Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Untitled
Uploaded by
1C-MAIK, AL-FALLAH P.Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Untitled
Uploaded by
1C-MAIK, AL-FALLAH P.Copyright:
Available Formats
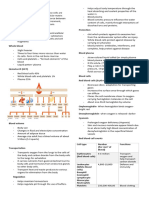
MLS 402 – LECTURE: CIRCULATORY SYSTEM oxygen and waste carbon dioxide is
removed through exhaling or the
process of exhalation
Key Points/Terms: o The network of organs and tissues that
Antecubital Fossa A region in the arm where the help us to breathe
3 major veins for venipuncture
is located
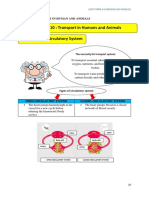
- Basilic vein II. Systemic System
- Cephalic vein o Supplies the cells with oxygen, fats,
- Median Cubital vein
carbs, and other energy sources while
The most
at the same time removing waste
preferred vein
for blood products
extraction o Carries oxygenated blood from the left
ventricle of the heart through the
Centrifuge A machine that separates the arteries to the capillaries of the tissues
blood components in the body
Diastolic The blood pressure when the
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
heart is at rest
Systolic The blood pressure when the Bone Marrow
heart is fully contracted
Endocarditis Infection of the inner veins of - The primary organ for blood cell production
the heart - The process called “Hemo” or “Hematopoiesis”
Erythrocytes Also known as RBC
5 Liters
Leukocytes Also known as WBC
Thrombocytes Also known as Platelets - The normal adult blood volume
Hemopoiesis Formation or production of - No more than 5% of the total blood volume can
blood cells be taken
Occluded Meaning blocked or normal
flow of the blood is prevented Blood
Plasma Blood fluid that contains blood
- Carries oxygen and nutrients to body tissues
clotting agents and seen in the
anticoagulated blood and to remove the waste product carbon
Serum Blood fluid without clotting dioxide and toxic metabolites
factors and is seen in the - Also carries nutrients to all parts of the bodies
coagulated blood and moves the products to the lungs, kidneys,
Pulmonary System Essential for the circulatory liver, and skin
system - Contains formed elements and liquid portion:
Systemic System Essential for the circulatory
system Solid Portion or Erythrocytes (RBC’s) –
Formed Elements 45%
(45% of the whole Leukocytes (WBC’s)
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM blood) Thrombocytes
(Platelets)
- Transportation system for the body to transfer - Leukocytes and
substances and wastes from one system to Thrombocytes
another are also known
as BUFFY COAT
2 Parts of Circulatory System: and is < 1% of
I. Pulmonary System the total blood
o Circulates blood through the lungs Liquid Portion Plasma – 55%
(55% of the whole
where the blood is enriched with
blood)
PLASMA VS. SERUM
MULTIPOTENTIAL HEMATOPOIETIC STEM CELL
Plasma - Liquid portion of
the
anticoagulated
blood Hemocytoblast
- Has clotting Common
factors / agents Common Myeloid
Progenitor
Lymphoid
Progenitor
Serum - Liquid portion of
Ntural Killer Cell
the coagulated Megakaryocyte (Large Granular
Lymphocyte)
Small Lymphocyte
blood
B
- Has no clotting Thrombocyte Thrombocyte
Lymphocyte
factors / agents
Eryhtrocyte Plasma Cell
Mast Cells
CENTRIFUGE
Myeloblast
- An instrument used to speed up the separation
of the blood components Basophil Neutrophil Eosinophil Monocyte
- It must be balanced
Macrophage Dendritic Cell
- Carrier holds the tube in an upright position and
the carrier spins a circle
- Blood components separates according to
weight
CELLULAR ELEMENTS OF BLOOD
RBC WBC Platelets
Function: Transport Body Stoppage of
of oxygen defense bleeding
&carbon
dioxide
Formation: Bone Bone Bone marrow
marrow marrow,
lymphatic
tissue
Size/ 6 to 7 9 to 6 1 to 4
Shape: micrometer micrometer micrometer,
, biconcave , different fragments of
disc, size, shape, megakaryocyt
anucleate and color of e
in mature nucleus
form
Lifespan: 100 to 120 Varies; 24 9 12 days
days hours to
years
