Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fungi
Uploaded by
Sean Kerby Palima0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views29 pagesThe document summarizes the kingdom of fungi. It describes their evolution from Opisthokonts around 460 million years ago. Fungi exhibit a variety of forms including unicellular, multicellular, filamentous hyphae and fruiting bodies. They are classified into phyla based on their body type and key features. Major phyla include Chytridiomycota, Zygomycota, Glomeromycota, Ascomycota, and Basidiomycota. Fungi play important roles in ecosystems through symbiosis, decay, and communication between organisms, and also impact society through medicine, food, and biofuels.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the kingdom of fungi. It describes their evolution from Opisthokonts around 460 million years ago. Fungi exhibit a variety of forms including unicellular, multicellular, filamentous hyphae and fruiting bodies. They are classified into phyla based on their body type and key features. Major phyla include Chytridiomycota, Zygomycota, Glomeromycota, Ascomycota, and Basidiomycota. Fungi play important roles in ecosystems through symbiosis, decay, and communication between organisms, and also impact society through medicine, food, and biofuels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views29 pagesFungi
Uploaded by
Sean Kerby PalimaThe document summarizes the kingdom of fungi. It describes their evolution from Opisthokonts around 460 million years ago. Fungi exhibit a variety of forms including unicellular, multicellular, filamentous hyphae and fruiting bodies. They are classified into phyla based on their body type and key features. Major phyla include Chytridiomycota, Zygomycota, Glomeromycota, Ascomycota, and Basidiomycota. Fungi play important roles in ecosystems through symbiosis, decay, and communication between organisms, and also impact society through medicine, food, and biofuels.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPS, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 29
The Fungi
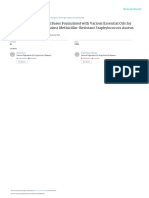
Evolution of the Kingdom
• lineages came from
Opisthokonts
• closely related to nucleariids
• appeared in strata 460 M
years ago
• form symbiotic association
crucial to land plants
Characteristics
• unicellular, multicellular, eukaryotic
• filamentous (hyphamycelium)
• sclerotium (hardened myceliumdormant
• mycelial cords, rhizomorph, fruiting body
• microscopic, macroscopic
• cell wall with chitin (most)
• food storage- lipid/glycogen
• haplontic life cycle
Mode of nutrition
Lichens
Fungal Phyla
Phylum Body Type Key feature
(Division)
Chytridiomycota one to several motile spores propelled by flagella; usually
cells asexual
Zygomycota hyphal sexual stage in which a resistant zygospore
forms for germination
Glomeromycota hyphal hyphae associated with plant roots, forming
arbuscular mycorrhizae
Ascomycota hyphal sexual spores produced in sacs called ascus
Basidiomycota Hyphal sexual spores form in basidia of a prominent
fruiting body
Division Chytridiomycota
• only fungal group that produce spores
propelled by flagella
• microscopic, aquatic
• reproduction: both sexual/ asexual
• exhibit alternation of generation
• obligate intracellular parasites
• disease causing fungus in aquatic
organisms
Ex. Chytriomyces
Batrachochytrium
Division Zygomycota
• fungi that reproduce
sexually- zygospore
• mostly saprophytic
• aseptated hypha
• mycelia (+, - mating
type) > gametangium
Division Glomeromycota
• specialized to form
associations with
plant roots-
mycorrhiza
• reproduce asexually
(spore) at hyphal tip
• hyphae secrete
enzymes to roots
Division Ascomycota
• include approx. 45, 000 species that
produce ascus (thus, sac fungi)
• micro/macroscopic
• some are plant-disease causing
• some medical importance
• fruiting body- ascocarp
