 318-08 Development and Splices of ReinforcementRal GLNo ratings yet
- Stored EnergyDocument38 pagesStored EnergySajid SattarNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons Laboratory - AgsaldaDocument3 pagesHydrocarbons Laboratory - AgsaldaEj Agsalda100% (1)
- Strengthening of Existing Composite Beams Using LRFD ProceduresDocument8 pagesStrengthening of Existing Composite Beams Using LRFD Proceduresalbertoxina100% (3)
- Precast Driven Pile 450x450-350x350Document55 pagesPrecast Driven Pile 450x450-350x350civixxNo ratings yet
- Design Procedure For Spur and Helical Gear PDFDocument15 pagesDesign Procedure For Spur and Helical Gear PDFBinoy K B100% (2)
- Nitrogen Plant Genertor CDocument8 pagesNitrogen Plant Genertor CDEVAM PATELNo ratings yet
- Samples: Experiment 6 - Comparative Investigations of Organic CompoundsDocument2 pagesSamples: Experiment 6 - Comparative Investigations of Organic CompoundsAlyssa CubillaNo ratings yet
- Manual 26260: Governing Fundamentals and Power ManagementDocument76 pagesManual 26260: Governing Fundamentals and Power Managementmarius_1959No ratings yet
- Non-Aqueous Acid Base TitrationDocument35 pagesNon-Aqueous Acid Base TitrationApurba Sarker Apu100% (9)
- C 13 SolutionsDocument13 pagesC 13 SolutionsAli Uy100% (1)
- K3VG-Datasheet Letter Cc19 191008 Final-NRDocument40 pagesK3VG-Datasheet Letter Cc19 191008 Final-NRcatur vallentNo ratings yet
- Acids - For MergeDocument5 pagesAcids - For Mergeseolux13No ratings yet
- Dehydration: Alcohols, Ethers, and ThiolsDocument3 pagesDehydration: Alcohols, Ethers, and ThiolsPaul Alfred SoNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Acid Base ReactionsDocument7 pagesModule 6 Acid Base Reactionsisaheqq12No ratings yet
- Alkenes and AlkynesDocument4 pagesAlkenes and Alkynesespiritumikhailehayah28No ratings yet
- CHEM - Ketones & Aldehydes Physical & Chemical PropertiesDocument2 pagesCHEM - Ketones & Aldehydes Physical & Chemical PropertiesRegina May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and Salts 9EDocument8 pagesAcid Base and Salts 9EOmair AhmedNo ratings yet
- 1 - Chemistry Unit 4Document31 pages1 - Chemistry Unit 4shirley wang100% (1)
- 26 Ch13 AcidsDocument29 pages26 Ch13 AcidsMoses AquinoNo ratings yet
- Ald and Ket Part 1Document3 pagesAld and Ket Part 1Aryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Partially Ionised in Water andDocument5 pagesPartially Ionised in Water andHikmaNo ratings yet
- XII - Physical Properties Organic ChemistryDocument6 pagesXII - Physical Properties Organic ChemistryVipin VNo ratings yet
- Intermolecular Forces: 1. Van Der Waals Forces or London Dispersion ForceDocument8 pagesIntermolecular Forces: 1. Van Der Waals Forces or London Dispersion ForcecjNo ratings yet
- Intro SummaryDocument1 pageIntro SummaryChastine CruzNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbon PDFDocument19 pagesHydrocarbon PDFPrincess Lou CarpenteroNo ratings yet
- Organic Chem PDFDocument22 pagesOrganic Chem PDFAlexia LudlowNo ratings yet
- Ibanez, Ivan David S Module # 01 Answer To The Activities and Exercises Bsed-Science-2bDocument10 pagesIbanez, Ivan David S Module # 01 Answer To The Activities and Exercises Bsed-Science-2bAlvin Andante IbañezNo ratings yet
- Classification of Organic Compound Chapter-1Document17 pagesClassification of Organic Compound Chapter-1Fikere'ab HabtamuNo ratings yet