Reference 3.8 to 5.9 x 3.5 to 11 x 150 to 450 x
Values: 1012 per 109 per liter 109 per liter
liter
CELLULAR ELEMENTS (Detailed Part) MAJOR BLOOD VESSELS IN THE BODY
Erythrocytes/RBC Arteries - Carries blood
away from the
- Lives about 120 days once they enter the heart
bloodstream - Carries
- Consists membrane that encases Hemoglobin oxygenated
- Contains antigens on the surface that determine blood
blood type (except
pulmonary
Hemoglobin artery)
Iron containing pigment - Bright red
Holds oxygen molecules - Elastic walls that
Releases oxygen to tissue and brings expand with the
surge of blood
carbon dioxide to lungs
- No valves
- Has pulse
Polycythemia - Have strong thick
The body has too much Hemoglobin walls constantly
expanding and
contracting
Leukocytes/WBC - Forms branches
called
- Vary greatly in size “Arterioles” that
- Appears as large white blood cells with purple branch even
centers or nuclei when viewed in a stained more to become
smear capillaries
- Some have granules that stain pink, blue, and Veins - Carries blood
orange towards the
- Medtech performs differential count that can heart
help in the identification of disease - Carries
deoxygenated
blood (expect
pulmonary vein)
Thrombocytes/Platelets
- Dark red
- Smallest of the formed elements - Less elastic
- Fragments of the Megakaryocyte - Thin walls
- Has valves to
- Aid in clotting process by sticking together
prevent backflow
of blood
- No pulse
- Majority are
small or medium
sized with < 1 cm
diameter
- Consist of semi-
lunar folds of
tunica intima
3 LAYERS OF THE BLOOD VESSELS Endocarditis
1) Tunica Intima - Infection of the endocardium
o Inner layer
Occlusion
o Lined by endothelium, areolar, and
elastic tissue - When coronary arteries are blocked, it leads to
o Regulates blood pressure myocardial infection (heart attack)
o Prevents blood clot
2) Tunica Media
o Middle layer of circular smooth muscles EXAMPLES OF TESTS FOR HEART DISEASE:
o Consists of elastic fibers
Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
3) Tunica Adventitia or Tunica Externa
Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
o Outer layer
Blood Gases
o Contains nerves and vessels
Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP)
o Consists primarily of collagen and elastic
Creatinine Kinase MB (CK-MB)
fibers
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
C-reactive Protein (CRP)
Lactate Dehydrogenase 1 (LDH 1)
Heart
Myoglobin
- The organ that keeps all blood flowing Troponin – I (most common ordered during
- Rhythmically contracting emergencies)
- Is a muscle that has 4 chambers:
Right atrium
Right ventricle BLOOD FLOW
Left atrium
Left ventricle - Deoxygenated blood enters the..
- Weighs in normal adult for about: 1. Superior/Inferior Vena Cava
250 – 300 g (Female) 2. Right Atrium
300 – 350 g (Male) Tricuspid Valve
3. Right Ventricle
Septum Pulmonary Valve
4. Pulmonary Artery
- Muscular wall that divides the heart into right
5. Blood enters the lungs (blood becomes
and left sides
oxygenated) it leaves the lungs and
enters..
6. Pulmonary Vein
STRUCTURES OF THE HEART
7. Left Atrium
Pericardium The sac that encloses the Bicuspid Valve
heart 8. Left Ventricle
Endocardium Membrane layer that Aortic Valve
lines the inner chambers 9. Aorta
of the heart and the 10. Oxygenated blood is then distributed in
valves the arteries, capillaries, and all
Myocardium Middle layer that is throughout the body. Then it loses its
muscle of the heart itself oxygen and gains carbon dioxide which
(cardiac muscle)
makes it become deoxygenated again
Epicardium Outermost membrane
and would enter back to the
that reduces friction
superior/inferior vena cava.
VEINS AND ARTERIES OF THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM FOR Veins on the Feet
THE PHLEBOTOMISTS
- Alternative when veins in arms aren’t available
Antecubital Fossa - Need permission from the physician
- Bend of the arm - Prone to clot formation that may cause blockage
- Back of the hand in other body parts.