• uni/multicellular, septated hypha
• reproduction: sexual/asexual
Division Basidiomycota
• club fungi (mushroom-
forming species)
• mostly macroscopic
• saprophytic
• fruiting body- basidiocarp
• septated hyphae
• agents of decay
Impacts of fungi to ecosystems and society
• agents of decay and disease
• symbiosis
• fungi-fungi-plant communication
• medicine
• food
• biofuel (alcohol)
You might also like
- Mushroom Spotter's Deck: A Field Guide to Fungi & Their Age-Old WisdomFrom EverandMushroom Spotter's Deck: A Field Guide to Fungi & Their Age-Old WisdomNo ratings yet
- L4 FungiDocument54 pagesL4 Fungif22b0054No ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument27 pagesFUNGILyrra Jorramie Rull GragedaNo ratings yet
- 1.5 FungiDocument57 pages1.5 FungiaixyaehNo ratings yet
- Kingdom FungiDocument31 pagesKingdom Fungiraul sinatoNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument38 pagesFungiRamayono RayNo ratings yet
- Fungi and Lichens: Rmba, Rph2019Document28 pagesFungi and Lichens: Rmba, Rph2019Arianne Nicole PinuelaNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Fungi: Part 6 Chapter 5Document37 pagesKingdom Fungi: Part 6 Chapter 5AtieyNoryhati-dzNo ratings yet
- Biological Classification IIIDocument20 pagesBiological Classification IIIAshrith KumarNo ratings yet
- BIO 102 by DR Keshinro OMDocument32 pagesBIO 102 by DR Keshinro OMfaborodeharyomideNo ratings yet
- FUNGIDocument33 pagesFUNGIGabz Gabby50% (6)
- Presentation 1Document4 pagesPresentation 1clarissafioNo ratings yet
- Mycv Lec FinalsDocument124 pagesMycv Lec FinalsRiel VillaminNo ratings yet
- Kingdom FungiDocument51 pagesKingdom FungiRISHIKHESANNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Fungi: The Characteristics of Fungi The Evolution of The Fungi Fungal Classification Fungal Life CyclesDocument27 pagesKingdom Fungi: The Characteristics of Fungi The Evolution of The Fungi Fungal Classification Fungal Life CyclesWastantiNo ratings yet
- Kousik - Ghoshevolution Fungi2020 04 05evolution FungiDocument27 pagesKousik - Ghoshevolution Fungi2020 04 05evolution FungiAlexis RamirezNo ratings yet
- Kingdom Fungi: The Characteristics of Fungi The Evolution of The Fungi Fungal Classification Fungal Life CyclesDocument27 pagesKingdom Fungi: The Characteristics of Fungi The Evolution of The Fungi Fungal Classification Fungal Life CyclesWastantiNo ratings yet
- Fungi: Level 1 Biological DiversityDocument23 pagesFungi: Level 1 Biological DiversityAmrGeldawyNo ratings yet
- Microbe On Argiculture PDFDocument34 pagesMicrobe On Argiculture PDFNEILYNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa and Slime Molds: Unit 2Document21 pagesLecture 3: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa and Slime Molds: Unit 2Nivashini VindhyaNo ratings yet
- FungiDocument44 pagesFungiapi-266618926No ratings yet
- l2 ch20Document4 pagesl2 ch20fatimaabdullahalarfajNo ratings yet
- Maseno University School of Public Health and Community Development Department of Public Health PHT 222:medical MicrobiologyDocument29 pagesMaseno University School of Public Health and Community Development Department of Public Health PHT 222:medical MicrobiologyOld LakeNo ratings yet
- NEW - Clinical Mycology - Aliazas 2020 Ver-CompressedDocument84 pagesNEW - Clinical Mycology - Aliazas 2020 Ver-CompressedTrisha RomeoNo ratings yet
- Kingdomfungi 170304171711Document34 pagesKingdomfungi 170304171711trisha abadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Infectious DiseasesDocument77 pagesIntroduction To Infectious DiseasesJanine AtesoraNo ratings yet
- Diversity of Eukaryotic Organisms-FungiDocument41 pagesDiversity of Eukaryotic Organisms-Fungishah_jalpan92911No ratings yet
- FFT1083 L3 FungiDocument32 pagesFFT1083 L3 Fungif22b0054No ratings yet
- Fungi Kingdom: By: Tio Magdalena Manurung, B.SCDocument50 pagesFungi Kingdom: By: Tio Magdalena Manurung, B.SCClara ClarestaNo ratings yet