- 4 - Non-Aqueous Titrimetry AnalDocument29 pages4 - Non-Aqueous Titrimetry AnalMtw WondNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Acids, Bases and Salts Week 16 Learning Objectives: 8.1 Acids and Base TheoriesDocument6 pagesGeneral Chemistry Acids, Bases and Salts Week 16 Learning Objectives: 8.1 Acids and Base TheoriesReygemae Quitoras-ObsidNo ratings yet
- CHEM 109-Chepter 5Document37 pagesCHEM 109-Chepter 5naifalfarraj3No ratings yet
- Quiz Discussion Organic Chemistry Act.Document4 pagesQuiz Discussion Organic Chemistry Act.quirenicoleNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 PDFDocument31 pagesChapter 2 PDFKEVAL PATELNo ratings yet
- Acid Base and Solubility of Organic Compounds PDFDocument31 pagesAcid Base and Solubility of Organic Compounds PDFPaolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4-Inorganic ChemDocument27 pagesChapter 4-Inorganic ChemMark Harold GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Organic CompoundsDocument51 pagesLesson 1 Organic CompoundsHyacinth AlbertoNo ratings yet
- Postlab 3Document20 pagesPostlab 3Lyra Ane IlaganNo ratings yet
- Module 4 in Gen ChemDocument8 pagesModule 4 in Gen ChemEarl Cris RiggsNo ratings yet
- Bases Acids: Strong Acid Strong BaseDocument1 pageBases Acids: Strong Acid Strong Baseshrikant raiNo ratings yet
- Acids and BasesDocument2 pagesAcids and BasesMihnea RotaruNo ratings yet
- CHM111 RevDocument2 pagesCHM111 RevLeeann LeeNo ratings yet
- Alcohol: Boiling Points and Water SolubilitiesDocument4 pagesAlcohol: Boiling Points and Water SolubilitiesChelsea ManioNo ratings yet
- Water: The Solvent For Biochemical ReactionsDocument53 pagesWater: The Solvent For Biochemical ReactionssarahyahayaNo ratings yet
- NS1Lab - Module3 - Nacionales, Windere MarieDocument3 pagesNS1Lab - Module3 - Nacionales, Windere MarieWindere Marie NacionalesNo ratings yet
- 04awater and Acid-Base SystemDocument27 pages04awater and Acid-Base SystemAtirahNo ratings yet
- Finals - Acid Base Equilibria: OutlineDocument17 pagesFinals - Acid Base Equilibria: OutlineJuren LasagaNo ratings yet
- Acids Bases and SaltsDocument31 pagesAcids Bases and SaltsHamza OmerNo ratings yet
- Acid BaseDocument25 pagesAcid BaseMuhammad Yaser RayyanNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases: Regents: Chapter 19 P. 586 - 629 Honors: Chapters 20, 21 P. 576 - 643Document103 pagesAcids and Bases: Regents: Chapter 19 P. 586 - 629 Honors: Chapters 20, 21 P. 576 - 643Zaina ZaliraNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec NotesDocument12 pagesBiochem Lec NotesGGonzales KarlaNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument27 pagesBiochemistryAasefa Shaikh100% (1)
- Preliminary NotesDocument17 pagesPreliminary NotesBEA FRANCINE DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Buhari, A. (2014, January 25) Science Revision. SlideshareDocument7 pagesBuhari, A. (2014, January 25) Science Revision. SlideshareHannah AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Odule 4: Acids & Bases Objectives:: WaterDocument3 pagesOdule 4: Acids & Bases Objectives:: WaterAbby SevillaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocarbons and Benzene: MVPS (2020)Document4 pagesHydrocarbons and Benzene: MVPS (2020)Paul Alfred SoNo ratings yet
- 4.2. Reactions of AcidsDocument1 page4.2. Reactions of AcidsAnais BegueNo ratings yet
- Non Aq SolventsDocument24 pagesNon Aq SolventsShamil GadaNo ratings yet
- Script For The Reporting in ChemDocument11 pagesScript For The Reporting in ChemJamaica SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Basic Pharmaceutical Chemistry 15Document108 pagesBasic Pharmaceutical Chemistry 15Gideon AntwiNo ratings yet