- Wrist
- Ankle or foot
1. Median Cubital Vein
Used majority of the time
Easiest to palpate and less tendency to
roll
Forms a bridge pathway between
cephalic and basilic veins
2. Cephalic Vein
The second choice
Follows along the thumb side of the
arm
Not prone to rolling but slightly more
difficult to feel
3. Basilic Vein
The third choice
More difficult to feel
Has a tendency to roll
Underlying this vein is the brachial
artery and median cutaneous nerve
Note!
- Choose the above mentioned sites upon
extraction of blood since veins are more
prominent and they are near in the surface in
those areas
- They frequently form “M” or “H” shaped
patterns in those areas
- Arteries may also be used in blood extraction
but it requires special training
Brachial Artery
- Arm
- Located under the basilic vein
Radial and Ulnar Arteries
- Wrist
- For blood gas analysis
- Puncturing these requires special techniques
You might also like
- CH10Document17 pagesCH10Kim BasicNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument25 pagesCirculatory SystemadnanNo ratings yet
- Physical AssessmentDocument66 pagesPhysical AssessmentShyvonne Elisan LosariaNo ratings yet
- Medmastery Handbook - Echo Masterclass - The ValvesDocument136 pagesMedmastery Handbook - Echo Masterclass - The ValvesVladlena Cucoș-CaraimanNo ratings yet
- Cardiac TransplantDocument44 pagesCardiac TransplantMavi SaldevarNo ratings yet
- Imaging Cardiac AmyloidosisDocument16 pagesImaging Cardiac Amyloidosiskromatin9462No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument67 pagesCirculatory SystemGideon Cavida80% (5)
- Radiology Clinics of North America Cardiac ImagingDocument200 pagesRadiology Clinics of North America Cardiac ImagingArie Dwisetyo Gusti Laksono100% (2)
- De Anisya Tri Ab - CBD - 30101507419 - FixDocument198 pagesDe Anisya Tri Ab - CBD - 30101507419 - FixFarah UlyaNo ratings yet
- Atlas of Cardiac Surgical Techniques 2e 2019 - ElsevierDocument756 pagesAtlas of Cardiac Surgical Techniques 2e 2019 - ElsevierViết Nho Lê NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Edexcel International A Levels Biology Unit 1 Wbi11 PDFDocument18 pagesEdexcel International A Levels Biology Unit 1 Wbi11 PDFtas xo100% (1)
- Cardiology Flash CardsDocument5 pagesCardiology Flash CardsRodrigo FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of DengueDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Dengueciarkai_18No ratings yet
- RHD Case StudyDocument94 pagesRHD Case StudyGel Jovenal100% (1)
- The Blood Clotting MechanismDocument20 pagesThe Blood Clotting Mechanismzynab123No ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 KSSM Chapter 10Document16 pagesBiology Form 4 KSSM Chapter 10Nik Husna100% (2)
- Cardiovascular Blood Autosaved Compress1Document11 pagesCardiovascular Blood Autosaved Compress1KIMBERLY TAC-ALNo ratings yet
- Biol 2301 - Unit 8 - Circulation StudentDocument82 pagesBiol 2301 - Unit 8 - Circulation Studentapi-664744800No ratings yet
- Transport in Humans - Blood Vessels & Blood LLo - UpdatedDocument58 pagesTransport in Humans - Blood Vessels & Blood LLo - UpdatedNeilson Alexandro TjheNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument51 pagesUntitledMuhammad FadhilNo ratings yet
- CIRCULATIONDocument55 pagesCIRCULATIONleo kadehjianNo ratings yet
- Sistem Kardiovaskular: MUKTI PRIASTOMO S.Farm., M.Si., AptDocument117 pagesSistem Kardiovaskular: MUKTI PRIASTOMO S.Farm., M.Si., Aptrahmanisa090No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 UNIT IVDocument24 pagesChapter 2 UNIT IVAyen LatosaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - CirculatoryDocument5 pagesModule 5 - CirculatoryRashid DayaoNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular SystemDocument18 pagesCardio Vascular SystemjeniferNo ratings yet