- Domain Eukarya (Kingdom Fungi)Document47 pagesDomain Eukarya (Kingdom Fungi)Mazlisya Nadhirah100% (1)
- Notes: Fungi Systematics: Yeasts Rusts Smuts Mildews Molds MushroomsDocument2 pagesNotes: Fungi Systematics: Yeasts Rusts Smuts Mildews Molds MushroomsPrabhavati GhotgalkarNo ratings yet
- Microorganisms Important in Food MicrobiologyDocument39 pagesMicroorganisms Important in Food MicrobiologyKumkum CRNo ratings yet
- First Sem LectureDocument43 pagesFirst Sem Lecturenabin sharmaNo ratings yet
- Biological ClassificationDocument59 pagesBiological ClassificationmithraprenjithNo ratings yet
- LESSON 5 Kingdom MycotaDocument21 pagesLESSON 5 Kingdom MycotaAldrens Strongs OliverosNo ratings yet
- MycologyDocument25 pagesMycologyShahid BashirNo ratings yet
- By: Mr. Shahrul Nidzam Bin Rozali: FungiDocument82 pagesBy: Mr. Shahrul Nidzam Bin Rozali: Fungiaizat_16690No ratings yet
- Kingdom FungiDocument4 pagesKingdom FungiAnnaNo ratings yet
- 1 - Mycology-Chapter-OneDocument70 pages1 - Mycology-Chapter-OneMimo HemadNo ratings yet
- General Biology Ii (Bly 102) - FungiDocument13 pagesGeneral Biology Ii (Bly 102) - FungiTolani Ayo100% (1)
- Ch45 Med Mycology 2017-2Document248 pagesCh45 Med Mycology 2017-2YugmaPandyaNo ratings yet
- Microbio ReviewerDocument2 pagesMicrobio ReviewerCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- 6 - FungiDocument32 pages6 - FungiRUSSEL MAE CATIMBANGNo ratings yet
- FUNGI - 6-Sem112Document42 pagesFUNGI - 6-Sem112menNo ratings yet
- Introduction To MycologyDocument44 pagesIntroduction To MycologyPrincewill SeiyefaNo ratings yet
- Fungi PDFDocument64 pagesFungi PDFSilvia Tri ayuNo ratings yet
- BotanyDocument25 pagesBotanynaagin12300No ratings yet
- TOPIC 5 The Kingdom of The Fungi (Part 2)Document35 pagesTOPIC 5 The Kingdom of The Fungi (Part 2)Ally AbadeoNo ratings yet
- Fungi Are Heterotrophs That Absorb Their Food.: Key ConceptDocument11 pagesFungi Are Heterotrophs That Absorb Their Food.: Key ConceptabdulazizNo ratings yet
- Day 2 Additional Lecture Notes For Genetics Cell Bio Microbio and AnaphyDocument91 pagesDay 2 Additional Lecture Notes For Genetics Cell Bio Microbio and AnaphyJeffrey PolisticoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Fungi: General MicrobiologyDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Fungi: General MicrobiologyAnonymousNo ratings yet
- ALE Review MycologyDocument44 pagesALE Review MycologyJayson BasiagNo ratings yet
- MBC 305 Pat 1and 2Document19 pagesMBC 305 Pat 1and 2Usman SurajNo ratings yet
- Fungal Biology: A. General CharacteristicsDocument11 pagesFungal Biology: A. General CharacteristicsFatima RiveraNo ratings yet
- Fungi ClassificationDocument8 pagesFungi ClassificationNAYAN JYOTI KALITA100% (1)
- Reading Assignment Soil Microbiology: An ExploratoryDocument43 pagesReading Assignment Soil Microbiology: An ExploratoryAndrae GenusNo ratings yet
- Fungi: Morphology and ClassificationDocument37 pagesFungi: Morphology and Classificationjihan faradhilaNo ratings yet
- Cute Mushrooms Newsletter by SlydesgoDocument11 pagesCute Mushrooms Newsletter by SlydesgoPPTI 296 Famelia DharmawanNo ratings yet
- 2 Classification of Bacteria Yeast and MoldDocument56 pages2 Classification of Bacteria Yeast and Moldhadi yusuf100% (1)
- Evaluation of Topical Gel Bases Formulated With VaDocument9 pagesEvaluation of Topical Gel Bases Formulated With VaSean Kerby PalimaNo ratings yet
- Principles and Patterns of Organization - Map of Ideas - 3rd - 2024Document43 pagesPrinciples and Patterns of Organization - Map of Ideas - 3rd - 2024Sean Kerby PalimaNo ratings yet
- Card Giving Day LetterDocument1 pageCard Giving Day LetterSean Kerby PalimaNo ratings yet
- Radio Broadcasting PPT Region Speaker MMGDocument49 pagesRadio Broadcasting PPT Region Speaker MMGSean Kerby PalimaNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report On AldehydesDocument2 pagesLaboratory Report On AldehydesSean Kerby PalimaNo ratings yet