- Org and Inorg Chem 1ST Year MedtechDocument11 pagesOrg and Inorg Chem 1ST Year MedtechALEXANDRA MAE MAIPIDNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases, Isomerism, HydrocarbonsDocument9 pagesAcids and Bases, Isomerism, HydrocarbonsTricia Mae TorresNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report SheetDocument6 pagesLaboratory Report SheetIres YuloNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Mod 6 Acid and Base Reactions NotesDocument27 pagesChemistry Mod 6 Acid and Base Reactions NotesdNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases PDFDocument4 pagesAcids and Bases PDFLeeann LeeNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionFrom EverandInorganic Hydrides: The Commonwealth and International Library: Chemistry DivisionNo ratings yet
- SCH4U Exam ReviewDocument3 pagesSCH4U Exam Reviewtaya guyNo ratings yet
- Apa Style: (American Psychological Association) 2020 UpdateDocument23 pagesApa Style: (American Psychological Association) 2020 Updatetaya guyNo ratings yet
- 4.1 VSEPR Chart - EmptyDocument2 pages4.1 VSEPR Chart - Emptytaya guyNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Review Fall 2017Document2 pagesBiochemistry Review Fall 2017taya guyNo ratings yet
- Name: - Date: - : Yeast Suspension ProtocolDocument3 pagesName: - Date: - : Yeast Suspension Protocoltaya guyNo ratings yet
- True or FalseDocument4 pagesTrue or Falsetaya guyNo ratings yet
- Lab NotesDocument60 pagesLab Notesqwerty123No ratings yet
- Fluorimetry MeasurementDocument2 pagesFluorimetry MeasurementGourav DasNo ratings yet
- Maintenance and Use ManualDocument1 pageMaintenance and Use ManualSebastian GanciNo ratings yet
- Gacv FP 080 1LF 4e 70 A 17y3 2FXMNPDocument2 pagesGacv FP 080 1LF 4e 70 A 17y3 2FXMNPMohamed ShalabyNo ratings yet
- Dia Lectrics PDFDocument582 pagesDia Lectrics PDFReinaldo LeiteNo ratings yet
- 2014 Parts and Accessories Guide No PricesDocument51 pages2014 Parts and Accessories Guide No Pricespopmart21No ratings yet
- Plastorit 0000 - Mica&Quartz PDFDocument1 pagePlastorit 0000 - Mica&Quartz PDFsriatul2006No ratings yet
- Coupling: Type of CouplingsDocument10 pagesCoupling: Type of Couplingsdaya shanker shuklaNo ratings yet
- EXP 9 Reynold's Number Shell & Tube Heat ExchangerDocument11 pagesEXP 9 Reynold's Number Shell & Tube Heat ExchangerHanish JierdhNo ratings yet
- B15T M Pressure: Standard ConnectionsDocument2 pagesB15T M Pressure: Standard ConnectionsSantos Oliva MuñozNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Fundamental: 1.1 SIGN ConventionDocument11 pagesHydraulic Fundamental: 1.1 SIGN ConventionAli AlengineerNo ratings yet
- Vibration DampingDocument13 pagesVibration Dampingnadeem UddinNo ratings yet
- Chem 112 A 2010Document145 pagesChem 112 A 2010Ry NeutronNo ratings yet
- En 14511-1-2011Document12 pagesEn 14511-1-2011BorisNo ratings yet
- Specification: KADPOL 980 / 941 / 940Document1 pageSpecification: KADPOL 980 / 941 / 940Михаил КузьминNo ratings yet
- Design of Tieback Retaining WallsDocument76 pagesDesign of Tieback Retaining WallsSteven SebastianNo ratings yet
- Che F211 1069 20230809113326Document3 pagesChe F211 1069 20230809113326ArchNo ratings yet
- Explain El Nino and The La Nina Weather PhenomenonDocument4 pagesExplain El Nino and The La Nina Weather Phenomenonjosephine_lim93No ratings yet
- H112-Heat Transfer Service UnitDocument3 pagesH112-Heat Transfer Service UnitJuan David mosquera garciaNo ratings yet
- CVI Optical SpecificationsDocument8 pagesCVI Optical SpecificationsAmir MolazecirovicNo ratings yet