- 16circulatory Istudent - 611629985pdf - 211102 - 105416Document8 pages16circulatory Istudent - 611629985pdf - 211102 - 105416Leslie CuevasNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument5 pagesBiology Reviewer13l4nk17No ratings yet
- Blood: (WBCS), Platelets, and A Fluid Matrix Called PlasmaDocument10 pagesBlood: (WBCS), Platelets, and A Fluid Matrix Called PlasmaShiela Mae SagayoNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System - BiologyDocument11 pagesCirculatory System - BiologyAmanda AllenNo ratings yet
- Circulation, Respiration & Excretion: at A GlanceDocument29 pagesCirculation, Respiration & Excretion: at A GlanceHasan Mahmud Maruf 1621513630No ratings yet
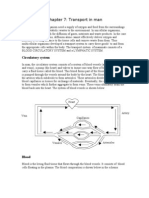
- Chapter 7 Transport in ManDocument3 pagesChapter 7 Transport in ManSheik Mohammud Muzzammil NabybaccusNo ratings yet
- Biology 2 Chapter 4Document61 pagesBiology 2 Chapter 4Malas Nak TaipNo ratings yet
- BIO 103 Circulation, Respiration, Excretion L12 Fall, 2018Document29 pagesBIO 103 Circulation, Respiration, Excretion L12 Fall, 2018Demi RoseNo ratings yet
- Blood and Hematopoiesis: From The Lab ManualDocument2 pagesBlood and Hematopoiesis: From The Lab ManualDwight Regan LopenaNo ratings yet
- Systemic Circulations, Such As The HeadDocument9 pagesSystemic Circulations, Such As The HeadRamil dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument37 pagesCirculatory SystemKathleen DuenasNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesCirculatory SystemyoudhffgNo ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculatoinDocument34 pagesBody Fluids and CirculatoinPrasmita BeheraNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: Parts and FunctionDocument14 pagesCardiovascular System: Parts and FunctionkeykeepNo ratings yet
- Composition of Human BloodDocument10 pagesComposition of Human BloodBtgPeiiYiingNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System - AnaphyDocument5 pagesCirculatory System - Anaphy4pxg7jgps8No ratings yet
- Cirulatory SystemDocument13 pagesCirulatory SystemmuhammadNo ratings yet
- For Quiz AnaphyDocument26 pagesFor Quiz AnaphyRuel AlejandroNo ratings yet
- 11 Biology Notes Ch18 Body Fluids and CirculationDocument6 pages11 Biology Notes Ch18 Body Fluids and CirculationKambaska Kumar BeheraNo ratings yet
- The Blood Clotting MechanismDocument20 pagesThe Blood Clotting Mechanismzynab123No ratings yet
- Body FluidsDocument20 pagesBody FluidsViragNo ratings yet
- f3 SC Chap 2Document31 pagesf3 SC Chap 2Chong Yek PhengNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System and Gas Exchange Powerpoint CUMMULATIVEDocument55 pagesCirculatory System and Gas Exchange Powerpoint CUMMULATIVEAjay N. SharmaNo ratings yet
- Heart, Blood Tissue Blood Vessels: The Circulatory System Includes The and TheDocument44 pagesHeart, Blood Tissue Blood Vessels: The Circulatory System Includes The and TheAnnah JeanNo ratings yet
- Human Circulatory SystemDocument8 pagesHuman Circulatory SystemSarada KasyapNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory System - 4th FormDocument25 pagesThe Circulatory System - 4th FormKristal CampbellNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesCardiovascular SystemWayneNo ratings yet
- BloodDocument6 pagesBloodAlther LorenNo ratings yet
- Haematology. BaharDocument14 pagesHaematology. BaharJustin OmwengaNo ratings yet
- Functions of The Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesFunctions of The Circulatory SystemMaria Charma AnlapNo ratings yet
- Blood PhysiologyyDocument142 pagesBlood PhysiologyylemmademewakeneNo ratings yet
- Q1 - Lesson 1Document26 pagesQ1 - Lesson 1Espher MacabitasNo ratings yet
- g9 Circulatory System LessonDocument44 pagesg9 Circulatory System LessonExposer NBNo ratings yet
- 089 44 Final Biologi Fasa4 DLP T4-29-61Document33 pages089 44 Final Biologi Fasa4 DLP T4-29-61BF CLNo ratings yet