- Behavior of Firms: Eman C. PatataDocument45 pagesBehavior of Firms: Eman C. PatataSean Kerby PalimaNo ratings yet
- RandomDocument1 pageRandomSean Kerby PalimaNo ratings yet
- Plant TissueDocument5 pagesPlant TissueClarenz100% (1)
- My StudyDocument11 pagesMy StudyGerimae BanoNo ratings yet
- Hristovski Et Al 2022 TraunsteineraDocument4 pagesHristovski Et Al 2022 TraunsteineraSlavco HristovskiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDocument18 pagesClass 12 Subject: Biology Chapter-2: FlowerDianna josephNo ratings yet
- 12th Botany EM WWW - Tntextbooks.inDocument304 pages12th Botany EM WWW - Tntextbooks.inAnitha SNo ratings yet
- w3 Autumn Season PlannerDocument2 pagesw3 Autumn Season PlannerBozena VrgocNo ratings yet
- Questions On Transport and Storage in PlantsDocument10 pagesQuestions On Transport and Storage in PlantsNathan mwapeNo ratings yet
- Etnobotani Pekarangan Di Dusun Kaliurang Barat, Kecamatan Pakem, Sleman-YogyakartaDocument28 pagesEtnobotani Pekarangan Di Dusun Kaliurang Barat, Kecamatan Pakem, Sleman-YogyakartaNicole de BellNo ratings yet
- Plant Tissue System MCQSDocument22 pagesPlant Tissue System MCQSphurlijharan1No ratings yet
- Fun AriaDocument13 pagesFun AriaSrijanNo ratings yet
- Mikropropagasi Pada AnggrekDocument15 pagesMikropropagasi Pada AnggrekRahmaNo ratings yet
- Q1-Fig. 2.1 Is A Photograph of A Cross-Section of A Vascular Bundle in A LeafDocument2 pagesQ1-Fig. 2.1 Is A Photograph of A Cross-Section of A Vascular Bundle in A LeafMuntaha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document5 pagesModule 6ZhajaNo ratings yet
- Indentification and Look-Alikes: Yarrow Key Characteristics ChecklistDocument1 pageIndentification and Look-Alikes: Yarrow Key Characteristics ChecklisttereNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plants of Kerala PDFDocument13 pagesFlowering Plants of Kerala PDFSarath VkNo ratings yet
- PSLE Science 2015 Answer KeyDocument5 pagesPSLE Science 2015 Answer Keycity aathithyaNo ratings yet
- Pteridophytic Flora of Rajasthan A ReviewDocument5 pagesPteridophytic Flora of Rajasthan A ReviewEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Phytotoxic Potential of Mangifera Indica Extracts To Cyperus Rotundus and CapsicumDocument9 pagesPhytotoxic Potential of Mangifera Indica Extracts To Cyperus Rotundus and CapsicumRyza Jamie SabaterNo ratings yet
- Preface To The 2020 Edition of The ISTA RulesDocument4 pagesPreface To The 2020 Edition of The ISTA RulesmaritzaNo ratings yet
- Traditional Knowledge of Botany and Agriculture Revealed in The Vēda Sa Hitās, Brāhma Ās, Ara Yakās and Upani AdsDocument15 pagesTraditional Knowledge of Botany and Agriculture Revealed in The Vēda Sa Hitās, Brāhma Ās, Ara Yakās and Upani AdsManeesh MisraNo ratings yet
- Shivmangal - Lab7 - Friday 3.15 - G1Document14 pagesShivmangal - Lab7 - Friday 3.15 - G1Anasatcia Mcpherson 9c FNo ratings yet
- LAB 2 Plant and Animal TissuesDocument5 pagesLAB 2 Plant and Animal TissuesFlordiles NavarroNo ratings yet
- 02 05 Forensic Botany WorksheetDocument2 pages02 05 Forensic Botany WorksheetBailey PoeNo ratings yet
- Foraging and Pollination Activity of XylocopaDocument8 pagesForaging and Pollination Activity of XylocopaRuyter JesusNo ratings yet
- Cross Breeding Peppers GraphicDocument1 pageCross Breeding Peppers GraphicDiogo LouroNo ratings yet
- Bio 100 Botany Course SyllabusDocument11 pagesBio 100 Botany Course Syllabusnourshamsia barosa100% (1)
- Spirit of TreesDocument5 pagesSpirit of TreesBoon TanNo ratings yet
- Woodley2001 StratiomyidaeWorldCatalogDocument483 pagesWoodley2001 StratiomyidaeWorldCatalogisabellejordanaNo ratings yet
- Ocampo, 2016Document14 pagesOcampo, 2016Stephanie SalasNo ratings yet
- Mosses Diversity From Lombok IDocument9 pagesMosses Diversity From Lombok IariNo ratings yet