- Core CH 8 Transport in HumansDocument10 pagesCore CH 8 Transport in Humansommp100% (1)
- Chapter 8 - Circulation and ImmunityDocument94 pagesChapter 8 - Circulation and Immunitychloe06muller.mNo ratings yet
- Body Fluid and CirculationDocument5 pagesBody Fluid and Circulationanshuroy524No ratings yet
- Body Fluids and CirculationDocument4 pagesBody Fluids and CirculationINTERESTING RECOVERSNo ratings yet
- PDF Blood LymphaDocument13 pagesPDF Blood LymphaGel Marie LobatonNo ratings yet
- Comparative Anatomy - Circulatory SystemDocument78 pagesComparative Anatomy - Circulatory SystemElaine MacasaetNo ratings yet
- ABT Cardivascual PPDocument44 pagesABT Cardivascual PPABT SchoolNo ratings yet
- Biology Chapter 10Document9 pagesBiology Chapter 10wongchengen2006No ratings yet
- Blood and Its Components-NotesDocument10 pagesBlood and Its Components-NotesKelvin RequenaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory PathwaysDocument5 pagesCirculatory Pathwaysaadeshthite476No ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Sex and GenderDocument5 pagesTopic 1 - Sex and Gender1C-MAIK, AL-FALLAH P.No ratings yet
- Arab CultureDocument7 pagesArab Culture1C-MAIK, AL-FALLAH P.No ratings yet
- Handout 2Document6 pagesHandout 21C-MAIK, AL-FALLAH P.No ratings yet
- Passion Death and Resurrection of Jesus Paschal MysteryDocument26 pagesPassion Death and Resurrection of Jesus Paschal Mystery1C-MAIK, AL-FALLAH P.No ratings yet
- N174 Physical Assessment-Final Study GuideDocument14 pagesN174 Physical Assessment-Final Study GuideMark Angelo Picar AbelleraNo ratings yet
- CV Physical ExamDocument17 pagesCV Physical ExamVenkatesan VidhyaNo ratings yet
- October 2016 (IAL) MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-LevelDocument24 pagesOctober 2016 (IAL) MS - Unit 1 Edexcel Biology A-LevelAyse KerimNo ratings yet
- 12 Transport of O2 & Co2Document169 pages12 Transport of O2 & Co2Bakhtiar Effendi YahyaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System: DR Charles A Simanjuntak, DR, Spot (K), MPDDocument34 pagesCardiovascular System: DR Charles A Simanjuntak, DR, Spot (K), MPDRobiatulAdawiyahNo ratings yet
- 5 Body Fluids and Circulation: SolutionsDocument13 pages5 Body Fluids and Circulation: SolutionsEkta ManglaniNo ratings yet
- Module Cardiovascular SystemDocument14 pagesModule Cardiovascular SystemVynz Morales CosepNo ratings yet
- Sow For Combined Science Year 10 (2+3 Programme) v2 - 3 YearsDocument47 pagesSow For Combined Science Year 10 (2+3 Programme) v2 - 3 YearsYenny Tiga100% (1)
- 7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraDocument57 pages7 PENYAKIT JANTUNG BAWAAN DR - YusraSurya ArhNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System SEDocument4 pagesCirculatory System SEOMAR ID-AGRAM100% (1)
- PICU BookDocument60 pagesPICU BookJoão RosaNo ratings yet
- IR 2022 Pediatric Nursing Handouts - Prof. Ma. Teresa VanguardiaDocument15 pagesIR 2022 Pediatric Nursing Handouts - Prof. Ma. Teresa VanguardiaJamie John EsplanadaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Physiology DengueDocument8 pagesAnatomy Physiology DengueArms PrielaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Worksheet, Student Version 2Document5 pagesCardiovascular System Worksheet, Student Version 2nicole thornNo ratings yet
- The Cardiovascular System: Learning ObjectivesDocument42 pagesThe Cardiovascular System: Learning ObjectivesMuba sonNo ratings yet
- 1 - Rheumatic Fever and Valvular Diseases (Summary and MCQS)Document12 pages1 - Rheumatic Fever and Valvular Diseases (Summary and MCQS)فرقان سلام عيسى عبدNo ratings yet
- Ερωτήσεις διάφορεςDocument108 pagesΕρωτήσεις διάφορεςyiafkaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Moyes ANSWERSDocument45 pagesChapter 8 Moyes ANSWERSCaleb DodgeNo ratings yet
- Echocardiography Thesis TopicsDocument4 pagesEchocardiography Thesis Topicsbsqw6cbt100% (1)